cb7f2d650d47ca04ed53e67bc1496435.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10
 Civil War 1861 -1865 PERSIA North • Politics • Economics • Religion? • Social • Intellectual • Arts South • Politics • Economics • Religion? • Social • Intellectual • Arts
Civil War 1861 -1865 PERSIA North • Politics • Economics • Religion? • Social • Intellectual • Arts South • Politics • Economics • Religion? • Social • Intellectual • Arts
 Advantages & Disadvantages • North • South Advantages: • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Extensive railroad network Strong industrial base Superior Navy Larger population Abundant supply of food Disadvantages: 1. Shortage of experienced & skilled military commanders 2. A divided population that did not fully support the war Advantages: • 1. A defensive war fought on their home territory • A long coastline that would be difficult to blockade • 3. An important cash crop in cotton • 4. A group of experienced and skilled military commanders • 5. A close economic relationship with Great Britain Disadvantages: 1. A smaller population than the North 2. A smaller industrial base than the North
Advantages & Disadvantages • North • South Advantages: • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Extensive railroad network Strong industrial base Superior Navy Larger population Abundant supply of food Disadvantages: 1. Shortage of experienced & skilled military commanders 2. A divided population that did not fully support the war Advantages: • 1. A defensive war fought on their home territory • A long coastline that would be difficult to blockade • 3. An important cash crop in cotton • 4. A group of experienced and skilled military commanders • 5. A close economic relationship with Great Britain Disadvantages: 1. A smaller population than the North 2. A smaller industrial base than the North
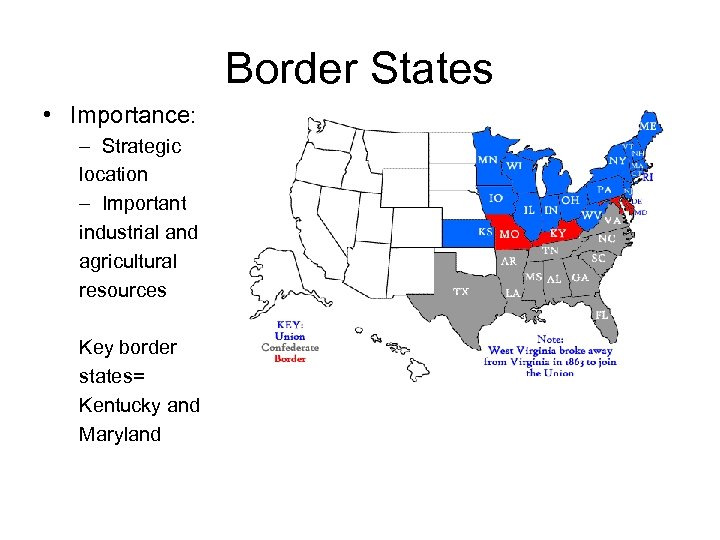 Border States • Importance: – Strategic location – Important industrial and agricultural resources Key border states= Kentucky and Maryland
Border States • Importance: – Strategic location – Important industrial and agricultural resources Key border states= Kentucky and Maryland
 Battles & leaders • • Key battle to know= Antietam – Why? – This Union victory persuaded England France to remain neutral. While both European powers saw advantages in a divided America, they followed a cautious policy toward both the North and South – This Union victory enabled Lincoln to issue the Emancipation Proclamation HINT – APUSH writers generally ignore the battles and leaders of the Civil War. Need to remember Antietam for sure though. But… 150 year anniversary of Civil War was last year…sometimes that makes a difference
Battles & leaders • • Key battle to know= Antietam – Why? – This Union victory persuaded England France to remain neutral. While both European powers saw advantages in a divided America, they followed a cautious policy toward both the North and South – This Union victory enabled Lincoln to issue the Emancipation Proclamation HINT – APUSH writers generally ignore the battles and leaders of the Civil War. Need to remember Antietam for sure though. But… 150 year anniversary of Civil War was last year…sometimes that makes a difference
 Turning Points Vicksburg – West – Siege of city – Took Mississippi River and split Confederacy Gettysburg -Confederate move into North again -most crucial battle & bloodiest -South CAN be beat & never regain offensive again
Turning Points Vicksburg – West – Siege of city – Took Mississippi River and split Confederacy Gettysburg -Confederate move into North again -most crucial battle & bloodiest -South CAN be beat & never regain offensive again
 Emancipation Proclamation • Lincoln delayed issuing it because he didn’t want to antagonize the slave owners in the border states • North originally went to war to preserve the Union. The EP strengthens the Union’s moral cause • The EP rallied anti-slavery support in England France • The EP did NOT free slaves in the border states • The EP freed only slaves in the Confederate states that were still in rebellion HINT- It is important to focus on what the EP did and did not do. It did Significantly enhance the Union’s moral cause. However, it did not actually free a single slave. Much stronger on proclamation than on emancipation. Slavery was legally abolished by the 13 th Amendment.
Emancipation Proclamation • Lincoln delayed issuing it because he didn’t want to antagonize the slave owners in the border states • North originally went to war to preserve the Union. The EP strengthens the Union’s moral cause • The EP rallied anti-slavery support in England France • The EP did NOT free slaves in the border states • The EP freed only slaves in the Confederate states that were still in rebellion HINT- It is important to focus on what the EP did and did not do. It did Significantly enhance the Union’s moral cause. However, it did not actually free a single slave. Much stronger on proclamation than on emancipation. Slavery was legally abolished by the 13 th Amendment.
 • Key Political Actions-put the “P” in PERSIA! Congressional Actions – National banking system to provide a uniform national currency – Chartered two corporations - the Union Pacific RR and Central Pacific RR- to build a transcontinental RR connecting Omaha, NE with Sacramento, CA – Homestead Act of 1862 offered cheap & sometimes free land to people who would settle West and improve the land – Passes high tariffs to protect American industry from foreign competition • Expansion of Presidential Power • Lincoln found the war required active & prompt presidential action • Lincoln suspended the writ of habeas corpus for everyone living between D. C. and Philly • Decide whether you think justified? National security? Abuse of power?
• Key Political Actions-put the “P” in PERSIA! Congressional Actions – National banking system to provide a uniform national currency – Chartered two corporations - the Union Pacific RR and Central Pacific RR- to build a transcontinental RR connecting Omaha, NE with Sacramento, CA – Homestead Act of 1862 offered cheap & sometimes free land to people who would settle West and improve the land – Passes high tariffs to protect American industry from foreign competition • Expansion of Presidential Power • Lincoln found the war required active & prompt presidential action • Lincoln suspended the writ of habeas corpus for everyone living between D. C. and Philly • Decide whether you think justified? National security? Abuse of power?
 Reconstruction Amendments 13 th Amendment- 1865 15 th Amendment- 1870 *Abolished slavery & involuntary servitude *amendment provided suffrage for black males *Completed the work of the EP *stirred controversy among women’s rights advocates…. 14 th Amendment- 1868 *Made former slaves citizens, invalidating the Dred Scott decision *Provided equal protection of the laws for all citizens *Enforced congressional legislation guaranteeing civil rights to former slaves *but some supported it like Lucy Stone, Julia Ward Howe & Frederick Douglas *others opposed like Susan B. Anthony, Elizabeth Cady Stantontried for universal suffrage amendment-failed
Reconstruction Amendments 13 th Amendment- 1865 15 th Amendment- 1870 *Abolished slavery & involuntary servitude *amendment provided suffrage for black males *Completed the work of the EP *stirred controversy among women’s rights advocates…. 14 th Amendment- 1868 *Made former slaves citizens, invalidating the Dred Scott decision *Provided equal protection of the laws for all citizens *Enforced congressional legislation guaranteeing civil rights to former slaves *but some supported it like Lucy Stone, Julia Ward Howe & Frederick Douglas *others opposed like Susan B. Anthony, Elizabeth Cady Stantontried for universal suffrage amendment-failed
 Radical Reconstruction • Causes: – Former Confederates elected to Congress – Black codes enacted in South – Race riots in New Orleans & Memphis – Attempts in the South to undermine the 14 th Amendment • Programs, Policies and Achievements: – Military occupation of South permitted – Punishment of Confederate leaders became policy – Restrictions placed on power of President Andrew Johnson – House of Rep impeached Johnson because he obstructed enforcement of the Reconstruction Acts Achievements -Public school systems in the South were improved -African Americans were elected to the House & Senate
Radical Reconstruction • Causes: – Former Confederates elected to Congress – Black codes enacted in South – Race riots in New Orleans & Memphis – Attempts in the South to undermine the 14 th Amendment • Programs, Policies and Achievements: – Military occupation of South permitted – Punishment of Confederate leaders became policy – Restrictions placed on power of President Andrew Johnson – House of Rep impeached Johnson because he obstructed enforcement of the Reconstruction Acts Achievements -Public school systems in the South were improved -African Americans were elected to the House & Senate
 Plight of African Americans • From slaves to sharecroppers: – Majority of freedmen entered sharecropping arrangements with their former masters – Sharecropping led to a cycle of debt & depression for Southern tenant farmers – Freedmen DID NOT receive 40 acres & a mule in the South- where? • Black Codes: – Codes passed by Southern state legislatures – Intended to place limits on the socioeconomic opportunities & freedoms open to Black people – The codes forced Black Americans to work under conditions that closely resembled slavery – Jim Crow segregation to follow quickly to separate races
Plight of African Americans • From slaves to sharecroppers: – Majority of freedmen entered sharecropping arrangements with their former masters – Sharecropping led to a cycle of debt & depression for Southern tenant farmers – Freedmen DID NOT receive 40 acres & a mule in the South- where? • Black Codes: – Codes passed by Southern state legislatures – Intended to place limits on the socioeconomic opportunities & freedoms open to Black people – The codes forced Black Americans to work under conditions that closely resembled slavery – Jim Crow segregation to follow quickly to separate races


