63da49bf92760fa0ac431532c589ce27.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Cleaner Production programme and Environment Dr. Azza MORSSY Tel : 43 1 26026 3841 Fax: 43 1 26026 6819 – Email: amorssy@unido. org
Cleaner Production programme and Environment Dr. Azza MORSSY Tel : 43 1 26026 3841 Fax: 43 1 26026 6819 – Email: amorssy@unido. org
 This presentation UNIDO priorities - engaging industry in sustainability /Sustainable consumption & production 2. Cleaner Production examples 1. 3. Synergies of inter-Agency cooperation WHO EMRO – UNIDO 2
This presentation UNIDO priorities - engaging industry in sustainability /Sustainable consumption & production 2. Cleaner Production examples 1. 3. Synergies of inter-Agency cooperation WHO EMRO – UNIDO 2
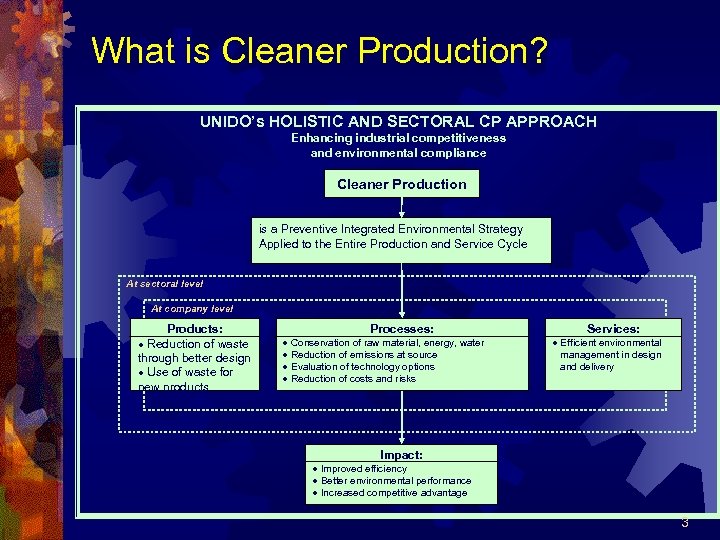 What is Cleaner Production? UNIDO’s HOLISTIC AND SECTORAL CP APPROACH Enhancing industrial competitiveness and environmental compliance Cleaner Production is a Preventive Integrated Environmental Strategy Applied to the Entire Production and Service Cycle At sectoral level At company level Products: · Reduction of waste through better design · Use of waste for new products Processes: · Conservation of raw material, energy, water · Reduction of emissions at source · Evaluation of technology options · Reduction of costs and risks Services: · Efficient environmental management in design and delivery Impact: · Improved efficiency · Better environmental performance · Increased competitive advantage 3
What is Cleaner Production? UNIDO’s HOLISTIC AND SECTORAL CP APPROACH Enhancing industrial competitiveness and environmental compliance Cleaner Production is a Preventive Integrated Environmental Strategy Applied to the Entire Production and Service Cycle At sectoral level At company level Products: · Reduction of waste through better design · Use of waste for new products Processes: · Conservation of raw material, energy, water · Reduction of emissions at source · Evaluation of technology options · Reduction of costs and risks Services: · Efficient environmental management in design and delivery Impact: · Improved efficiency · Better environmental performance · Increased competitive advantage 3
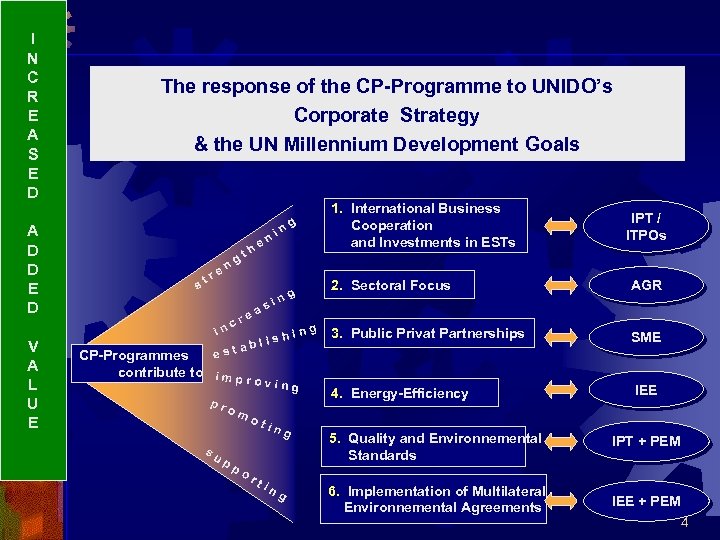 I N C R E A S E D A D D E D V A L U E The response of the CP-Programme to UNIDO’s Corporate Strategy & the UN Millennium Development Goals st r g en in t n he e cr est as i is abl hin su om pp ot or ti in g ng IPT / ITPOs 2. Sectoral Focus g in CP-Programmes contribute to i m p r oving pr 1. International Business Cooperation and Investments in ESTs ng g AGR 3. Public Privat Partnerships SME 4. Energy-Efficiency IEE 5. Quality and Environnemental Standards IPT + PEM 6. Implementation of Multilateral Environnemental Agreements IEE + PEM 4
I N C R E A S E D A D D E D V A L U E The response of the CP-Programme to UNIDO’s Corporate Strategy & the UN Millennium Development Goals st r g en in t n he e cr est as i is abl hin su om pp ot or ti in g ng IPT / ITPOs 2. Sectoral Focus g in CP-Programmes contribute to i m p r oving pr 1. International Business Cooperation and Investments in ESTs ng g AGR 3. Public Privat Partnerships SME 4. Energy-Efficiency IEE 5. Quality and Environnemental Standards IPT + PEM 6. Implementation of Multilateral Environnemental Agreements IEE + PEM 4
 Sustainable Development: A balance between: • • Environmental protection Economic growth & employment creation Reducing the environmental impact of industry (without impinging on its abilities to drive development) • Preventing the generation & emission of waste “Elimination & reduction in production & use” • Re-using & recycling materials • ‘Safe’ Disposal 5
Sustainable Development: A balance between: • • Environmental protection Economic growth & employment creation Reducing the environmental impact of industry (without impinging on its abilities to drive development) • Preventing the generation & emission of waste “Elimination & reduction in production & use” • Re-using & recycling materials • ‘Safe’ Disposal 5
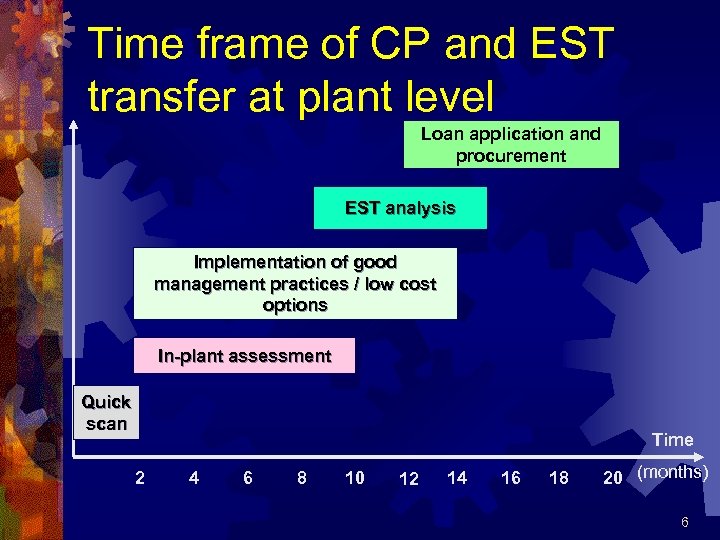 Time frame of CP and EST transfer at plant level Loan application and procurement EST analysis Implementation of good management practices / low cost options In-plant assessment Quick scan Time 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 (months) 6
Time frame of CP and EST transfer at plant level Loan application and procurement EST analysis Implementation of good management practices / low cost options In-plant assessment Quick scan Time 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 (months) 6
 How to implement CP ? • Develop National Sector Specific CP Strategies: • Sector Analysis • Analysis of process factors that delay the efficiency of the sector • Analysis of national policies that delay the efficiency of the sector and the application of CP • Potential to increase the efficiency of the sector through the application of CP and the transfer of ESTs • Quantitative and qualitative description of concrete CP techniques and ESTs to be applied in the 7 sector
How to implement CP ? • Develop National Sector Specific CP Strategies: • Sector Analysis • Analysis of process factors that delay the efficiency of the sector • Analysis of national policies that delay the efficiency of the sector and the application of CP • Potential to increase the efficiency of the sector through the application of CP and the transfer of ESTs • Quantitative and qualitative description of concrete CP techniques and ESTs to be applied in the 7 sector
 Evaluate environmental aspects • reduction in quantity of pollutants and waste generated; • reduction of pollutant/waste toxicity; • reduction in materials consumption; • reduction in use of non-renewable materials; • reduction in energy consumption; • reduction in consumption of energy from nonrenewable resources; • reduction of water consumption; • reduction of “nuisance”: noise, dust, smoke, 8 smell, etc.
Evaluate environmental aspects • reduction in quantity of pollutants and waste generated; • reduction of pollutant/waste toxicity; • reduction in materials consumption; • reduction in use of non-renewable materials; • reduction in energy consumption; • reduction in consumption of energy from nonrenewable resources; • reduction of water consumption; • reduction of “nuisance”: noise, dust, smoke, 8 smell, etc.
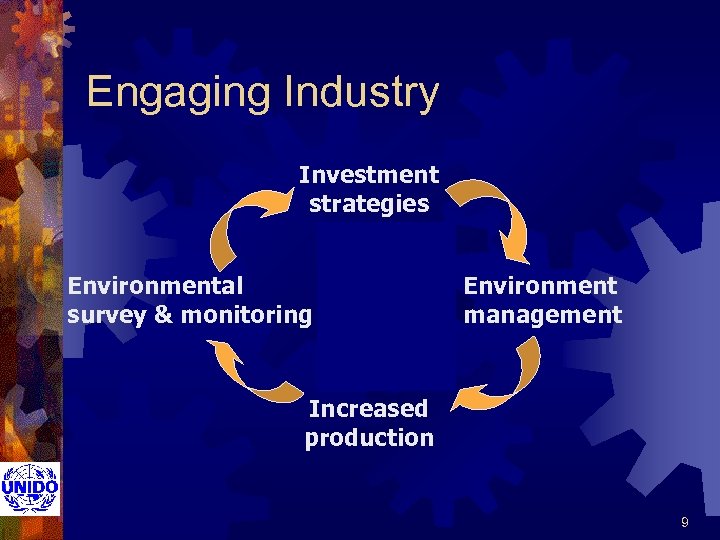 Engaging Industry Investment strategies Environmental survey & monitoring Environment management Increased production 9
Engaging Industry Investment strategies Environmental survey & monitoring Environment management Increased production 9
 Lasting improvements Audits & Quality assurance ‘green’ confidence Improved competitiveness Planning efficiency Faster investment Less consumption & waste Developing consensus 10
Lasting improvements Audits & Quality assurance ‘green’ confidence Improved competitiveness Planning efficiency Faster investment Less consumption & waste Developing consensus 10
 Cleaner Production not only environmental improvements profits but also benefits to the bottom line continuing environmental improvements lower resource & energy costs lower waste disposal charges improved productivity at lower unit cost lower volumes of air, water and solid emissions lower pollutant loadings workers health & safety improved product quality & market access towards compliance & community acceptance 11
Cleaner Production not only environmental improvements profits but also benefits to the bottom line continuing environmental improvements lower resource & energy costs lower waste disposal charges improved productivity at lower unit cost lower volumes of air, water and solid emissions lower pollutant loadings workers health & safety improved product quality & market access towards compliance & community acceptance 11
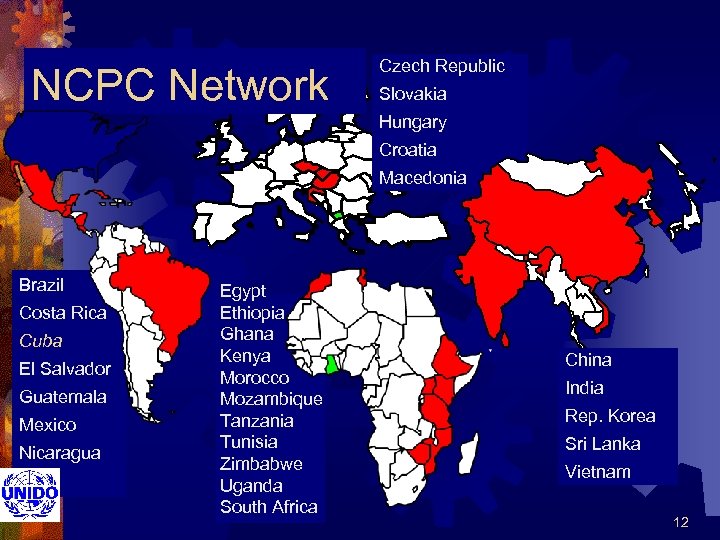 NCPC Network Czech Republic Slovakia Hungary Croatia Macedonia Brazil Costa Rica Cuba El Salvador Guatemala Mexico Nicaragua Egypt Ethiopia Ghana Kenya Morocco Mozambique Tanzania Tunisia Zimbabwe Uganda South Africa China India Rep. Korea Sri Lanka Vietnam 12
NCPC Network Czech Republic Slovakia Hungary Croatia Macedonia Brazil Costa Rica Cuba El Salvador Guatemala Mexico Nicaragua Egypt Ethiopia Ghana Kenya Morocco Mozambique Tanzania Tunisia Zimbabwe Uganda South Africa China India Rep. Korea Sri Lanka Vietnam 12
 Other CP Projects CP Demonstration Projects (‘NCPCs-to-be’? ): 2. Uzbekistan Macedonia 3. Ghana 1. Sector-Specific CP Centre & activities: Oil and Gas CP Centre - Russia 2. ‘Virtual NCPC’; networked sector-specific units - Cuba Developing: a) Clean fuels centre - Pakistan b) CP in textiles - Nigeria 1. CP in other units & branches of UNIDO • • Artisanal Gold Mining Leather (tanning) Textiles (dyeing) Agro-Processing Wood Processing Pulp and Paper Industrial Energy Efficiency Montreal Protocol 13
Other CP Projects CP Demonstration Projects (‘NCPCs-to-be’? ): 2. Uzbekistan Macedonia 3. Ghana 1. Sector-Specific CP Centre & activities: Oil and Gas CP Centre - Russia 2. ‘Virtual NCPC’; networked sector-specific units - Cuba Developing: a) Clean fuels centre - Pakistan b) CP in textiles - Nigeria 1. CP in other units & branches of UNIDO • • Artisanal Gold Mining Leather (tanning) Textiles (dyeing) Agro-Processing Wood Processing Pulp and Paper Industrial Energy Efficiency Montreal Protocol 13
 Main Actors Host Institutions • • • Public sector industry research centres University departments Chambers of commerce Counterpart Institutions • • Technical University Departments Consulting Companies Donors Austria Brazil Italy Japan Netherlands Norway Russia Sweden Switzerland UNEP UNDP 14
Main Actors Host Institutions • • • Public sector industry research centres University departments Chambers of commerce Counterpart Institutions • • Technical University Departments Consulting Companies Donors Austria Brazil Italy Japan Netherlands Norway Russia Sweden Switzerland UNEP UNDP 14
 Centres provide Practical production management assistance • Training & demonstrations • ‘Gateways’ to information & networks • • • From products-based market to a more service-oriented economy Zero waste through Closing the loops ( changing from linear economy to circular economy ) recycling of industrial& municipal waste • Expanding capabilities • • Area-wide environmental/ecosystem quality management Baselines and monitoring Environmental management systems Policy support 15
Centres provide Practical production management assistance • Training & demonstrations • ‘Gateways’ to information & networks • • • From products-based market to a more service-oriented economy Zero waste through Closing the loops ( changing from linear economy to circular economy ) recycling of industrial& municipal waste • Expanding capabilities • • Area-wide environmental/ecosystem quality management Baselines and monitoring Environmental management systems Policy support 15
 NCPC customer base • Manufacturing Industry • • principally SMEs Service Industry • Hospitals • Tourism … Universities training & curriculum development • Municipalities • Government Departments • policy & enabling environment 16
NCPC customer base • Manufacturing Industry • • principally SMEs Service Industry • Hospitals • Tourism … Universities training & curriculum development • Municipalities • Government Departments • policy & enabling environment 16
 Cleaner Production steps Analyzing process steps Prepare process flow charts (List Process steps & identify waste streams), Collect & verify baseline data, Establish material & energy balances. Assign costs, Identify causes of wastage & excess resource consumption, Select audit focus Generating Cleaner Production opportunities Identify CP options; Preliminary screening & ranking of CP options Assessing CP option feasibility Assess technical feasibility, economic viability & environmental impact. Rank and select CP options. Present to management Implementing & monitoring CP solutions Prepare implementation plans & costs. Executing implementation. Monitor & evaluate Identify next audit focus 17
Cleaner Production steps Analyzing process steps Prepare process flow charts (List Process steps & identify waste streams), Collect & verify baseline data, Establish material & energy balances. Assign costs, Identify causes of wastage & excess resource consumption, Select audit focus Generating Cleaner Production opportunities Identify CP options; Preliminary screening & ranking of CP options Assessing CP option feasibility Assess technical feasibility, economic viability & environmental impact. Rank and select CP options. Present to management Implementing & monitoring CP solutions Prepare implementation plans & costs. Executing implementation. Monitor & evaluate Identify next audit focus 17
 Examples from Viet Nam (i) Environmental benefits: Food 1 = instant noodle factory; Food 2 = slaughterhouse NQ = Not Quantified 18
Examples from Viet Nam (i) Environmental benefits: Food 1 = instant noodle factory; Food 2 = slaughterhouse NQ = Not Quantified 18
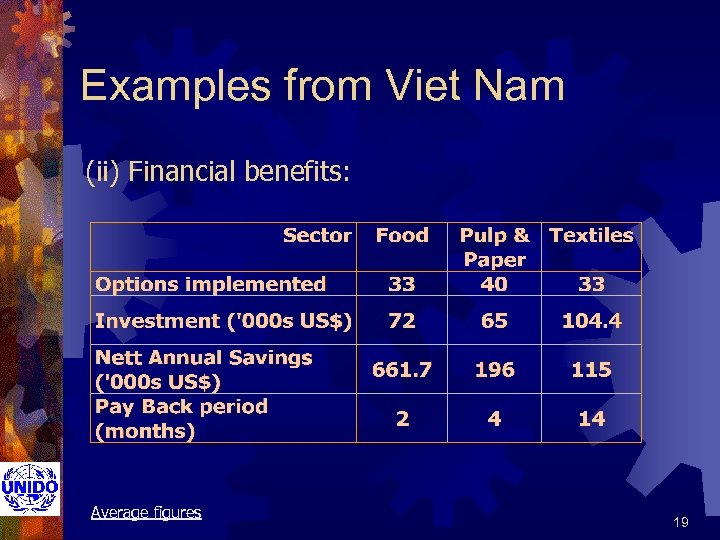 Examples from Viet Nam (ii) Financial benefits: Average figures 19
Examples from Viet Nam (ii) Financial benefits: Average figures 19
 What next ? Process change • Production management • Investment for technology • Skills mix of the Centre • CP ‘bankability’ change Country driven ? • Standard methodology Modular approach Wider services and skills Closer integration with Govt. FDI units, investors - the precautionary principle CP + ? • Environmental compliance • Financial viability of centre Technology choice • ‘Retrofitting’ • Influencing new investment Sector-specific approach Production engineering vs Environmental engineering CP financing initiatives 20
What next ? Process change • Production management • Investment for technology • Skills mix of the Centre • CP ‘bankability’ change Country driven ? • Standard methodology Modular approach Wider services and skills Closer integration with Govt. FDI units, investors - the precautionary principle CP + ? • Environmental compliance • Financial viability of centre Technology choice • ‘Retrofitting’ • Influencing new investment Sector-specific approach Production engineering vs Environmental engineering CP financing initiatives 20
 Eco-efficiency The efficient use of materials and energy in order to reduce costs and environmental impacts 21
Eco-efficiency The efficient use of materials and energy in order to reduce costs and environmental impacts 21
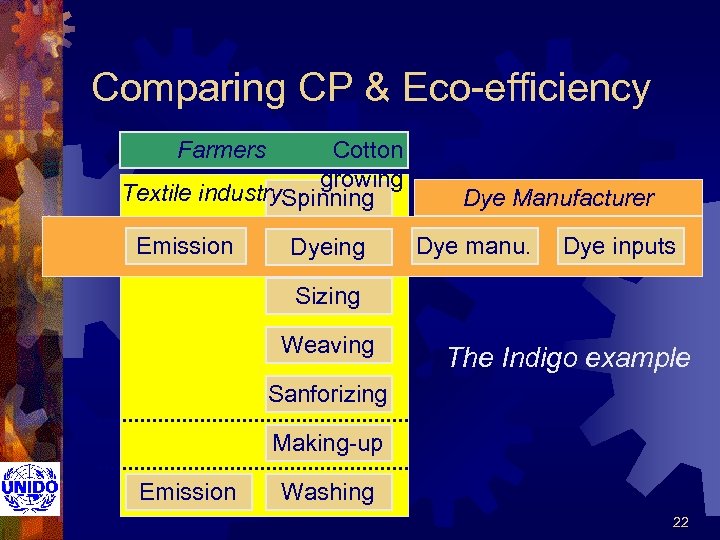 Comparing CP & Eco-efficiency Farmers Cotton growing Textile industry. Spinning Emission Dyeing Dye Manufacturer Dye manu. Dye inputs Sizing Weaving The Indigo example Sanforizing Making-up Emission Washing 22
Comparing CP & Eco-efficiency Farmers Cotton growing Textile industry. Spinning Emission Dyeing Dye Manufacturer Dye manu. Dye inputs Sizing Weaving The Indigo example Sanforizing Making-up Emission Washing 22
 Cleaner Production • Process oriented, within factory Relative to status ‘baseline’ • Continuous management tool • Eco-efficiency • Product & application oriented • Absolute impacts • ‘One-off’ decision tool Modular approach • Standard methodology • • Identifies need for technology change • • Applicable to all Assists in technology choices • Larger integrated producers 23
Cleaner Production • Process oriented, within factory Relative to status ‘baseline’ • Continuous management tool • Eco-efficiency • Product & application oriented • Absolute impacts • ‘One-off’ decision tool Modular approach • Standard methodology • • Identifies need for technology change • • Applicable to all Assists in technology choices • Larger integrated producers 23
 Synergies of inter-Agency cooperation WHO EMRO – UNIDO Draft proposal for Arab League, October 2004
Synergies of inter-Agency cooperation WHO EMRO – UNIDO Draft proposal for Arab League, October 2004
 Health and Income Experience has shown that in mobilized communities with healthy people, significantly higher recovery rates of micro-credit can occur; Healthy people are in principle more productive, provided that other factors for economical success are taken care of, such as access to finance and land, marketing channels and business support. 25
Health and Income Experience has shown that in mobilized communities with healthy people, significantly higher recovery rates of micro-credit can occur; Healthy people are in principle more productive, provided that other factors for economical success are taken care of, such as access to finance and land, marketing channels and business support. 25
 Cooperation Overview WHO UNIDO Community Based Initiatives; Social Mobilization and Health; Healthy City and Healthy Village Agro-based income generation, marketing and Professional Association building; Women entrepreneurship development Food Safety and Nutrition Food -production, -storage and -transport; Quality inspection systems, HACCP hygienic practices. Efficient operation of Hospitals and Health systems Pollution prevention and efficiency improvement through structured energy-, material- and water- flow analysis; Development of industries that supply products to the health system. Impact of Environmental Pollution on Health Industrial and Agricultural pollution prevention, Cleaner Production methodologies and Urban waste collection, -recycling and -treatment systems. 26
Cooperation Overview WHO UNIDO Community Based Initiatives; Social Mobilization and Health; Healthy City and Healthy Village Agro-based income generation, marketing and Professional Association building; Women entrepreneurship development Food Safety and Nutrition Food -production, -storage and -transport; Quality inspection systems, HACCP hygienic practices. Efficient operation of Hospitals and Health systems Pollution prevention and efficiency improvement through structured energy-, material- and water- flow analysis; Development of industries that supply products to the health system. Impact of Environmental Pollution on Health Industrial and Agricultural pollution prevention, Cleaner Production methodologies and Urban waste collection, -recycling and -treatment systems. 26
 Status • A joint pilot project is initiated in the city of Shendi in Sudan. Similar joint pilots foreseen for three other countries • Strategic goal • To maximize on the ground the mutual reinforcement of health and income as a major driver for community development to self -reliance and social equity. • Direct objective To provide comprehensive multidisciplinary tools to enable planning and implementation of joint interventions for improving health and reducing inequalities, thus increasing quality of life. 27
Status • A joint pilot project is initiated in the city of Shendi in Sudan. Similar joint pilots foreseen for three other countries • Strategic goal • To maximize on the ground the mutual reinforcement of health and income as a major driver for community development to self -reliance and social equity. • Direct objective To provide comprehensive multidisciplinary tools to enable planning and implementation of joint interventions for improving health and reducing inequalities, thus increasing quality of life. 27
 Thank you very much Cleaner Production A. MORSSY Tel : 43 1 26026 3841 Fax: 43 1 26026 6819 Email: amorssy@unido. or
Thank you very much Cleaner Production A. MORSSY Tel : 43 1 26026 3841 Fax: 43 1 26026 6819 Email: amorssy@unido. or


