d37b3a42e92c2f3c42b540e6625e8f99.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Climate Change, and the Scientific Process Let’s review last week: sometimes Venus, Earth and Mars are called the Goldilocks planets
Climate Change, and the Scientific Process Let’s review last week: sometimes Venus, Earth and Mars are called the Goldilocks planets
 Compare these Three: Venus Earth Mars Temp at surface 880 F 59 F -58 F Pressure at surface ~ 90 atmospheres 1 atmosphere (14. 7 lbs/sq in) 0. 007 atmospheres Atmosphere composition CO 2 and sulfuric acid clouds Nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor clouds, CO 2, nitrogen Dist. from sun 0. 7 A. U. 1. 5 A. U. One word description? Let’s look at atmosphere more carefully:
Compare these Three: Venus Earth Mars Temp at surface 880 F 59 F -58 F Pressure at surface ~ 90 atmospheres 1 atmosphere (14. 7 lbs/sq in) 0. 007 atmospheres Atmosphere composition CO 2 and sulfuric acid clouds Nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor clouds, CO 2, nitrogen Dist. from sun 0. 7 A. U. 1. 5 A. U. One word description? Let’s look at atmosphere more carefully:
 Venus Earth Mars Carbon Dioxide: 96% Nitrogen: 78% Carbon Dioxide: 95% Nitrogen: 3. 5% Oxygen: 21 % Argon: 0. 9% Water: > 1% Carbon Dioxide: 0. 004% * Nitrogen: 3% Argon: 2%
Venus Earth Mars Carbon Dioxide: 96% Nitrogen: 78% Carbon Dioxide: 95% Nitrogen: 3. 5% Oxygen: 21 % Argon: 0. 9% Water: > 1% Carbon Dioxide: 0. 004% * Nitrogen: 3% Argon: 2%
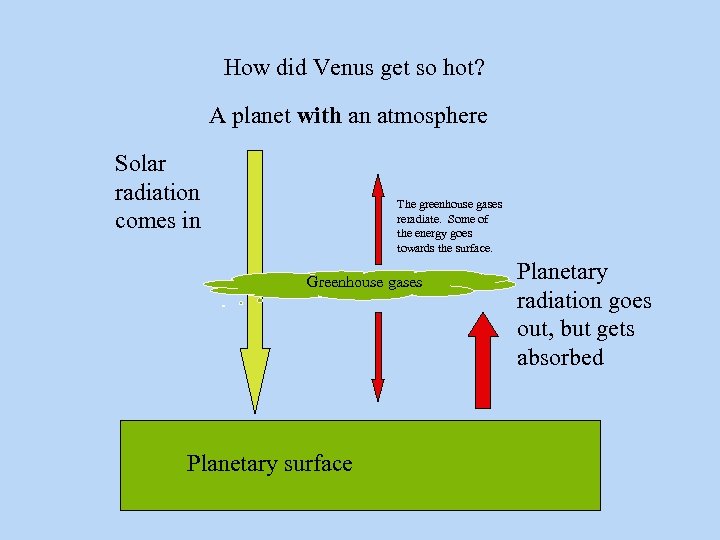 How did Venus get so hot? A planet with an atmosphere Solar radiation comes in The greenhouse gases reradiate. Some of the energy goes towards the surface. Greenhouse gases Planetary surface Planetary radiation goes out, but gets absorbed
How did Venus get so hot? A planet with an atmosphere Solar radiation comes in The greenhouse gases reradiate. Some of the energy goes towards the surface. Greenhouse gases Planetary surface Planetary radiation goes out, but gets absorbed
 In class, or lab exercise: Greenhouse effect Go to http: //phet. colorado. edu/en/simulation/greenhouse
In class, or lab exercise: Greenhouse effect Go to http: //phet. colorado. edu/en/simulation/greenhouse
 How do greenhouse gases naturally get into the atmosphere? Water: evaporation CO 2: vaporization of rocks, release from volcanos, vaporization of biotic material (like fossil fuels), respiration Methane: release from earth, biology (bacteria, cows, rice)
How do greenhouse gases naturally get into the atmosphere? Water: evaporation CO 2: vaporization of rocks, release from volcanos, vaporization of biotic material (like fossil fuels), respiration Methane: release from earth, biology (bacteria, cows, rice)
 1. Volcanos brought up gas trapped in rock 7
1. Volcanos brought up gas trapped in rock 7
 2. Comets hitting the young earth brought water, water vapor and carbon dioxide. 8
2. Comets hitting the young earth brought water, water vapor and carbon dioxide. 8
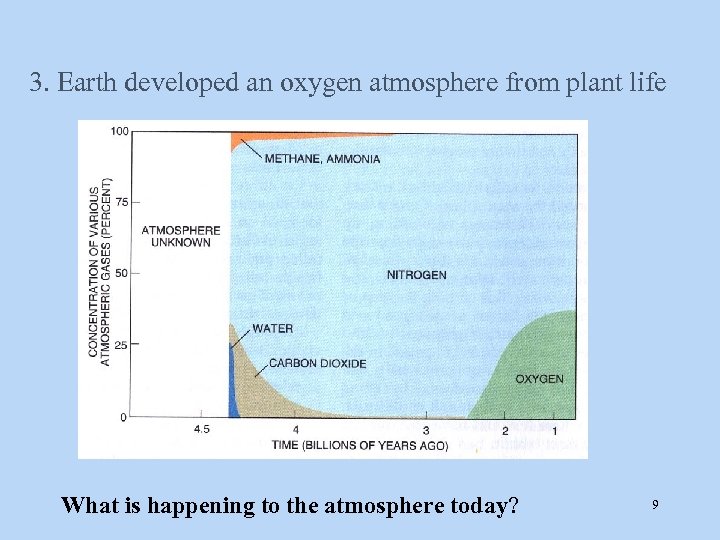 3. Earth developed an oxygen atmosphere from plant life What is happening to the atmosphere today? 9
3. Earth developed an oxygen atmosphere from plant life What is happening to the atmosphere today? 9
 Report on Global Climate Change – IPCC 2013* “Warming of the climate system is unequivocal, and since the 1950 s, many of the observed changes are unprecedented over decades to millennia. The atmosphere and ocean have warmed, the amounts of snow and ice have diminished, sea level has risen, and the concentrations of greenhouse gases have increased. ” * Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: A total of 209 Lead Authors and 50 Review Editors from 39 countries and more than 600 Contributing Authors from 32 countries contributed to the preparation
Report on Global Climate Change – IPCC 2013* “Warming of the climate system is unequivocal, and since the 1950 s, many of the observed changes are unprecedented over decades to millennia. The atmosphere and ocean have warmed, the amounts of snow and ice have diminished, sea level has risen, and the concentrations of greenhouse gases have increased. ” * Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: A total of 209 Lead Authors and 50 Review Editors from 39 countries and more than 600 Contributing Authors from 32 countries contributed to the preparation
 Articles published in peer review journals support idea that this is happening, and that it is caused by humans Peer review, or refereed: article has been anonymously approved by another expert in the field before publication
Articles published in peer review journals support idea that this is happening, and that it is caused by humans Peer review, or refereed: article has been anonymously approved by another expert in the field before publication
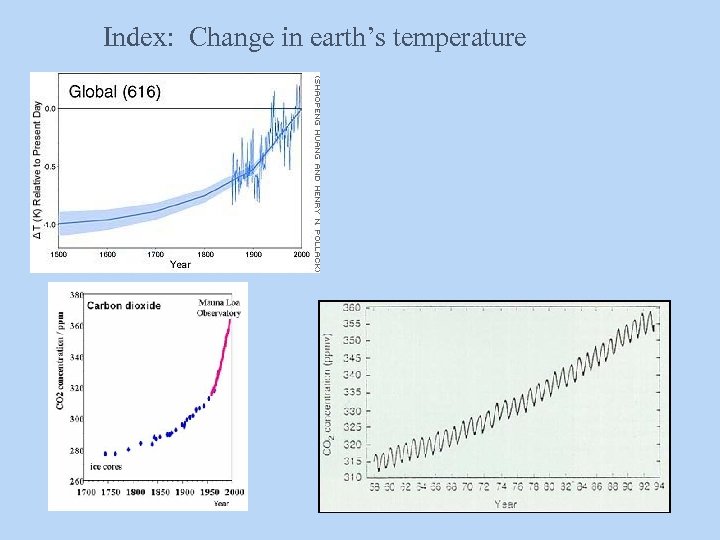
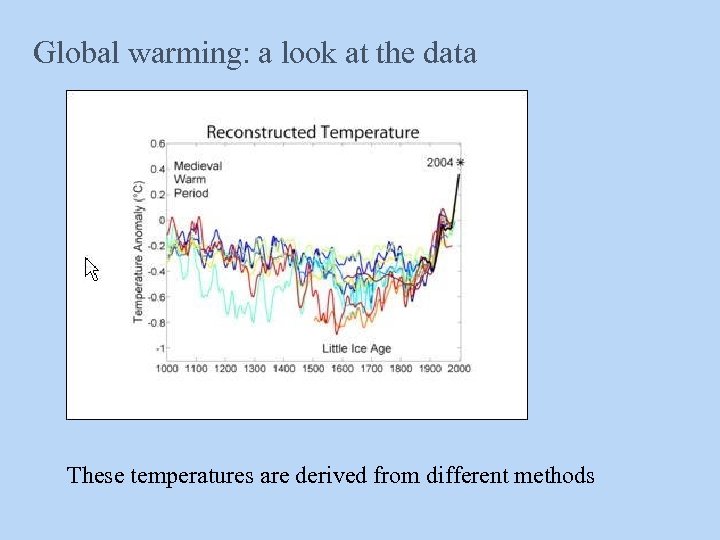 Global warming: a look at the data These temperatures are derived from different methods
Global warming: a look at the data These temperatures are derived from different methods
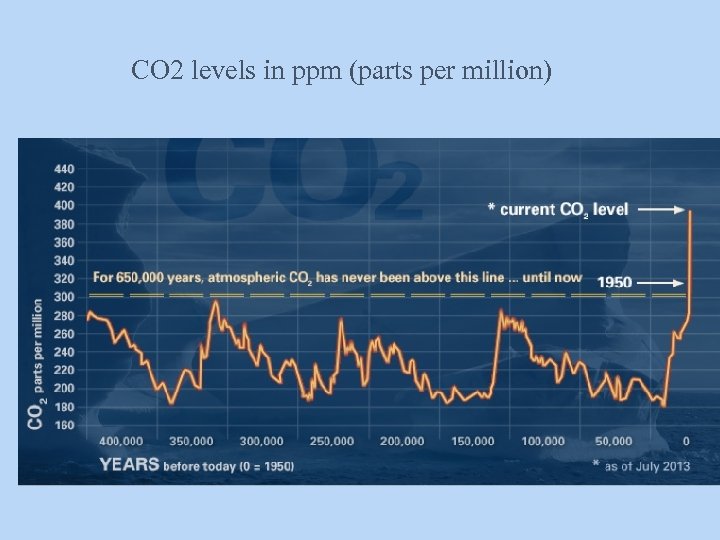 CO 2 levels in ppm (parts per million)
CO 2 levels in ppm (parts per million)
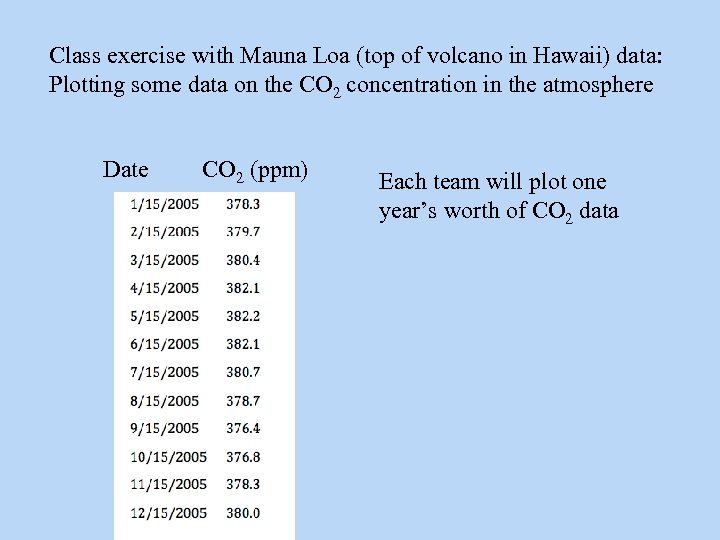 Class exercise with Mauna Loa (top of volcano in Hawaii) data: Plotting some data on the CO 2 concentration in the atmosphere Date CO 2 (ppm) Each team will plot one year’s worth of CO 2 data
Class exercise with Mauna Loa (top of volcano in Hawaii) data: Plotting some data on the CO 2 concentration in the atmosphere Date CO 2 (ppm) Each team will plot one year’s worth of CO 2 data
 395 Group # ______ 394 393 392 CO 2 Concentration (ppm) 391 390 389 388 387 386 385 384 383 382 381 380 379 378 377 376 2011 July 2010 July 2009 July 2008 July 2007 July 2006 July 2005 July 375 2012
395 Group # ______ 394 393 392 CO 2 Concentration (ppm) 391 390 389 388 387 386 385 384 383 382 381 380 379 378 377 376 2011 July 2010 July 2009 July 2008 July 2007 July 2006 July 2005 July 375 2012
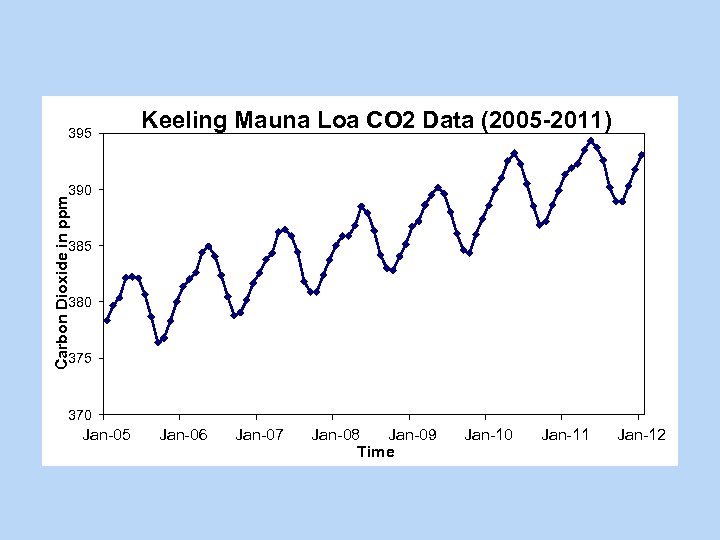 395 Keeling Mauna Loa CO 2 Data (2005 -2011) Carbon Dioxide in ppm 390 385 380 375 370 Jan-05 Jan-06 Jan-07 Jan-08 Jan-09 Time Jan-10 Jan-11 Jan-12
395 Keeling Mauna Loa CO 2 Data (2005 -2011) Carbon Dioxide in ppm 390 385 380 375 370 Jan-05 Jan-06 Jan-07 Jan-08 Jan-09 Time Jan-10 Jan-11 Jan-12
 Various effects of climate change today
Various effects of climate change today



 Summary of effects: Shrinking ice sheets Declining arctic ice Melting glaciers Sea level rise Global temperature rise Warming oceans
Summary of effects: Shrinking ice sheets Declining arctic ice Melting glaciers Sea level rise Global temperature rise Warming oceans
 What can we do to reverse this? Currently, 30% of both the US House and Senate are on record as denying climate change, or its importance. Solution requires many nations to address the problem: China in particular
What can we do to reverse this? Currently, 30% of both the US House and Senate are on record as denying climate change, or its importance. Solution requires many nations to address the problem: China in particular
 What can we do… • Buy more fuel efficient cars and trucks, do less driving, do more car pooling, use CFL (compact fluorescent) light bulbs, use solar cooker… • Develop Solar power on homes • Burn less coal (which creates much of our electricity) • Develop alternative energy: wind, nuclear • What are your ideas?
What can we do… • Buy more fuel efficient cars and trucks, do less driving, do more car pooling, use CFL (compact fluorescent) light bulbs, use solar cooker… • Develop Solar power on homes • Burn less coal (which creates much of our electricity) • Develop alternative energy: wind, nuclear • What are your ideas?
 Take away message: Earth’s temperature is increasing because carbon dioxide concentration is increasing. All evidence is that this is caused by human activity. Lecture tutorial, Greenhouse effect 24
Take away message: Earth’s temperature is increasing because carbon dioxide concentration is increasing. All evidence is that this is caused by human activity. Lecture tutorial, Greenhouse effect 24
 Index: Change in earth’s temperature 25
Index: Change in earth’s temperature 25


