b27d9431789da0c95225fe7ff50a939c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

Climate Adaptation: Risk, Uncertainty and Decision-Making Dr. Robert Willows Environmental Forecasting Manager National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
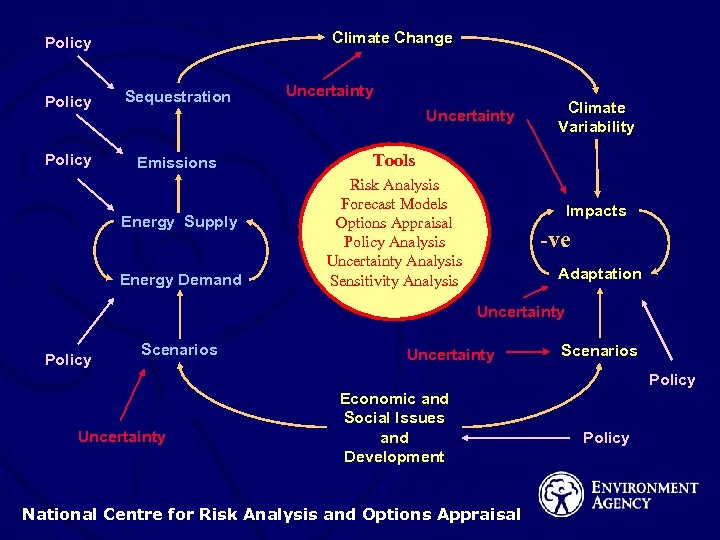
Climate Change Policy Sequestration Policy Emissions Uncertainty Energy Supply Energy Demand Climate Variability Tools Risk Analysis Forecast Models Options Appraisal Policy Analysis Uncertainty Analysis Sensitivity Analysis Impacts -ve Adaptation Uncertainty Policy Scenarios Uncertainty Scenarios Policy Uncertainty Economic and Social Issues and Development National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal Policy

Study objectives • Help identify ‘climate-sensitive’ decisions • Help achieve better decisions • Provides guidance on the use of tools and techniques • Should provide generic guidance on climate risks • Consistent with DETR guidelines for Environmental Risk Assessment (‘Greenleaves 2’) Decision/ Policy makers Science

UKCIP Technical Report • Part 1 : A review of Climate Adaptation: Risk, Uncertainty and Decision Making – Risk and uncertainty – Decision-making under uncertainty – Risk-based climate impact assessment • Part 2 : Framework and Guidance – Stage by Stage guidance to support the process of undertaking risk-based appraisal of climate influenced decisions National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
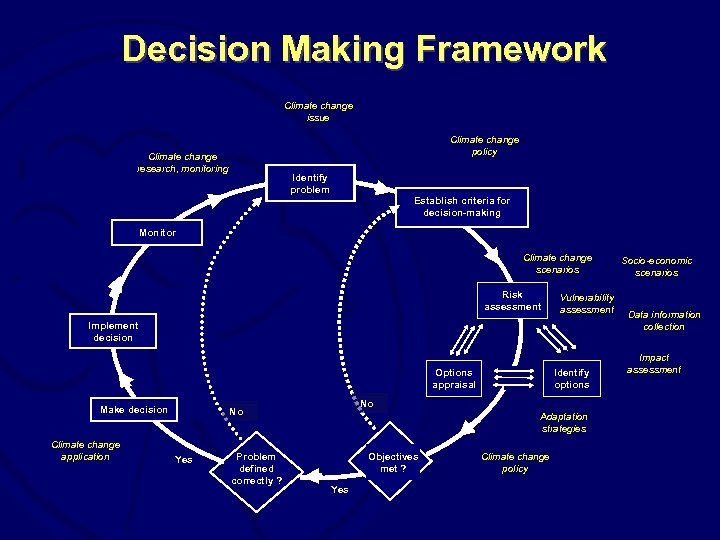
Decision Making Framework Climate change issue Climate change policy Climate change research, monitoring Identify problem Establish criteria for decision-making Monitor Climate change scenarios Risk assessment Vulnerability assessment Implement decision Options appraisal Make decision Climate change application No No Yes Problem defined correctly ? Identify options Adaptation strategies Objectives met ? Yes Climate change policy Socio-economic scenarios Data information collection Impact assessment
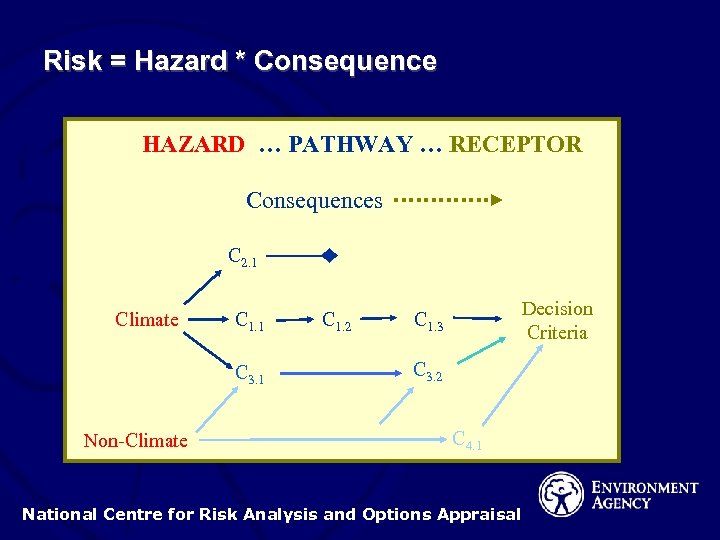
Risk = Hazard * Consequence HAZARD … PATHWAY … RECEPTOR Consequences C 2. 1 Climate C 1. 1 C 3. 1 Non-Climate C 1. 2 Decision Criteria C 1. 3 C 3. 2 C 4. 1 National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
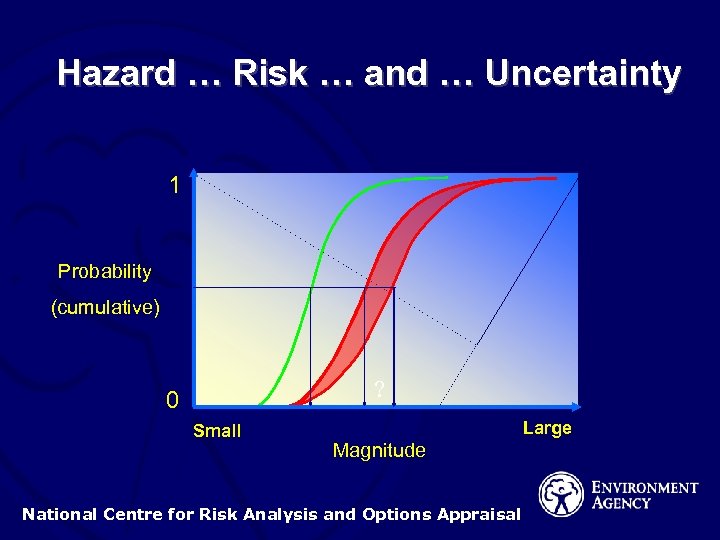
Hazard … Risk … and … Uncertainty 1 Probability (cumulative) ? 0 Small Large Magnitude National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
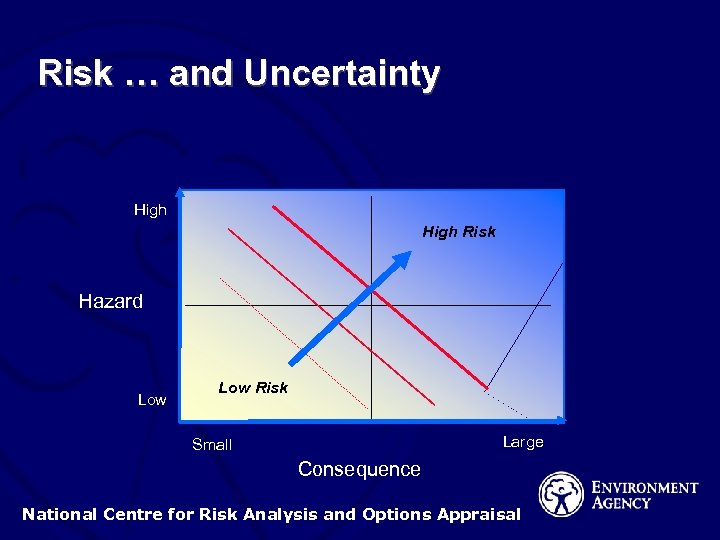
Risk … and Uncertainty High Risk Hazard Low Risk Large Small Consequence National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
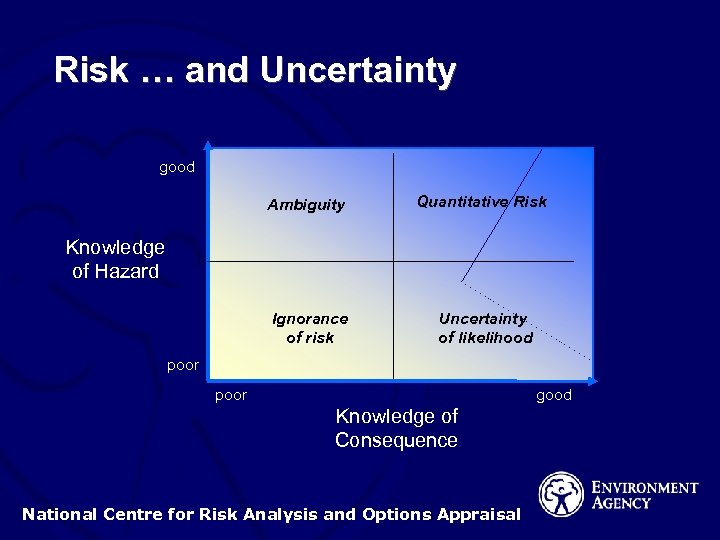
Risk … and Uncertainty good Ambiguity Quantitative Risk Ignorance of risk Uncertainty of likelihood Knowledge of Hazard poor good Knowledge of Consequence National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
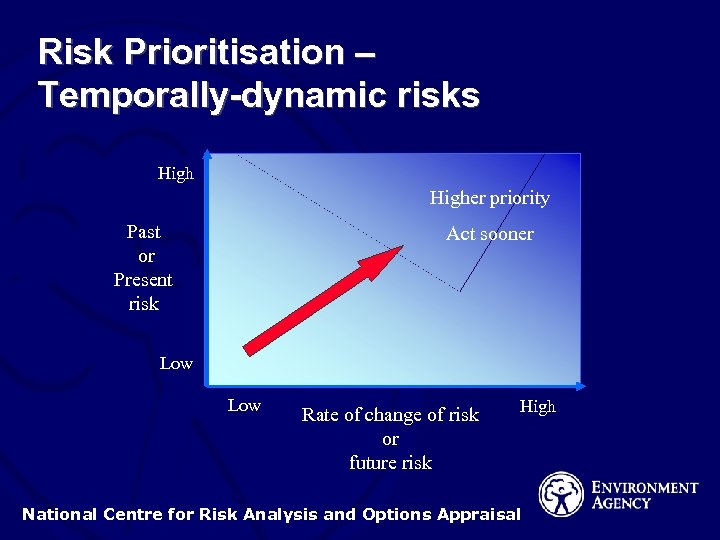
Risk Prioritisation – Temporally-dynamic risks Higher priority Past or Present risk Act sooner Low Rate of change of risk or future risk High National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
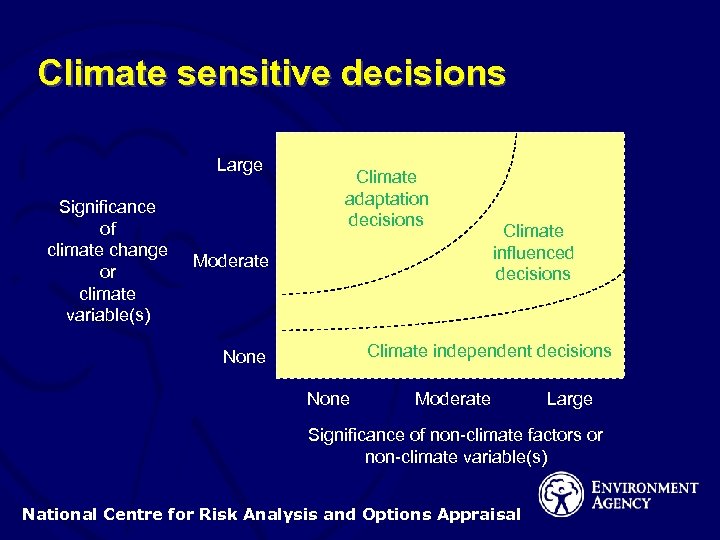
Climate sensitive decisions Large Significance of climate change or climate variable(s) Climate adaptation decisions Moderate Climate influenced decisions Climate independent decisions None Moderate Large Significance of non-climate factors or non-climate variable(s) National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
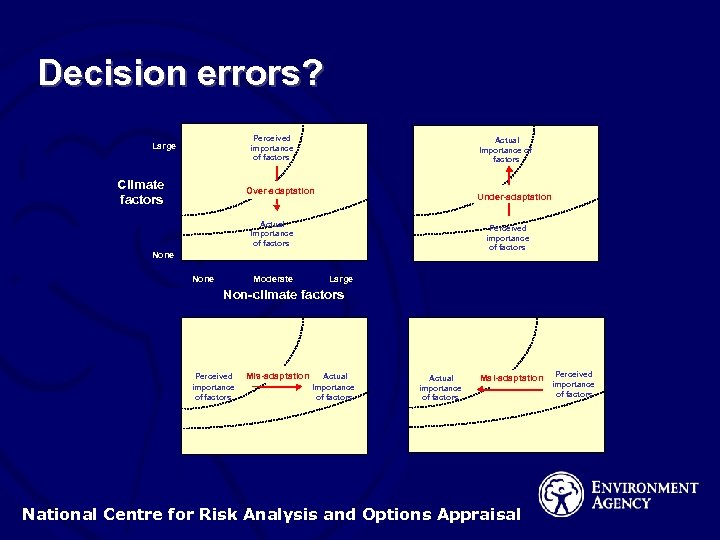
Decision errors? Perceived importance of factors Large Climate factors Actual Importance of factors Over-adaptation Under-adaptation Actual Importance of factors Perceived importance of factors None Moderate Large Non-climate factors Perceived importance of factors Mis-adaptation Actual Importance of factors Actual importance of factors Mal-adaptation National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal Perceived importance of factors
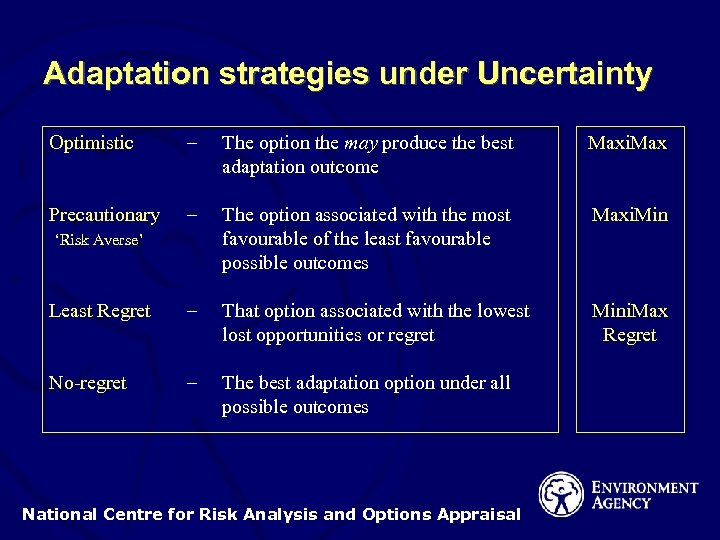
Adaptation strategies under Uncertainty Optimistic – The option the may produce the best adaptation outcome Maxi. Max Precautionary – The option associated with the most favourable of the least favourable possible outcomes Maxi. Min Least Regret – That option associated with the lowest lost opportunities or regret Mini. Max Regret No-regret – The best adaptation option under all possible outcomes ‘Risk Averse’ National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal

Generic options for climate risk management • Wider use of risk assessment, forecasts and options appraisal – preferably proactive technical response • Delay and buy-time – proactive technical response to reduce uncertainty • Research e. g. modelling, technology, ‘adaptive capacity’ • Monitoring – system performance monitoring - proactive technical response – climate impact monitoring - reactive technical response • Data and information supply, and education, awareness raising – proactive and reactive • Contingency planning – low probability, high consequence events – strategic planning response National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal

Generic options for climate risk management • Diversification or bet-hedging – proactive technical or policy response • Insurance proactive, fiscal response • Defend and Manage - reactive technical measures • Change of use – proactive or reactive, planning response +/- technical measures • Retreat and Abandon – strategic planning response • Safety factors, climate headroom, buffering measures – technical and regulatory response National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
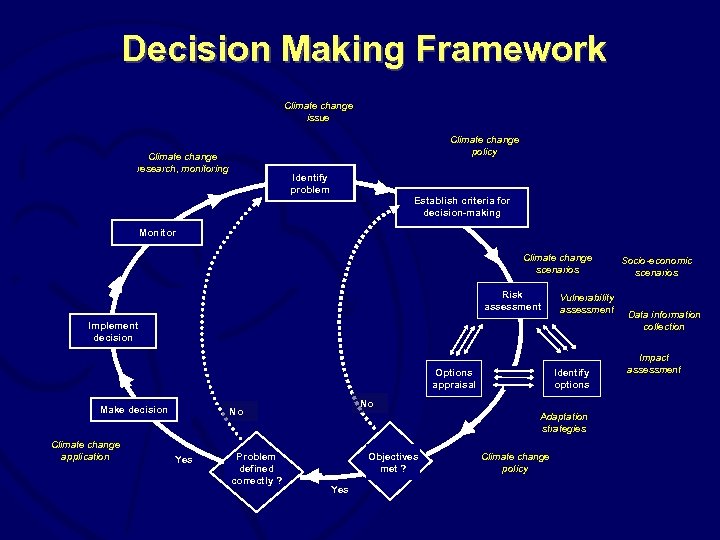
Decision Making Framework Climate change issue Climate change policy Climate change research, monitoring Identify problem Establish criteria for decision-making Monitor Climate change scenarios Risk assessment Vulnerability assessment Implement decision Options appraisal Make decision Climate change application No No Yes Problem defined correctly ? Identify options Adaptation strategies Objectives met ? Yes Climate change policy Socio-economic scenarios Data information collection Impact assessment

Risk screening - climate variable checklist • Helps to both identify (Table 1) and define the different characteristics (Table 2) of potentially significant or relevant climate variables • Includes preliminary assessment of sensitivity and confidence • Useful for screening of variables • Not constrained by availability of climate forecast variables (e. g. from GCM’s or RCM’s) • Encourages rigorous analysis of climate influence • Table 1 is not complete - proxy and compound variables will depend on nature of particular assessment National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal

Climate variable checklist Types of variables Examples • Primary CO 2, sea-level, temperature, precipitation, wind, cloud cover • Synoptic Weather types, pressure, storm track, lightning • Compound Humidity, evapotranspiration, mist, fog, growth season • Proxy Soil Moisture, river flow, wave climate National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal

Climate variable checklist Characteristics of variables Examples • Magnitude and Direction Increase, decrease, rate of change • Statistic Average, time-integrated, variability and frequency • Averaging period Instantaneous. . . hourly …. Annual …. . decadal • Joint probability events Consecutive, coincident or joint occurrence, and variables correlation National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
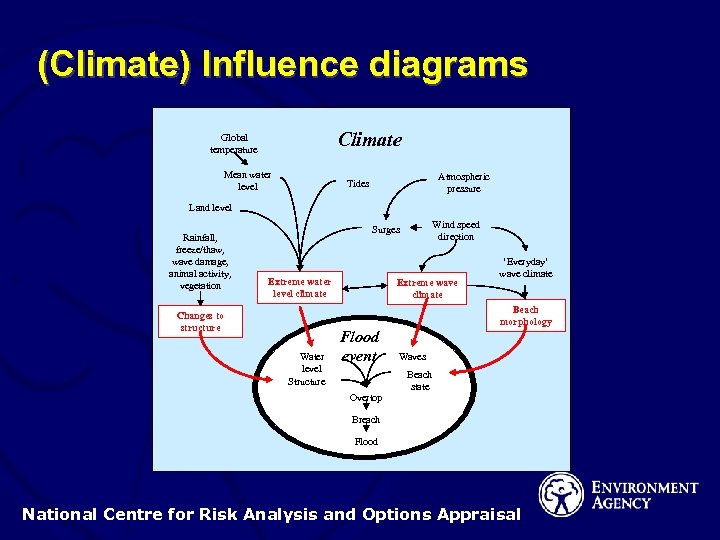
(Climate) Influence diagrams Climate Global temperature Mean water level Atmospheric pressure Tides Land level Rainfall, freeze/thaw, wave damage, animal activity, vegetation Wind speed direction Surges Extreme water level climate Extreme wave climate ‘Everyday’ wave climate Beach morphology Changes to structure Water level Structure Flood event Overtop Waves Beach state Breach Flood National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
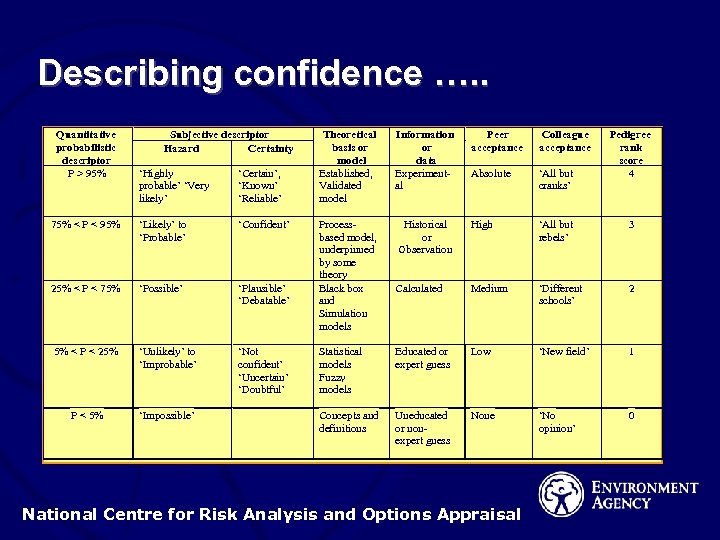
Describing confidence …. . Quantitative probabilistic descriptor P > 95% Subjective descriptor Hazard Certainty ‘Highly probable’ ‘Very likely’ ‘Certain’, ‘Known’ ‘Reliable’ 75% < P < 95% ‘Likely’ to ‘Probable’ ‘Confident’ 25% < P < 75% ‘Possible’ ‘Plausible’ ‘Debatable’ 5% < P < 25% ‘Unlikely’ to ‘Improbable’ ‘Not confident’ ‘Uncertain’ ‘Doubtful’ P < 5% ‘Impossible’ Theoretical basis or model Established, Validated model Information or data Experimental Peer acceptance Colleague acceptance Processbased model, underpinned by some theory Black box and Simulation models Absolute ‘All but cranks’ Historical or Observation High ‘All but rebels’ 3 Calculated Medium ‘Different schools’ 2 Statistical models Fuzzy models Educated or expert guess Low ‘New field’ 1 Concepts and definitions Uneducated or nonexpert guess None ‘No opinion’ 0 National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal Pedigree rank score 4
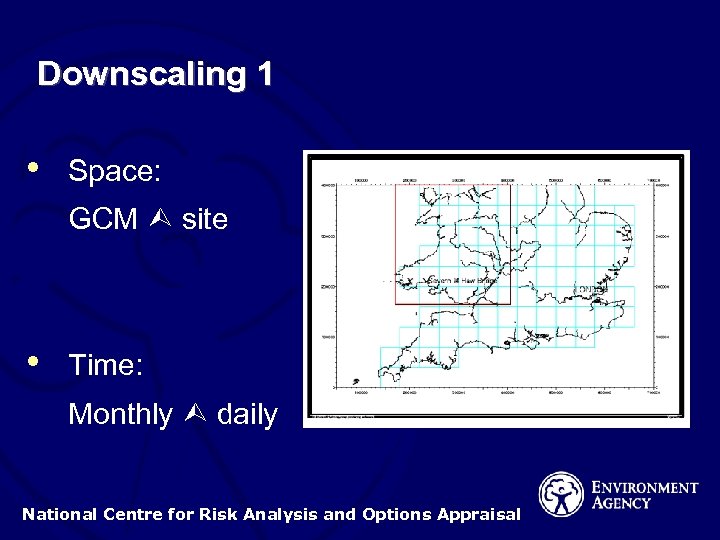
Downscaling 1 • Space: GCM site • Time: Monthly daily National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
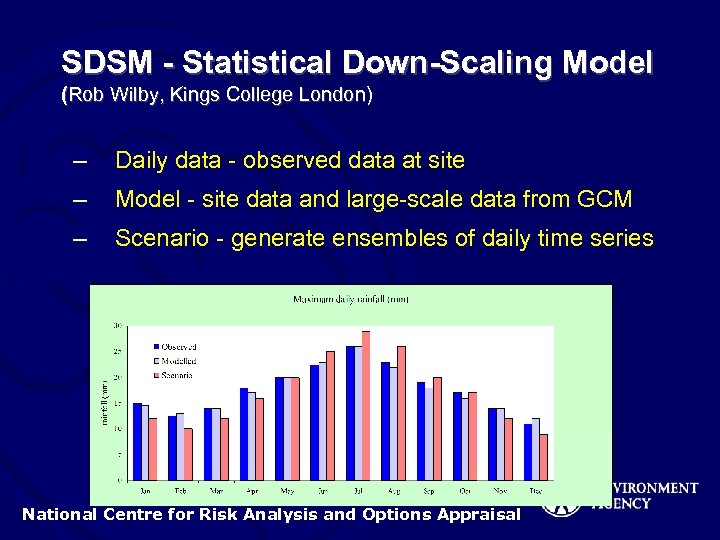
SDSM - Statistical Down-Scaling Model (Rob Wilby, Kings College London) – Daily data - observed data at site – Model - site data and large-scale data from GCM – Scenario - generate ensembles of daily time series National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
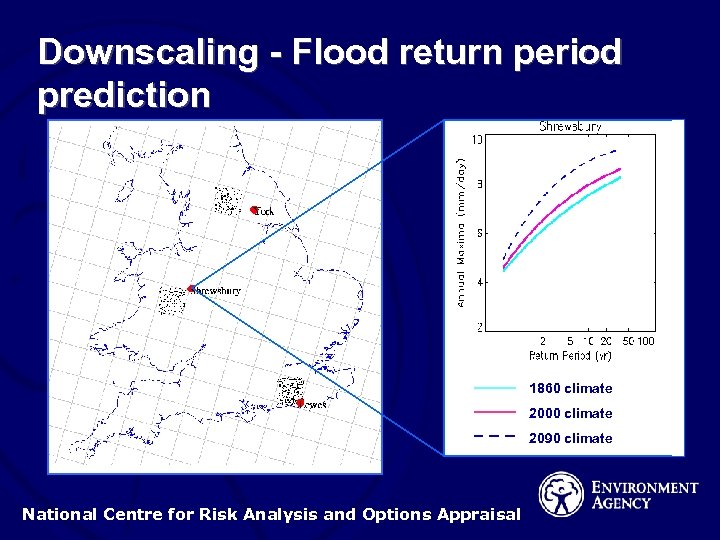
Downscaling - Flood return period prediction 1860 climate 2000 climate 2090 climate National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal

Scenario analysis and risk assessment Q. Can we create scenarios which reflect changes in variability as well as the mean? A. YES - but it is difficult… and scenarios remain contingent on assumptions and non-quantified uncertainties Q. Can we assign probabilities to different scenarios? A. Probably. Expert judgement can be used to assign probability to the range encompassed by any two scenarios … but uncertainty components within suite of scenarios have to be well-posed National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
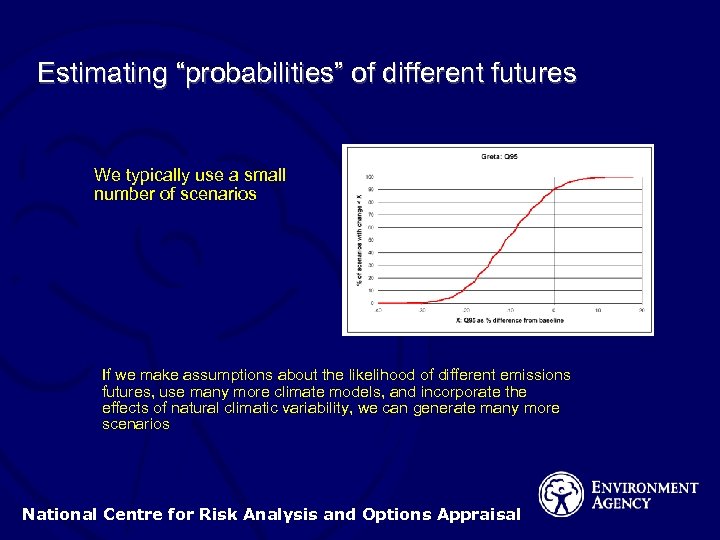
Estimating “probabilities” of different futures We typically use a small number of scenarios If we make assumptions about the likelihood of different emissions futures, use many more climate models, and incorporate the effects of natural climatic variability, we can generate many more scenarios National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal

Incorporating climate change into water resources management The future hydrological resource base will not be the same as the present resource base Mean climate will be different, due to climate change and natural climatic variability Variability in climate will be different. Altered frequency of successive dry years? …. but we don’t know how different…. National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
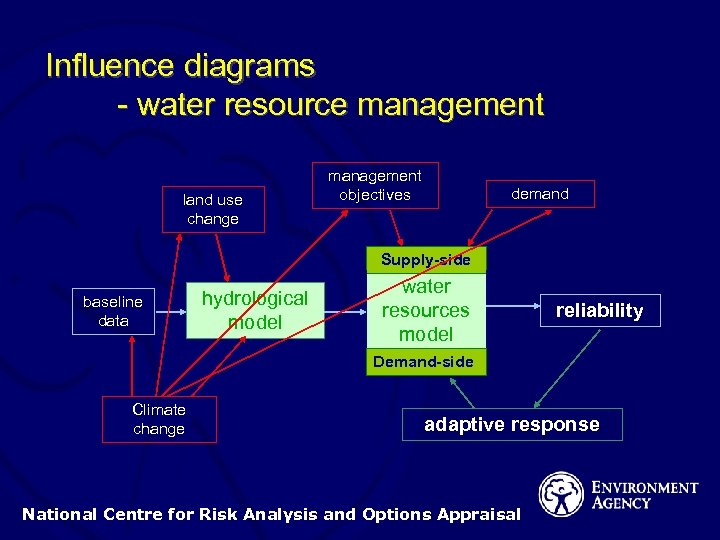
Influence diagrams - water resource management land use change management objectives demand Supply-side baseline data hydrological model water resources model reliability Demand-side Climate change adaptive response National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
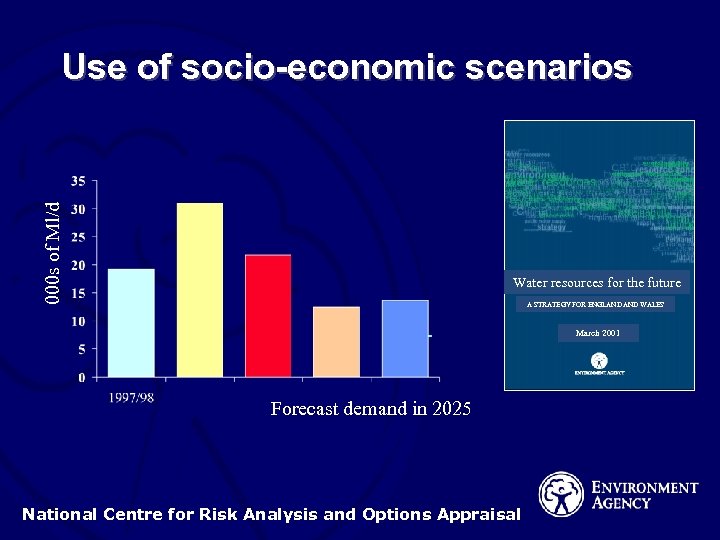
000 s of Ml/d Use of socio-economic scenarios Water resources for the future A STRATEGY FOR ENGLAND WALES March 2001 Forecast demand in 2025 National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal

Coping with uncertainty 1. Flexible management approaches - review situation and adjust plans if appropriate - continued monitoring 2. Improved seasonal forecasts - based on understanding of causes of seasonal climatic variability 3. Scenario analysis and risk assessment National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal

Conclusions and recommendations (for decision-makers) • Emphasis on understanding impact of present-day observed climate variability • Future climate change is only one source of decision uncertainty • Assessment of climate risk should be hierarchical /tiered • Climate adaptation should be iterative • Assumptions and sources of uncertainty should be treated explicitly in risk and impact assessments in order to reach robust decisions National Centre for Risk Analysis and Options Appraisal
b27d9431789da0c95225fe7ff50a939c.ppt