a60750d2534c647a8dfd93aab59f4c66.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 74
 Cleanliness is next to Godliness. . ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Cleanliness is next to Godliness. . ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 CONTENTS MATERIALS STANDARDIZATION CLASSIFICATION FILE DESIGN HAND INSTRUMENTS HANDPIECES INSTRUMENTS CONCLUSION ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
CONTENTS MATERIALS STANDARDIZATION CLASSIFICATION FILE DESIGN HAND INSTRUMENTS HANDPIECES INSTRUMENTS CONCLUSION ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 MATERIALS USED ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
MATERIALS USED ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
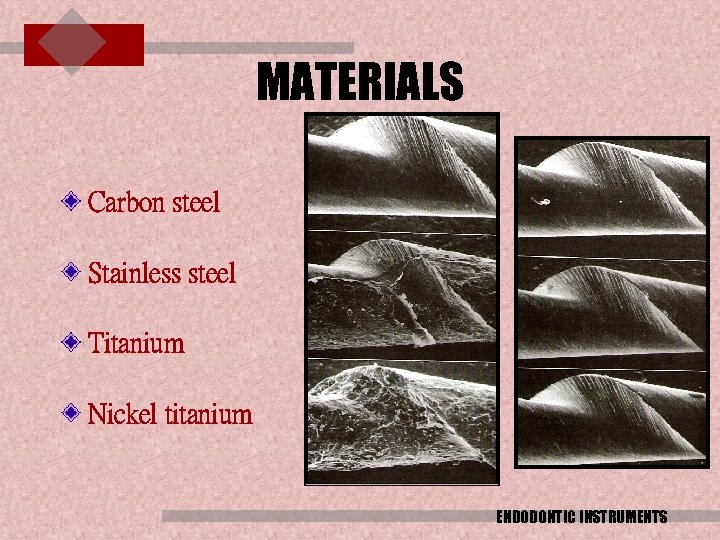 MATERIALS Carbon steel Stainless steel Titanium Nickel titanium ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
MATERIALS Carbon steel Stainless steel Titanium Nickel titanium ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Materials used: a) In 19 th century carbon steel was used for manufacturing of instruments. Disadvantages fracture tendency due to the brittleness of metal. corrosion along with Na. OCl irrigant and during steam sterilisation. b) In 20 th century stainless steel was used by Kerr manufacturing company. Advantages : It is flexible , hence less likely to fracture when strained. less susceptible to corrosion. Disadvantage: when canal curvature is > 450 it may fracture Disadvantage
Materials used: a) In 19 th century carbon steel was used for manufacturing of instruments. Disadvantages fracture tendency due to the brittleness of metal. corrosion along with Na. OCl irrigant and during steam sterilisation. b) In 20 th century stainless steel was used by Kerr manufacturing company. Advantages : It is flexible , hence less likely to fracture when strained. less susceptible to corrosion. Disadvantage: when canal curvature is > 450 it may fracture Disadvantage
 c) Nickel titanium (nitinol) Ni. Ti__most flexible Advantages – low elastic modulus and thus provides very good elastic flexibility to instrument , hence used in curved canal shape memory alloy ---it has the ability to recover from plastic strain when unloaded. Dis advantage –expensive difficult to manufacture and mill. d) Titanium and aluminium alloy.
c) Nickel titanium (nitinol) Ni. Ti__most flexible Advantages – low elastic modulus and thus provides very good elastic flexibility to instrument , hence used in curved canal shape memory alloy ---it has the ability to recover from plastic strain when unloaded. Dis advantage –expensive difficult to manufacture and mill. d) Titanium and aluminium alloy.
 ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
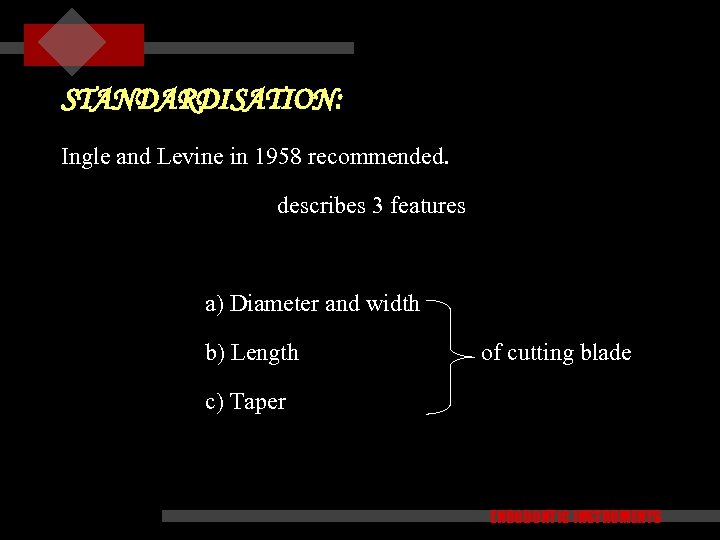 STANDARDISATION: Ingle and Levine in 1958 recommended. describes 3 features a) Diameter and width b) Length of cutting blade c) Taper ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
STANDARDISATION: Ingle and Levine in 1958 recommended. describes 3 features a) Diameter and width b) Length of cutting blade c) Taper ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
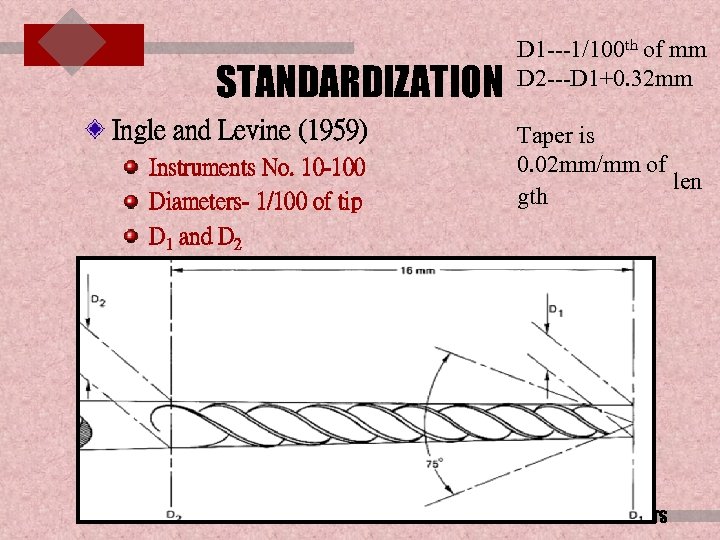 STANDARDIZATION Ingle and Levine (1959) Instruments No. 10 -100 Diameters- 1/100 of tip D 1 and D 2 D 1 ---1/100 th of mm D 2 ---D 1+0. 32 mm Taper is 0. 02 mm/mm of len gth ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
STANDARDIZATION Ingle and Levine (1959) Instruments No. 10 -100 Diameters- 1/100 of tip D 1 and D 2 D 1 ---1/100 th of mm D 2 ---D 1+0. 32 mm Taper is 0. 02 mm/mm of len gth ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 1) Instrument are numbered from 10 to 100, the numbers to advance by 5 units to size 60 and then by 10 units till size 100 2) Each number shall describe the diameter of instrument in 100 th of a mm at the tip eg: size 10 -tip is 0. 1 mm 3) The working blade (flutes) shall begin at the tip designated as D 1, and the flutes extends to the length of 16 mm designated as D 2 Taper of the instrument from D 1 to D 2 is in increments of 0. 02 mm in width/mm of length ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
1) Instrument are numbered from 10 to 100, the numbers to advance by 5 units to size 60 and then by 10 units till size 100 2) Each number shall describe the diameter of instrument in 100 th of a mm at the tip eg: size 10 -tip is 0. 1 mm 3) The working blade (flutes) shall begin at the tip designated as D 1, and the flutes extends to the length of 16 mm designated as D 2 Taper of the instrument from D 1 to D 2 is in increments of 0. 02 mm in width/mm of length ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 So, the diameter of D 2 shall be 0. 32 mm greater than D 1 ex: 20 reamer-------D 1 is 0. 2 D 2 is 0. 2+0. 32= 0. 52 Other specifications: a) Tip angle of instrument----75 ± 15 b) Instrument sizes should increase by 0. 05 mm at D 1 between 10 to 60 And by 0. 1 mm from 60 to 100 for increased instrument selection. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
So, the diameter of D 2 shall be 0. 32 mm greater than D 1 ex: 20 reamer-------D 1 is 0. 2 D 2 is 0. 2+0. 32= 0. 52 Other specifications: a) Tip angle of instrument----75 ± 15 b) Instrument sizes should increase by 0. 05 mm at D 1 between 10 to 60 And by 0. 1 mm from 60 to 100 for increased instrument selection. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 3) Instruments are available in different lengths 21 mm, 25 mm, 28 mm, 30 mm, 40 mm 21 mm length is used for molars 25 mm length is used for anteriors 28 & 30 mm length is used for cuspids 40 mm reamers used in preparing canals for endodontic implants ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
3) Instruments are available in different lengths 21 mm, 25 mm, 28 mm, 30 mm, 40 mm 21 mm length is used for molars 25 mm length is used for anteriors 28 & 30 mm length is used for cuspids 40 mm reamers used in preparing canals for endodontic implants ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
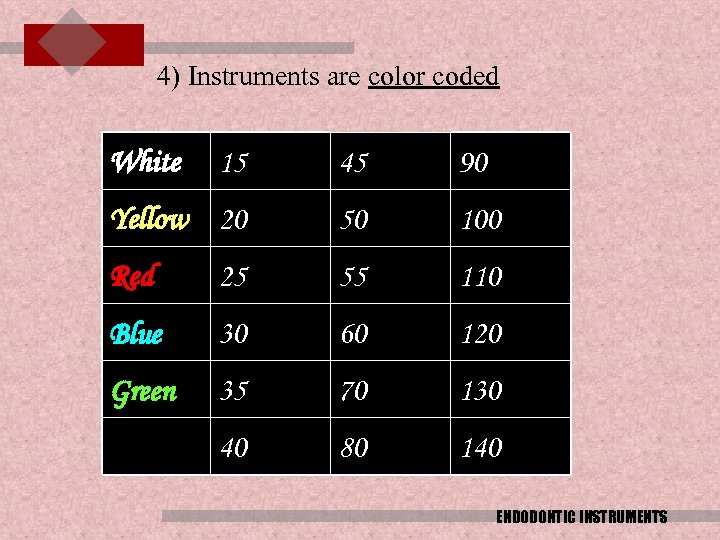 4) Instruments are color coded White 15 45 90 Yellow 20 50 100 Red 25 55 110 Blue 30 60 120 Green 35 70 130 black 40 80 140 ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
4) Instruments are color coded White 15 45 90 Yellow 20 50 100 Red 25 55 110 Blue 30 60 120 Green 35 70 130 black 40 80 140 ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 For narrow Root canals- size 06, 08 , 10 are used pink grey purple Modifications –of k-flex files Length of flutes is 18 mm from tip to extent I. e D 1 and D 2 not signified This recommends use of D 0 and D 16 D 0 ------- D 16 1 mm above D 0 is D 17 - D 18 are also present ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
For narrow Root canals- size 06, 08 , 10 are used pink grey purple Modifications –of k-flex files Length of flutes is 18 mm from tip to extent I. e D 1 and D 2 not signified This recommends use of D 0 and D 16 D 0 ------- D 16 1 mm above D 0 is D 17 - D 18 are also present ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
![In Jan 1976, ASI [American std institute] granted approval of ADA Specification. No. 28 In Jan 1976, ASI [American std institute] granted approval of ADA Specification. No. 28](https://present5.com/presentation/a60750d2534c647a8dfd93aab59f4c66/image-16.jpg) In Jan 1976, ASI [American std institute] granted approval of ADA Specification. No. 28 for endo files and reamer No. 58 for H files ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
In Jan 1976, ASI [American std institute] granted approval of ADA Specification. No. 28 for endo files and reamer No. 58 for H files ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 ADA Specification. No. 28 revision in March 1981 stated 1) instrument sizes No. 6, 8, 10, 15 were added to original standardisation 2) D 1 and D 2 changed to D 0 and D 16 Six factors considered while analyzing endo instrument 1) Material that is cut 2) Anatomic configuration of r. c 3) Material of cutting instrument 4) Manufacturing process (grinding / twisting) 5) Design of instrument (files – reamer) 6) Fluid used during procedure. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
ADA Specification. No. 28 revision in March 1981 stated 1) instrument sizes No. 6, 8, 10, 15 were added to original standardisation 2) D 1 and D 2 changed to D 0 and D 16 Six factors considered while analyzing endo instrument 1) Material that is cut 2) Anatomic configuration of r. c 3) Material of cutting instrument 4) Manufacturing process (grinding / twisting) 5) Design of instrument (files – reamer) 6) Fluid used during procedure. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Manufacture of instrument ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Manufacture of instrument ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Manufacture of instrument: In early 1900’s Kerr manufacturing company designed and manufactured new K type endodontic instrument. Initially the instrument were manufactured from round tapered piano wire (carbon steel), but now they are made from st. steel blanks. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Manufacture of instrument: In early 1900’s Kerr manufacturing company designed and manufactured new K type endodontic instrument. Initially the instrument were manufactured from round tapered piano wire (carbon steel), but now they are made from st. steel blanks. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 The st. steel wire is ground along its long axis into a 4 Sided (square c. s) or 3 sided (triangular c. s) tapered shaft that is twisted into flutes extending 16 mm from the top to the tip of blade. The number of flutes twisted into each blade determines whether instrument is a file or reamer. Files---tighter flutes Reamers---looser flutes ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
The st. steel wire is ground along its long axis into a 4 Sided (square c. s) or 3 sided (triangular c. s) tapered shaft that is twisted into flutes extending 16 mm from the top to the tip of blade. The number of flutes twisted into each blade determines whether instrument is a file or reamer. Files---tighter flutes Reamers---looser flutes ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Recently rhomboidal or diamond shaped blanks are twisted to produce a file---K flex to increase flexibility & cutting efficiency. H files– Manufactured from round st. steel wire machined to produce spiral flutes resembling cones or screw. Unifiles Machined from round st. steel wire by cutting 2 superficial grooves to produce flutes in a double helix design. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Recently rhomboidal or diamond shaped blanks are twisted to produce a file---K flex to increase flexibility & cutting efficiency. H files– Manufactured from round st. steel wire machined to produce spiral flutes resembling cones or screw. Unifiles Machined from round st. steel wire by cutting 2 superficial grooves to produce flutes in a double helix design. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 CLASSIFICATION ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
CLASSIFICATION ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 CLASSIFICATION According to Grossman Exploring instruments Instruments for debridement Shaping instruments Obturating instruments ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
CLASSIFICATION According to Grossman Exploring instruments Instruments for debridement Shaping instruments Obturating instruments ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
![According to Grossman [based on the function] 1) Exploring : to locate the canal According to Grossman [based on the function] 1) Exploring : to locate the canal](https://present5.com/presentation/a60750d2534c647a8dfd93aab59f4c66/image-25.jpg) According to Grossman [based on the function] 1) Exploring : to locate the canal orifices. to determine or assist in obtaining patency of the R C Egs : Endodontic explorer & smooth broaches 2) Debridement : to extirpate the pulp to remove cotton pellets or paper points Egs : barbed broach 3) Cleaning & Shaping Egs : Reamers and file ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
According to Grossman [based on the function] 1) Exploring : to locate the canal orifices. to determine or assist in obtaining patency of the R C Egs : Endodontic explorer & smooth broaches 2) Debridement : to extirpate the pulp to remove cotton pellets or paper points Egs : barbed broach 3) Cleaning & Shaping Egs : Reamers and file ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
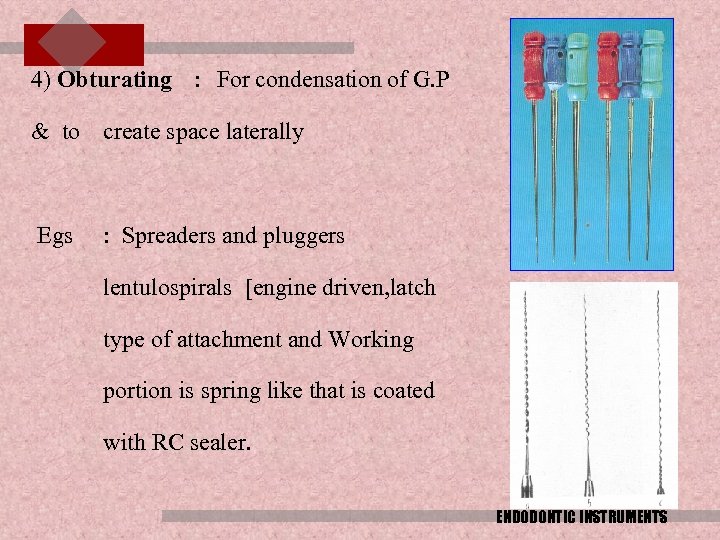 4) Obturating : For condensation of G. P & to create space laterally Egs : Spreaders and pluggers lentulospirals [engine driven, latch type of attachment and Working portion is spring like that is coated with RC sealer. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
4) Obturating : For condensation of G. P & to create space laterally Egs : Spreaders and pluggers lentulospirals [engine driven, latch type of attachment and Working portion is spring like that is coated with RC sealer. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 International Standards Organization (ISO) has grouped root canal instruments according to their use: Group I: hand use only: Files H-type K-type reamers and files Broaches Group II: engine driven latch type Same design as in group I but made to attach to hand piece. Profile, Lightspeed ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
International Standards Organization (ISO) has grouped root canal instruments according to their use: Group I: hand use only: Files H-type K-type reamers and files Broaches Group II: engine driven latch type Same design as in group I but made to attach to hand piece. Profile, Lightspeed ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Group III: engine driven latch type Low speed instruments where latch type attachment is in one piece with working part. Gates Glidden drills and Peeso reamers. Group IV: root canal points. Gutta percha, silver points and paper points. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Group III: engine driven latch type Low speed instruments where latch type attachment is in one piece with working part. Gates Glidden drills and Peeso reamers. Group IV: root canal points. Gutta percha, silver points and paper points. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 According to Stock: Twisted Machined K-files H file K- reamer Flex R K-flex file Canal master Flexo Heliapical Zipper flexicut Flexogates Mc spadden engine file ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
According to Stock: Twisted Machined K-files H file K- reamer Flex R K-flex file Canal master Flexo Heliapical Zipper flexicut Flexogates Mc spadden engine file ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Broaches and Rasps : oldest endo instrument : used for removal of pulp tissue : used for removal of cotton or paper points from R. c Broach 1. Barb height is large 2. As the barb comes out of instrument, broach is a weaker instrument compared to rasp 3. Taper is 0. 007 to 0. 01 mm/mm Rasp It is small Taper is 0. 015 mm/mm ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Broaches and Rasps : oldest endo instrument : used for removal of pulp tissue : used for removal of cotton or paper points from R. c Broach 1. Barb height is large 2. As the barb comes out of instrument, broach is a weaker instrument compared to rasp 3. Taper is 0. 007 to 0. 01 mm/mm Rasp It is small Taper is 0. 015 mm/mm ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 4. More fragile because of depth of cut 5. Coronally angulated barbs shallower and rounded barbs perpendicular to long axis of metal Both are not used beyond middle 3 rd of R. c and also entangle in R. c and get separated ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
4. More fragile because of depth of cut 5. Coronally angulated barbs shallower and rounded barbs perpendicular to long axis of metal Both are not used beyond middle 3 rd of R. c and also entangle in R. c and get separated ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
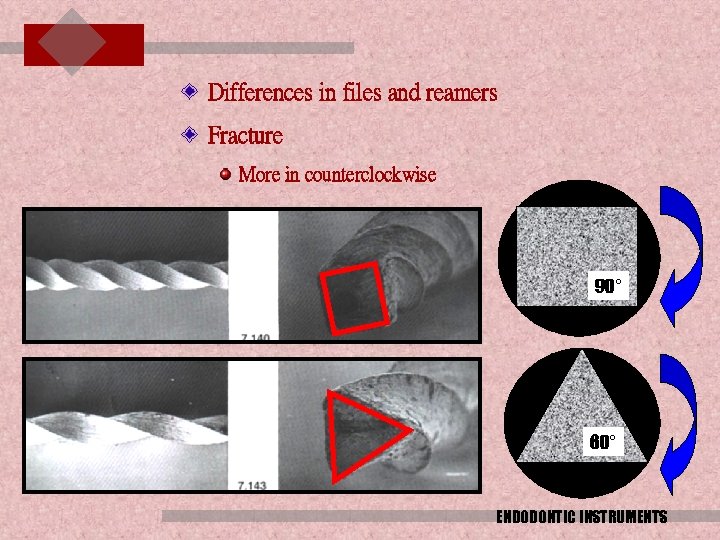 Differences in files and reamers Fracture More in counterclockwise 90° 60° ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Differences in files and reamers Fracture More in counterclockwise 90° 60° ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
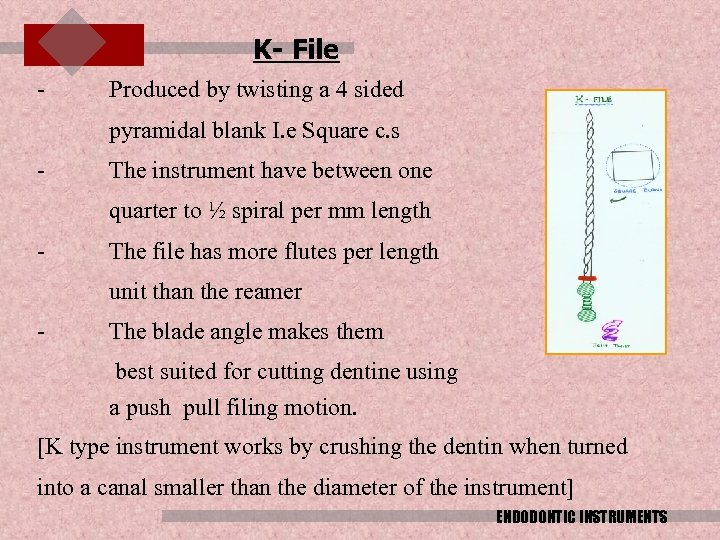 K- File - Produced by twisting a 4 sided pyramidal blank I. e Square c. s - The instrument have between one quarter to ½ spiral per mm length - The file has more flutes per length unit than the reamer - The blade angle makes them best suited for cutting dentine using a push pull filing motion. [K type instrument works by crushing the dentin when turned into a canal smaller than the diameter of the instrument] ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
K- File - Produced by twisting a 4 sided pyramidal blank I. e Square c. s - The instrument have between one quarter to ½ spiral per mm length - The file has more flutes per length unit than the reamer - The blade angle makes them best suited for cutting dentine using a push pull filing motion. [K type instrument works by crushing the dentin when turned into a canal smaller than the diameter of the instrument] ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
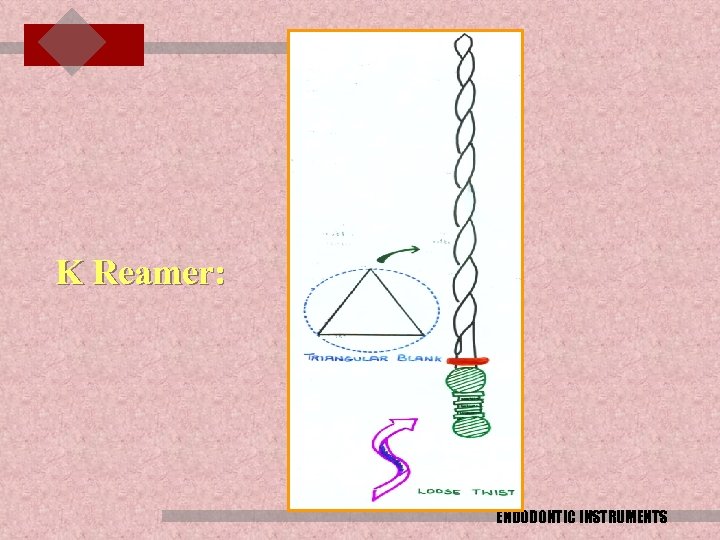 K Reamer: ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
K Reamer: ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 K Reamer: The instrument is produced by twisting a 3 sided blank i. e triangular c. s which makes reamer more flexible than files. These instruments have less than one tenth and one quarter of a spiral per mm of length giving a rake angle which cuts more efficiently using a rotary motion , hence reaming motion. They are used with a rotating pushing motion limited to half turn and disengage with a pulling motion ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
K Reamer: The instrument is produced by twisting a 3 sided blank i. e triangular c. s which makes reamer more flexible than files. These instruments have less than one tenth and one quarter of a spiral per mm of length giving a rake angle which cuts more efficiently using a rotary motion , hence reaming motion. They are used with a rotating pushing motion limited to half turn and disengage with a pulling motion ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Flutes are placed farther apart and hence more space between flutes allowing better transport of dentin debris Angle less than 90 , cutting efficiency is more. If surface area is less , then flexibility is more. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Flutes are placed farther apart and hence more space between flutes allowing better transport of dentin debris Angle less than 90 , cutting efficiency is more. If surface area is less , then flexibility is more. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Reaming— place instrument till apical constriction and give ¼ to ½ turn and pull out. In narrow canal-less turn is given and in wider canal large turn is given. Files can be used in reaming motion, but reamer does not cut efficiently in filing motion. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Reaming— place instrument till apical constriction and give ¼ to ½ turn and pull out. In narrow canal-less turn is given and in wider canal large turn is given. Files can be used in reaming motion, but reamer does not cut efficiently in filing motion. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Files Reamer Square c. s triangular c. s Tighter flutes loose spirals Resists fracture better. Cutting efficiency is 2. 5 times more Maintains keen edge sharpness is lost rapidly More number of flutes less number of flutes Filing and reaming motion ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Files Reamer Square c. s triangular c. s Tighter flutes loose spirals Resists fracture better. Cutting efficiency is 2. 5 times more Maintains keen edge sharpness is lost rapidly More number of flutes less number of flutes Filing and reaming motion ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
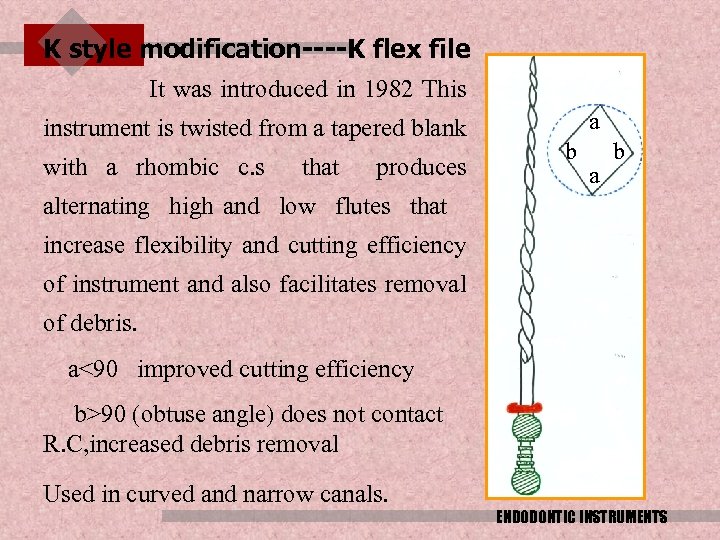 K style modification----K flex file It was introduced in 1982 This instrument is twisted from a tapered blank with a rhombic c. s that produces alternating high and low flutes that increase flexibility and cutting efficiency of instrument and also facilitates removal of debris. a b a<90 improved cutting efficiency b>90 (obtuse angle) does not contact R. C, increased debris removal Used in curved and narrow canals. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
K style modification----K flex file It was introduced in 1982 This instrument is twisted from a tapered blank with a rhombic c. s that produces alternating high and low flutes that increase flexibility and cutting efficiency of instrument and also facilitates removal of debris. a b a<90 improved cutting efficiency b>90 (obtuse angle) does not contact R. C, increased debris removal Used in curved and narrow canals. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Flex O files ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Flex O files ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Golden medium: Range of intermediate files described by Weine provide half sizes between traditional instruments for narrow canals (instrument should be intermediate to 12 -20 Sizes from 12 -32 (12, 17, 22, 27, 32, 37) manufactured by maillefer. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Golden medium: Range of intermediate files described by Weine provide half sizes between traditional instruments for narrow canals (instrument should be intermediate to 12 -20 Sizes from 12 -32 (12, 17, 22, 27, 32, 37) manufactured by maillefer. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 (weine suggested trimming 1 mm from the tip of the file rounding off sharp edges on diamond nail file) In this way, file sizes 10, 15 20 25 may be converted to 12, 17, 22, 27. Disadvantage is files are made disposable , and edges are difficult to smooth. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
(weine suggested trimming 1 mm from the tip of the file rounding off sharp edges on diamond nail file) In this way, file sizes 10, 15 20 25 may be converted to 12, 17, 22, 27. Disadvantage is files are made disposable , and edges are difficult to smooth. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Flex R file: designed to be used in balanced force technique. Machined from blank of triangular c. s Non cutting tip ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Flex R file: designed to be used in balanced force technique. Machined from blank of triangular c. s Non cutting tip ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
![§ instrument An rotated quarter isaturn [clockwise] as gentle pressure is exerted to insert § instrument An rotated quarter isaturn [clockwise] as gentle pressure is exerted to insert](https://present5.com/presentation/a60750d2534c647a8dfd93aab59f4c66/image-44.jpg) § instrument An rotated quarter isaturn [clockwise] as gentle pressure is exerted to insert it. This§action the positions the walls. § revolution. § Simultaneous apical pressure and anticlockwise rotation of file sustains a balance between tooth structure and instrument so that it is near the canal axis. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
§ instrument An rotated quarter isaturn [clockwise] as gentle pressure is exerted to insert it. This§action the positions the walls. § revolution. § Simultaneous apical pressure and anticlockwise rotation of file sustains a balance between tooth structure and instrument so that it is near the canal axis. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Heliapical: This instrument resembles conventional file in the apical 4 -5 mm the remainder being a narrow blank shank Small sizes fracture ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Heliapical: This instrument resembles conventional file in the apical 4 -5 mm the remainder being a narrow blank shank Small sizes fracture ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 HEDSTROM FILES (ANSI 58) Milled instrument- multiaxial grinding Positive rake angle Cuts in pull motion Uses ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
HEDSTROM FILES (ANSI 58) Milled instrument- multiaxial grinding Positive rake angle Cuts in pull motion Uses ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
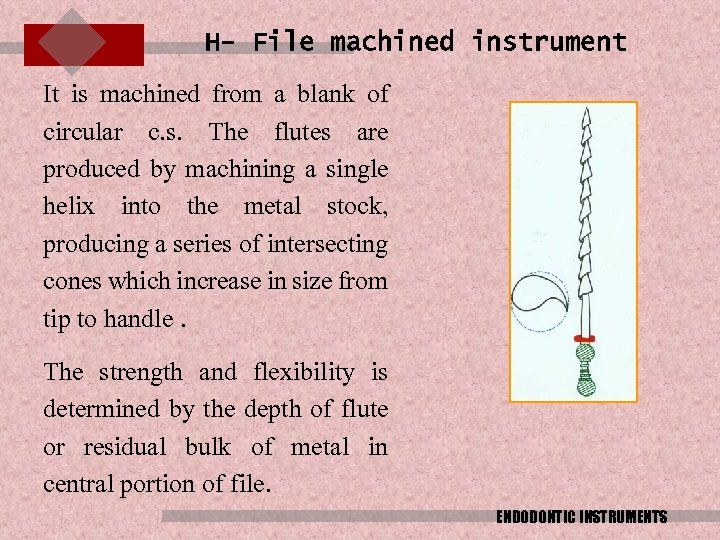 H- File machined instrument It is machined from a blank of circular c. s. The flutes are produced by machining a single helix into the metal stock, producing a series of intersecting cones which increase in size from tip to handle. The strength and flexibility is determined by the depth of flute or residual bulk of metal in central portion of file. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
H- File machined instrument It is machined from a blank of circular c. s. The flutes are produced by machining a single helix into the metal stock, producing a series of intersecting cones which increase in size from tip to handle. The strength and flexibility is determined by the depth of flute or residual bulk of metal in central portion of file. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 The blades are at right angles to dentine surface and so most efficient cutting motion is a pulling stroke. No dentine is removed by push stroke Rotating the instrument with a tip of file engaged in dentin is a common cause of fracture. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
The blades are at right angles to dentine surface and so most efficient cutting motion is a pulling stroke. No dentine is removed by push stroke Rotating the instrument with a tip of file engaged in dentin is a common cause of fracture. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
![They are aggressive cutters. It resembles ‘Christmas tree’ appearance. [cone over cone] used to They are aggressive cutters. It resembles ‘Christmas tree’ appearance. [cone over cone] used to](https://present5.com/presentation/a60750d2534c647a8dfd93aab59f4c66/image-49.jpg) They are aggressive cutters. It resembles ‘Christmas tree’ appearance. [cone over cone] used to remove loose broken instrument. Disadvantage: Fracture tendency because of depression between flutes causing narrowness between core material. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
They are aggressive cutters. It resembles ‘Christmas tree’ appearance. [cone over cone] used to remove loose broken instrument. Disadvantage: Fracture tendency because of depression between flutes causing narrowness between core material. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 H- Style Modification: Burns uni file: It is identical to H file but it has two cutting blades instead of single cutting blade. S-shaped c. s or double helix design cuts more efficiently ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
H- Style Modification: Burns uni file: It is identical to H file but it has two cutting blades instead of single cutting blade. S-shaped c. s or double helix design cuts more efficiently ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Canal Master: § The cutting portion resembles a reamer with blunted edges and is reduced to 1 -2 mm with a 0. 75 mm non cutting pilot tip. § The rest of the instrument consists of a parallel sided blank of round c. s, narrower than the cutting tip. § The most efficient means of cutting is using a clockwise rotary motion through 600 § Fracture potential is more. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Canal Master: § The cutting portion resembles a reamer with blunted edges and is reduced to 1 -2 mm with a 0. 75 mm non cutting pilot tip. § The rest of the instrument consists of a parallel sided blank of round c. s, narrower than the cutting tip. § The most efficient means of cutting is using a clockwise rotary motion through 600 § Fracture potential is more. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Canal Master & Canal Master U Wildey and Senia 1 -2 mm cutting head 0. 75 mm non-cutting head Blank shaft Sizes available Now available in Ni Ti ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Canal Master & Canal Master U Wildey and Senia 1 -2 mm cutting head 0. 75 mm non-cutting head Blank shaft Sizes available Now available in Ni Ti ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Flexogates : St. steel instrument resembles canal master § circular and small in c. s § spiral of fluting on an expanded head carried on the shank. § removal of broken instrument ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Flexogates : St. steel instrument resembles canal master § circular and small in c. s § spiral of fluting on an expanded head carried on the shank. § removal of broken instrument ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Mc Spadden Engine file Used in rotary hand piece at slow speed (300 r pm) Made from Ni – Ti alloy. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Mc Spadden Engine file Used in rotary hand piece at slow speed (300 r pm) Made from Ni – Ti alloy. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 - S- file: Variation of unifile A- File Modified by levy Available as hand automated files steep depth of flutes (400 helical angle ) non cutting tip avoids ledges and perforations. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
- S- file: Variation of unifile A- File Modified by levy Available as hand automated files steep depth of flutes (400 helical angle ) non cutting tip avoids ledges and perforations. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 he Greater taper Hand Files Ø Made of Niti. Ø activeto counter Each is instrument inbe designed clockwise direction and has a D 0 diameter 0. 2 [D 0 – 0. 2] increasing havetapers filesof 0. 10, 0. 08, Ø 0. 06, GT 0. 12 mm/mm Ø depending on the taper. Ø Designed towardshank cut more their side to cutting blades. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
he Greater taper Hand Files Ø Made of Niti. Ø activeto counter Each is instrument inbe designed clockwise direction and has a D 0 diameter 0. 2 [D 0 – 0. 2] increasing havetapers filesof 0. 10, 0. 08, Ø 0. 06, GT 0. 12 mm/mm Ø depending on the taper. Ø Designed towardshank cut more their side to cutting blades. ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 International Standards Organization (ISO) Group I: hand use only Group II: engine-driven latch type Group IV: root canal points ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
International Standards Organization (ISO) Group I: hand use only Group II: engine-driven latch type Group IV: root canal points ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 According to Cohen Hand instruments: those specific to endodontics Instruments for pulp space preparation v. Group III Devices for root canal length measurements Instruments for root canal obturation Devices for removal of root canal obstructions ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
According to Cohen Hand instruments: those specific to endodontics Instruments for pulp space preparation v. Group III Devices for root canal length measurements Instruments for root canal obturation Devices for removal of root canal obstructions ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 ADA classification Type I : Reamers Type II : Files Type III : Hedstroem files Type IV : Rasps Type V : Broaches Type VI : Probes Type VII : Applicators Type VIII : Condensers Type IX : Spreaders ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
ADA classification Type I : Reamers Type II : Files Type III : Hedstroem files Type IV : Rasps Type V : Broaches Type VI : Probes Type VII : Applicators Type VIII : Condensers Type IX : Spreaders ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 According to Harty For access cavity preparation v Basic instruments v Burs v Rubber dam For root canal preparation v Hand instruments v Power assisted root canal instruments v Electronic canal measuring system v Measuring instruments, gauge and stands v Instruments for retrieval of broken instruments and pastes Instruments for root canal filling ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
According to Harty For access cavity preparation v Basic instruments v Burs v Rubber dam For root canal preparation v Hand instruments v Power assisted root canal instruments v Electronic canal measuring system v Measuring instruments, gauge and stands v Instruments for retrieval of broken instruments and pastes Instruments for root canal filling ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 HAND INSTRUMENTS ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
HAND INSTRUMENTS ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
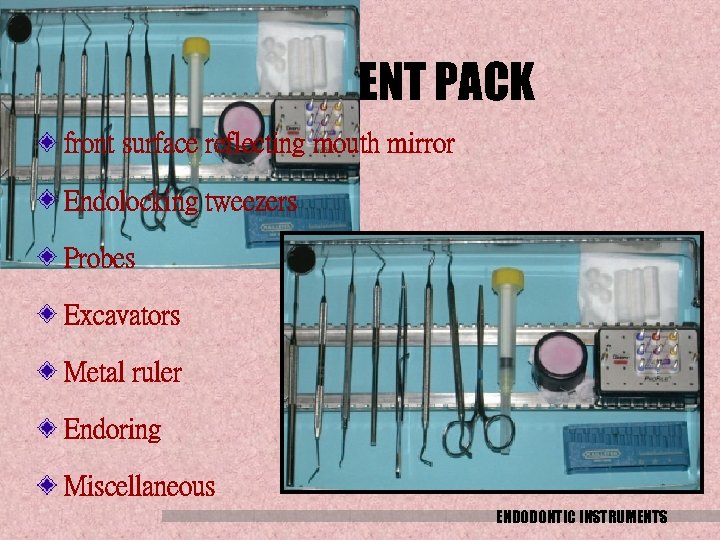 INSTRUMENT PACK front surface reflecting mouth mirror Endolocking tweezers Probes Excavators Metal ruler Endoring Miscellaneous ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
INSTRUMENT PACK front surface reflecting mouth mirror Endolocking tweezers Probes Excavators Metal ruler Endoring Miscellaneous ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Endo locking tweezer Mirror Long shank excavator ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Endo locking tweezer Mirror Long shank excavator ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
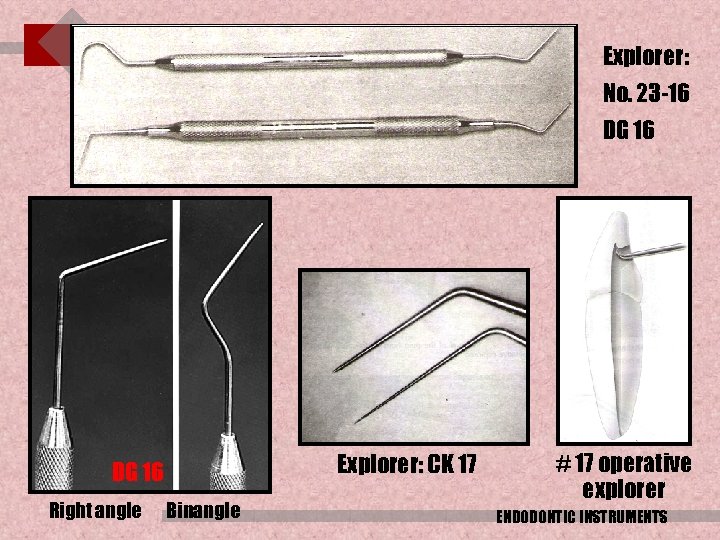 Explorer: No. 23 -16 DG 16 Explorer: CK 17 DG 16 Right angle Binangle # 17 operative explorer ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Explorer: No. 23 -16 DG 16 Explorer: CK 17 DG 16 Right angle Binangle # 17 operative explorer ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
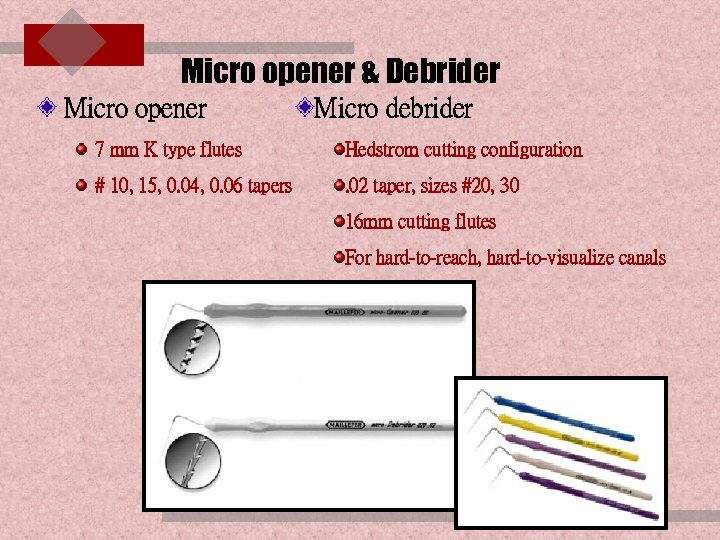 Micro opener & Debrider Micro opener Micro debrider 7 mm K type flutes Hedstrom cutting configuration # 10, 15, 0. 04, 0. 06 tapers . 02 taper, sizes #20, 30 16 mm cutting flutes For hard-to-reach, hard-to-visualize canals ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Micro opener & Debrider Micro opener Micro debrider 7 mm K type flutes Hedstrom cutting configuration # 10, 15, 0. 04, 0. 06 tapers . 02 taper, sizes #20, 30 16 mm cutting flutes For hard-to-reach, hard-to-visualize canals ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Selection of file holders Other instruments/equipment ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Selection of file holders Other instruments/equipment ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 ACCESS CAVITY INSTRUMENTS ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
ACCESS CAVITY INSTRUMENTS ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Round carbide burs Fissure carbide burs Tapered diamond burs ENDO ACCESS BUR ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Round carbide burs Fissure carbide burs Tapered diamond burs ENDO ACCESS BUR ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
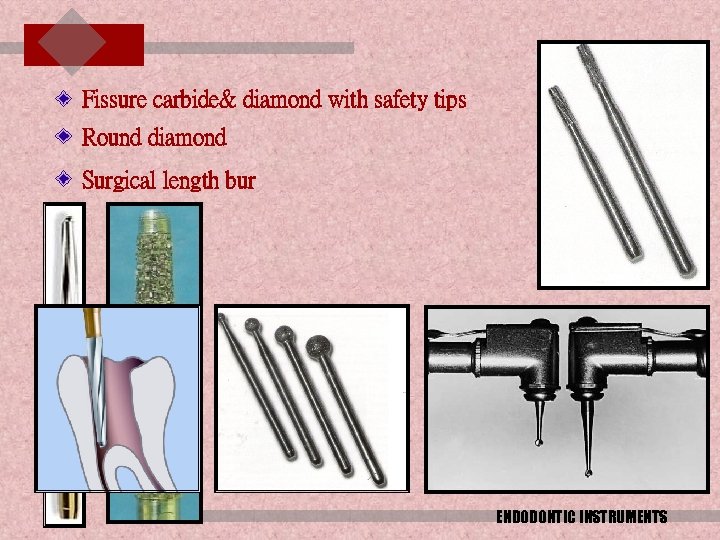 Fissure carbide& diamond with safety tips Round diamond Surgical length bur ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Fissure carbide& diamond with safety tips Round diamond Surgical length bur ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
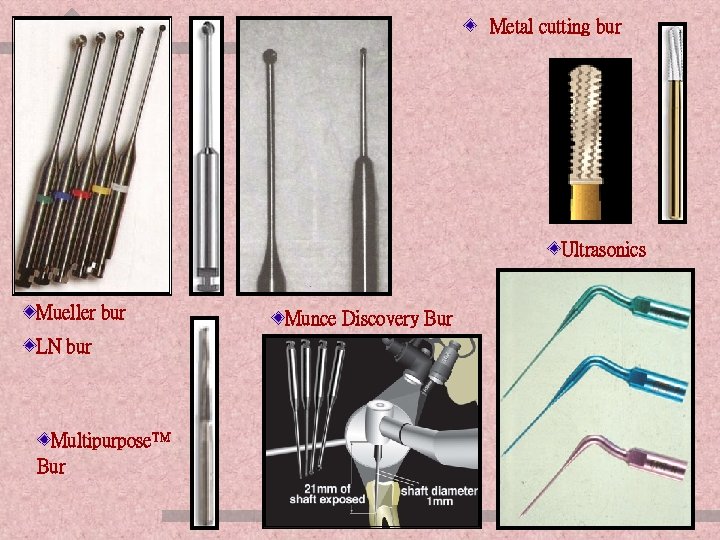 Metal cutting bur Ultrasonics Mueller bur Munce Discovery Bur LN bur Multipurpose™ Bur ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
Metal cutting bur Ultrasonics Mueller bur Munce Discovery Bur LN bur Multipurpose™ Bur ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 FILE DESIGN ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
FILE DESIGN ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 FILE DESIGN According to Twisted or Machined Taper Tip design Types v. Cutting v. Non cutting v. Partially cutting Functions Problems and its management ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
FILE DESIGN According to Twisted or Machined Taper Tip design Types v. Cutting v. Non cutting v. Partially cutting Functions Problems and its management ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 STERILIZATION Cleaning instruments v Ultrasonic bath Chemicals Dry heat Moist heat Salt / glass bead Checking sterilization Browne’s tubes Sterilization bags Lav. Endo-for disinfection ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
STERILIZATION Cleaning instruments v Ultrasonic bath Chemicals Dry heat Moist heat Salt / glass bead Checking sterilization Browne’s tubes Sterilization bags Lav. Endo-for disinfection ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENTS
 Knowledge is the antidote to fear. - Ralph Waldo Emerson CONCLUSION
Knowledge is the antidote to fear. - Ralph Waldo Emerson CONCLUSION


