33978f97dfe9b2649400e5d8f1d91c74.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 CIS 234: File Input & Output Dr. Ralph D. Westfall May, 2007
CIS 234: File Input & Output Dr. Ralph D. Westfall May, 2007
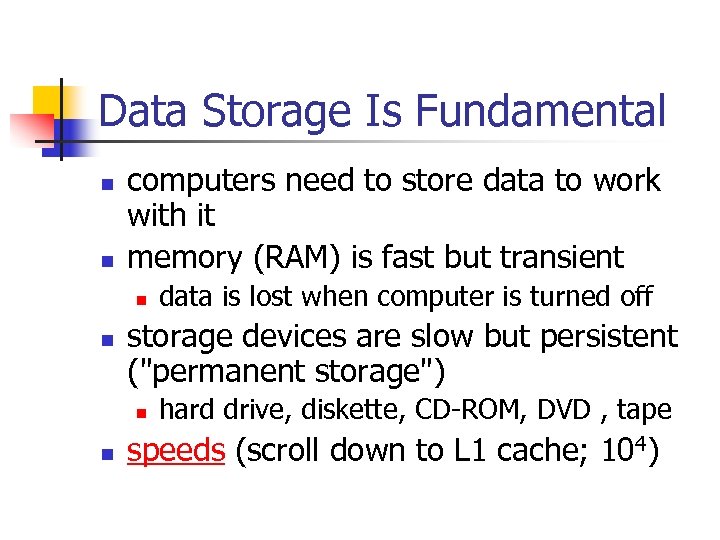 Data Storage Is Fundamental n n computers need to store data to work with it memory (RAM) is fast but transient n n storage devices are slow but persistent ("permanent storage") n n data is lost when computer is turned off hard drive, diskette, CD-ROM, DVD , tape speeds (scroll down to L 1 cache; 104)
Data Storage Is Fundamental n n computers need to store data to work with it memory (RAM) is fast but transient n n storage devices are slow but persistent ("permanent storage") n n data is lost when computer is turned off hard drive, diskette, CD-ROM, DVD , tape speeds (scroll down to L 1 cache; 104)
 Files on External Devices n data n n n accounting data in "flat" files data in database files documents in word processor files images in graphics files stored programs in files n some early computers did not use files for their programs (Altair)
Files on External Devices n data n n n accounting data in "flat" files data in database files documents in word processor files images in graphics files stored programs in files n some early computers did not use files for their programs (Altair)
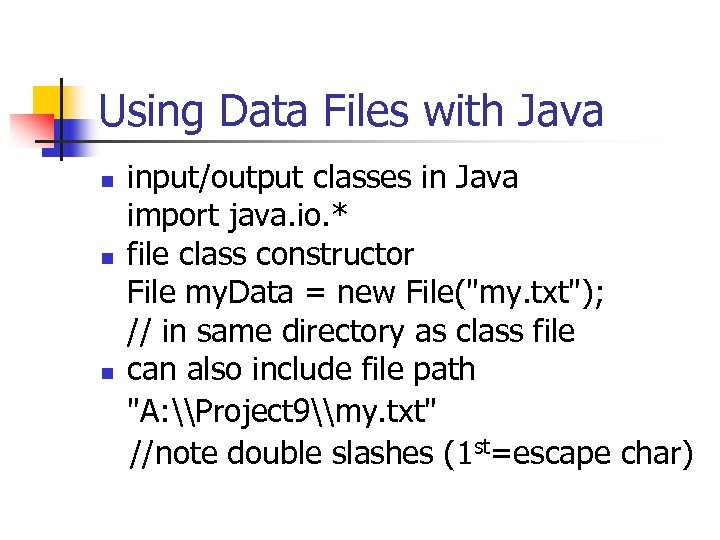 Using Data Files with Java n n n input/output classes in Java import java. io. * file class constructor File my. Data = new File("my. txt"); // in same directory as class file can also include file path "A: \Project 9\my. txt" //note double slashes (1 st=escape char)
Using Data Files with Java n n n input/output classes in Java import java. io. * file class constructor File my. Data = new File("my. txt"); // in same directory as class file can also include file path "A: \Project 9\my. txt" //note double slashes (1 st=escape char)
 Files Have Properties n name = file identifier + extension mydata n n txt parent = drive + directory(s) A: My DocumentsProject 5 full path = parent + name A: My DocumentsProject 5mydata. txt
Files Have Properties n name = file identifier + extension mydata n n txt parent = drive + directory(s) A: My DocumentsProject 5 full path = parent + name A: My DocumentsProject 5mydata. txt
 File Properties - 2 n n n readable – by a program writeable – can save data into it length – file size in bytes last modified – date last saved etc.
File Properties - 2 n n n readable – by a program writeable – can save data into it length – file size in bytes last modified – date last saved etc.
 File Organization "Hierarchy" n n a hierarchy is like an outline from top down (in a "flat" file): n n n file has records (1 or more) which have fields (1 or more) which are made up of character(s) (each is 2 bytes) made up of bits what's above the top?
File Organization "Hierarchy" n n a hierarchy is like an outline from top down (in a "flat" file): n n n file has records (1 or more) which have fields (1 or more) which are made up of character(s) (each is 2 bytes) made up of bits what's above the top?
 Java's File Class Methods n to get data about a file n n can. Read() – readable (true/false) if (my. Data. can. Read()) { some code} can. Write() – can save to it (true/false) length() – size in bytes last. Modified() – date
Java's File Class Methods n to get data about a file n n can. Read() – readable (true/false) if (my. Data. can. Read()) { some code} can. Write() – can save to it (true/false) length() – size in bytes last. Modified() – date
 File Class Methods - 2 n can break a full path into parts n n get. Name() //from full path String file. Name = my. Data. get. Name(); get. Path() //if identified when created get. Parent() //if identified when created exists() – check to see if it's there n don't try to read it if it's not there
File Class Methods - 2 n can break a full path into parts n n get. Name() //from full path String file. Name = my. Data. get. Name(); get. Path() //if identified when created get. Parent() //if identified when created exists() – check to see if it's there n don't try to read it if it's not there
 Operating System Opens File n n n sets up an area in memory to receive data sends message to storage device finds location of file data on media n n in DOS, uses file allocation table (FAT) may lock file so other programs can't use it at same time
Operating System Opens File n n n sets up an area in memory to receive data sends message to storage device finds location of file data on media n n in DOS, uses file allocation table (FAT) may lock file so other programs can't use it at same time
 OS Closes File n n n may write unsaved data to output medium frees up memory unlocks file n if it was locked while being used
OS Closes File n n n may write unsaved data to output medium frees up memory unlocks file n if it was locked while being used
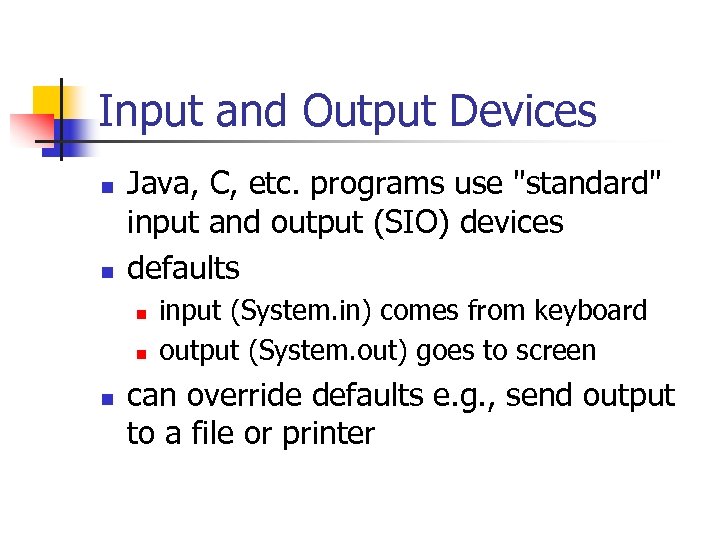 Input and Output Devices n n Java, C, etc. programs use "standard" input and output (SIO) devices defaults n n n input (System. in) comes from keyboard output (System. out) goes to screen can override defaults e. g. , send output to a file or printer
Input and Output Devices n n Java, C, etc. programs use "standard" input and output (SIO) devices defaults n n n input (System. in) comes from keyboard output (System. out) goes to screen can override defaults e. g. , send output to a file or printer
 "Streams" n two ways to deal with data n 1 record at a time ("flat" file organization) n n COBOL works with records as a stream of data in individual bytes n n n better for multiplatform systems Java and C work with streams can be broken up with n (newline characters) into logical partitions
"Streams" n two ways to deal with data n 1 record at a time ("flat" file organization) n n COBOL works with records as a stream of data in individual bytes n n n better for multiplatform systems Java and C work with streams can be broken up with n (newline characters) into logical partitions
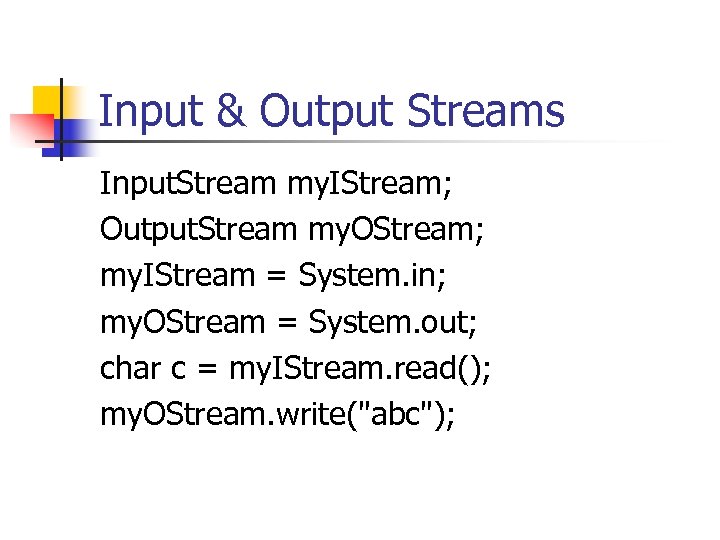 Input & Output Streams Input. Stream my. IStream; Output. Stream my. OStream; my. IStream = System. in; my. OStream = System. out; char c = my. IStream. read(); my. OStream. write("abc");
Input & Output Streams Input. Stream my. IStream; Output. Stream my. OStream; my. IStream = System. in; my. OStream = System. out; char c = my. IStream. read(); my. OStream. write("abc");
 Buffer n area in memory to hold input or output data temporarily n n n after being read but before being used in a program before being written to disk buffers can improve performance n program can read data from one part of a buffer while more data is coming in from disk to another (part of) buffer
Buffer n area in memory to hold input or output data temporarily n n n after being read but before being used in a program before being written to disk buffers can improve performance n program can read data from one part of a buffer while more data is coming in from disk to another (part of) buffer
 Creating an Output File n two ways to associate a file with an output stream n n pass filename argument to File. Output. Stream constructor pass filename argument to File constructor, then pass file object to File. Output. Stream constructor
Creating an Output File n two ways to associate a file with an output stream n n pass filename argument to File. Output. Stream constructor pass filename argument to File constructor, then pass file object to File. Output. Stream constructor
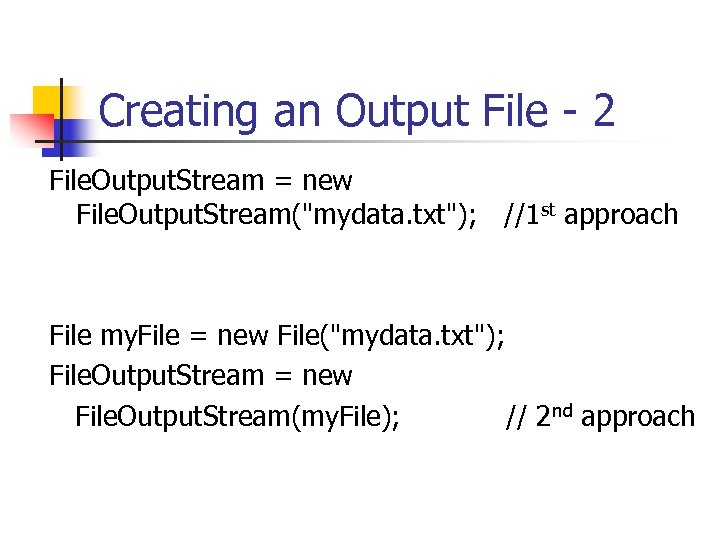 Creating an Output File - 2 File. Output. Stream = new File. Output. Stream("mydata. txt"); //1 st approach File my. File = new File("mydata. txt"); File. Output. Stream = new File. Output. Stream(my. File); // 2 nd approach
Creating an Output File - 2 File. Output. Stream = new File. Output. Stream("mydata. txt"); //1 st approach File my. File = new File("mydata. txt"); File. Output. Stream = new File. Output. Stream(my. File); // 2 nd approach
 File. Writer class n Java "convenience* class" for writing character files * convenience means easier to use n constructors assume that default character encoding and buffer size are OK
File. Writer class n Java "convenience* class" for writing character files * convenience means easier to use n constructors assume that default character encoding and buffer size are OK
 Using File. Writer n n n put code inside a try block create File. Writer object with filename can use write method to write outputs n n or could create a Print. Writer object using a println() method with it (p. 527 -528) be sure to use close() method after finish writing output n file will lose all its data if it isn't closed
Using File. Writer n n n put code inside a try block create File. Writer object with filename can use write method to write outputs n n or could create a Print. Writer object using a println() method with it (p. 527 -528) be sure to use close() method after finish writing output n file will lose all its data if it isn't closed
 File. Writer Example (code) try{ File. Writer outs = new File. Writer("demo. Io. txt" ); outs. write("Hello", 0, 5); //String, start, length outs. write("n" + 1); // n=new line outs. close(); // don't forget to use this line!!! } // view demo. Io. txt with editor [ catch (IOException e) {[some code]} ]
File. Writer Example (code) try{ File. Writer outs = new File. Writer("demo. Io. txt" ); outs. write("Hello", 0, 5); //String, start, length outs. write("n" + 1); // n=new line outs. close(); // don't forget to use this line!!! } // view demo. Io. txt with editor [ catch (IOException e) {[some code]} ]
 Review n n n Compare and contrast memory (RAM, cache) and storage devices (disk, CDs) Identify some types of data, etc. that can be stored in files What is a “flat file? ” What do you need at the top of a. java file to use file data? import. java. ___? Identify some file properties.
Review n n n Compare and contrast memory (RAM, cache) and storage devices (disk, CDs) Identify some types of data, etc. that can be stored in files What is a “flat file? ” What do you need at the top of a. java file to use file data? import. java. ___? Identify some file properties.
 Review - 2 n n Identify some types of file handling methods. Identify some parts of a file identifier. Name some low level items in the “file hierarchy”? What has to or might have to happen when a file is opened? n Is closed?
Review - 2 n n Identify some types of file handling methods. Identify some parts of a file identifier. Name some low level items in the “file hierarchy”? What has to or might have to happen when a file is opened? n Is closed?
 Review - 3 n n n What does SIO mean? What are the default SIO devices? What are some differences between streams and records? n n Which does Java use? What is a buffer? n How are buffers used in playing videos?
Review - 3 n n n What does SIO mean? What are the default SIO devices? What are some differences between streams and records? n n Which does Java use? What is a buffer? n How are buffers used in playing videos?


