e0c1f94c9e50b6c341e0ff3da71a8155.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10

Climate, Community & Biodiversity • Climate, Community and Biodiversity Alliance (CCBA) • Review of multiple-benefit projects in Madagascar • Current carbon market opportunities & limitations with respect to sustainable development

www. climate-standards. org Standards for ensuring integrity of carbon offset projects

CCB Standards Ensuring integrity of claimed outcomes: • Climate protection • Conserving biodiversity • Supporting sustainable development in poor communities www. climate-standards. org
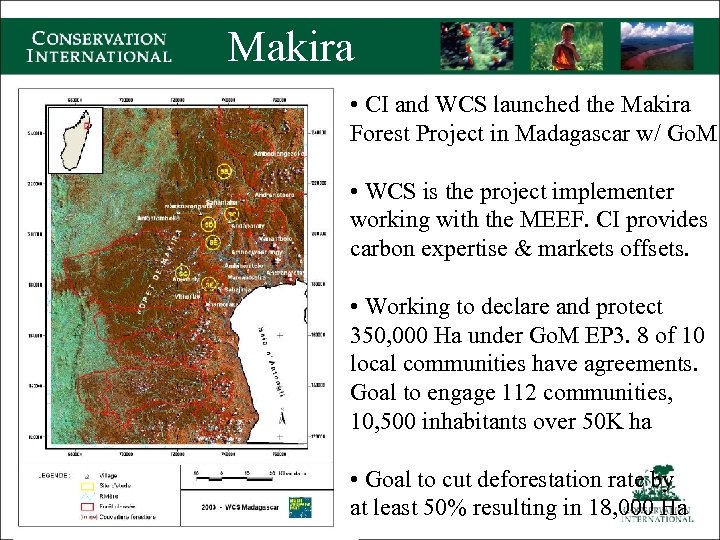
Makira • CI and WCS launched the Makira Forest Project in Madagascar w/ Go. M • WCS is the project implementer working with the MEEF. CI provides carbon expertise & markets offsets. • Working to declare and protect 350, 000 Ha under Go. M EP 3. 8 of 10 local communities have agreements. Goal to engage 112 communities, 10, 500 inhabitants over 50 K ha • Goal to cut deforestation rate by at least 50% resulting in 18, 000 Ha
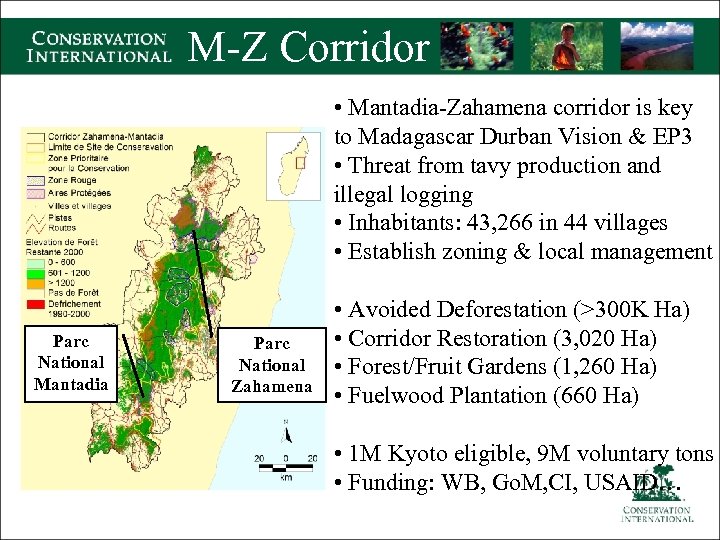
M-Z Corridor • Mantadia-Zahamena corridor is key to Madagascar Durban Vision & EP 3 • Threat from tavy production and illegal logging • Inhabitants: 43, 266 in 44 villages • Establish zoning & local management Parc National Mantadia Parc National Zahamena • Avoided Deforestation (>300 K Ha) • Corridor Restoration (3, 020 Ha) • Forest/Fruit Gardens (1, 260 Ha) • Fuelwood Plantation (660 Ha) • 1 M Kyoto eligible, 9 M voluntary tons • Funding: WB, Go. M, CI, USAID…
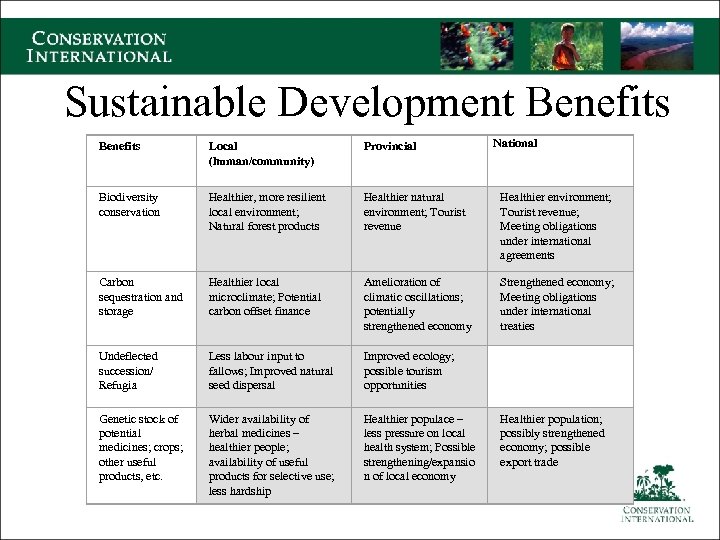
Sustainable Development Benefits National Benefits Local (human/community) Provincial Biodiversity conservation Healthier, more resilient local environment; Natural forest products Healthier natural environment; Tourist revenue Healthier environment; Tourist revenue; Meeting obligations under international agreements Carbon sequestration and storage Healthier local microclimate; Potential carbon offset finance Amelioration of climatic oscillations; potentially strengthened economy Strengthened economy; Meeting obligations under international treaties Undeflected succession/ Refugia Less labour input to fallows; Improved natural seed dispersal Improved ecology; possible tourism opportunities Genetic stock of potential medicines; crops; other useful products, etc. Wider availability of herbal medicines – healthier people; availability of useful products for selective use; less hardship Healthier populace – less pressure on local health system; Possible strengthening/expansio n of local economy Healthier population; possibly strengthened economy; possible export trade
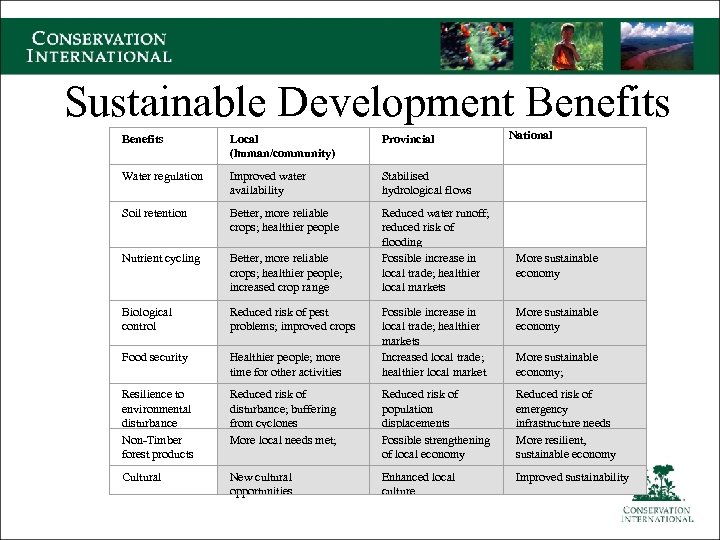
Sustainable Development Benefits National Benefits Local (human/community) Provincial Water regulation Improved water availability Stabilised hydrological flows Soil retention Better, more reliable crops; healthier people Nutrient cycling Better, more reliable crops; healthier people; increased crop range Reduced water runoff; reduced risk of flooding Possible increase in local trade; healthier local markets Biological control Reduced risk of pest problems; improved crops More sustainable economy Food security Healthier people; more time for other activities Possible increase in local trade; healthier markets Increased local trade; healthier local market Resilience to environmental disturbance Non-Timber forest products Reduced risk of disturbance; buffering from cyclones More local needs met; Reduced risk of population displacements Possible strengthening of local economy Reduced risk of emergency infrastructure needs More resilient, sustainable economy Cultural New cultural opportunities Enhanced local culture Improved sustainability More sustainable economy;

Some Project Lessons Learned • • • Technical carbon project experience needed Early funding for project definition and community outreach Projects must mitigate risks and be ‘investment grade’ Difficult to meet Kyoto regulatory rules and laws Where government lands and enforcement are required, governments must commit to delivery of carbon offsets Project complexities, low understanding of carbon, and delayed carbon funding slows community and government acceptance Role of Ministry of Env & Kyoto DNA are critical Carbon funding will usually only cover a portion of overall corridor-scale project costs (20 -35%) Perpetuity cost structure not solved, typical projects 30 years

Carbon Market: Scaling Up • Avoided deforestation, if included in policies, may provide single largest source of conservation financing for tropical forests • Pricing for Kyoto compliant and EU ERs $5 -$15/t. CO 2 • Pricing supports only limited sustainable development benefits • Japan and EU ETS focusing more on regulatory purchases • Land-use not included in EU ETS is significant disadvantage • Only niche market interested in multiple-benefit land-use projects • Risk profile of CDM and land-use projects results in price discount • Responsibility to validate premise that land-use projects provide better development and biodiversity benefits through CCBA

Thank You!
e0c1f94c9e50b6c341e0ff3da71a8155.ppt