CLASSIFICATION OF COSTS: managerial aspect Alina V. RABOSHUK,


CLASSIFICATION OF COSTS: managerial aspect Alina V. RABOSHUK, PhD Zhytomyr State Technological University

Cost of the item = a physical quantity measurement x a price measurement Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 2

Traditional types of cost classification Variable costs and fixed costs Direct costs and indirect costs Product costs and period costs Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 3
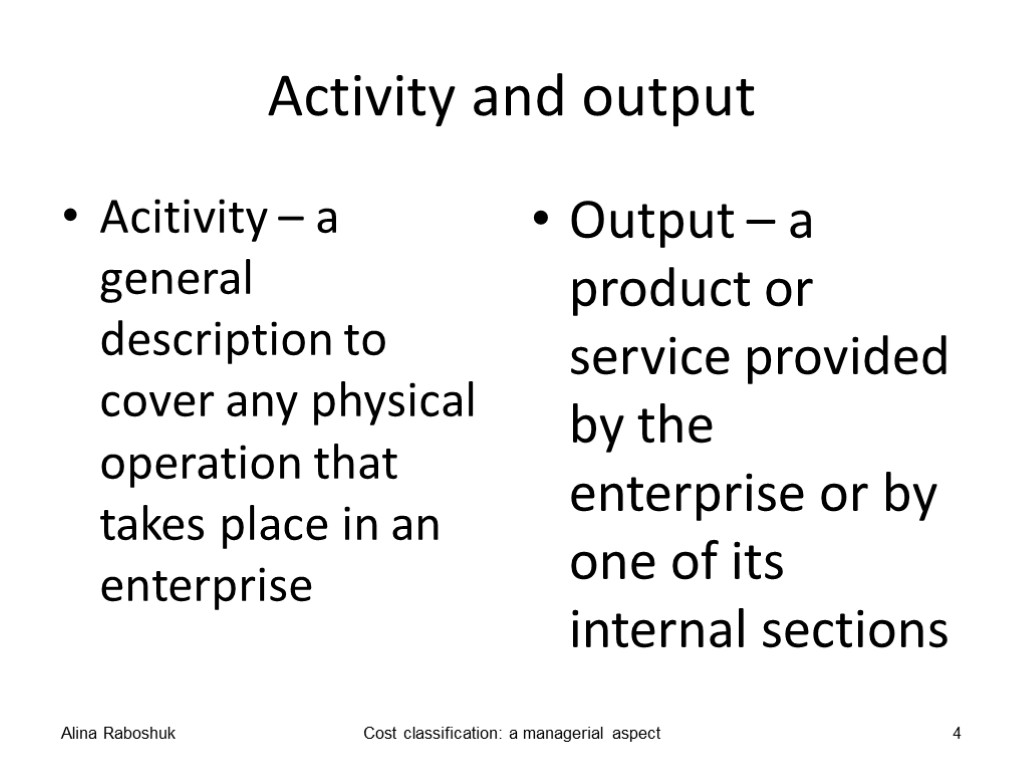
Activity and output Acitivity – a general description to cover any physical operation that takes place in an enterprise Output – a product or service provided by the enterprise or by one of its internal sections Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 4

A variable cost is one which varies directly with changes in the level of activity, over a defined period of time Examples of variable cost are: material used to manufacture a unit of output or to provide a type of service; labor costs of manufacturing a unit of output or providing a type of service; commission paid to a salesperson. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 5

A fixed cost is one which is not affected by changes in the level of activity, over a defined period of time Examples of fixed cost are: rent of buildings; salary paid to a supervisor; advertising in the trade journal; business rates paid to the local authority; depreciation of machinery calculated on the straight-line basis. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 6
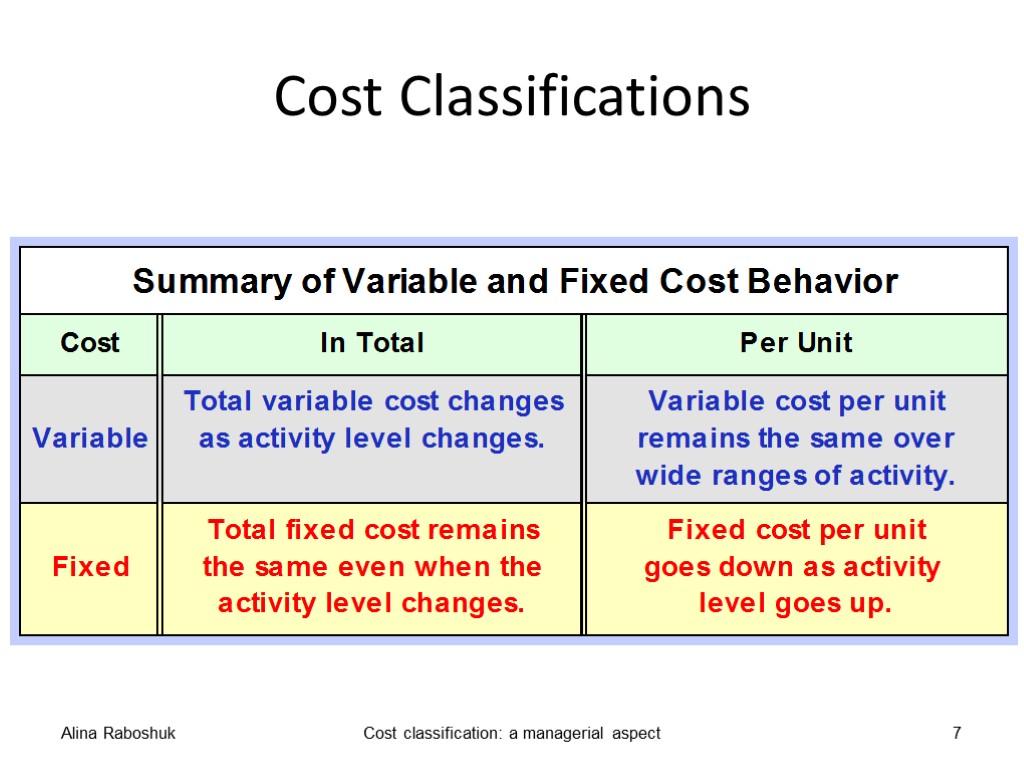
Cost Classifications Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 7
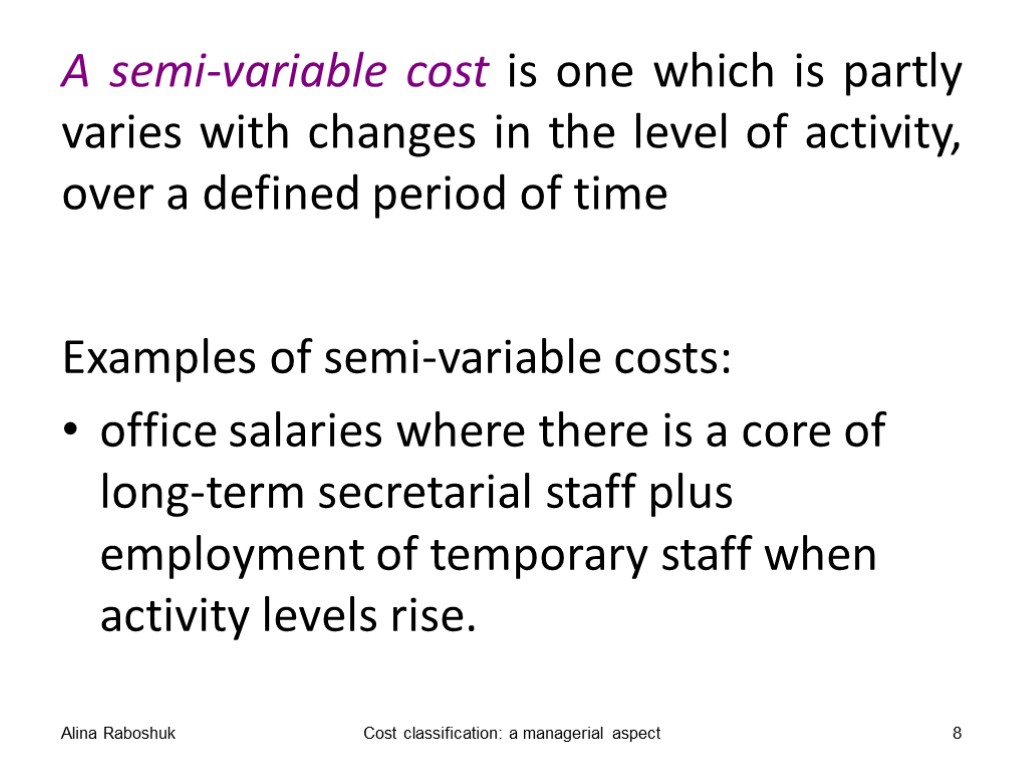
A semi-variable cost is one which is partly varies with changes in the level of activity, over a defined period of time Examples of semi-variable costs: office salaries where there is a core of long-term secretarial staff plus employment of temporary staff when activity levels rise. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 8

Step costs A fixed cost that increases in steps is called a step cost. Examples: the cost of renting storage space; The cost of paying a supervisor of a team of employees. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 9
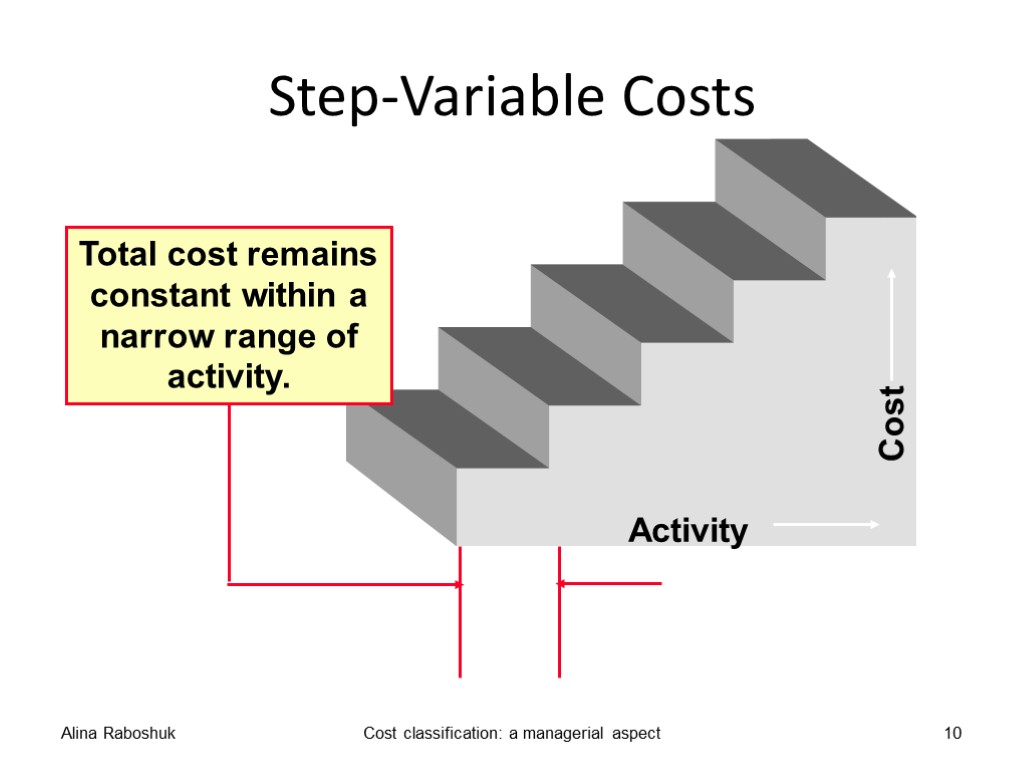
Step-Variable Costs Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 10
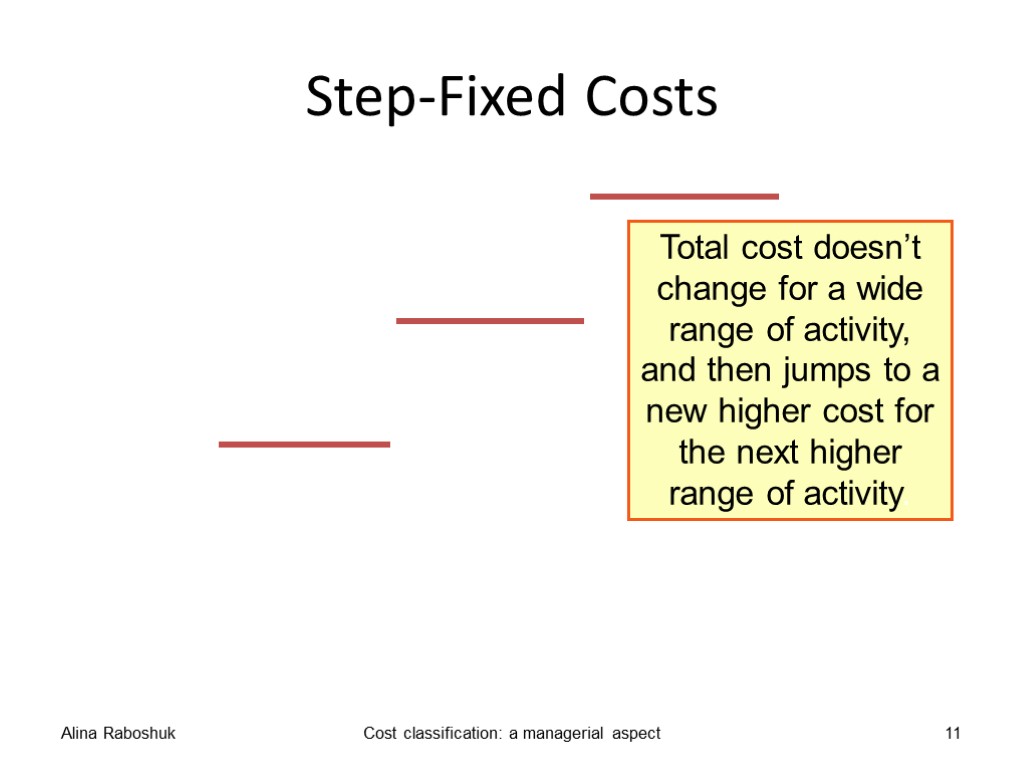
Step-Fixed Costs Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 11 Rented Area (m2)

The definition of direct and indirect costs depends on the purpose for which the cost will be used. Direct costs are directly traceable to an identifiable unit, such as product or service or department of the business, for which costs are to be determined. Indirect costs are spread over a number of identifiable units of the business, such as products or services or departments, for which costs are to be determined. Indirect costs are also called overhead costs. Overhead costs are the costs which cannot be identified directly with products or services. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 12
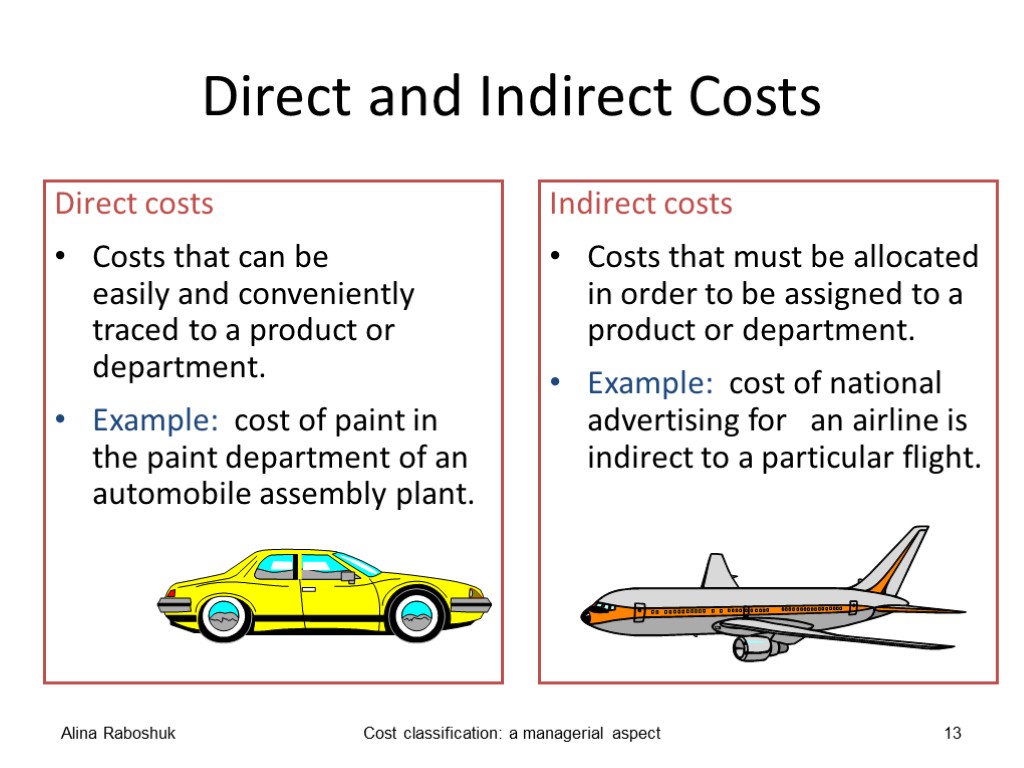
Direct and Indirect Costs Direct costs Costs that can be easily and conveniently traced to a product or department. Example: cost of paint in the paint department of an automobile assembly plant. Indirect costs Costs that must be allocated in order to be assigned to a product or department. Example: cost of national advertising for an airline is indirect to a particular flight. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 13

Product costs are those costs associated with goods or services purchased, or produced, for sale to customers. Period costs are those costs which are treated as expenses in the period in which they are incurred. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 14

Prime cost of production is the total of direct materials, direct labor and other direct costs. Production overhead costs comprises indirect materials, indirect labor and other indirect costs of production. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 15
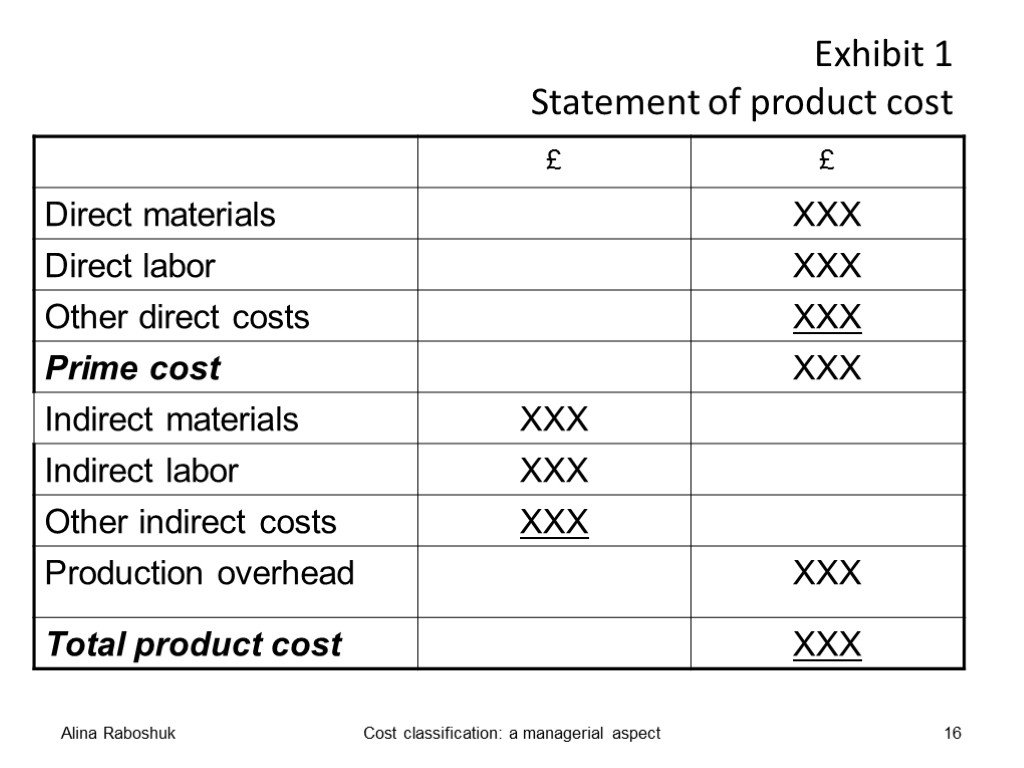
Exhibit 1 Statement of product cost Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 16
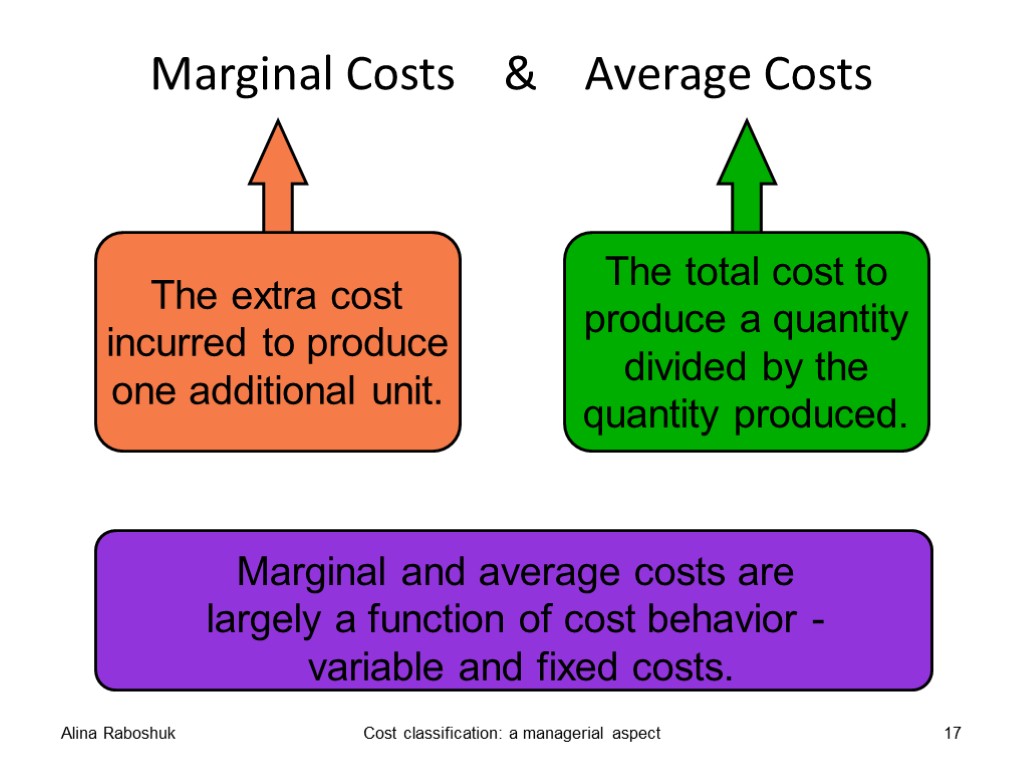
Marginal Costs & Average Costs Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 17 The extra cost incurred to produce one additional unit. The total cost to produce a quantity divided by the quantity produced. Marginal and average costs are largely a function of cost behavior - variable and fixed costs.

Planning Planning involves looking forward and asking questions of the type “what if … ?” Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 18
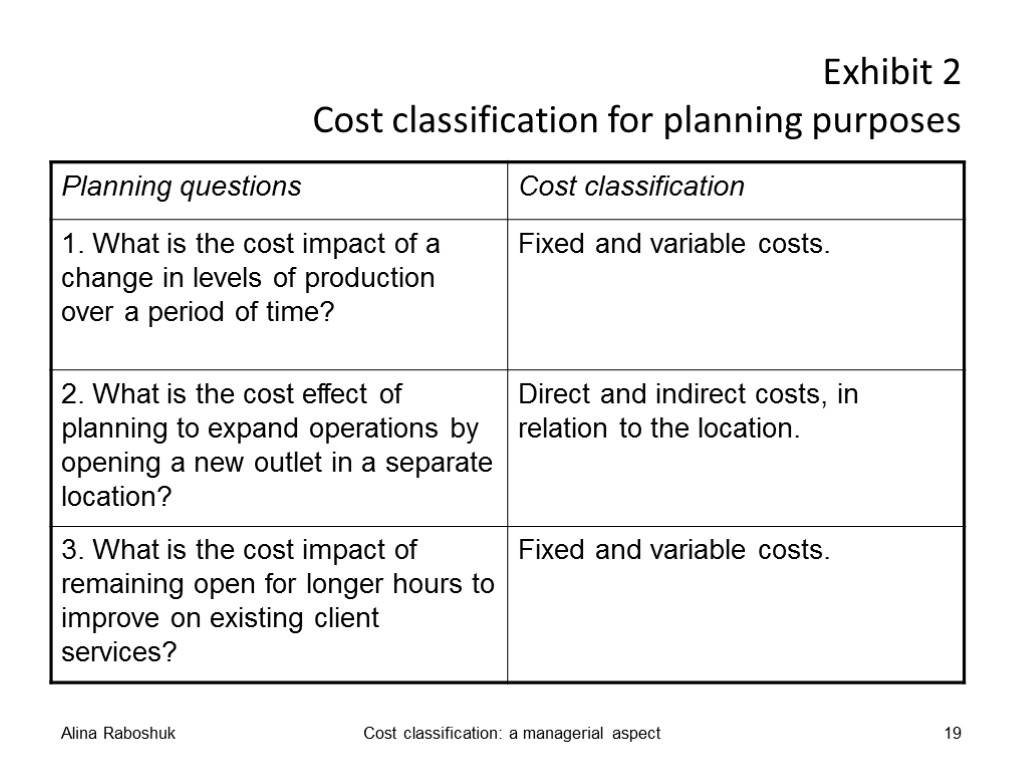
Exhibit 2 Cost classification for planning purposes Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 19
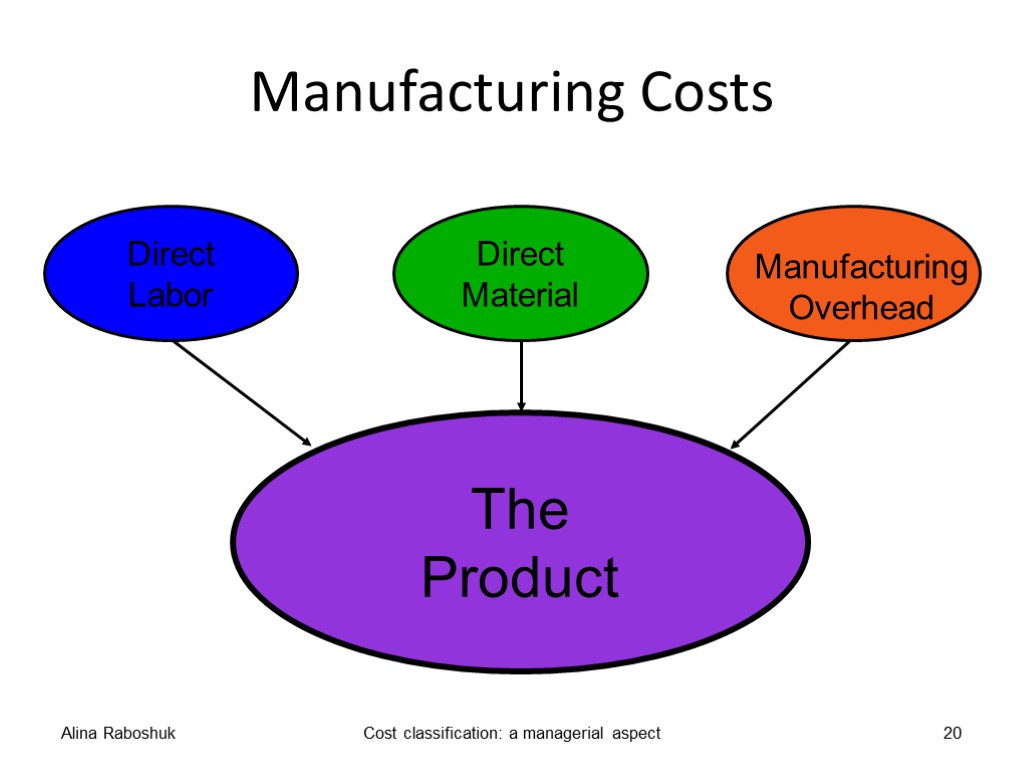
Manufacturing Costs Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 20

Decision making Decision making involves asking questions of the type “Should we do … ?” Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 21
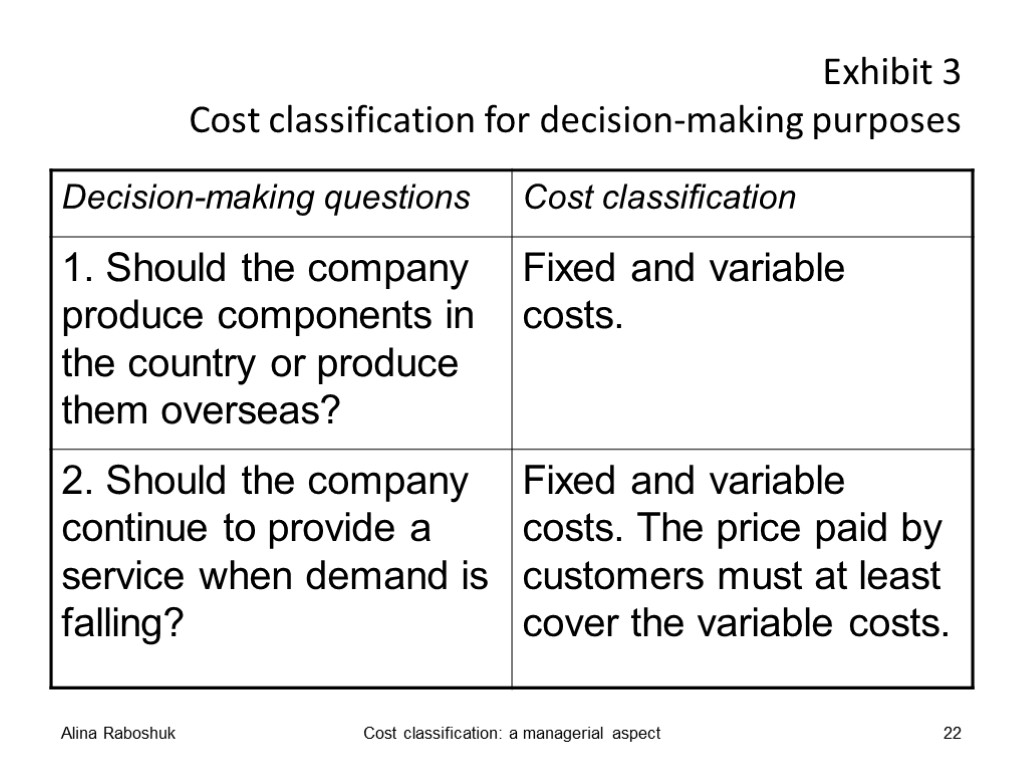
Exhibit 3 Cost classification for decision-making purposes Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 22
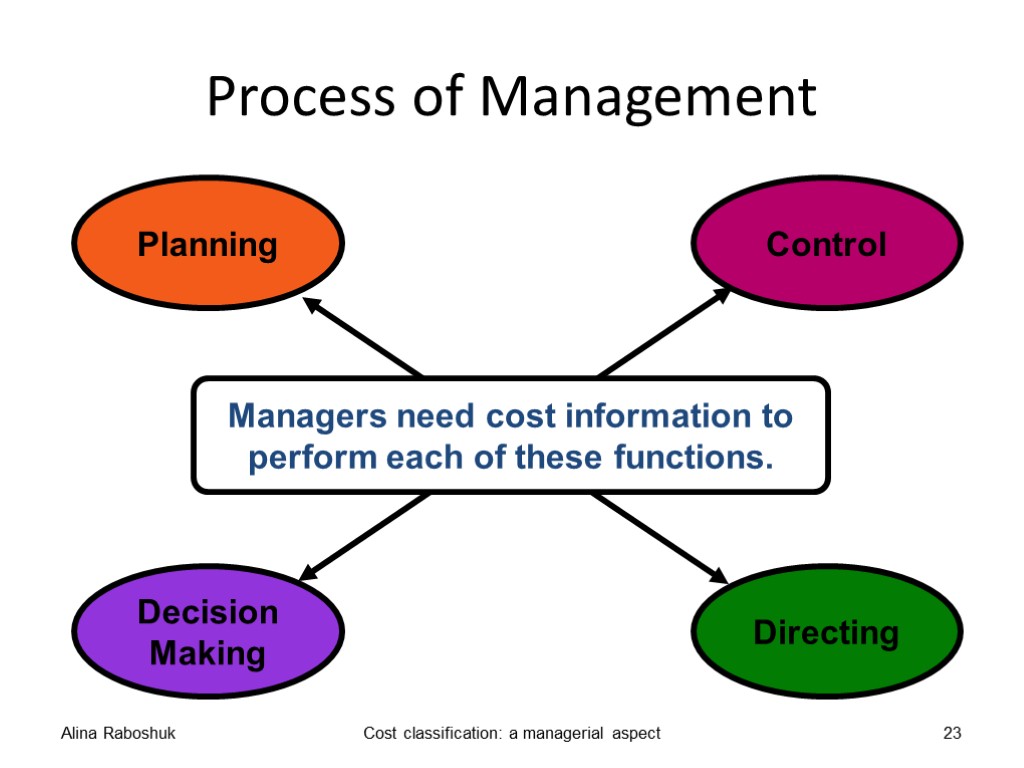
Process of Management Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 23 Managers need cost information to perform each of these functions.

Control Control involves looking back and asking question of the “how and why … ?” type. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 24
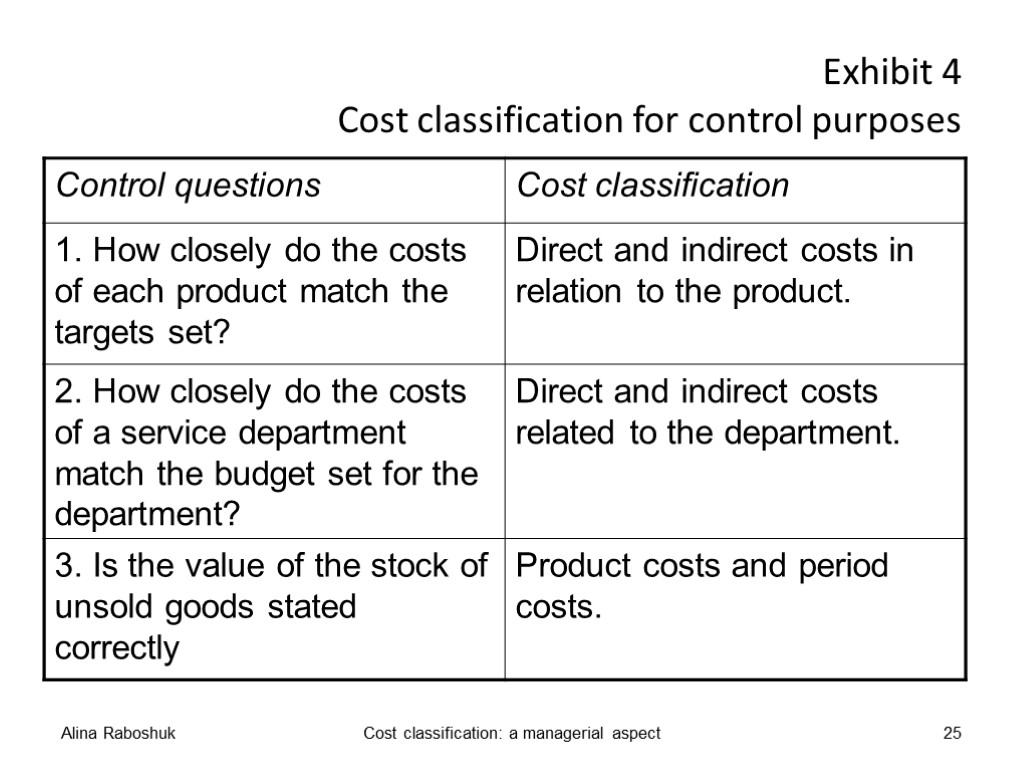
Exhibit 4 Cost classification for control purposes Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 25
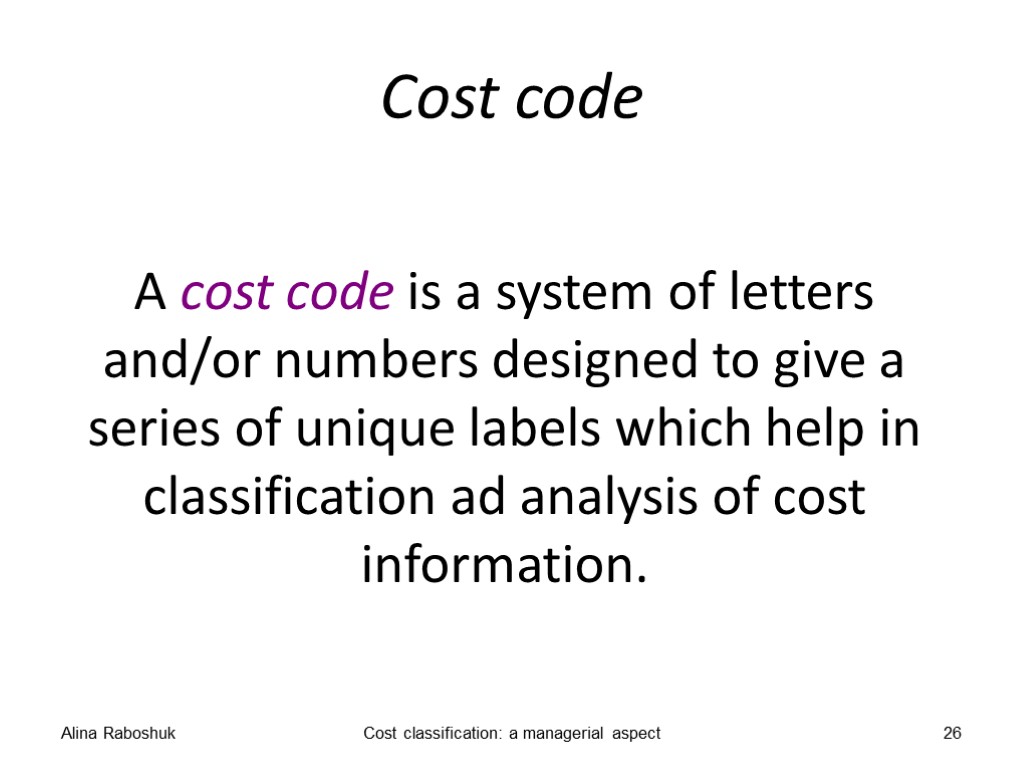
Cost code A cost code is a system of letters and/or numbers designed to give a series of unique labels which help in classification ad analysis of cost information. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 26

Cost selection and reporting A cost centre is the unit of the organization in respect of which a manager is responsible for costs under his or her control. A cost centre should be a location (e.g. a department) or a function (e.g. the manufacture of a product), or it could even be a production machine or group of similar machines. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 27

Profit centre A profit centre is a unit of organization in respect of which a manager is responsible for revenue as well as costs. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 28

Investment centre An investment centre is a unit of organization in respect of which a manager is responsible for capital investment decisions as well as revenue and costs. These decisions could be related to such matters as purchases and disposal of equipment. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 29

Controllable cost A controllable cost is one which is capable of being managed by the person responsible for the cost centre, profit centre or investment centre to which the cost is reported. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 30
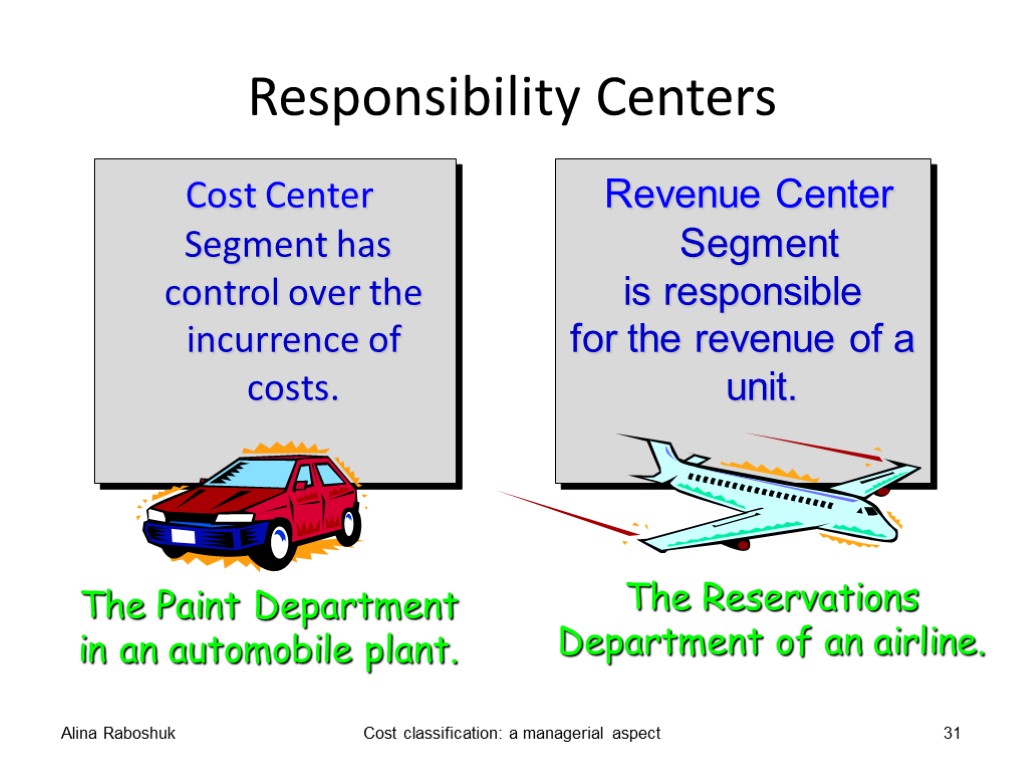
Responsibility Centers Cost Center Segment has control over the incurrence of costs. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 31 The Paint Department in an automobile plant. Revenue Center Segment is responsible for the revenue of a unit. The Reservations Department of an airline.
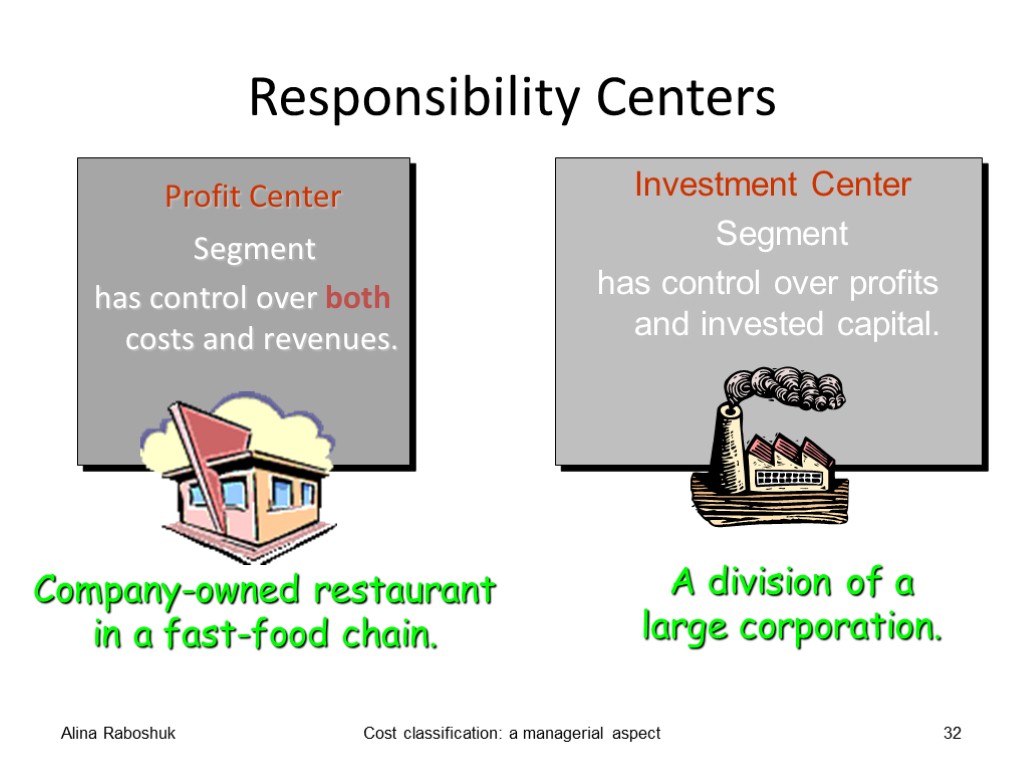
Responsibility Centers Profit Center Segment has control over both costs and revenues. Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 32 Company-owned restaurant in a fast-food chain. Investment Center Segment has control over profits and invested capital. A division of a large corporation.
Costs and Benefits of Information Alina Raboshuk Cost classification: a managerial aspect 33 More information does not mean more benefits if information overload results.
managerial_accounting_costs.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33

