43ed87b105f94889f97cab693c3af9c2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78
 Cisco Storage Networking FICON James Long Storage Networking Systems Engineer jalong@cisco. com © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 1
Cisco Storage Networking FICON James Long Storage Networking Systems Engineer jalong@cisco. com © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 1
 Cisco MDS 9000 Family Industry Leading Investment Protection Across a Comprehensive Product Line MDS 9100/9200 Multilayer Fabric Switches MDS 9120 MDS 9140 Supervisor 16 -port FC 32 -port FC MDS 9500 Multilayer Directors MDS 9216 i MDS 9216 4 -port GE 8 -port GE MDS 9506 Multi. Protocol Services Module MDS 9509 Advanced Services Module Caching Services Module SANOS - Fabric Manager - Device Manager - IOS compatible CLI © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 2
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Industry Leading Investment Protection Across a Comprehensive Product Line MDS 9100/9200 Multilayer Fabric Switches MDS 9120 MDS 9140 Supervisor 16 -port FC 32 -port FC MDS 9500 Multilayer Directors MDS 9216 i MDS 9216 4 -port GE 8 -port GE MDS 9506 Multi. Protocol Services Module MDS 9509 Advanced Services Module Caching Services Module SANOS - Fabric Manager - Device Manager - IOS compatible CLI © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 2
 Cisco MDS 9509 Director • • Up to 112 FICON ports in 14 RUs Full FC-SB-2 and FC-SB-3 compliance Support for every FICON feature Supports FICON, FCIP and i. SCSI Non-blocking, S&F architecture 80 Gbps per slot (full-duplex, redundant) Hardware-based services Storage intelligence - Virtualization Security services - VSANs, Zones, VLANs, ACLs Traffic management - Qo. S, FCC, Port. Channel Diagnostics - SPAN, FC Traceroute, Fabric Analyzer © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 3
Cisco MDS 9509 Director • • Up to 112 FICON ports in 14 RUs Full FC-SB-2 and FC-SB-3 compliance Support for every FICON feature Supports FICON, FCIP and i. SCSI Non-blocking, S&F architecture 80 Gbps per slot (full-duplex, redundant) Hardware-based services Storage intelligence - Virtualization Security services - VSANs, Zones, VLANs, ACLs Traffic management - Qo. S, FCC, Port. Channel Diagnostics - SPAN, FC Traceroute, Fabric Analyzer © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 3
 Cisco MDS 9513 Director Coming Soon! • Up to 528 FICON ports in 14 RUs • Full FC-SB-2 and FC-SB-3 compliance • Support for every FICON feature • • Supports FICON, FCIP and i. SCSI Non-blocking, S&F architecture 96 Gbps per slot (full-duplex, redundant) Hardware-based services Storage intelligence - Virtualization Security services - VSANs, Zones, VLANs, ACLs Traffic management - Qo. S, FCC, Port. Channel Diagnostics - SPAN, FC Traceroute, Fabric Analyzer © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 4
Cisco MDS 9513 Director Coming Soon! • Up to 528 FICON ports in 14 RUs • Full FC-SB-2 and FC-SB-3 compliance • Support for every FICON feature • • Supports FICON, FCIP and i. SCSI Non-blocking, S&F architecture 96 Gbps per slot (full-duplex, redundant) Hardware-based services Storage intelligence - Virtualization Security services - VSANs, Zones, VLANs, ACLs Traffic management - Qo. S, FCC, Port. Channel Diagnostics - SPAN, FC Traceroute, Fabric Analyzer © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 4
 Ultra Resilient Hardware Architecture • 99. 999% Availability • No Single Point of Failure Dual Power Supplies Dual Supervisors Dual Cross-bars Dual backplane data channels Dual backplane control channels Dual system clocks 9 independent fans with failure monitors (9509) • • All components are modular and hot swappable Power and cooling management Environmental monitoring Majority voting for critical signals © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 5
Ultra Resilient Hardware Architecture • 99. 999% Availability • No Single Point of Failure Dual Power Supplies Dual Supervisors Dual Cross-bars Dual backplane data channels Dual backplane control channels Dual system clocks 9 independent fans with failure monitors (9509) • • All components are modular and hot swappable Power and cooling management Environmental monitoring Majority voting for critical signals © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 5
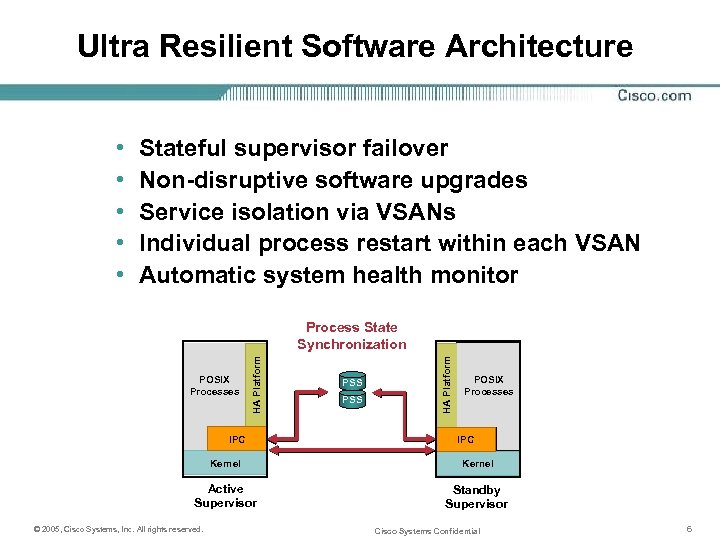 Ultra Resilient Software Architecture • • • Stateful supervisor failover Non-disruptive software upgrades Service isolation via VSANs Individual process restart within each VSAN Automatic system health monitor IPC PSS HA Platform POSIX Processes HA Platform Process State Synchronization POSIX Processes IPC Kernel Active Supervisor Standby Supervisor © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 6
Ultra Resilient Software Architecture • • • Stateful supervisor failover Non-disruptive software upgrades Service isolation via VSANs Individual process restart within each VSAN Automatic system health monitor IPC PSS HA Platform POSIX Processes HA Platform Process State Synchronization POSIX Processes IPC Kernel Active Supervisor Standby Supervisor © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 6
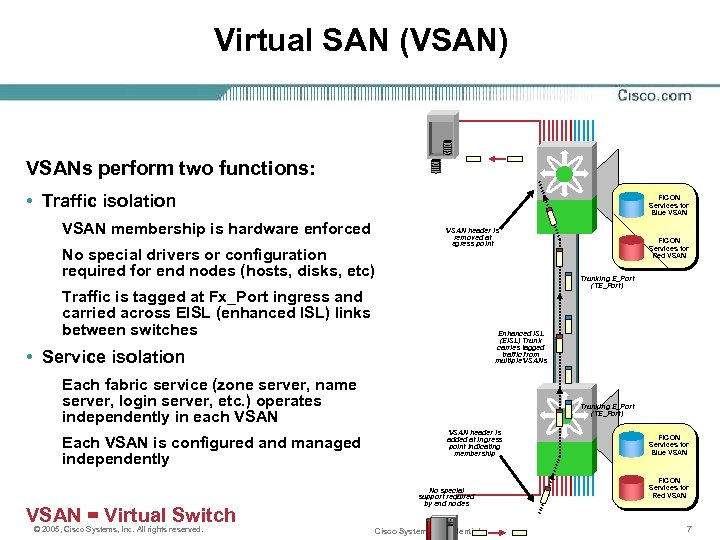 Virtual SAN (VSAN) VSANs perform two functions: • Traffic isolation FICON Services for Blue VSAN membership is hardware enforced No special drivers or configuration required for end nodes (hosts, disks, etc) VSAN header is removed at egress point Trunking E_Port (TE_Port) Traffic is tagged at Fx_Port ingress and carried across EISL (enhanced ISL) links between switches Enhanced ISL (EISL) Trunk carries tagged traffic from multiple VSANs • Service isolation Each fabric service (zone server, name server, login server, etc. ) operates independently in each VSAN Each VSAN is configured and managed independently VSAN = Virtual Switch © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FICON Services for Red VSAN Trunking E_Port (TE_Port) VSAN header is added at ingress point indicating membership No special support required by end nodes Cisco Systems Confidential FICON Services for Blue VSAN FICON Services for Red VSAN 7
Virtual SAN (VSAN) VSANs perform two functions: • Traffic isolation FICON Services for Blue VSAN membership is hardware enforced No special drivers or configuration required for end nodes (hosts, disks, etc) VSAN header is removed at egress point Trunking E_Port (TE_Port) Traffic is tagged at Fx_Port ingress and carried across EISL (enhanced ISL) links between switches Enhanced ISL (EISL) Trunk carries tagged traffic from multiple VSANs • Service isolation Each fabric service (zone server, name server, login server, etc. ) operates independently in each VSAN Each VSAN is configured and managed independently VSAN = Virtual Switch © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FICON Services for Red VSAN Trunking E_Port (TE_Port) VSAN header is added at ingress point indicating membership No special support required by end nodes Cisco Systems Confidential FICON Services for Blue VSAN FICON Services for Red VSAN 7
 Cisco MDS 9000 FICON Advantages • Enhanced Intermix (Supermix) • Enhanced SAN Consolidation • Enhanced Cascading • Enhanced Remote Connectivity • Advanced Management MDS 9500 Series © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 8
Cisco MDS 9000 FICON Advantages • Enhanced Intermix (Supermix) • Enhanced SAN Consolidation • Enhanced Cascading • Enhanced Remote Connectivity • Advanced Management MDS 9500 Series © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 8
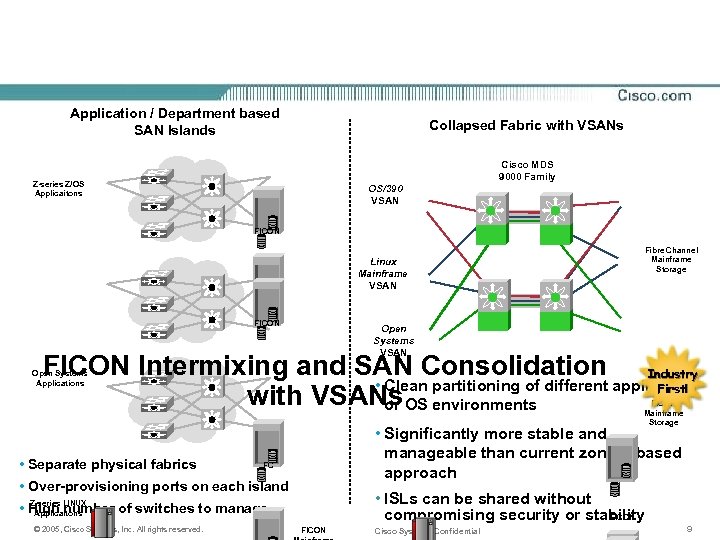 Application / Department based SAN Islands Collapsed Fabric with VSANs Cisco MDS 9000 Family Z-series Z/OS Applicaitons OS/390 VSAN FICON Linux Mainframe VSAN Fibre Channel Mainframe Storage FC FICON Open Systems VSAN FICON Intermixing and SAN Consolidation Industry • Clean partitioning of different application First! with VSANs OS environments or Open Systems Applications FICON Mainframe Storage • Separate physical fabrics • Significantly more stable and manageable than current zoning-based approach FC • Over-provisioning ports on each island • ISLs can be shared without FICON compromising security or stability Z-series • High LINUX number of switches to manage Applicaitons © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FICON Cisco Systems Confidential 9
Application / Department based SAN Islands Collapsed Fabric with VSANs Cisco MDS 9000 Family Z-series Z/OS Applicaitons OS/390 VSAN FICON Linux Mainframe VSAN Fibre Channel Mainframe Storage FC FICON Open Systems VSAN FICON Intermixing and SAN Consolidation Industry • Clean partitioning of different application First! with VSANs OS environments or Open Systems Applications FICON Mainframe Storage • Separate physical fabrics • Significantly more stable and manageable than current zoning-based approach FC • Over-provisioning ports on each island • ISLs can be shared without FICON compromising security or stability Z-series • High LINUX number of switches to manage Applicaitons © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FICON Cisco Systems Confidential 9
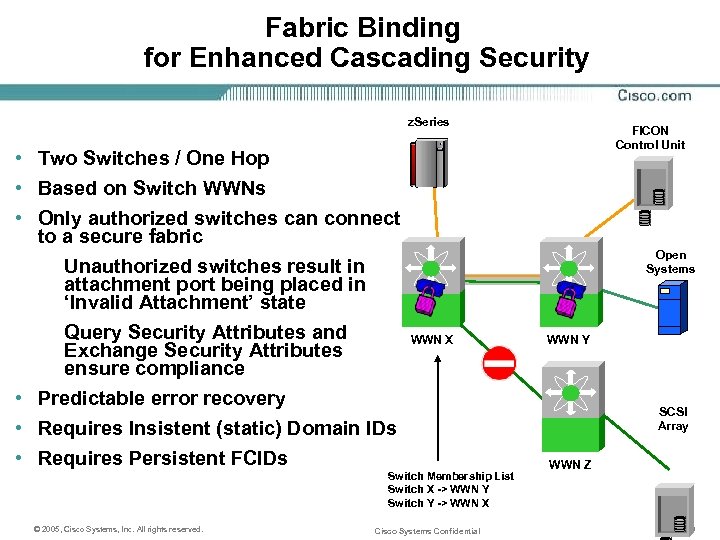 Fabric Binding for Enhanced Cascading Security z. Series • Two Switches / One Hop • Based on Switch WWNs • Only authorized switches can connect to a secure fabric Unauthorized switches result in attachment port being placed in ‘Invalid Attachment’ state Query Security Attributes and Exchange Security Attributes ensure compliance • Predictable error recovery • Requires Insistent (static) Domain IDs • Requires Persistent FCIDs Open Systems WWN X Switch Membership List Switch X -> WWN Y Switch Y -> WWN X © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FICON Control Unit Cisco Systems Confidential WWN Y SCSI Array WWN Z 10
Fabric Binding for Enhanced Cascading Security z. Series • Two Switches / One Hop • Based on Switch WWNs • Only authorized switches can connect to a secure fabric Unauthorized switches result in attachment port being placed in ‘Invalid Attachment’ state Query Security Attributes and Exchange Security Attributes ensure compliance • Predictable error recovery • Requires Insistent (static) Domain IDs • Requires Persistent FCIDs Open Systems WWN X Switch Membership List Switch X -> WWN Y Switch Y -> WWN X © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FICON Control Unit Cisco Systems Confidential WWN Y SCSI Array WWN Z 10
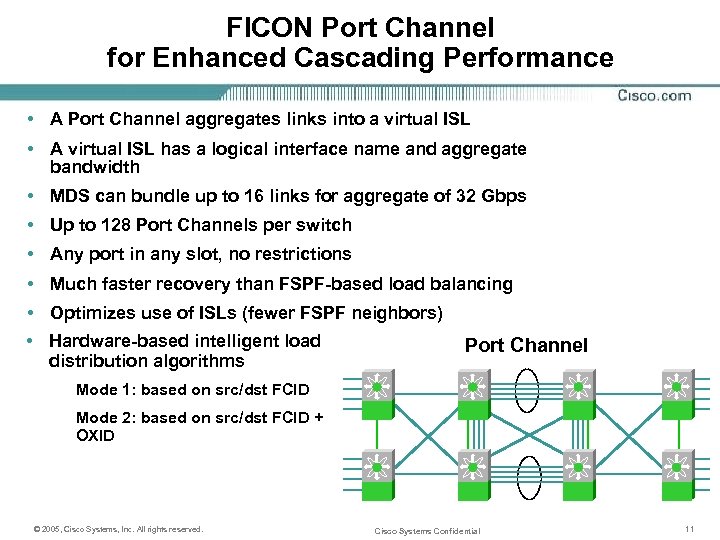 FICON Port Channel for Enhanced Cascading Performance • A Port Channel aggregates links into a virtual ISL • A virtual ISL has a logical interface name and aggregate bandwidth • MDS can bundle up to 16 links for aggregate of 32 Gbps • Up to 128 Port Channels per switch • Any port in any slot, no restrictions • Much faster recovery than FSPF-based load balancing • Optimizes use of ISLs (fewer FSPF neighbors) • Hardware-based intelligent load distribution algorithms Port Channel Mode 1: based on src/dst FCID Mode 2: based on src/dst FCID + OXID © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 11
FICON Port Channel for Enhanced Cascading Performance • A Port Channel aggregates links into a virtual ISL • A virtual ISL has a logical interface name and aggregate bandwidth • MDS can bundle up to 16 links for aggregate of 32 Gbps • Up to 128 Port Channels per switch • Any port in any slot, no restrictions • Much faster recovery than FSPF-based load balancing • Optimizes use of ISLs (fewer FSPF neighbors) • Hardware-based intelligent load distribution algorithms Port Channel Mode 1: based on src/dst FCID Mode 2: based on src/dst FCID + OXID © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 11
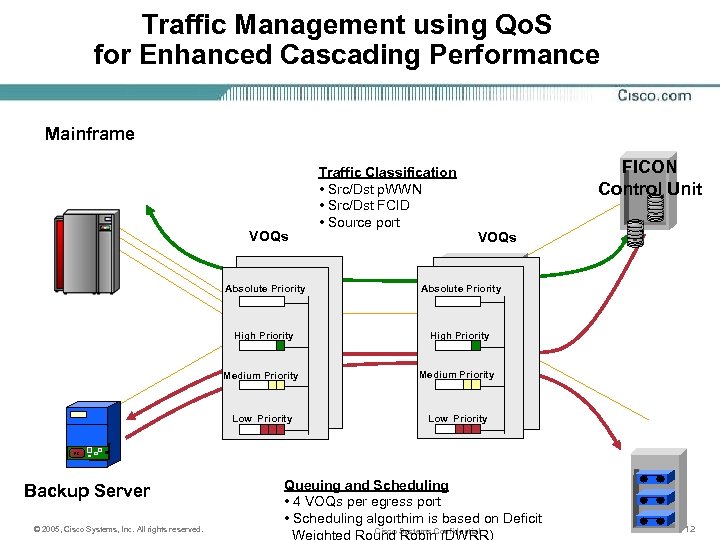 Traffic Management using Qo. S for Enhanced Cascading Performance Mainframe VOQs Traffic Classification • Src/Dst p. WWN • Src/Dst FCID • Source port FICON Control Unit VOQs Absolute Priority High Priority Medium Priority Low Priority FC Backup Server © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Queuing and Scheduling • 4 VOQs per egress port • Scheduling algorthim is based on Deficit Cisco Systems Confidential Tape 12
Traffic Management using Qo. S for Enhanced Cascading Performance Mainframe VOQs Traffic Classification • Src/Dst p. WWN • Src/Dst FCID • Source port FICON Control Unit VOQs Absolute Priority High Priority Medium Priority Low Priority FC Backup Server © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Queuing and Scheduling • 4 VOQs per egress port • Scheduling algorthim is based on Deficit Cisco Systems Confidential Tape 12
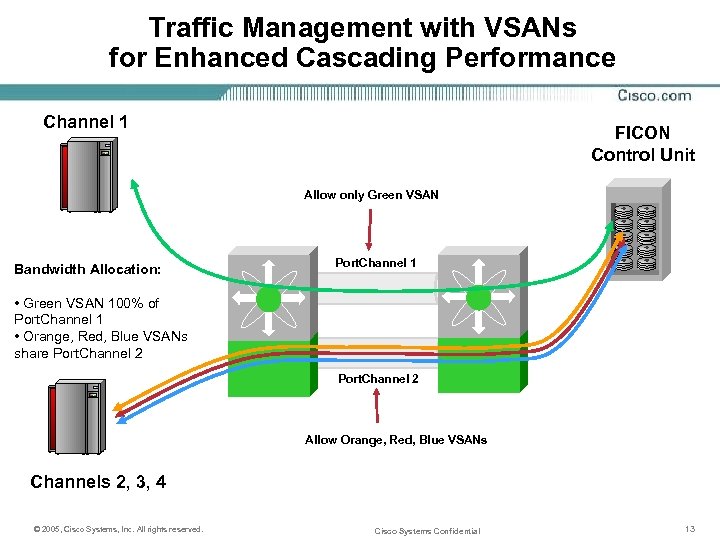 Traffic Management with VSANs for Enhanced Cascading Performance Channel 1 FICON Control Unit Allow only Green VSAN Bandwidth Allocation: Port. Channel 1 • Green VSAN 100% of Port. Channel 1 • Orange, Red, Blue VSANs share Port. Channel 2 Allow Orange, Red, Blue VSANs Channels 2, 3, 4 © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 13
Traffic Management with VSANs for Enhanced Cascading Performance Channel 1 FICON Control Unit Allow only Green VSAN Bandwidth Allocation: Port. Channel 1 • Green VSAN 100% of Port. Channel 1 • Orange, Red, Blue VSANs share Port. Channel 2 Allow Orange, Red, Blue VSANs Channels 2, 3, 4 © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 13
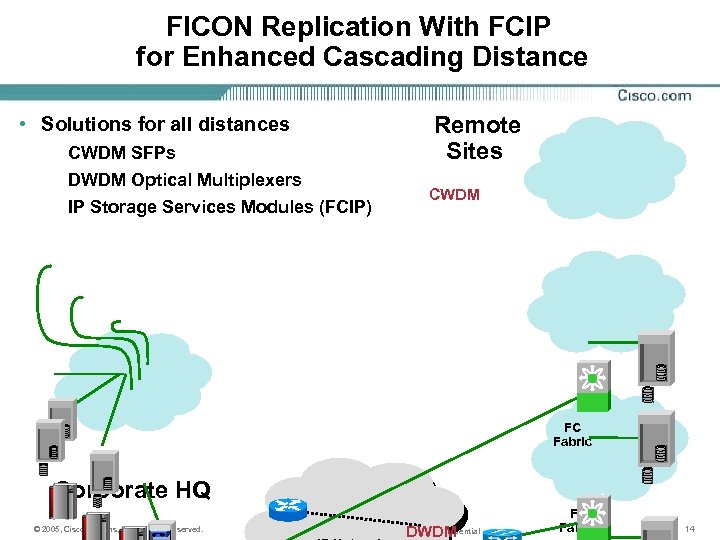 FICON Replication With FCIP for Enhanced Cascading Distance • Solutions for all distances CWDM SFPs DWDM Optical Multiplexers IP Storage Services Modules (FCIP) Remote Sites CWDM Backup Servers FC Fabric Corporate HQ © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. DWDM Cisco Systems Confidential FC Fabric 14
FICON Replication With FCIP for Enhanced Cascading Distance • Solutions for all distances CWDM SFPs DWDM Optical Multiplexers IP Storage Services Modules (FCIP) Remote Sites CWDM Backup Servers FC Fabric Corporate HQ © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. DWDM Cisco Systems Confidential FC Fabric 14
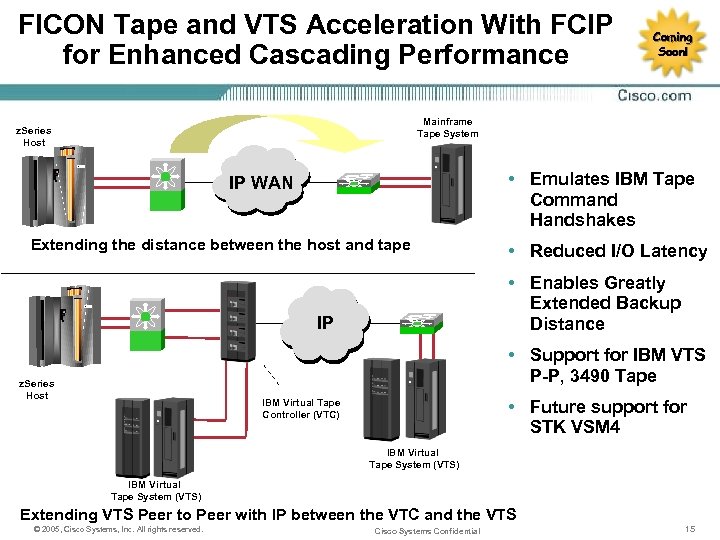 FICON Tape and VTS Acceleration With FCIP for Enhanced Cascading Performance Coming Soon! Mainframe Tape System z. Series Host • Emulates IBM Tape Command Handshakes IP WAN Extending the distance between the host and tape • Reduced I/O Latency • Enables Greatly Extended Backup Distance IP • Support for IBM VTS P-P, 3490 Tape z. Series Host • Future support for STK VSM 4 IBM Virtual Tape Controller (VTC) IBM Virtual Tape System (VTS) Extending VTS Peer to Peer with IP between the VTC and the VTS © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 15
FICON Tape and VTS Acceleration With FCIP for Enhanced Cascading Performance Coming Soon! Mainframe Tape System z. Series Host • Emulates IBM Tape Command Handshakes IP WAN Extending the distance between the host and tape • Reduced I/O Latency • Enables Greatly Extended Backup Distance IP • Support for IBM VTS P-P, 3490 Tape z. Series Host • Future support for STK VSM 4 IBM Virtual Tape Controller (VTC) IBM Virtual Tape System (VTS) Extending VTS Peer to Peer with IP between the VTC and the VTS © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 15
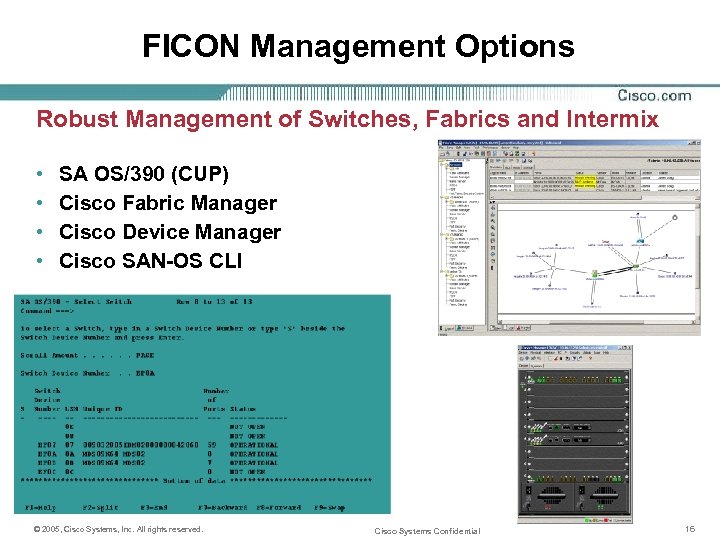 FICON Management Options Robust Management of Switches, Fabrics and Intermix • • SA OS/390 (CUP) Cisco Fabric Manager Cisco Device Manager Cisco SAN-OS CLI © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 16
FICON Management Options Robust Management of Switches, Fabrics and Intermix • • SA OS/390 (CUP) Cisco Fabric Manager Cisco Device Manager Cisco SAN-OS CLI © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 16
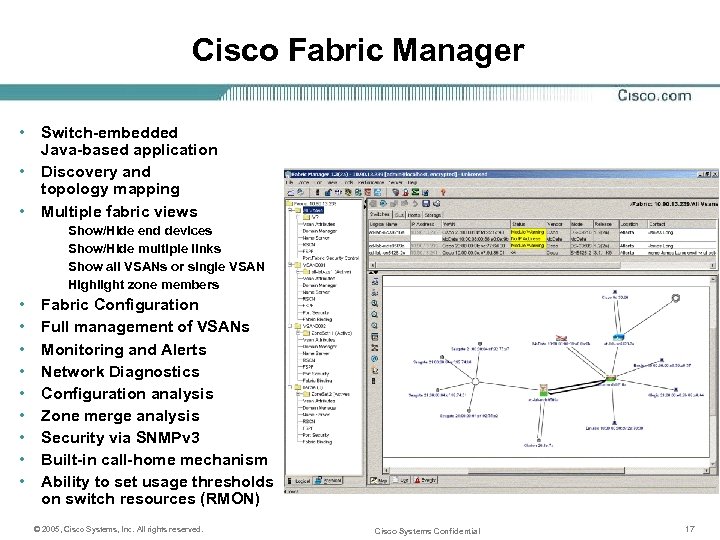 Cisco Fabric Manager • • • Switch-embedded Java-based application Discovery and topology mapping Multiple fabric views Show/Hide end devices Show/Hide multiple links Show all VSANs or single VSAN Highlight zone members • • • Fabric Configuration Full management of VSANs Monitoring and Alerts Network Diagnostics Configuration analysis Zone merge analysis Security via SNMPv 3 Built-in call-home mechanism Ability to set usage thresholds on switch resources (RMON) © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 17
Cisco Fabric Manager • • • Switch-embedded Java-based application Discovery and topology mapping Multiple fabric views Show/Hide end devices Show/Hide multiple links Show all VSANs or single VSAN Highlight zone members • • • Fabric Configuration Full management of VSANs Monitoring and Alerts Network Diagnostics Configuration analysis Zone merge analysis Security via SNMPv 3 Built-in call-home mechanism Ability to set usage thresholds on switch resources (RMON) © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 17
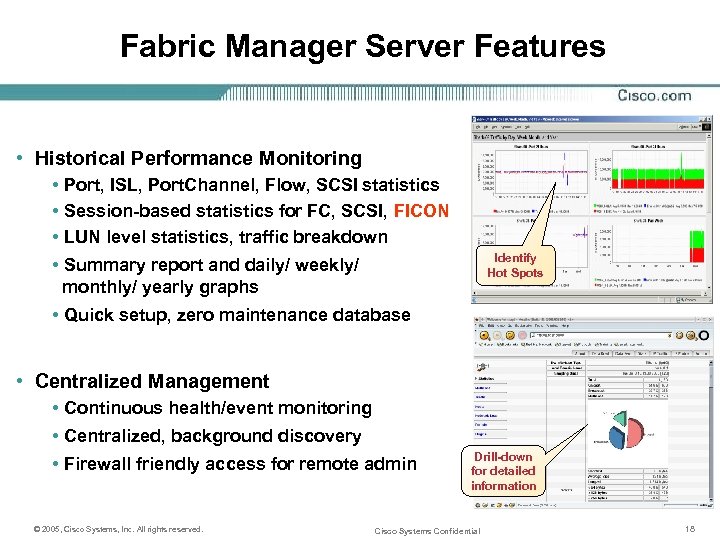 Fabric Manager Server Features • Historical Performance Monitoring • Port, ISL, Port. Channel, Flow, SCSI statistics • Session-based statistics for FC, SCSI, FICON • LUN level statistics, traffic breakdown Identify Hot Spots • Summary report and daily/ weekly/ monthly/ yearly graphs • Quick setup, zero maintenance database • Centralized Management • Continuous health/event monitoring • Centralized, background discovery • Firewall friendly access for remote admin © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Drill-down for detailed information Cisco Systems Confidential 18
Fabric Manager Server Features • Historical Performance Monitoring • Port, ISL, Port. Channel, Flow, SCSI statistics • Session-based statistics for FC, SCSI, FICON • LUN level statistics, traffic breakdown Identify Hot Spots • Summary report and daily/ weekly/ monthly/ yearly graphs • Quick setup, zero maintenance database • Centralized Management • Continuous health/event monitoring • Centralized, background discovery • Firewall friendly access for remote admin © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Drill-down for detailed information Cisco Systems Confidential 18
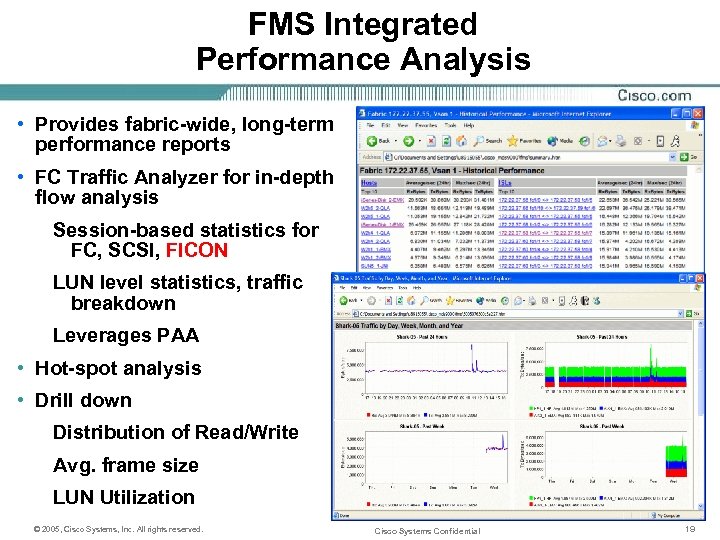 FMS Integrated Performance Analysis • Provides fabric-wide, long-term performance reports • FC Traffic Analyzer for in-depth flow analysis Session-based statistics for FC, SCSI, FICON LUN level statistics, traffic breakdown Leverages PAA • Hot-spot analysis • Drill down Distribution of Read/Write Avg. frame size LUN Utilization © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 19
FMS Integrated Performance Analysis • Provides fabric-wide, long-term performance reports • FC Traffic Analyzer for in-depth flow analysis Session-based statistics for FC, SCSI, FICON LUN level statistics, traffic breakdown Leverages PAA • Hot-spot analysis • Drill down Distribution of Read/Write Avg. frame size LUN Utilization © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 19
 Supplemental MDS Slides © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 20
Supplemental MDS Slides © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 20
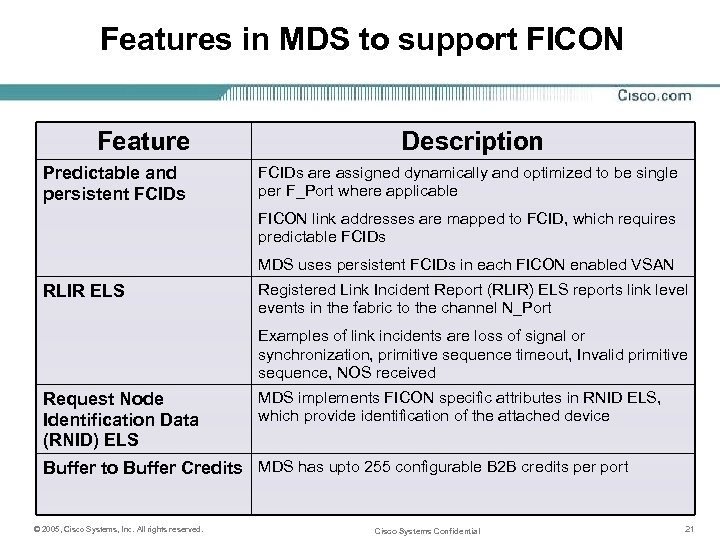 Features in MDS to support FICON Feature Predictable and persistent FCIDs Description FCIDs are assigned dynamically and optimized to be single per F_Port where applicable FICON link addresses are mapped to FCID, which requires predictable FCIDs MDS uses persistent FCIDs in each FICON enabled VSAN RLIR ELS Registered Link Incident Report (RLIR) ELS reports link level events in the fabric to the channel N_Port Examples of link incidents are loss of signal or synchronization, primitive sequence timeout, Invalid primitive sequence, NOS received Request Node Identification Data (RNID) ELS MDS implements FICON specific attributes in RNID ELS, which provide identification of the attached device Buffer to Buffer Credits MDS has upto 255 configurable B 2 B credits per port © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 21
Features in MDS to support FICON Feature Predictable and persistent FCIDs Description FCIDs are assigned dynamically and optimized to be single per F_Port where applicable FICON link addresses are mapped to FCID, which requires predictable FCIDs MDS uses persistent FCIDs in each FICON enabled VSAN RLIR ELS Registered Link Incident Report (RLIR) ELS reports link level events in the fabric to the channel N_Port Examples of link incidents are loss of signal or synchronization, primitive sequence timeout, Invalid primitive sequence, NOS received Request Node Identification Data (RNID) ELS MDS implements FICON specific attributes in RNID ELS, which provide identification of the attached device Buffer to Buffer Credits MDS has upto 255 configurable B 2 B credits per port © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 21
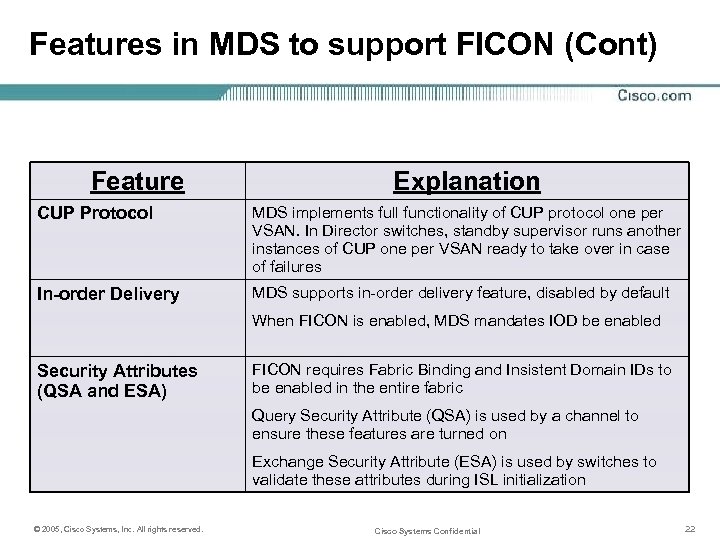 Features in MDS to support FICON (Cont) Feature Explanation CUP Protocol MDS implements full functionality of CUP protocol one per VSAN. In Director switches, standby supervisor runs another instances of CUP one per VSAN ready to take over in case of failures In-order Delivery MDS supports in-order delivery feature, disabled by default When FICON is enabled, MDS mandates IOD be enabled Security Attributes (QSA and ESA) FICON requires Fabric Binding and Insistent Domain IDs to be enabled in the entire fabric Query Security Attribute (QSA) is used by a channel to ensure these features are turned on Exchange Security Attribute (ESA) is used by switches to validate these attributes during ISL initialization © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 22
Features in MDS to support FICON (Cont) Feature Explanation CUP Protocol MDS implements full functionality of CUP protocol one per VSAN. In Director switches, standby supervisor runs another instances of CUP one per VSAN ready to take over in case of failures In-order Delivery MDS supports in-order delivery feature, disabled by default When FICON is enabled, MDS mandates IOD be enabled Security Attributes (QSA and ESA) FICON requires Fabric Binding and Insistent Domain IDs to be enabled in the entire fabric Query Security Attribute (QSA) is used by a channel to ensure these features are turned on Exchange Security Attribute (ESA) is used by switches to validate these attributes during ISL initialization © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 22
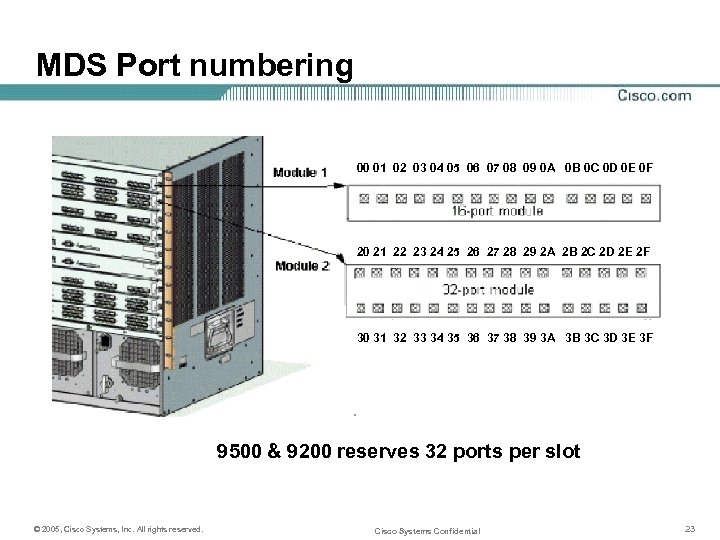 MDS Port numbering 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0 A 0 B 0 C 0 D 0 E 0 F 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 2 A 2 B 2 C 2 D 2 E 2 F 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 3 A 3 B 3 C 3 D 3 E 3 F 9500 & 9200 reserves 32 ports per slot © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 23
MDS Port numbering 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0 A 0 B 0 C 0 D 0 E 0 F 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 2 A 2 B 2 C 2 D 2 E 2 F 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 3 A 3 B 3 C 3 D 3 E 3 F 9500 & 9200 reserves 32 ports per slot © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 23
 FICON Management Interfaces • MDS has IOS like CLI which can used in configuring and managing FICON. • MDS provide Device Manager which uses SNMP to manage the switch. • MDS doesn’t have EFC/console based GUI. The only EFC server we have is CLI. For the same reason, we keep “snmp control” enabled by default. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 24
FICON Management Interfaces • MDS has IOS like CLI which can used in configuring and managing FICON. • MDS provide Device Manager which uses SNMP to manage the switch. • MDS doesn’t have EFC/console based GUI. The only EFC server we have is CLI. For the same reason, we keep “snmp control” enabled by default. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 24
 Enabling FICON • In MDS Switches, FICON is packaged as a “Mainframe” licensed feature. • Up to 8 VSAN can be configured to carry FICON traffic. • Before enabling FICON, following pre-requisites must be configured: • • In Order Delivery • • Fabric Binding Static Domain ID FICON can be enabled through CLI either using “setup ficon” command or by manually addressing each of the above pre-requisites. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 25
Enabling FICON • In MDS Switches, FICON is packaged as a “Mainframe” licensed feature. • Up to 8 VSAN can be configured to carry FICON traffic. • Before enabling FICON, following pre-requisites must be configured: • • In Order Delivery • • Fabric Binding Static Domain ID FICON can be enabled through CLI either using “setup ficon” command or by manually addressing each of the above pre-requisites. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 25
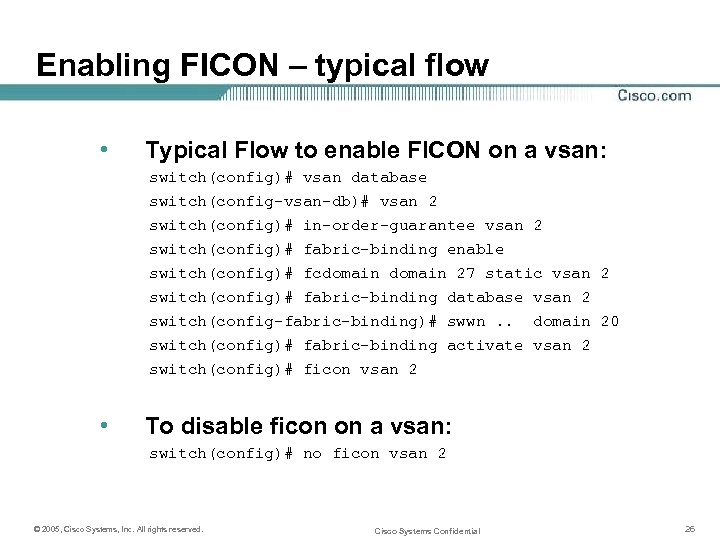 Enabling FICON – typical flow • Typical Flow to enable FICON on a vsan: switch(config)# vsan database switch(config-vsan-db)# vsan 2 switch(config)# in-order-guarantee vsan 2 switch(config)# fabric-binding enable switch(config)# fcdomain 27 static vsan 2 switch(config)# fabric-binding database vsan 2 switch(config-fabric-binding)# swwn. . domain 20 switch(config)# fabric-binding activate vsan 2 switch(config)# ficon vsan 2 • To disable ficon on a vsan: switch(config)# no ficon vsan 2 © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 26
Enabling FICON – typical flow • Typical Flow to enable FICON on a vsan: switch(config)# vsan database switch(config-vsan-db)# vsan 2 switch(config)# in-order-guarantee vsan 2 switch(config)# fabric-binding enable switch(config)# fcdomain 27 static vsan 2 switch(config)# fabric-binding database vsan 2 switch(config-fabric-binding)# swwn. . domain 20 switch(config)# fabric-binding activate vsan 2 switch(config)# ficon vsan 2 • To disable ficon on a vsan: switch(config)# no ficon vsan 2 © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 26
 Enabling FICON – CUP and Zone • If CUP feature is to be used, then CUP Nport needs to be in the same zone as the Channel. • ‘setup ficon’ sets the default zone to permit. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 27
Enabling FICON – CUP and Zone • If CUP feature is to be used, then CUP Nport needs to be in the same zone as the Channel. • ‘setup ficon’ sets the default zone to permit. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 27
 Enabling FICON – Other effects • FCID allocation is based on port-address. • FICON will not come up if any persistent FCIDs are configured. • Load-balancing scheme for the vsan is set to srcid-destid. • fcdroplatency for the vsan is set to 500 msec. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 28
Enabling FICON – Other effects • FCID allocation is based on port-address. • FICON will not come up if any persistent FCIDs are configured. • Load-balancing scheme for the vsan is set to srcid-destid. • fcdroplatency for the vsan is set to 500 msec. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 28
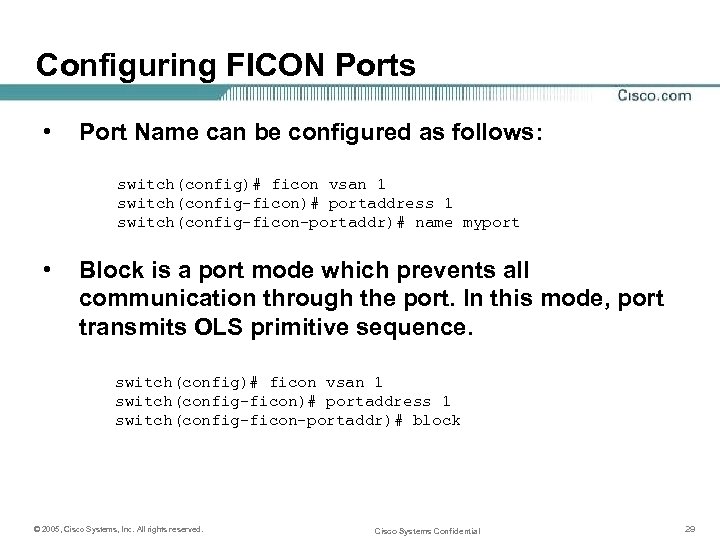 Configuring FICON Ports • Port Name can be configured as follows: switch(config)# ficon vsan 1 switch(config-ficon)# portaddress 1 switch(config-ficon-portaddr)# name myport • Block is a port mode which prevents all communication through the port. In this mode, port transmits OLS primitive sequence. switch(config)# ficon vsan 1 switch(config-ficon)# portaddress 1 switch(config-ficon-portaddr)# block © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 29
Configuring FICON Ports • Port Name can be configured as follows: switch(config)# ficon vsan 1 switch(config-ficon)# portaddress 1 switch(config-ficon-portaddr)# name myport • Block is a port mode which prevents all communication through the port. In this mode, port transmits OLS primitive sequence. switch(config)# ficon vsan 1 switch(config-ficon)# portaddress 1 switch(config-ficon-portaddr)# block © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 29
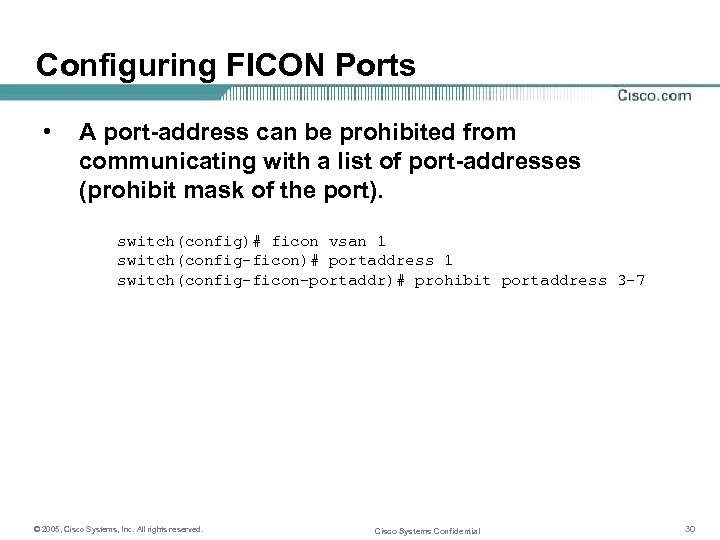 Configuring FICON Ports • A port-address can be prohibited from communicating with a list of port-addresses (prohibit mask of the port). switch(config)# ficon vsan 1 switch(config-ficon)# portaddress 1 switch(config-ficon-portaddr)# prohibit portaddress 3 -7 © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 30
Configuring FICON Ports • A port-address can be prohibited from communicating with a list of port-addresses (prohibit mask of the port). switch(config)# ficon vsan 1 switch(config-ficon)# portaddress 1 switch(config-ficon-portaddr)# prohibit portaddress 3 -7 © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 30
 Configuring Port-Channels for FICON • Port channels need to be assigned a FICON portnumber to be able to come up in FICON VSAN. switch(config)# int port-channel 1 switch(config-if)# ficon portnumber 230 • The following command can be used to find the first unused port-number available for logical interfaces. switch# show ficon first-available port-number Port number 224(0 xe 0) is available © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 31
Configuring Port-Channels for FICON • Port channels need to be assigned a FICON portnumber to be able to come up in FICON VSAN. switch(config)# int port-channel 1 switch(config-if)# ficon portnumber 230 • The following command can be used to find the first unused port-number available for logical interfaces. switch# show ficon first-available port-number Port number 224(0 xe 0) is available © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 31
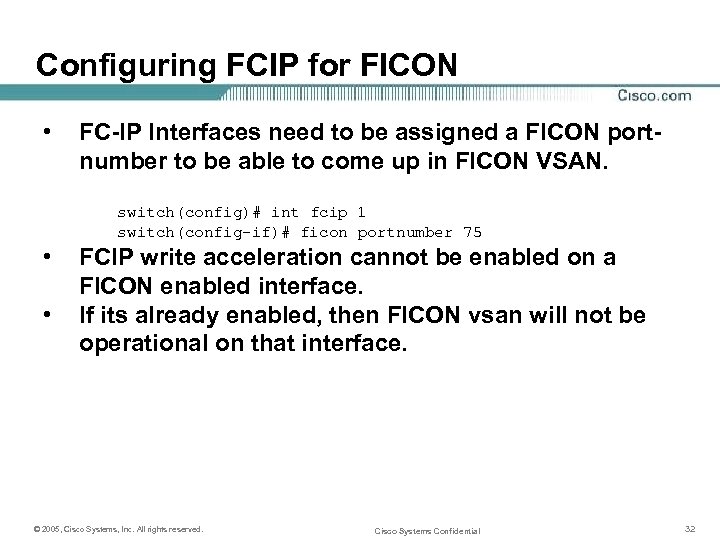 Configuring FCIP for FICON • FC-IP Interfaces need to be assigned a FICON portnumber to be able to come up in FICON VSAN. switch(config)# int fcip 1 switch(config-if)# ficon portnumber 75 • • FCIP write acceleration cannot be enabled on a FICON enabled interface. If its already enabled, then FICON vsan will not be operational on that interface. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 32
Configuring FCIP for FICON • FC-IP Interfaces need to be assigned a FICON portnumber to be able to come up in FICON VSAN. switch(config)# int fcip 1 switch(config-if)# ficon portnumber 75 • • FCIP write acceleration cannot be enabled on a FICON enabled interface. If its already enabled, then FICON vsan will not be operational on that interface. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 32
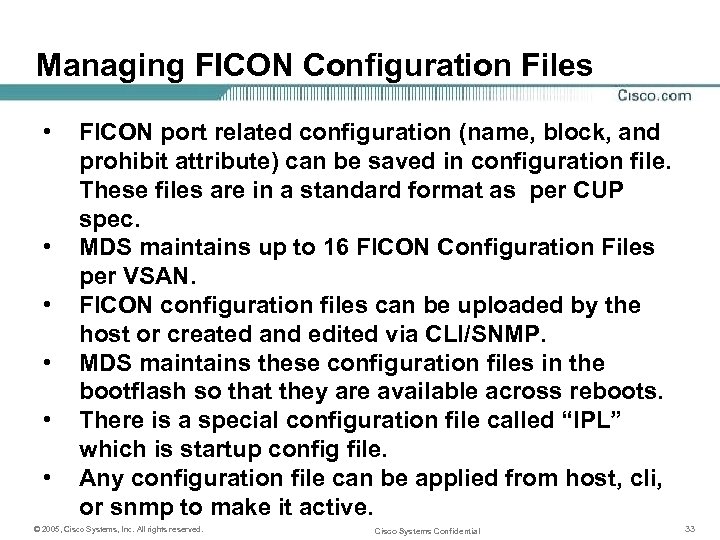 Managing FICON Configuration Files • • • FICON port related configuration (name, block, and prohibit attribute) can be saved in configuration file. These files are in a standard format as per CUP spec. MDS maintains up to 16 FICON Configuration Files per VSAN. FICON configuration files can be uploaded by the host or created and edited via CLI/SNMP. MDS maintains these configuration files in the bootflash so that they are available across reboots. There is a special configuration file called “IPL” which is startup config file. Any configuration file can be applied from host, cli, or snmp to make it active. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 33
Managing FICON Configuration Files • • • FICON port related configuration (name, block, and prohibit attribute) can be saved in configuration file. These files are in a standard format as per CUP spec. MDS maintains up to 16 FICON Configuration Files per VSAN. FICON configuration files can be uploaded by the host or created and edited via CLI/SNMP. MDS maintains these configuration files in the bootflash so that they are available across reboots. There is a special configuration file called “IPL” which is startup config file. Any configuration file can be applied from host, cli, or snmp to make it active. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 33
 Managing FICON Configuration Files • FICON Configuration files are managed through file sub-mode: switch(config)# ficon vsan 1 switch(config-ficon)# file my. File switch(config-ficon-file)# portaddress 1 switch(config-ficon-file-portaddr)# name myport switch(config-ficon-file-portaddr)# prohibit portaddress 3 -7 • CLI/SNMP can “apply” a saved FICON configuration file. This operation causes the configuration in the file to become the running configuration: switch# ficon vsan 1 apply file myfile • Deleting FICON Configuration File: switch(config-ficon)# no file my. File © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 34
Managing FICON Configuration Files • FICON Configuration files are managed through file sub-mode: switch(config)# ficon vsan 1 switch(config-ficon)# file my. File switch(config-ficon-file)# portaddress 1 switch(config-ficon-file-portaddr)# name myport switch(config-ficon-file-portaddr)# prohibit portaddress 3 -7 • CLI/SNMP can “apply” a saved FICON configuration file. This operation causes the configuration in the file to become the running configuration: switch# ficon vsan 1 apply file myfile • Deleting FICON Configuration File: switch(config-ficon)# no file my. File © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 34
 Saving FICON Configuration to Startup • • In MDS switches, running configuration is saved to startup (for next reload) only on issuing “copy running startup” command. However changes to FICON configuration files and global FICON configuration like (snmp/host control) saved immediately to the startup. Other FICON configuration enable/disable, portnumber to port-channel/fcip mapping is saved only when “copy running startup” command is issued There is a mode in FICON called “active=saved” switch(config-ficon)# [no] active equals saved • • If this mode is on, all changes to port configuration are written to IPL file immediately. If this mode is “off”, changes are written only when “copy running startup” command is issued. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 35
Saving FICON Configuration to Startup • • In MDS switches, running configuration is saved to startup (for next reload) only on issuing “copy running startup” command. However changes to FICON configuration files and global FICON configuration like (snmp/host control) saved immediately to the startup. Other FICON configuration enable/disable, portnumber to port-channel/fcip mapping is saved only when “copy running startup” command is issued There is a mode in FICON called “active=saved” switch(config-ficon)# [no] active equals saved • • If this mode is on, all changes to port configuration are written to IPL file immediately. If this mode is “off”, changes are written only when “copy running startup” command is issued. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 35
 Swapping Port Configuration • Port configuration can be swapped using following command. switch# ficon swap portnumber 1 6 • MDS doesn’t allow port swap operation on portchannels and FCIP links. • Swapped configuration is saved when “copy running startup” is issued. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 36
Swapping Port Configuration • Port configuration can be swapped using following command. switch# ficon swap portnumber 1 6 • MDS doesn’t allow port swap operation on portchannels and FCIP links. • Swapped configuration is saved when “copy running startup” is issued. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 36
 Miscellaneous Configuration • Whether host is permitted to perform inband management is controlled through “Host Control” parameter. switch(config-ficon)#[no] host port control • Whether host is permitted to put Director in offline mode (all ports transmitting OLSs) is controlled through “Host Offline Control”. switch(config-ficon)#[no] host control switch offline • Whether SNMP is allowed to change Port Connectivity parameters (block, name, prohibit) is controlled through “SNMP Control”. switch(config-ficon)#[no] snmp port control © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 37
Miscellaneous Configuration • Whether host is permitted to perform inband management is controlled through “Host Control” parameter. switch(config-ficon)#[no] host port control • Whether host is permitted to put Director in offline mode (all ports transmitting OLSs) is controlled through “Host Offline Control”. switch(config-ficon)#[no] host control switch offline • Whether SNMP is allowed to change Port Connectivity parameters (block, name, prohibit) is controlled through “SNMP Control”. switch(config-ficon)#[no] snmp port control © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 37
 Miscellaneous Configuration • EBCDIC code is used for exchanging a number of text fields between host and Director. By default EBCDIC code page is “us-canada”. Users can change this code page as follows: switch(config-ficon)#code-page uk • Device Allegiance allows only one mgmt entity (CLI/SNMP/Host) to configure FICON attributes in Director at any given instance. This allegiance can be reset from cli. switch#ficon vsan 3 reset device-allegiance • “User Alert Mode”, when set, requires director to prompt the user for any configuration change. It can only be turned on by the host. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 38
Miscellaneous Configuration • EBCDIC code is used for exchanging a number of text fields between host and Director. By default EBCDIC code page is “us-canada”. Users can change this code page as follows: switch(config-ficon)#code-page uk • Device Allegiance allows only one mgmt entity (CLI/SNMP/Host) to configure FICON attributes in Director at any given instance. This allegiance can be reset from cli. switch#ficon vsan 3 reset device-allegiance • “User Alert Mode”, when set, requires director to prompt the user for any configuration change. It can only be turned on by the host. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 38
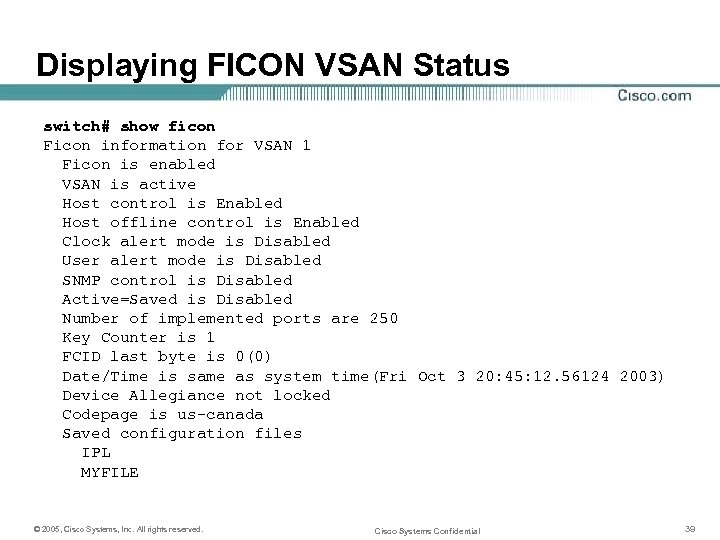 Displaying FICON VSAN Status switch# show ficon Ficon information for VSAN 1 Ficon is enabled VSAN is active Host control is Enabled Host offline control is Enabled Clock alert mode is Disabled User alert mode is Disabled SNMP control is Disabled Active=Saved is Disabled Number of implemented ports are 250 Key Counter is 1 FCID last byte is 0(0) Date/Time is same as system time(Fri Oct 3 20: 45: 12. 56124 2003) Device Allegiance not locked Codepage is us-canada Saved configuration files IPL MYFILE © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 39
Displaying FICON VSAN Status switch# show ficon Ficon information for VSAN 1 Ficon is enabled VSAN is active Host control is Enabled Host offline control is Enabled Clock alert mode is Disabled User alert mode is Disabled SNMP control is Disabled Active=Saved is Disabled Number of implemented ports are 250 Key Counter is 1 FCID last byte is 0(0) Date/Time is same as system time(Fri Oct 3 20: 45: 12. 56124 2003) Device Allegiance not locked Codepage is us-canada Saved configuration files IPL MYFILE © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 39
 FICON Per VSAN Clock • • Host programming can control the clock on the Director. MDS VSANs provide Virtual Directors and hence clock can be set by host programming for each VSAN independently. This is maintained as a difference w. r. t the MDS global system clock time. It is possible for an user to clear the per-vsan clock on a vsan basis. [ It defaults to global system clock. ] We display host clock in syslog and accounting log. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 40
FICON Per VSAN Clock • • Host programming can control the clock on the Director. MDS VSANs provide Virtual Directors and hence clock can be set by host programming for each VSAN independently. This is maintained as a difference w. r. t the MDS global system clock time. It is possible for an user to clear the per-vsan clock on a vsan basis. [ It defaults to global system clock. ] We display host clock in syslog and accounting log. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 40
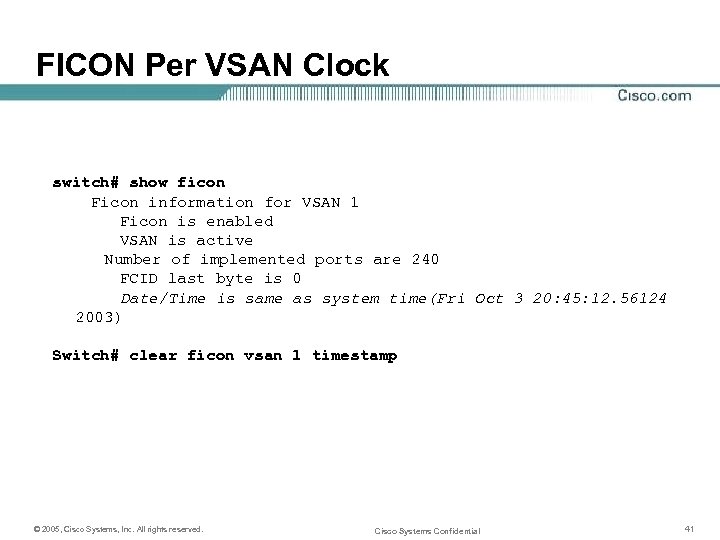 FICON Per VSAN Clock switch# show ficon Ficon information for VSAN 1 Ficon is enabled VSAN is active Number of implemented ports are 240 FCID last byte is 0 Date/Time is same as system time(Fri Oct 3 20: 45: 12. 56124 2003) Switch# clear ficon vsan 1 timestamp © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 41
FICON Per VSAN Clock switch# show ficon Ficon information for VSAN 1 Ficon is enabled VSAN is active Number of implemented ports are 240 FCID last byte is 0 Date/Time is same as system time(Fri Oct 3 20: 45: 12. 56124 2003) Switch# clear ficon vsan 1 timestamp © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 41
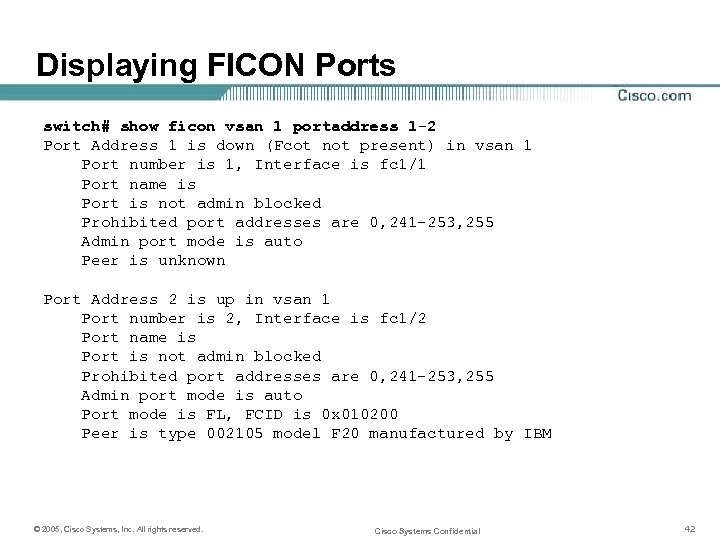 Displaying FICON Ports switch# show ficon vsan 1 portaddress 1 -2 Port Address 1 is down (Fcot not present) in vsan 1 Port number is 1, Interface is fc 1/1 Port name is Port is not admin blocked Prohibited port addresses are 0, 241 -253, 255 Admin port mode is auto Peer is unknown Port Address 2 is up in vsan 1 Port number is 2, Interface is fc 1/2 Port name is Port is not admin blocked Prohibited port addresses are 0, 241 -253, 255 Admin port mode is auto Port mode is FL, FCID is 0 x 010200 Peer is type 002105 model F 20 manufactured by IBM © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 42
Displaying FICON Ports switch# show ficon vsan 1 portaddress 1 -2 Port Address 1 is down (Fcot not present) in vsan 1 Port number is 1, Interface is fc 1/1 Port name is Port is not admin blocked Prohibited port addresses are 0, 241 -253, 255 Admin port mode is auto Peer is unknown Port Address 2 is up in vsan 1 Port number is 2, Interface is fc 1/2 Port name is Port is not admin blocked Prohibited port addresses are 0, 241 -253, 255 Admin port mode is auto Port mode is FL, FCID is 0 x 010200 Peer is type 002105 model F 20 manufactured by IBM © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 42
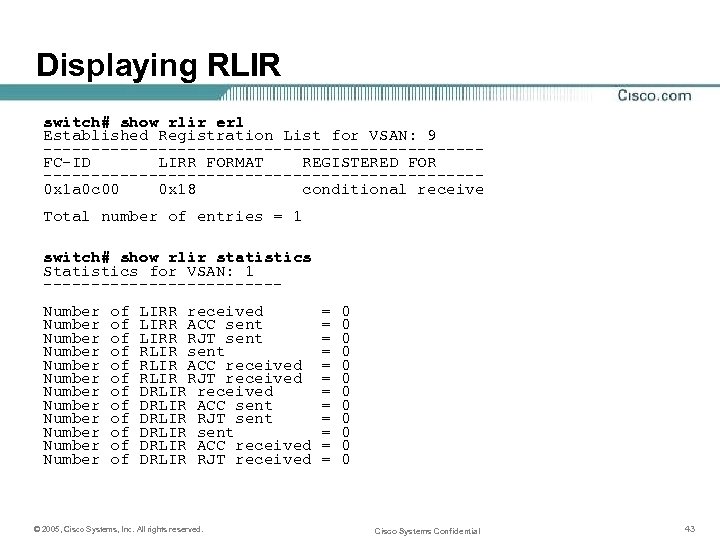 Displaying RLIR switch# show rlir erl Established Registration List for VSAN: 9 -----------------------FC-ID LIRR FORMAT REGISTERED FOR -----------------------0 x 1 a 0 c 00 0 x 18 conditional receive Total number of entries = 1 switch# show rlir statistics Statistics for VSAN: 1 ------------Number Number Number of of of LIRR received LIRR ACC sent LIRR RJT sent RLIR ACC received RLIR RJT received DRLIR ACC sent DRLIR RJT sent DRLIR ACC received DRLIR RJT received © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. = = = 0 0 0 Cisco Systems Confidential 43
Displaying RLIR switch# show rlir erl Established Registration List for VSAN: 9 -----------------------FC-ID LIRR FORMAT REGISTERED FOR -----------------------0 x 1 a 0 c 00 0 x 18 conditional receive Total number of entries = 1 switch# show rlir statistics Statistics for VSAN: 1 ------------Number Number Number of of of LIRR received LIRR ACC sent LIRR RJT sent RLIR ACC received RLIR RJT received DRLIR ACC sent DRLIR RJT sent DRLIR ACC received DRLIR RJT received © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. = = = 0 0 0 Cisco Systems Confidential 43
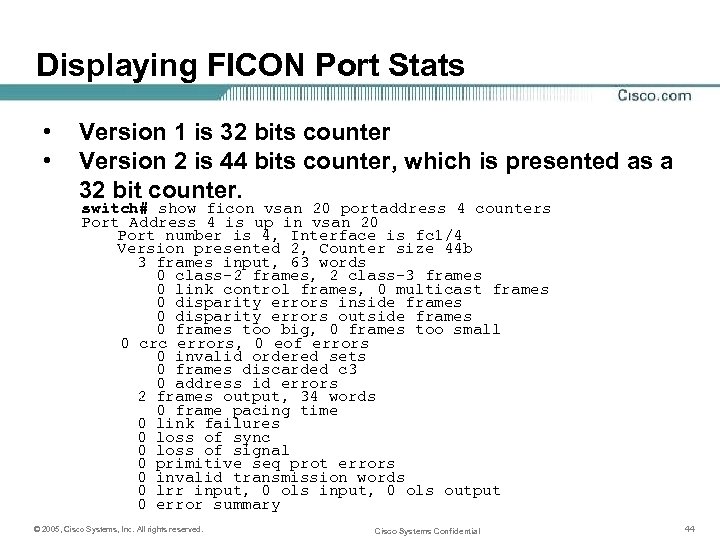 Displaying FICON Port Stats • • Version 1 is 32 bits counter Version 2 is 44 bits counter, which is presented as a 32 bit counter. switch# show ficon vsan 20 portaddress 4 counters Port Address 4 is up in vsan 20 Port number is 4, Interface is fc 1/4 Version presented 2, Counter size 44 b 3 frames input, 63 words 0 class-2 frames, 2 class-3 frames 0 link control frames, 0 multicast frames 0 disparity errors inside frames 0 disparity errors outside frames 0 frames too big, 0 frames too small 0 crc errors, 0 eof errors 0 invalid ordered sets 0 frames discarded c 3 0 address id errors 2 frames output, 34 words 0 frame pacing time 0 link failures 0 loss of sync 0 loss of signal 0 primitive seq prot errors 0 invalid transmission words 0 lrr input, 0 ols output 0 error summary © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 44
Displaying FICON Port Stats • • Version 1 is 32 bits counter Version 2 is 44 bits counter, which is presented as a 32 bit counter. switch# show ficon vsan 20 portaddress 4 counters Port Address 4 is up in vsan 20 Port number is 4, Interface is fc 1/4 Version presented 2, Counter size 44 b 3 frames input, 63 words 0 class-2 frames, 2 class-3 frames 0 link control frames, 0 multicast frames 0 disparity errors inside frames 0 disparity errors outside frames 0 frames too big, 0 frames too small 0 crc errors, 0 eof errors 0 invalid ordered sets 0 frames discarded c 3 0 address id errors 2 frames output, 34 words 0 frame pacing time 0 link failures 0 loss of sync 0 loss of signal 0 primitive seq prot errors 0 invalid transmission words 0 lrr input, 0 ols output 0 error summary © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 44
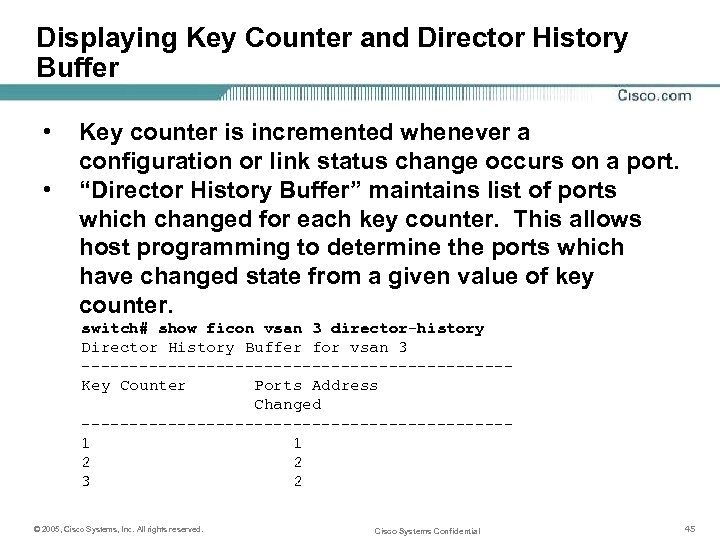 Displaying Key Counter and Director History Buffer • • Key counter is incremented whenever a configuration or link status change occurs on a port. “Director History Buffer” maintains list of ports which changed for each key counter. This allows host programming to determine the ports which have changed state from a given value of key counter. switch# show ficon vsan 3 director-history Director History Buffer for vsan 3 ----------------------Key Counter Ports Address Changed ----------------------1 1 2 2 3 2 © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 45
Displaying Key Counter and Director History Buffer • • Key counter is incremented whenever a configuration or link status change occurs on a port. “Director History Buffer” maintains list of ports which changed for each key counter. This allows host programming to determine the ports which have changed state from a given value of key counter. switch# show ficon vsan 3 director-history Director History Buffer for vsan 3 ----------------------Key Counter Ports Address Changed ----------------------1 1 2 2 3 2 © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 45
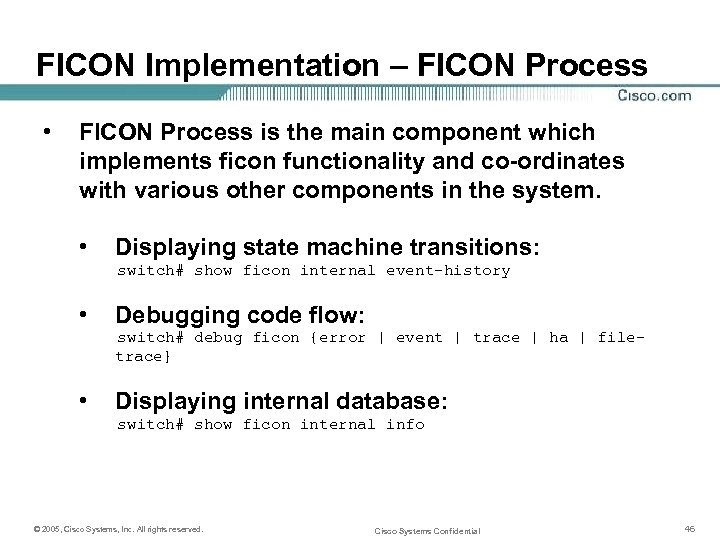 FICON Implementation – FICON Process • FICON Process is the main component which implements ficon functionality and co-ordinates with various other components in the system. • Displaying state machine transitions: switch# show ficon internal event-history • Debugging code flow: switch# debug ficon {error | event | trace | ha | filetrace} • Displaying internal database: switch# show ficon internal info © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 46
FICON Implementation – FICON Process • FICON Process is the main component which implements ficon functionality and co-ordinates with various other components in the system. • Displaying state machine transitions: switch# show ficon internal event-history • Debugging code flow: switch# debug ficon {error | event | trace | ha | filetrace} • Displaying internal database: switch# show ficon internal info © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 46
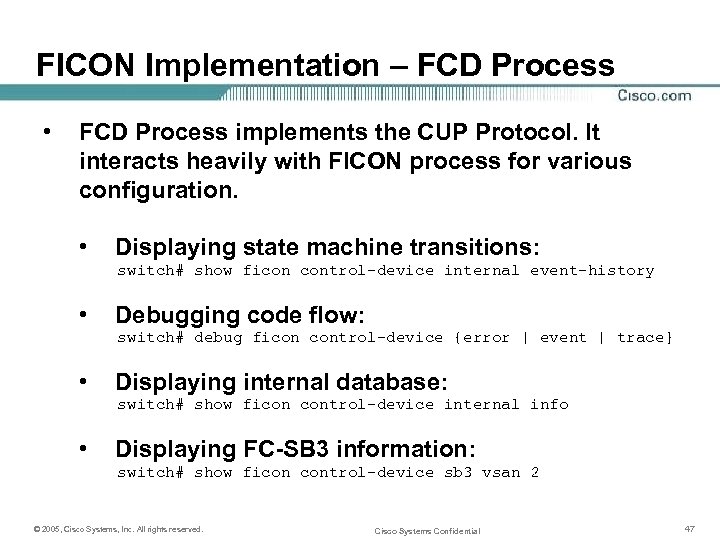 FICON Implementation – FCD Process • FCD Process implements the CUP Protocol. It interacts heavily with FICON process for various configuration. • Displaying state machine transitions: switch# show ficon control-device internal event-history • Debugging code flow: switch# debug ficon control-device {error | event | trace} • Displaying internal database: switch# show ficon control-device internal info • Displaying FC-SB 3 information: switch# show ficon control-device sb 3 vsan 2 © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 47
FICON Implementation – FCD Process • FCD Process implements the CUP Protocol. It interacts heavily with FICON process for various configuration. • Displaying state machine transitions: switch# show ficon control-device internal event-history • Debugging code flow: switch# debug ficon control-device {error | event | trace} • Displaying internal database: switch# show ficon control-device internal info • Displaying FC-SB 3 information: switch# show ficon control-device sb 3 vsan 2 © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 47
 FICON Implementation – FICONSTAT Process • FICONSTAT Process implements Statistics Collection Protocol. It interacts with all the linecards to obtain the statistics information to be presented to FICON process. • Displaying state machine transitions: switch# show ficon stat internal event-history • Debugging code flow: switch# debug ficon stat {error | event | trace } • Displaying internal database: switch# show ficon stat internal info © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 48
FICON Implementation – FICONSTAT Process • FICONSTAT Process implements Statistics Collection Protocol. It interacts with all the linecards to obtain the statistics information to be presented to FICON process. • Displaying state machine transitions: switch# show ficon stat internal event-history • Debugging code flow: switch# debug ficon stat {error | event | trace } • Displaying internal database: switch# show ficon stat internal info © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 48
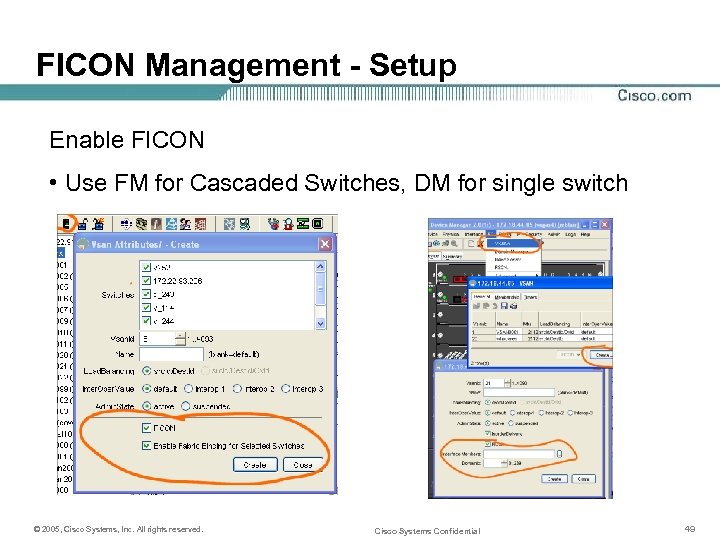 FICON Management - Setup Enable FICON • Use FM for Cascaded Switches, DM for single switch © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 49
FICON Management - Setup Enable FICON • Use FM for Cascaded Switches, DM for single switch © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 49
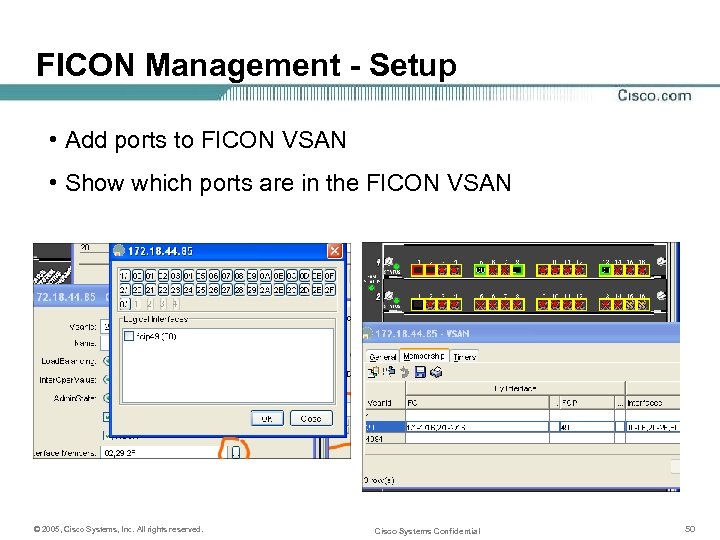 FICON Management - Setup • Add ports to FICON VSAN • Show which ports are in the FICON VSAN © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 50
FICON Management - Setup • Add ports to FICON VSAN • Show which ports are in the FICON VSAN © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 50
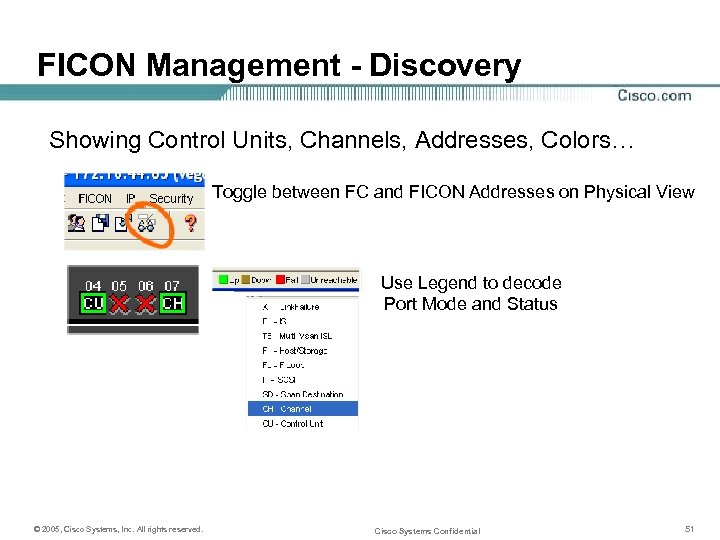 FICON Management - Discovery Showing Control Units, Channels, Addresses, Colors… Toggle between FC and FICON Addresses on Physical View Use Legend to decode Port Mode and Status © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 51
FICON Management - Discovery Showing Control Units, Channels, Addresses, Colors… Toggle between FC and FICON Addresses on Physical View Use Legend to decode Port Mode and Status © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 51
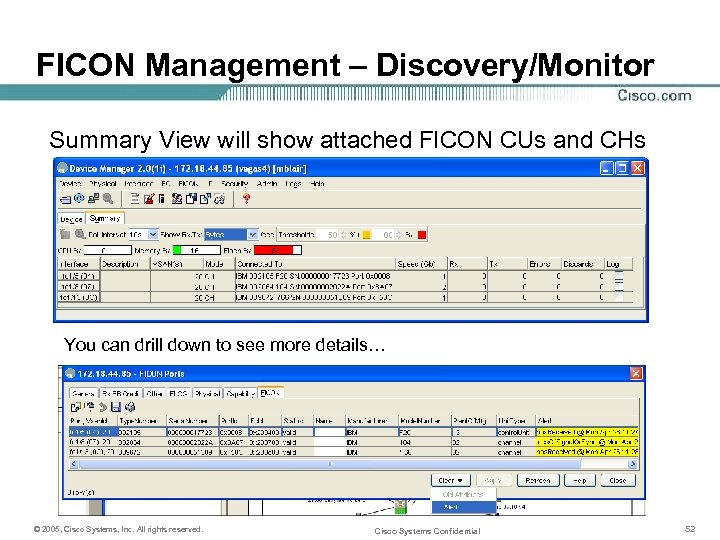 FICON Management – Discovery/Monitor Summary View will show attached FICON CUs and CHs You can drill down to see more details… © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 52
FICON Management – Discovery/Monitor Summary View will show attached FICON CUs and CHs You can drill down to see more details… © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 52
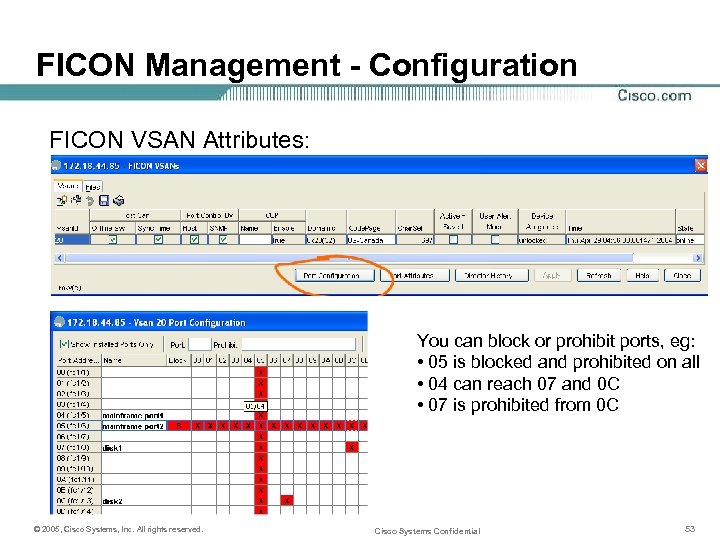 FICON Management - Configuration FICON VSAN Attributes: You can block or prohibit ports, eg: • 05 is blocked and prohibited on all • 04 can reach 07 and 0 C • 07 is prohibited from 0 C © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 53
FICON Management - Configuration FICON VSAN Attributes: You can block or prohibit ports, eg: • 05 is blocked and prohibited on all • 04 can reach 07 and 0 C • 07 is prohibited from 0 C © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 53
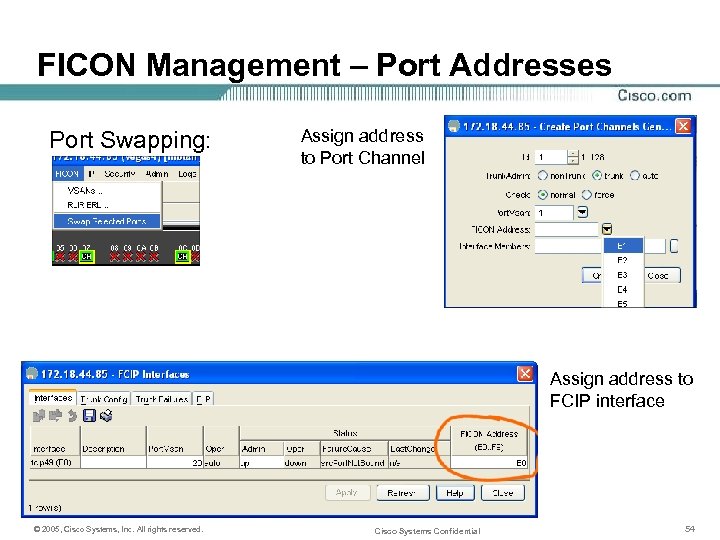 FICON Management – Port Addresses Port Swapping: Assign address to Port Channel Assign address to FCIP interface © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 54
FICON Management – Port Addresses Port Swapping: Assign address to Port Channel Assign address to FCIP interface © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 54
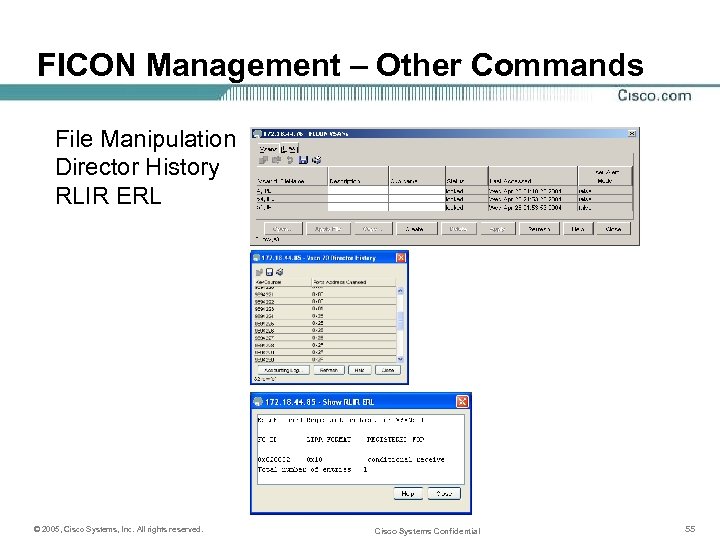 FICON Management – Other Commands File Manipulation Director History RLIR ERL © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 55
FICON Management – Other Commands File Manipulation Director History RLIR ERL © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 55
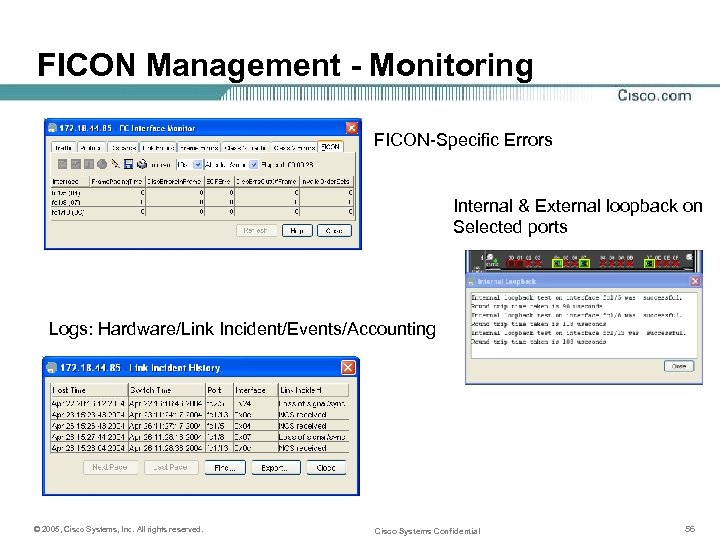 FICON Management - Monitoring FICON-Specific Errors Internal & External loopback on Selected ports Logs: Hardware/Link Incident/Events/Accounting © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 56
FICON Management - Monitoring FICON-Specific Errors Internal & External loopback on Selected ports Logs: Hardware/Link Incident/Events/Accounting © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 56
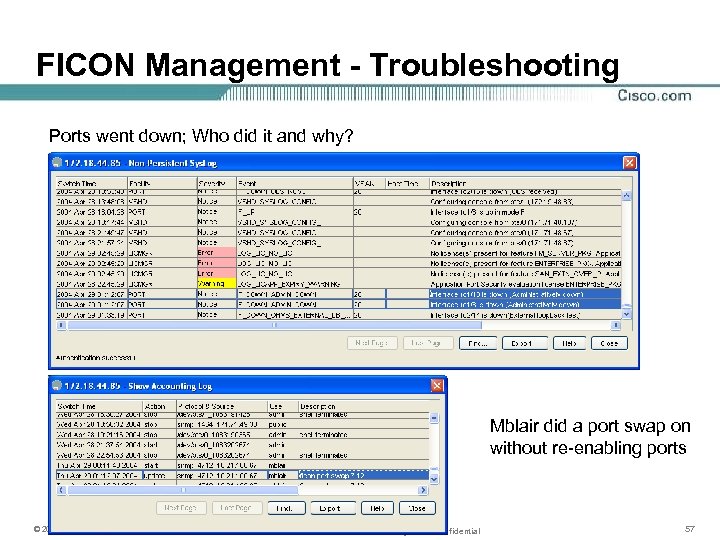 FICON Management - Troubleshooting Ports went down; Who did it and why? Mblair did a port swap on without re-enabling ports © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 57
FICON Management - Troubleshooting Ports went down; Who did it and why? Mblair did a port swap on without re-enabling ports © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 57
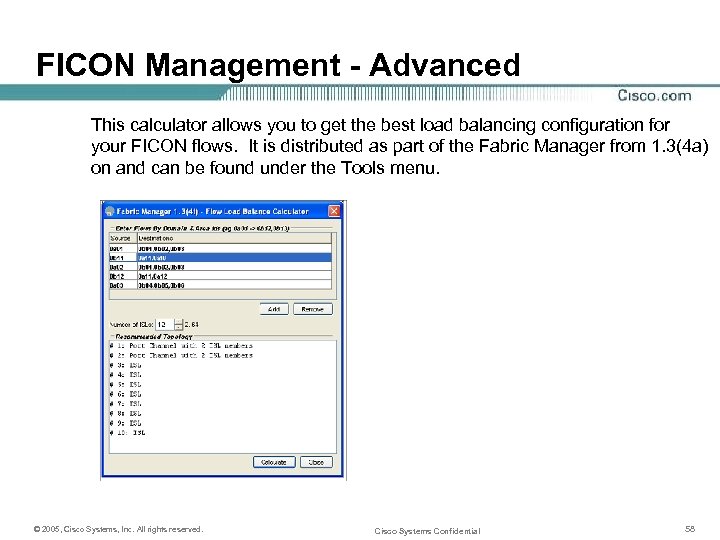 FICON Management - Advanced This calculator allows you to get the best load balancing configuration for your FICON flows. It is distributed as part of the Fabric Manager from 1. 3(4 a) on and can be found under the Tools menu. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 58
FICON Management - Advanced This calculator allows you to get the best load balancing configuration for your FICON flows. It is distributed as part of the Fabric Manager from 1. 3(4 a) on and can be found under the Tools menu. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 58
 FICON Management - Help All windows have context-sensitive online help: © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 59
FICON Management - Help All windows have context-sensitive online help: © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 59
 Supplemental FICON Slides © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 60
Supplemental FICON Slides © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 60
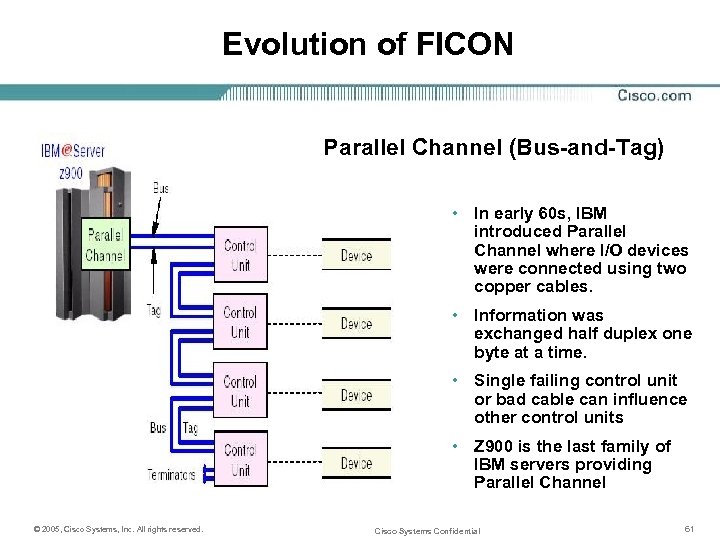 Evolution of FICON Parallel Channel (Bus-and-Tag) • In early 60 s, IBM introduced Parallel Channel where I/O devices were connected using two copper cables. • Information was exchanged half duplex one byte at a time. • Single failing control unit or bad cable can influence other control units • Z 900 is the last family of IBM servers providing Parallel Channel © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 61
Evolution of FICON Parallel Channel (Bus-and-Tag) • In early 60 s, IBM introduced Parallel Channel where I/O devices were connected using two copper cables. • Information was exchanged half duplex one byte at a time. • Single failing control unit or bad cable can influence other control units • Z 900 is the last family of IBM servers providing Parallel Channel © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 61
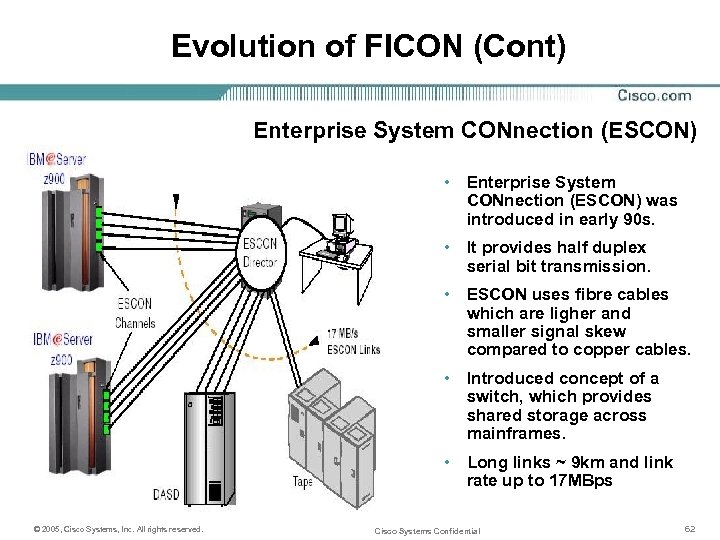 Evolution of FICON (Cont) Enterprise System CONnection (ESCON) • Enterprise System CONnection (ESCON) was introduced in early 90 s. • It provides half duplex serial bit transmission. • ESCON uses fibre cables which are ligher and smaller signal skew compared to copper cables. • Introduced concept of a switch, which provides shared storage across mainframes. • Long links ~ 9 km and link rate up to 17 MBps © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 62
Evolution of FICON (Cont) Enterprise System CONnection (ESCON) • Enterprise System CONnection (ESCON) was introduced in early 90 s. • It provides half duplex serial bit transmission. • ESCON uses fibre cables which are ligher and smaller signal skew compared to copper cables. • Introduced concept of a switch, which provides shared storage across mainframes. • Long links ~ 9 km and link rate up to 17 MBps © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 62
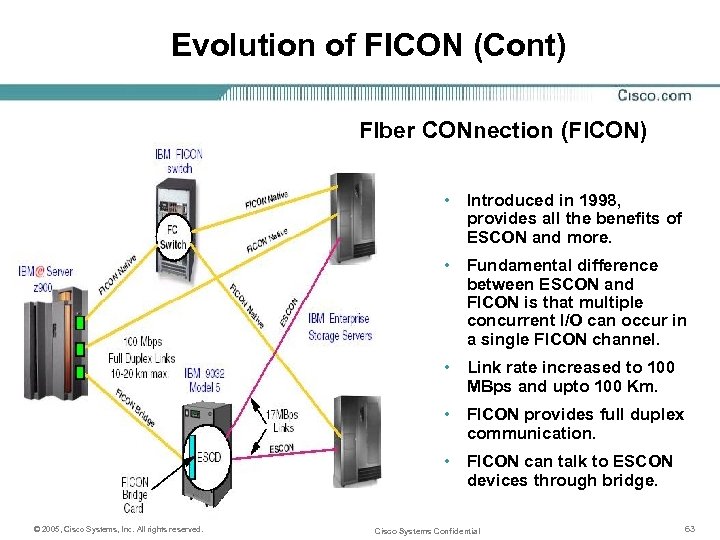 Evolution of FICON (Cont) FIber CONnection (FICON) • Introduced in 1998, provides all the benefits of ESCON and more. • Fundamental difference between ESCON and FICON is that multiple concurrent I/O can occur in a single FICON channel. • Link rate increased to 100 MBps and upto 100 Km. • FICON provides full duplex communication. • FICON can talk to ESCON devices through bridge. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 63
Evolution of FICON (Cont) FIber CONnection (FICON) • Introduced in 1998, provides all the benefits of ESCON and more. • Fundamental difference between ESCON and FICON is that multiple concurrent I/O can occur in a single FICON channel. • Link rate increased to 100 MBps and upto 100 Km. • FICON provides full duplex communication. • FICON can talk to ESCON devices through bridge. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 63
 Why FICON? • S/390 environments have strained limits of ESCON Addressing constraints Channel constraints Performance bottlenecks Distance limitations These constraints are inhibiting customers’ business and impacting their bottom line… • FICON provides relief from ESCON limitations More Addresses, Channels, Bandwidth and Distance Means More Flexibility Co-Existence with ESCON for seamless migration Enables business to grow, consolidate workloads and complete Mergers/Acquisitions Applications have stressed and outgrown the capabilities of ESCON © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 64
Why FICON? • S/390 environments have strained limits of ESCON Addressing constraints Channel constraints Performance bottlenecks Distance limitations These constraints are inhibiting customers’ business and impacting their bottom line… • FICON provides relief from ESCON limitations More Addresses, Channels, Bandwidth and Distance Means More Flexibility Co-Existence with ESCON for seamless migration Enables business to grow, consolidate workloads and complete Mergers/Acquisitions Applications have stressed and outgrown the capabilities of ESCON © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 64
 Mainframes: G 5 / G 6 • FICON point to point and bridge, NO cascade support • 9672 FICON Channel Card SC connector, 1 GB • G 5 First generation Channel to support FICON 24 Max CHIPIDs per CEC, 24 9672 FICON Channel Cards 32 Control Units per links per Channel • G 6 36 Max CHIPIDs per CEC, 36 9672 FICON Channel Cards 64 Control Units per links per Channel © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 65
Mainframes: G 5 / G 6 • FICON point to point and bridge, NO cascade support • 9672 FICON Channel Card SC connector, 1 GB • G 5 First generation Channel to support FICON 24 Max CHIPIDs per CEC, 24 9672 FICON Channel Cards 32 Control Units per links per Channel • G 6 36 Max CHIPIDs per CEC, 36 9672 FICON Channel Cards 64 Control Units per links per Channel © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 65
 Mainframes: z. Series • FICON Point to Point, Bridge, and Cascade support • Channel Card (2315 and 2318) Two Channels per Card, SC connector, 1 GB • FICON Express Channel Card (2319 and 2320) Two Channels per Card, LC connector, 1 and 2 GB • z 800 32 Max CHIPIDs per CEC, 16 FICON Channel Cards • z 900 96 Max CHIPIDs per CEC, 48 FICON Channel Cards 128 Control Units per links per Channel • z 990 128 Max CHIPIDs per CEC, 64 FICON Channel Cards © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential z 900 66
Mainframes: z. Series • FICON Point to Point, Bridge, and Cascade support • Channel Card (2315 and 2318) Two Channels per Card, SC connector, 1 GB • FICON Express Channel Card (2319 and 2320) Two Channels per Card, LC connector, 1 and 2 GB • z 800 32 Max CHIPIDs per CEC, 16 FICON Channel Cards • z 900 96 Max CHIPIDs per CEC, 48 FICON Channel Cards 128 Control Units per links per Channel • z 990 128 Max CHIPIDs per CEC, 64 FICON Channel Cards © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential z 900 66
 FICON Control Units • IBM Tape - 3494, 3590, VTS Disk - 2105 • EMC Disk - Symmetrix, DMX • HDS Disk - 9910, 9960 • SUN/Storage. Tek Tape - T 9840 B, T 9840 C, T 9940 B Disk - SVA © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 67
FICON Control Units • IBM Tape - 3494, 3590, VTS Disk - 2105 • EMC Disk - Symmetrix, DMX • HDS Disk - 9910, 9960 • SUN/Storage. Tek Tape - T 9840 B, T 9840 C, T 9940 B Disk - SVA © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 67
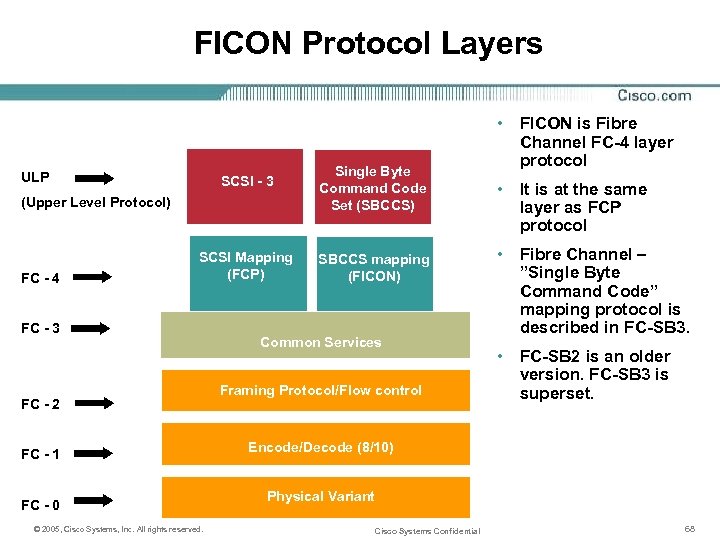 FICON Protocol Layers SCSI - 3 Single Byte Command Code Set (SBCCS) SCSI Mapping (FCP) SBCCS mapping (FICON) ULP (Upper Level Protocol) FC - 4 FC - 3 FC - 2 FC - 1 FC - 0 © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Common Services Framing Protocol/Flow control • FICON is Fibre Channel FC-4 layer protocol • It is at the same layer as FCP protocol • Fibre Channel – ”Single Byte Command Code” mapping protocol is described in FC-SB 3. • FC-SB 2 is an older version. FC-SB 3 is superset. Encode/Decode (8/10) Physical Variant Cisco Systems Confidential 68
FICON Protocol Layers SCSI - 3 Single Byte Command Code Set (SBCCS) SCSI Mapping (FCP) SBCCS mapping (FICON) ULP (Upper Level Protocol) FC - 4 FC - 3 FC - 2 FC - 1 FC - 0 © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Common Services Framing Protocol/Flow control • FICON is Fibre Channel FC-4 layer protocol • It is at the same layer as FCP protocol • Fibre Channel – ”Single Byte Command Code” mapping protocol is described in FC-SB 3. • FC-SB 2 is an older version. FC-SB 3 is superset. Encode/Decode (8/10) Physical Variant Cisco Systems Confidential 68
 FICON vs FCP • A “Channel” is an entity typically mapped to an N-port in a host computer which performs access to I/O devices. • A “Channel” is similar to a SCSI initiator. • A “Control Unit” is the interface to I/O devices such as printer, disks etc. • A “Control Unit” is similar to a SCSI target. • In a single Fibre Channel network, FCP and FICON traffic is independent of each other. • Traditionally Zoning is used to isolate FICON and FCP devices. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 69
FICON vs FCP • A “Channel” is an entity typically mapped to an N-port in a host computer which performs access to I/O devices. • A “Channel” is similar to a SCSI initiator. • A “Control Unit” is the interface to I/O devices such as printer, disks etc. • A “Control Unit” is similar to a SCSI target. • In a single Fibre Channel network, FCP and FICON traffic is independent of each other. • Traditionally Zoning is used to isolate FICON and FCP devices. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 69
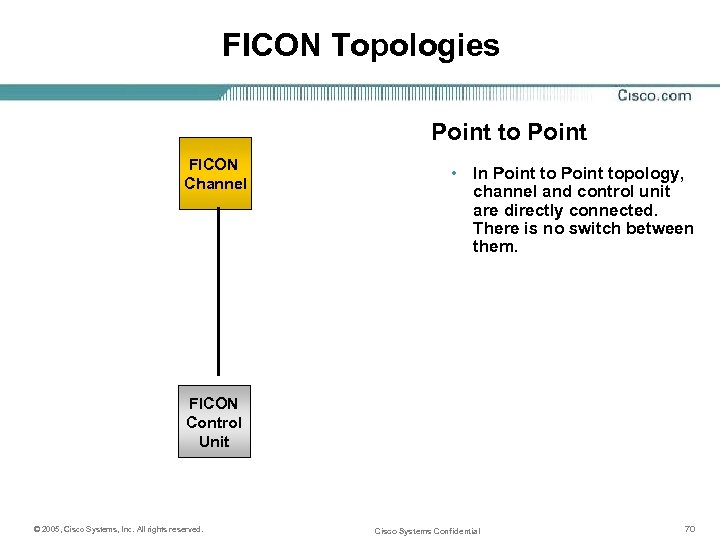 FICON Topologies Point to Point FICON Channel • In Point topology, channel and control unit are directly connected. There is no switch between them. FICON Control Unit © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 70
FICON Topologies Point to Point FICON Channel • In Point topology, channel and control unit are directly connected. There is no switch between them. FICON Control Unit © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 70
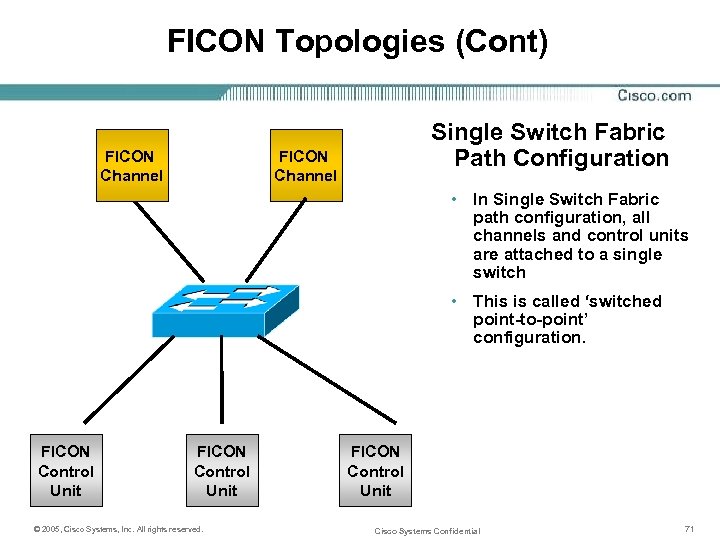 FICON Topologies (Cont) FICON Channel Single Switch Fabric Path Configuration FICON Channel • In Single Switch Fabric path configuration, all channels and control units are attached to a single switch • This is called ‘switched point-to-point’ configuration. FICON Control Unit © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FICON Control Unit Cisco Systems Confidential 71
FICON Topologies (Cont) FICON Channel Single Switch Fabric Path Configuration FICON Channel • In Single Switch Fabric path configuration, all channels and control units are attached to a single switch • This is called ‘switched point-to-point’ configuration. FICON Control Unit © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FICON Control Unit Cisco Systems Confidential 71
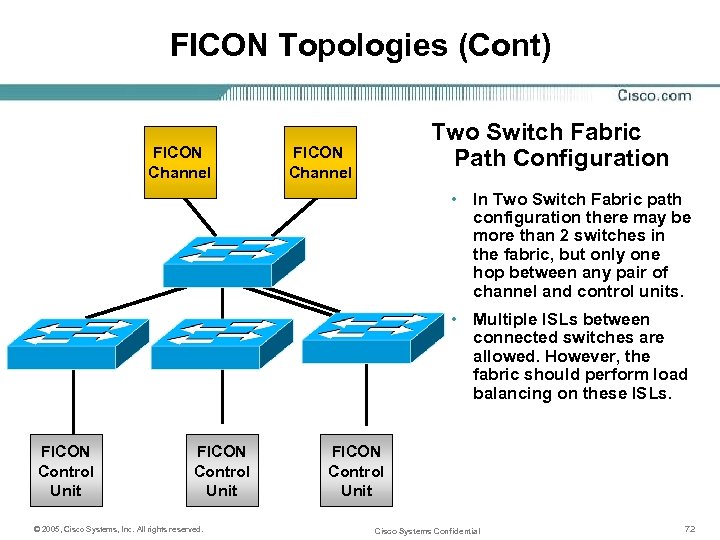 FICON Topologies (Cont) FICON Channel Two Switch Fabric Path Configuration FICON Channel • In Two Switch Fabric path configuration there may be more than 2 switches in the fabric, but only one hop between any pair of channel and control units. • Multiple ISLs between connected switches are allowed. However, the fabric should perform load balancing on these ISLs. FICON Control Unit © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FICON Control Unit Cisco Systems Confidential 72
FICON Topologies (Cont) FICON Channel Two Switch Fabric Path Configuration FICON Channel • In Two Switch Fabric path configuration there may be more than 2 switches in the fabric, but only one hop between any pair of channel and control units. • Multiple ISLs between connected switches are allowed. However, the fabric should perform load balancing on these ISLs. FICON Control Unit © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FICON Control Unit Cisco Systems Confidential 72
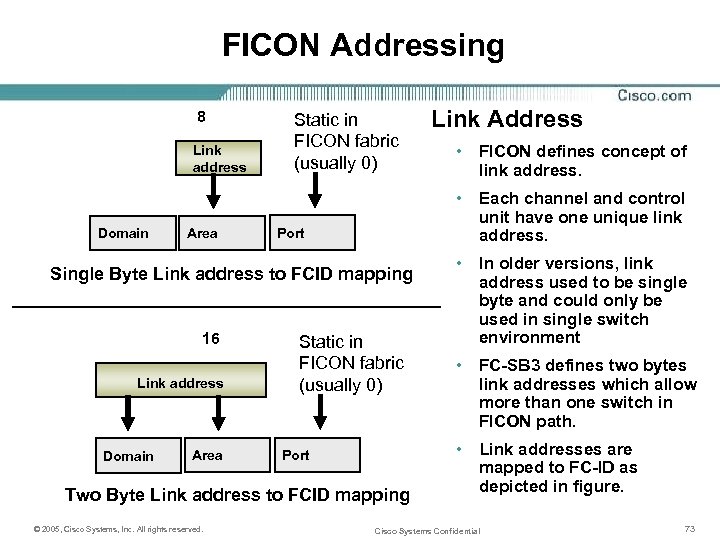 FICON Addressing 8 Link address Domain Area Static in FICON fabric (usually 0) Link address Domain Area Port Static in FICON fabric (usually 0) Port Two Byte Link address to FCID mapping © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. • FICON defines concept of link address. • Each channel and control unit have one unique link address. Single Byte Link address to FCID mapping 16 Link Address • In older versions, link address used to be single byte and could only be used in single switch environment • FC-SB 3 defines two bytes link addresses which allow more than one switch in FICON path. • Link addresses are mapped to FC-ID as depicted in figure. Cisco Systems Confidential 73
FICON Addressing 8 Link address Domain Area Static in FICON fabric (usually 0) Link address Domain Area Port Static in FICON fabric (usually 0) Port Two Byte Link address to FCID mapping © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. • FICON defines concept of link address. • Each channel and control unit have one unique link address. Single Byte Link address to FCID mapping 16 Link Address • In older versions, link address used to be single byte and could only be used in single switch environment • FC-SB 3 defines two bytes link addresses which allow more than one switch in FICON path. • Link addresses are mapped to FC-ID as depicted in figure. Cisco Systems Confidential 73
 Definitions - Port Number • Port number is a unique 8 bit value that identifies a physical port on the FICON Director. • There associated terms called “Implemented Ports” which refers to number of ports Director can support and “Installed Ports” which refers to number of ports currently installed in the switch. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 74
Definitions - Port Number • Port number is a unique 8 bit value that identifies a physical port on the FICON Director. • There associated terms called “Implemented Ports” which refers to number of ports Director can support and “Installed Ports” which refers to number of ports currently installed in the switch. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 74
 Definitions - Port Swap • Port Swap feature which allows administrators to swap configuration of two ports. • This is useful in the event port is down/offline and administrator wants to continue operation on some other spare port. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 75
Definitions - Port Swap • Port Swap feature which allows administrators to swap configuration of two ports. • This is useful in the event port is down/offline and administrator wants to continue operation on some other spare port. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 75
 Definitions - Port Address • Port address is a unique 8 bit value which indirectly refers to the port. • Initially Port Address is same as Port Number. During a port swap command, the Port Address is exchanged, but the Port Numbers remain unchanged. • Thus all FICON configuration is performed on “Port Address” so that swap operation still retains the config on the new port. Port Address is used in figuring out FC-ID associated with the port. • © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 76
Definitions - Port Address • Port address is a unique 8 bit value which indirectly refers to the port. • Initially Port Address is same as Port Number. During a port swap command, the Port Address is exchanged, but the Port Numbers remain unchanged. • Thus all FICON configuration is performed on “Port Address” so that swap operation still retains the config on the new port. Port Address is used in figuring out FC-ID associated with the port. • © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 76
 FICON Inband Management: Control Unit Port (CUP) • FICON Inband Management allows FICON hosts to control various attributes in the FICON Director. • These attributes include port connectivity parameters like block and prohibit, statistics gathering etc. • This is implemented as a special control device called “Ficon Control Device” or FCD [historically also called “Control Unit Port” or CUP] implemented in the Director. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 77
FICON Inband Management: Control Unit Port (CUP) • FICON Inband Management allows FICON hosts to control various attributes in the FICON Director. • These attributes include port connectivity parameters like block and prohibit, statistics gathering etc. • This is implemented as a special control device called “Ficon Control Device” or FCD [historically also called “Control Unit Port” or CUP] implemented in the Director. © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 77
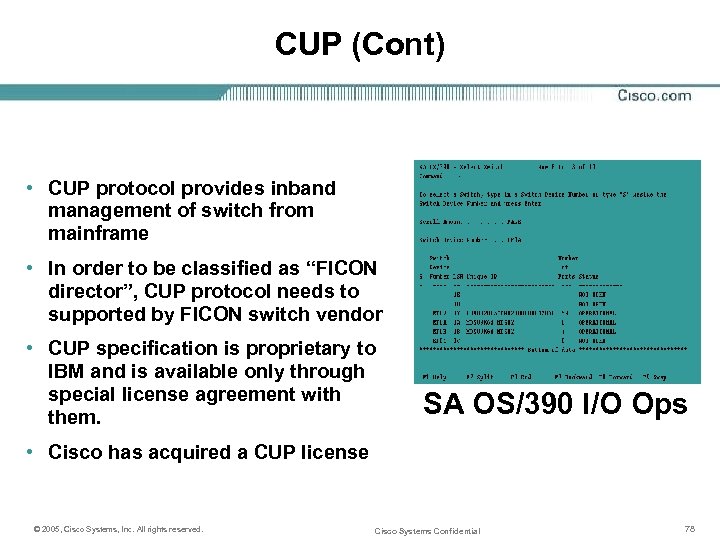 CUP (Cont) • CUP protocol provides inband management of switch from mainframe • In order to be classified as “FICON director”, CUP protocol needs to supported by FICON switch vendor • CUP specification is proprietary to IBM and is available only through special license agreement with them. SA OS/390 I/O Ops • Cisco has acquired a CUP license © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 78
CUP (Cont) • CUP protocol provides inband management of switch from mainframe • In order to be classified as “FICON director”, CUP protocol needs to supported by FICON switch vendor • CUP specification is proprietary to IBM and is available only through special license agreement with them. SA OS/390 I/O Ops • Cisco has acquired a CUP license © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Systems Confidential 78


