Климат.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 13

Climate By Oleg Gordienko Epb-131

Definition of climate Climate is a measure of the average pattern of variation in temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, precipitation, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological variables in a given region over long periods of time.

Climate is different from weather, in that weather only describes the short-term conditions of these variables in a given region.

A region's climate is generated by the climate system, which has five components: atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere.

Climatology - the science of climate. Climate change in the past studying paleoclimatology. Besides the Earth, the concept of "climate" may refer to other celestial bodies (planets, moons and asteroids), having the atmosphere.
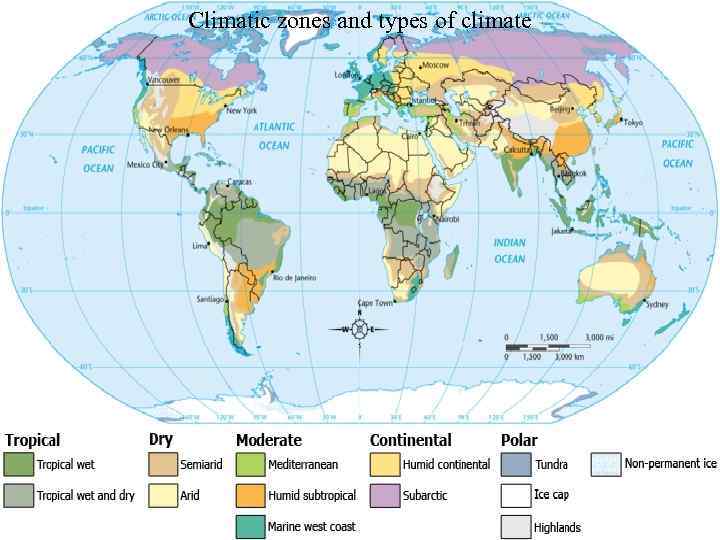
Climatic zones and types of climate

Climate classification. The Köppen classification depends on average monthly values of temperature and precipitation. The classification is based on taking into account the mode of temperature and precipitation. Planned 5 types of climate zones, namely: A - humid tropical zone without winter; B - two dry zones, one in each hemisphere; C - two moderately warm areas without regular snow cover; D - two areas of the boreal climate on the continents with distinct borders in winter and summer; Ε - two polar regions of the snow climate.

Methods of study To identify the features of the climate, both typical and rarely observed, required perennial series of meteorological observations. Climatic data are statistical conclusions from long-term series of observations of the weather, especially on the following basic meteorological elements: atmospheric pressure, wind speed and direction, air temperature and humidity, cloudiness and precipitation. Also consider the length of the solar radiation, the duration of the frost-free period, the range of visibility, the temperature of the upper layers of the soil and water bodies, evaporation of water from the surface to the atmosphere, and the height of the snow conditions, the different atmospheric conditions and ground hydrometeors (dew, ice, fog, thunderstorms, blizzards and so forth. )



Climatic factors

External factors • The parameters of the earth's orbit and axis: 1. The distance between the earth and the sun. 2. The slope of the earth's rotation axis to the orbital plane 3. The eccentricity of earth's orbit Internal factors • Volcanic eruptions • Albedo of the earth's atmosphere and surface • Air masses • The influence of the oceans and seas • The nature of the underlying surface • Human activities (fuel combustion, emissions of different gases, agricultural practices, deforestation, urbanization). • Heat flows planet.

Thank you for your attention
Климат.pptx