9c5ea88e6dff3be06353d7ef0087bd19.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Class 9: Motives, Emotions, and Perception
Class 9: Motives, Emotions, and Perception
 Updates and Exam Today’s class: Complete New Look Begin Resources and Perception Thursday Class 1. Complete Recourses and Perception 2. Quiz 1 (25 min) 3. Catch up on Student Q&A presentations Exam 1. Thursday following conclusion of Resources and Perception lecture 2. 20 multiple choice: Class 1 to Resources and Perception
Updates and Exam Today’s class: Complete New Look Begin Resources and Perception Thursday Class 1. Complete Recourses and Perception 2. Quiz 1 (25 min) 3. Catch up on Student Q&A presentations Exam 1. Thursday following conclusion of Resources and Perception lecture 2. 20 multiple choice: Class 1 to Resources and Perception
 Jacoby, et al. Uncon. definitely exists—question is how and where it influences thought and behavior. Uncon defined: psych states (thoughts, behaviors) that lack conscious control Is uncons. an uptown gent or a downtown dude? a. clean, dry, cognition-based entity b. dirty, wet, emotion/need based entity c. Jacoby agnostic on this question
Jacoby, et al. Uncon. definitely exists—question is how and where it influences thought and behavior. Uncon defined: psych states (thoughts, behaviors) that lack conscious control Is uncons. an uptown gent or a downtown dude? a. clean, dry, cognition-based entity b. dirty, wet, emotion/need based entity c. Jacoby agnostic on this question
 Evidence of "Cool" Unconscious Amnesiacs -- recall of negative events (pin prick), word stem completions and priming. Blindsight patients -- can't consciously see, but behave as if they did see. Prospagnosia --Can't consciously recognize face, but show GSR to familiar faces. Normals -- mere exposure, perceptual fluency, implicit covariation; Bartlett: Schemas and reconstructive memory
Evidence of "Cool" Unconscious Amnesiacs -- recall of negative events (pin prick), word stem completions and priming. Blindsight patients -- can't consciously see, but behave as if they did see. Prospagnosia --Can't consciously recognize face, but show GSR to familiar faces. Normals -- mere exposure, perceptual fluency, implicit covariation; Bartlett: Schemas and reconstructive memory
 War of the Ghosts: The Power of What Students Heard Schemas One night two young men from the Egulac went down to the river. . . Then they heard war cries and thought: "Maybe this is a war party". . Now canoes came up, . . . There were five men in the canoe, and they said: "What do you think? We wish to take you along. We are going up the river to make war on the people". One young man joined them. And the warriors went. . . to a town on the Kalama. The people came down. . . and they began to fight, and many were killed. The young man heard one warrior say ". . . that Indian has been hit. " He thought "Oh, they are ghosts" So the canoes went back to the Egulac, and the young man went to his house. And told everybody. . . "Behold I accompanied the Sir Fredrick Bartlett, 18861969 What Students Recalled (Modified for Comic Effect) Two blokes were on holiday by the Thames when some ruffians approached them and lured them into rowdy cavorting. Well of course no good came of it, and the young master who went along was seriously hurt, and had to go
War of the Ghosts: The Power of What Students Heard Schemas One night two young men from the Egulac went down to the river. . . Then they heard war cries and thought: "Maybe this is a war party". . Now canoes came up, . . . There were five men in the canoe, and they said: "What do you think? We wish to take you along. We are going up the river to make war on the people". One young man joined them. And the warriors went. . . to a town on the Kalama. The people came down. . . and they began to fight, and many were killed. The young man heard one warrior say ". . . that Indian has been hit. " He thought "Oh, they are ghosts" So the canoes went back to the Egulac, and the young man went to his house. And told everybody. . . "Behold I accompanied the Sir Fredrick Bartlett, 18861969 What Students Recalled (Modified for Comic Effect) Two blokes were on holiday by the Thames when some ruffians approached them and lured them into rowdy cavorting. Well of course no good came of it, and the young master who went along was seriously hurt, and had to go
 Jacoby et al. Method -- Memory Dissociations Noise Judgments -- Ease of processing and rating of background noise. Study 1: Background noise more/less loud for previously heard sentences? Study 2: Background noise more/less loud for emote. arousing sentences? False Fame -- Mistake familiarity of name with fame of named person. Unconscious influence -- Question of control
Jacoby et al. Method -- Memory Dissociations Noise Judgments -- Ease of processing and rating of background noise. Study 1: Background noise more/less loud for previously heard sentences? Study 2: Background noise more/less loud for emote. arousing sentences? False Fame -- Mistake familiarity of name with fame of named person. Unconscious influence -- Question of control
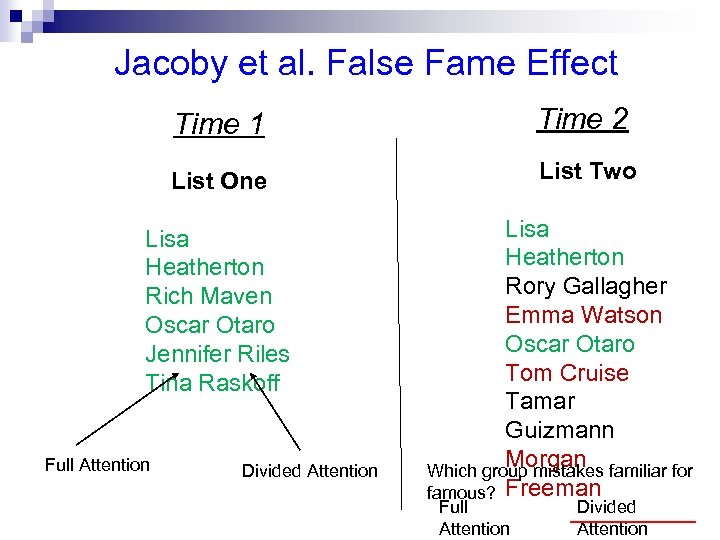 Jacoby et al. False Fame Effect Time 1 Time 2 List One List Two Lisa Heatherton Rich Maven Oscar Otaro Jennifer Riles Tina Raskoff Full Attention Divided Attention Lisa Heatherton Rory Gallagher Emma Watson Oscar Otaro Tom Cruise Tamar Guizmann Morgan Which group mistakes familiar for famous? Freeman Full Attention Divided Attention
Jacoby et al. False Fame Effect Time 1 Time 2 List One List Two Lisa Heatherton Rich Maven Oscar Otaro Jennifer Riles Tina Raskoff Full Attention Divided Attention Lisa Heatherton Rory Gallagher Emma Watson Oscar Otaro Tom Cruise Tamar Guizmann Morgan Which group mistakes familiar for famous? Freeman Full Attention Divided Attention
 “Warm” Unconscious Influences on Perception-1 Unconscious Emotions and Consumption Behavior Winkielman, Berridge, & Wilbarger, 2005
“Warm” Unconscious Influences on Perception-1 Unconscious Emotions and Consumption Behavior Winkielman, Berridge, & Wilbarger, 2005
 Alliesthesia Motivational state shapes “incentive value” of stimuli Water tastes better when thirsty Food tastes better when hungry Aromas more appealing when hungry Question: Would subliminal cue (face indicating go/no go) affect desirability of consumable product? NOTE: How does this prediction relate to Joe Campos “emotional signaling” with infants?
Alliesthesia Motivational state shapes “incentive value” of stimuli Water tastes better when thirsty Food tastes better when hungry Aromas more appealing when hungry Question: Would subliminal cue (face indicating go/no go) affect desirability of consumable product? NOTE: How does this prediction relate to Joe Campos “emotional signaling” with infants?
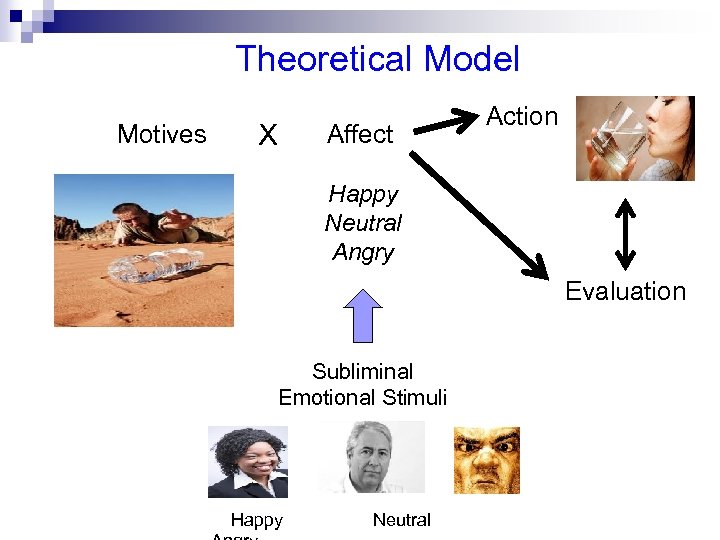 Theoretical Model Motives X Affect Action Happy Neutral Angry Evaluation Subliminal Emotional Stimuli Happy Neutral
Theoretical Model Motives X Affect Action Happy Neutral Angry Evaluation Subliminal Emotional Stimuli Happy Neutral
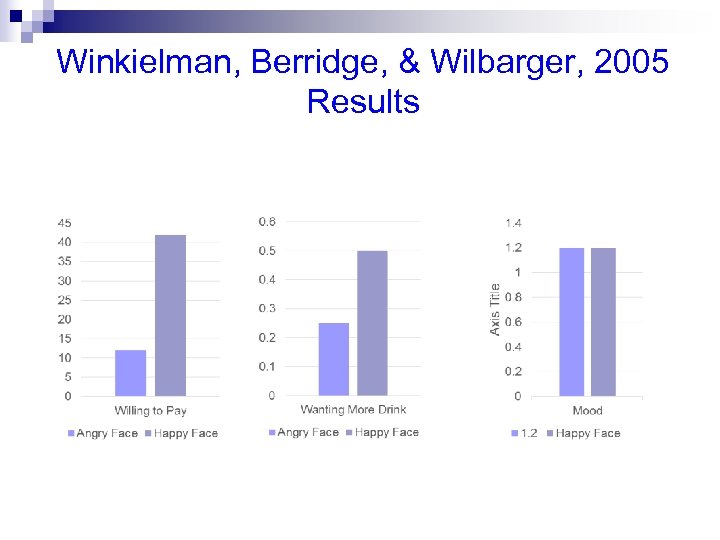 Winkielman, Berridge, & Wilbarger, 2005 Results
Winkielman, Berridge, & Wilbarger, 2005 Results
 “Warm” Unconscious Influences on Perception -2 Pooping Babies: Biological States, Primed Goals, and Emotional Reactions Shidlovksi & Hassin, 2011
“Warm” Unconscious Influences on Perception -2 Pooping Babies: Biological States, Primed Goals, and Emotional Reactions Shidlovksi & Hassin, 2011
 Unconscious Goals Conscious Emotions obstacles to goals, and self Old View: Emotions once seen as control New view: Emotions can abet goals (e. g. , Maya Tamir, 2014, 2016) 1. Provide feedback on progress [HOW SO? ] 2. People prefer emotions that advance goals: Anger, excitement [WHY? ] Emotions modulate goal-related behavior. Act as “accelerator” or “brake”
Unconscious Goals Conscious Emotions obstacles to goals, and self Old View: Emotions once seen as control New view: Emotions can abet goals (e. g. , Maya Tamir, 2014, 2016) 1. Provide feedback on progress [HOW SO? ] 2. People prefer emotions that advance goals: Anger, excitement [WHY? ] Emotions modulate goal-related behavior. Act as “accelerator” or “brake”
 Study Design Goal Relevant (peak fertility Ss) Motherho Neutral od Prime Goal Irrelevant (low fertility Ss) Motherho Neutral od Prime Disgusting Stim Goal Relevant Goal Irrelevant How disgusting is this picture? 1 – 9 EMOTION] [MEASURES GOAL-REL. How much want to establish family? 1– 9 CONSCIOUSNESS OF GOAL] [MEASURES
Study Design Goal Relevant (peak fertility Ss) Motherho Neutral od Prime Goal Irrelevant (low fertility Ss) Motherho Neutral od Prime Disgusting Stim Goal Relevant Goal Irrelevant How disgusting is this picture? 1 – 9 EMOTION] [MEASURES GOAL-REL. How much want to establish family? 1– 9 CONSCIOUSNESS OF GOAL] [MEASURES
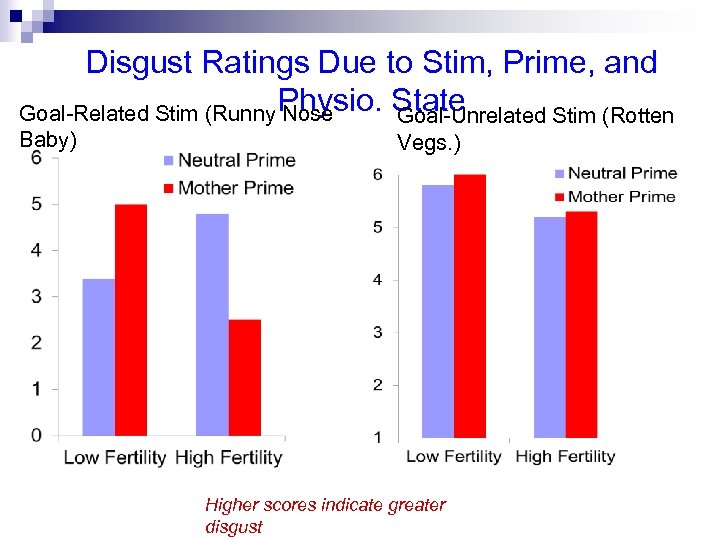 Disgust Ratings Due to Stim, Prime, and Goal-Related Stim (Runny Physio. State Nose Goal-Unrelated Stim (Rotten Baby) Vegs. ) Higher scores indicate greater disgust
Disgust Ratings Due to Stim, Prime, and Goal-Related Stim (Runny Physio. State Nose Goal-Unrelated Stim (Rotten Baby) Vegs. ) Higher scores indicate greater disgust
 Questions and Issues with "Pooping Babies" 1. Unexpected outcome #1: Low fertility women primed with "motherhood" esp. disgusted with snotty baby. Why? 2. Unexpected outcome #2: High fertility women, regardless of prime, are less disgusted by gross things 3. Problems with study? unrelated to babies. Why? a. Very high attrition -- lost over 50% of subjects b. No replication--just single study. Psych. Sci. should require rep. c. Generalizability: What other motivational states are like fertility?
Questions and Issues with "Pooping Babies" 1. Unexpected outcome #1: Low fertility women primed with "motherhood" esp. disgusted with snotty baby. Why? 2. Unexpected outcome #2: High fertility women, regardless of prime, are less disgusted by gross things 3. Problems with study? unrelated to babies. Why? a. Very high attrition -- lost over 50% of subjects b. No replication--just single study. Psych. Sci. should require rep. c. Generalizability: What other motivational states are like fertility?
 Social Support and Slant Perception (Evidence of "Smart" Unconscious? ) Schnall, Harber, Stefanucci, & Proffitt (2008) Conscious slant perception of hills is exaggerated (5% is seen as 20%, etc. ). Slant distortion is lessened under lower physical load ----- Light back pack vs. heavy back pack Physically refreshed vs. fatigued Good physical cond. vs. poor cond. Younger vs. older Is slant distortion reduced under lower psychological load?
Social Support and Slant Perception (Evidence of "Smart" Unconscious? ) Schnall, Harber, Stefanucci, & Proffitt (2008) Conscious slant perception of hills is exaggerated (5% is seen as 20%, etc. ). Slant distortion is lessened under lower physical load ----- Light back pack vs. heavy back pack Physically refreshed vs. fatigued Good physical cond. vs. poor cond. Younger vs. older Is slant distortion reduced under lower psychological load?
 Study 1: Do hills appear different when alone vs. with a friend? Participants Passersby at campus walk Alone (n = 14) Same-sex friend pairs (n = 17; both participate) All wear heavy backpack, face steep hill Hand protractor Measures Verbal: “How steep is this hill, in degrees? ” Visual Judgment: hand protractor Haptic: palm board Palm board
Study 1: Do hills appear different when alone vs. with a friend? Participants Passersby at campus walk Alone (n = 14) Same-sex friend pairs (n = 17; both participate) All wear heavy backpack, face steep hill Hand protractor Measures Verbal: “How steep is this hill, in degrees? ” Visual Judgment: hand protractor Haptic: palm board Palm board
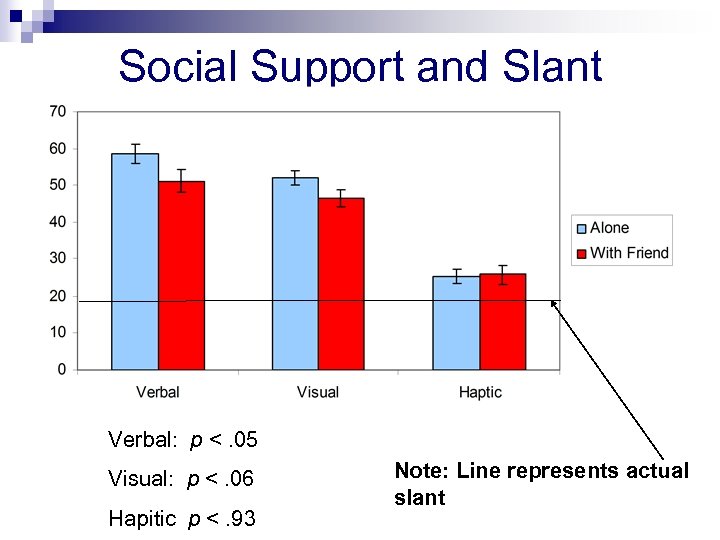 Social Support and Slant Verbal: p <. 05 Visual: p <. 06 Hapitic p <. 93 Note: Line represents actual slant
Social Support and Slant Verbal: p <. 05 Visual: p <. 06 Hapitic p <. 93 Note: Line represents actual slant
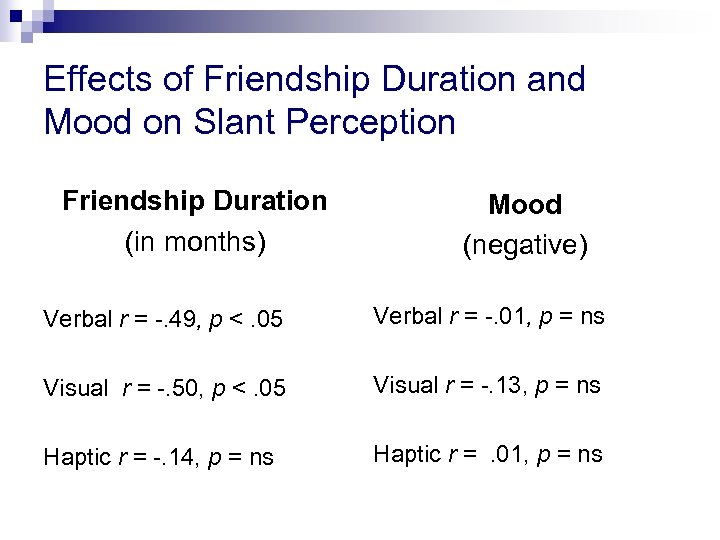 Effects of Friendship Duration and Mood on Slant Perception Friendship Duration (in months) Mood (negative) Verbal r = -. 49, p <. 05 Verbal r = -. 01, p = ns Visual r = -. 50, p <. 05 Visual r = -. 13, p = ns Haptic r = -. 14, p = ns Haptic r =. 01, p = ns
Effects of Friendship Duration and Mood on Slant Perception Friendship Duration (in months) Mood (negative) Verbal r = -. 49, p <. 05 Verbal r = -. 01, p = ns Visual r = -. 50, p <. 05 Visual r = -. 13, p = ns Haptic r = -. 14, p = ns Haptic r =. 01, p = ns
 Study 1 Alternative Explanations Instrumental support Desirability Social Facilitation Sampling bias Study 2 Remedies n = 36, 49% female Imaged other: Positive, Neutral, Negative Random Assignment
Study 1 Alternative Explanations Instrumental support Desirability Social Facilitation Sampling bias Study 2 Remedies n = 36, 49% female Imaged other: Positive, Neutral, Negative Random Assignment
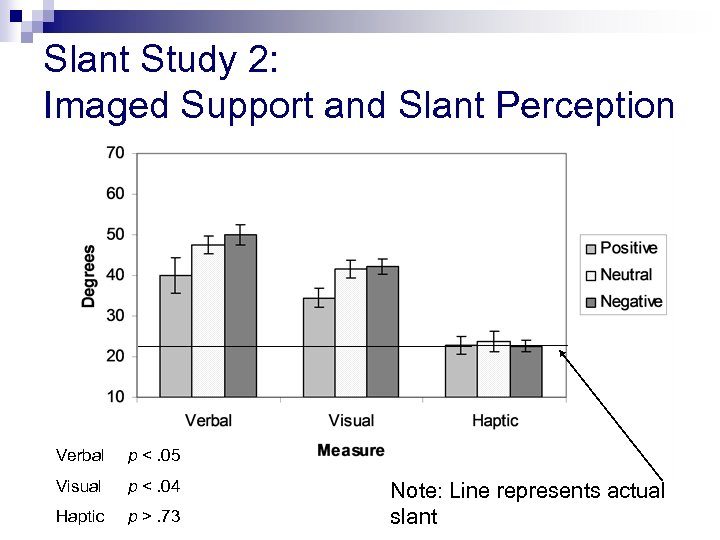 Slant Study 2: Imaged Support and Slant Perception Verbal p <. 05 Visual p <. 04 Haptic p >. 73 Note: Line represents actual slant
Slant Study 2: Imaged Support and Slant Perception Verbal p <. 05 Visual p <. 04 Haptic p >. 73 Note: Line represents actual slant
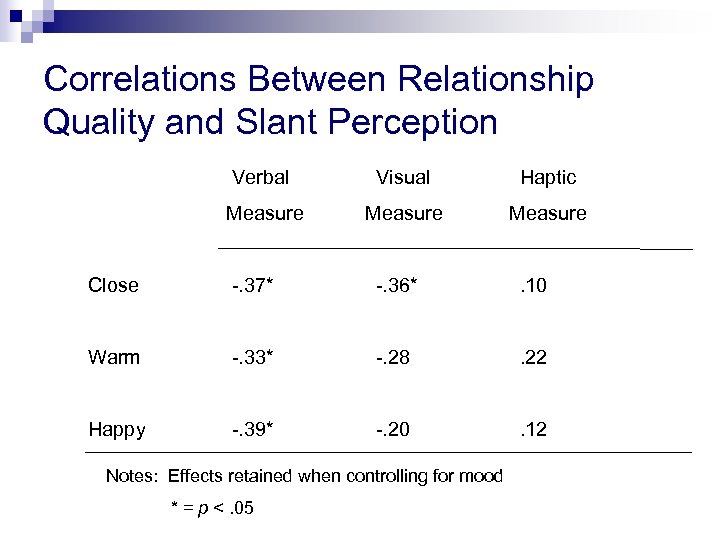 Correlations Between Relationship Quality and Slant Perception Verbal Visual Haptic Measure Close -. 37* -. 36* . 10 Warm -. 33* -. 28 . 22 Happy -. 39* -. 20 . 12 Notes: Effects retained when controlling for mood * = p <. 05
Correlations Between Relationship Quality and Slant Perception Verbal Visual Haptic Measure Close -. 37* -. 36* . 10 Warm -. 33* -. 28 . 22 Happy -. 39* -. 20 . 12 Notes: Effects retained when controlling for mood * = p <. 05
 Resources and Distance Perception Harber, Iacovelli, & Yeung, in prep n Will psychosocial resources also moderate distance perception? n Will self-worth serve as resource?
Resources and Distance Perception Harber, Iacovelli, & Yeung, in prep n Will psychosocial resources also moderate distance perception? n Will self-worth serve as resource?
 Self Worth Induction Boosted: Image best success Unchanged: Image doing laundry Depleted: Image worst failure N = 107, 63% female
Self Worth Induction Boosted: Image best success Unchanged: Image doing laundry Depleted: Image worst failure N = 107, 63% female
 Distance Estimation Task
Distance Estimation Task
 Target Objects Low Threat High Threat
Target Objects Low Threat High Threat
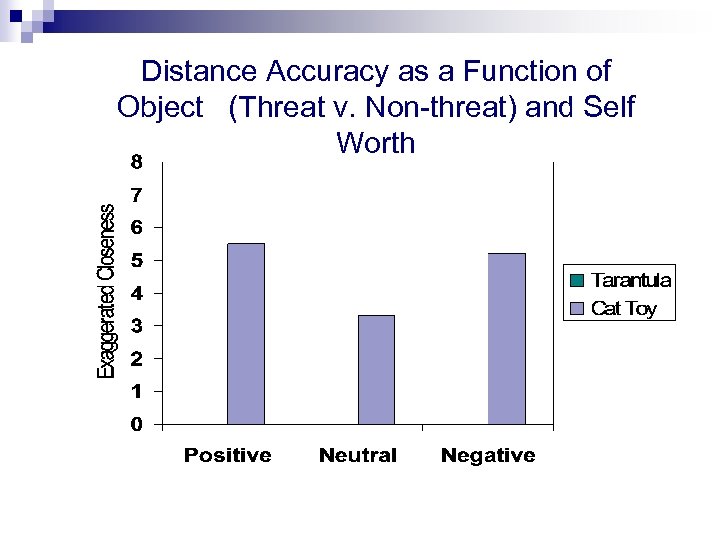 Distance Accuracy as a Function of Object (Threat v. Non-threat) and Self Worth
Distance Accuracy as a Function of Object (Threat v. Non-threat) and Self Worth
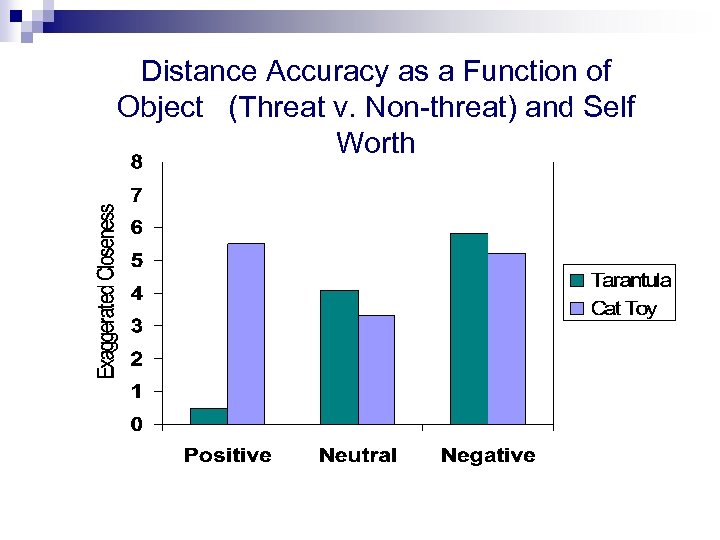 Distance Accuracy as a Function of Object (Threat v. Non-threat) and Self Worth
Distance Accuracy as a Function of Object (Threat v. Non-threat) and Self Worth
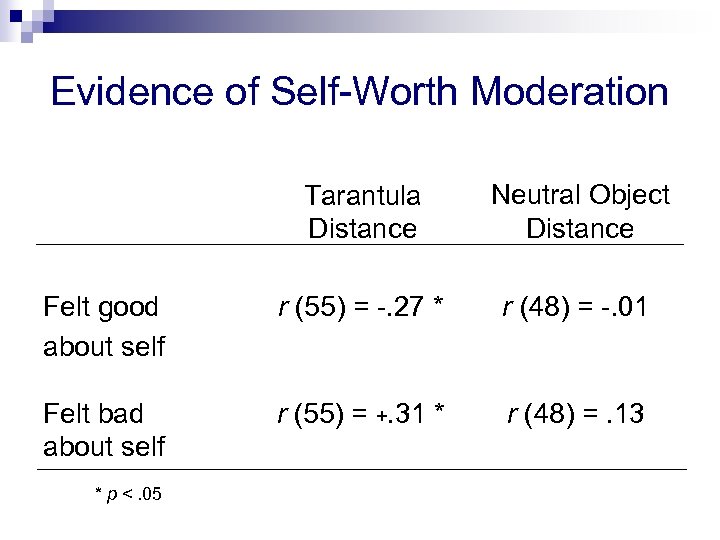 Evidence of Self-Worth Moderation Tarantula Distance Neutral Object Distance Felt good about self r (55) = -. 27 * r (48) = -. 01 Felt bad about self r (55) = +. 31 * r (48) =. 13 * p <. 05
Evidence of Self-Worth Moderation Tarantula Distance Neutral Object Distance Felt good about self r (55) = -. 27 * r (48) = -. 01 Felt bad about self r (55) = +. 31 * r (48) =. 13 * p <. 05
 Self Esteem, External Support, and Height Judgments Harber, Yeung, Valree, & Escobar, in preparation PHOTO LOOKING DOWN STAIRWELL N = XXX, XX% female, age = XX. XX
Self Esteem, External Support, and Height Judgments Harber, Yeung, Valree, & Escobar, in preparation PHOTO LOOKING DOWN STAIRWELL N = XXX, XX% female, age = XX. XX
 Do resources moderate height judgments? Does trait self esteem operate as a resource? Do internal resources supplement external resources?
Do resources moderate height judgments? Does trait self esteem operate as a resource? Do internal resources supplement external resources?

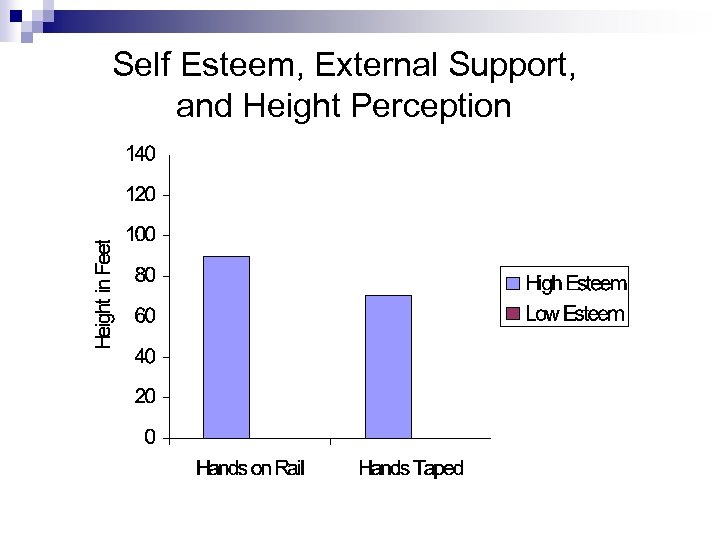 Self Esteem, External Support, and Height Perception
Self Esteem, External Support, and Height Perception
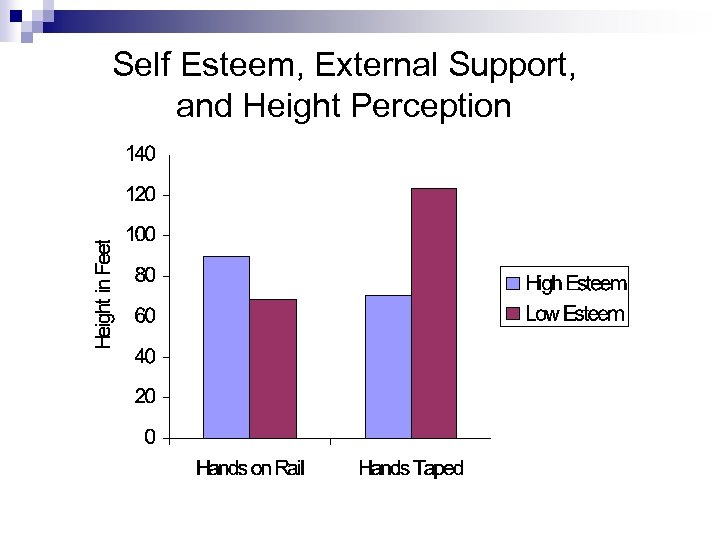 Self Esteem, External Support, and Height Perception
Self Esteem, External Support, and Height Perception
 Conclusions n Resources affect the perception of : Others’ distress (baby cries) Distance to stressors (tarantulas) Heights Hill slants n Similar effects derive from different resources: Social support (baby cries, hill slant) Emotional disclosure (baby cries) Self worth (distance to tarantula) Self esteem (height) n Resources may enhance coping by moderating stressor perception
Conclusions n Resources affect the perception of : Others’ distress (baby cries) Distance to stressors (tarantulas) Heights Hill slants n Similar effects derive from different resources: Social support (baby cries, hill slant) Emotional disclosure (baby cries) Self worth (distance to tarantula) Self esteem (height) n Resources may enhance coping by moderating stressor perception
 The “I” Sees Through the Lens of the “Me”.
The “I” Sees Through the Lens of the “Me”.


