1. classificaion tree of life and domains.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 19
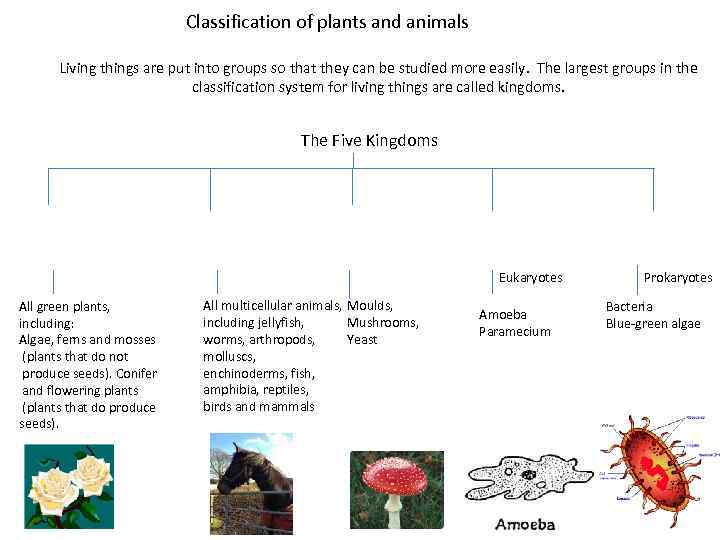 Classification of plants and animals Living things are put into groups so that they can be studied more easily. The largest groups in the classification system for living things are called kingdoms. The Five Kingdoms Eukaryotes All green plants, including: Algae, ferns and mosses (plants that do not produce seeds). Conifer and flowering plants (plants that do produce seeds). All multicellular animals, Moulds, including jellyfish, Mushrooms, worms, arthropods, Yeast molluscs, enchinoderms, fish, amphibia, reptiles, birds and mammals Amoeba Paramecium Prokaryotes Bacteria Blue-green algae
Classification of plants and animals Living things are put into groups so that they can be studied more easily. The largest groups in the classification system for living things are called kingdoms. The Five Kingdoms Eukaryotes All green plants, including: Algae, ferns and mosses (plants that do not produce seeds). Conifer and flowering plants (plants that do produce seeds). All multicellular animals, Moulds, including jellyfish, Mushrooms, worms, arthropods, Yeast molluscs, enchinoderms, fish, amphibia, reptiles, birds and mammals Amoeba Paramecium Prokaryotes Bacteria Blue-green algae
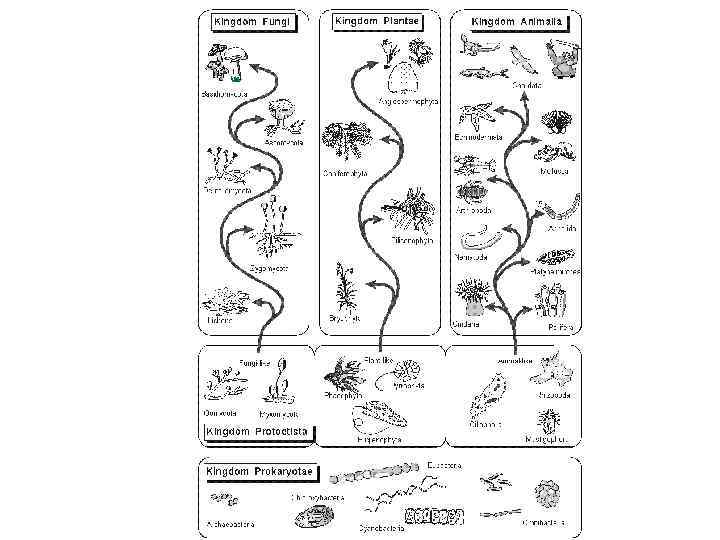
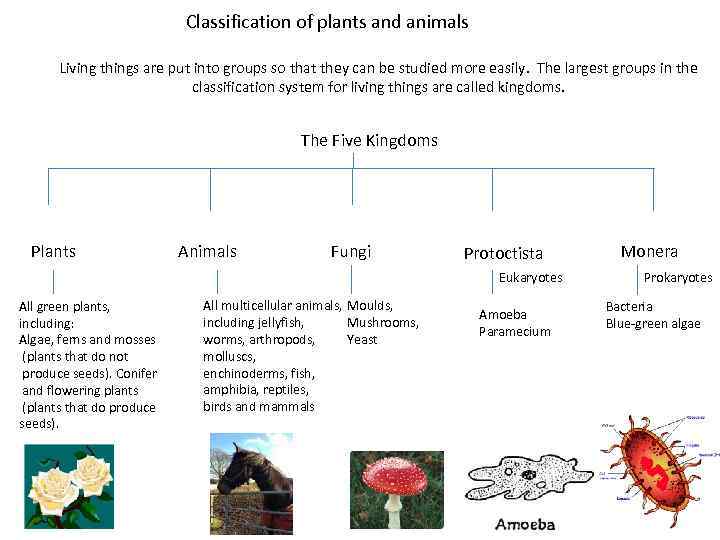 Classification of plants and animals Living things are put into groups so that they can be studied more easily. The largest groups in the classification system for living things are called kingdoms. The Five Kingdoms Plants Animals Fungi Protoctista Eukaryotes All green plants, including: Algae, ferns and mosses (plants that do not produce seeds). Conifer and flowering plants (plants that do produce seeds). All multicellular animals, Moulds, including jellyfish, Mushrooms, worms, arthropods, Yeast molluscs, enchinoderms, fish, amphibia, reptiles, birds and mammals Amoeba Paramecium Monera Prokaryotes Bacteria Blue-green algae
Classification of plants and animals Living things are put into groups so that they can be studied more easily. The largest groups in the classification system for living things are called kingdoms. The Five Kingdoms Plants Animals Fungi Protoctista Eukaryotes All green plants, including: Algae, ferns and mosses (plants that do not produce seeds). Conifer and flowering plants (plants that do produce seeds). All multicellular animals, Moulds, including jellyfish, Mushrooms, worms, arthropods, Yeast molluscs, enchinoderms, fish, amphibia, reptiles, birds and mammals Amoeba Paramecium Monera Prokaryotes Bacteria Blue-green algae
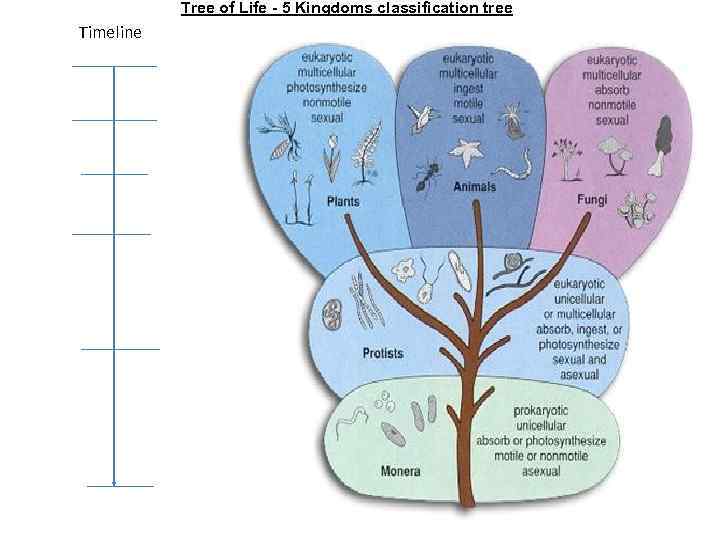 Tree of Life - 5 Kingdoms classification tree Timeline
Tree of Life - 5 Kingdoms classification tree Timeline
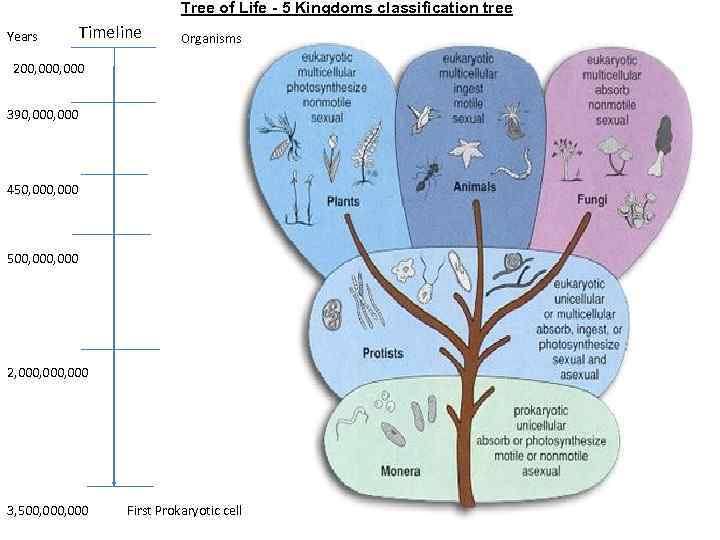 Tree of Life - 5 Kingdoms classification tree Years Timeline Organisms 200, 000 390, 000 450, 000 500, 000 2, 000, 000 3, 500, 000 First Prokaryotic cell
Tree of Life - 5 Kingdoms classification tree Years Timeline Organisms 200, 000 390, 000 450, 000 500, 000 2, 000, 000 3, 500, 000 First Prokaryotic cell
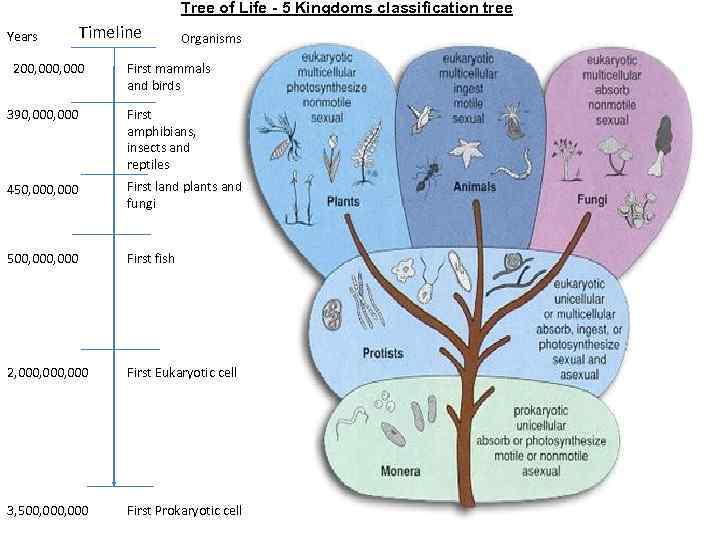 Tree of Life - 5 Kingdoms classification tree Years Timeline 200, 000 Organisms First mammals and birds 390, 000 First amphibians, insects and reptiles 450, 000 First land plants and fungi 500, 000 First fish 2, 000, 000 First Eukaryotic cell 3, 500, 000 First Prokaryotic cell
Tree of Life - 5 Kingdoms classification tree Years Timeline 200, 000 Organisms First mammals and birds 390, 000 First amphibians, insects and reptiles 450, 000 First land plants and fungi 500, 000 First fish 2, 000, 000 First Eukaryotic cell 3, 500, 000 First Prokaryotic cell
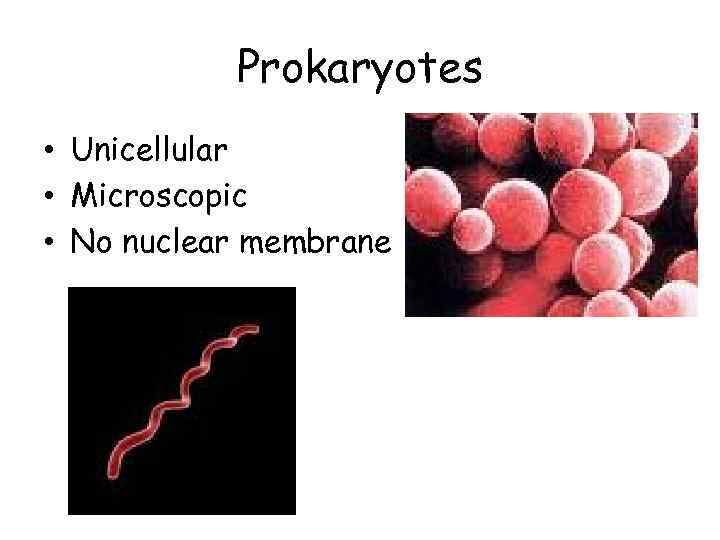 Prokaryotes • Unicellular • Microscopic • No nuclear membrane
Prokaryotes • Unicellular • Microscopic • No nuclear membrane
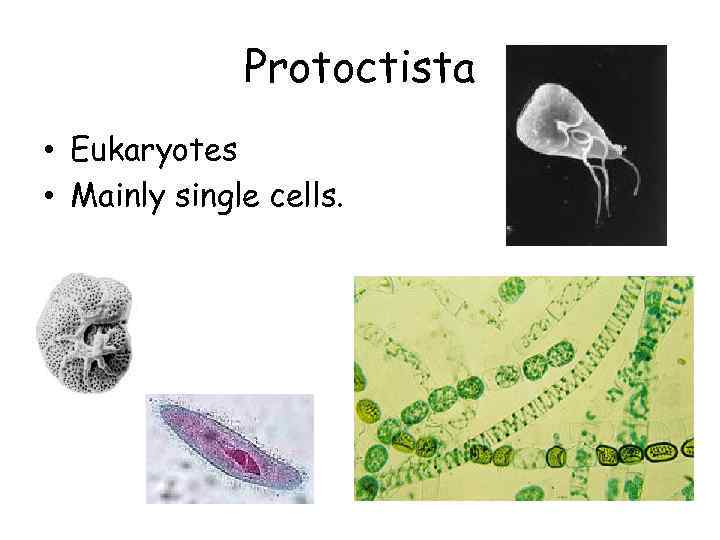 Protoctista • Eukaryotes • Mainly single cells.
Protoctista • Eukaryotes • Mainly single cells.
 Plantae • Multicellular eukaryotes • Photosynthetic • Cellulose cell wall.
Plantae • Multicellular eukaryotes • Photosynthetic • Cellulose cell wall.
 Fungi • Heterotrophic eukaryotes • Rigid cell wall of chitin • Reproduce by spores
Fungi • Heterotrophic eukaryotes • Rigid cell wall of chitin • Reproduce by spores
 Animalia • • Heterotropic Multicellular eukaryotes No cell wall Nervous coordination
Animalia • • Heterotropic Multicellular eukaryotes No cell wall Nervous coordination
 The grouping together of animals is called classification. A group of similar organisms is called a taxon. The study of classification is called taxonomy.
The grouping together of animals is called classification. A group of similar organisms is called a taxon. The study of classification is called taxonomy.
 Hierarchical classification system Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species : Eukaryotes : Animalia : Chordata (vertebrates) : Mammals : Primates : Hominidae : Homo sapiens
Hierarchical classification system Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species : Eukaryotes : Animalia : Chordata (vertebrates) : Mammals : Primates : Hominidae : Homo sapiens
 Linnaeus (1707 -1778)
Linnaeus (1707 -1778)
 The Binomial system of naming • Uses Latin or Greek names • The first name is the generic name and this is the Genus to which the organism belongs – (Similar to the surname of a person) • The second name is the specific name and this is the species. – (Similar to the first name of a person) E. g. Homo sapiens
The Binomial system of naming • Uses Latin or Greek names • The first name is the generic name and this is the Genus to which the organism belongs – (Similar to the surname of a person) • The second name is the specific name and this is the species. – (Similar to the first name of a person) E. g. Homo sapiens
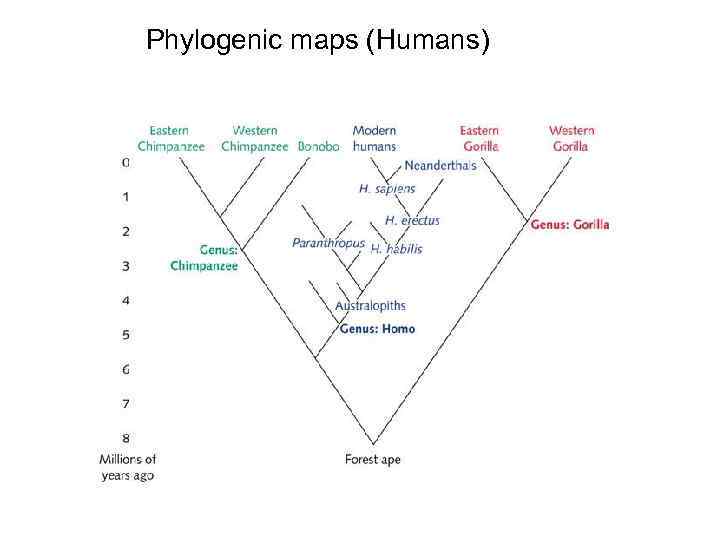 Phylogenic maps (Humans)
Phylogenic maps (Humans)
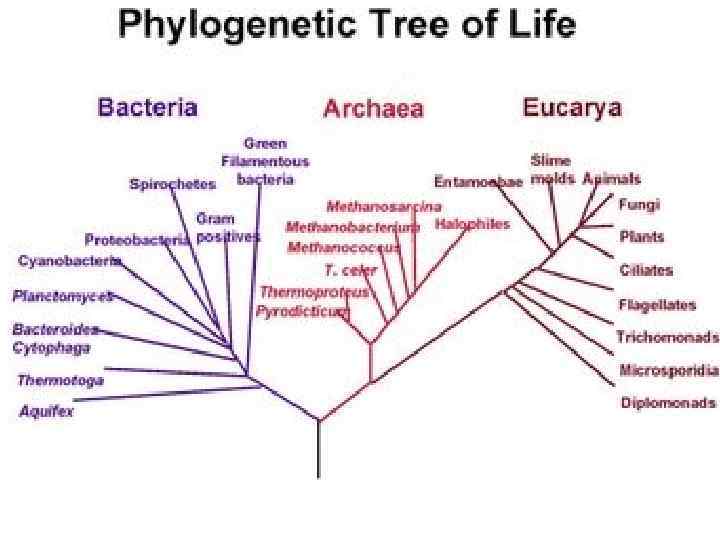
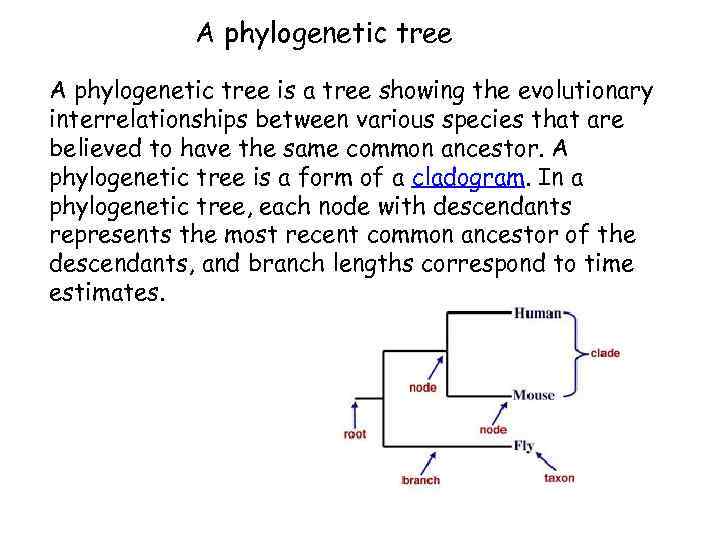 A phylogenetic tree is a tree showing the evolutionary interrelationships between various species that are believed to have the same common ancestor. A phylogenetic tree is a form of a cladogram. In a phylogenetic tree, each node with descendants represents the most recent common ancestor of the descendants, and branch lengths correspond to time estimates.
A phylogenetic tree is a tree showing the evolutionary interrelationships between various species that are believed to have the same common ancestor. A phylogenetic tree is a form of a cladogram. In a phylogenetic tree, each node with descendants represents the most recent common ancestor of the descendants, and branch lengths correspond to time estimates.
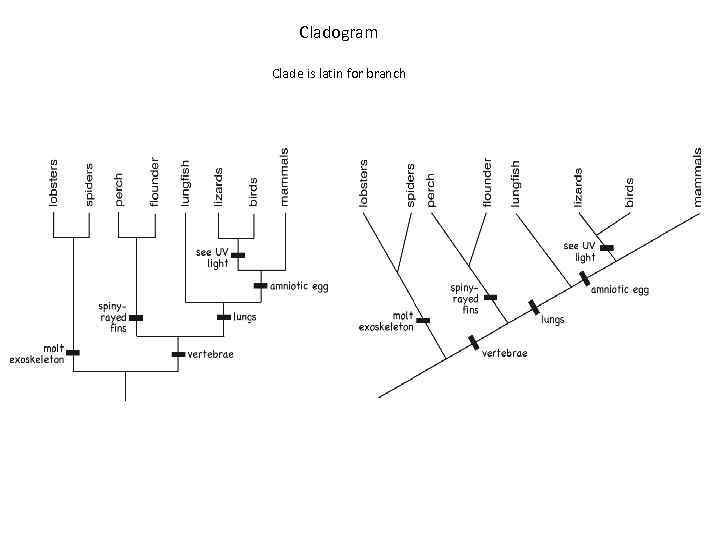 Cladogram Clade is latin for branch
Cladogram Clade is latin for branch