9d2f15bf5c2a61929d5dda3ff6db6487.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 73
 CIRS-A Certification for Information and Referral Specialists Examination Preparation Training Prepared by: Illinois Department on Aging
CIRS-A Certification for Information and Referral Specialists Examination Preparation Training Prepared by: Illinois Department on Aging
 Certification is. . . ¡ A measurement of documented ability in the field of I&R … reflecting specific competencies and related performance criteria, which describe the knowledge, skills, attitudes and work-related behaviors needed by I&R practitioners to successfully execute their duties
Certification is. . . ¡ A measurement of documented ability in the field of I&R … reflecting specific competencies and related performance criteria, which describe the knowledge, skills, attitudes and work-related behaviors needed by I&R practitioners to successfully execute their duties
 Preparing for AIRS CIRS-A Overview of materials to study Principles of the AIRS Certification Program ¡ ABC’s of I&R (preferably 2006 edition or later) ¡ History of Older Americans Act I&R ¡ CIRS-A Performance Based Competencies ¡ Tenants/Bill of Rights, Philosophy of Aging I&R ¡ Information and Referral Models to Remember (an AIRS Journal article available from AIRS web site at www. airs. org) ¡ ¡ Professional Standards for Information and Referral
Preparing for AIRS CIRS-A Overview of materials to study Principles of the AIRS Certification Program ¡ ABC’s of I&R (preferably 2006 edition or later) ¡ History of Older Americans Act I&R ¡ CIRS-A Performance Based Competencies ¡ Tenants/Bill of Rights, Philosophy of Aging I&R ¡ Information and Referral Models to Remember (an AIRS Journal article available from AIRS web site at www. airs. org) ¡ ¡ Professional Standards for Information and Referral
 For CIRS-A Examination: I&R Systems/Services 10% of exam ¡ I&R Process 40% of exam ¡ Special Interventions 10% of exam ¡ Special Populations Aging Specific 10% of exam ¡ Information/Scenarios 30% of exam ¡ (all approximate)
For CIRS-A Examination: I&R Systems/Services 10% of exam ¡ I&R Process 40% of exam ¡ Special Interventions 10% of exam ¡ Special Populations Aging Specific 10% of exam ¡ Information/Scenarios 30% of exam ¡ (all approximate)
 The CIRS-A Exam What to expect: ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ 100 multiple choice questions with 4 options for each answer 75% correct to pass (varies slightly on each exam because of varying degrees of difficulty) Pass/Fail– no grade, no score Review questions Interactive training-review Easy as ANE, CCP and CCC tests You know most of the materials already!!
The CIRS-A Exam What to expect: ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ 100 multiple choice questions with 4 options for each answer 75% correct to pass (varies slightly on each exam because of varying degrees of difficulty) Pass/Fail– no grade, no score Review questions Interactive training-review Easy as ANE, CCP and CCC tests You know most of the materials already!!
 CRIS-A Materials and Handouts ¡ ¡ ¡ PPT Outline AIRS Standards ABCs of I&R sections CIRS-A Competencies NASUA online study outline – (for outline only, not for review of web sites) ¡ ¡ ¡ Tenents Principles of Certification History of Older Americans Act I&R
CRIS-A Materials and Handouts ¡ ¡ ¡ PPT Outline AIRS Standards ABCs of I&R sections CIRS-A Competencies NASUA online study outline – (for outline only, not for review of web sites) ¡ ¡ ¡ Tenents Principles of Certification History of Older Americans Act I&R
 What is AIRS? ¡ AIRS mission: “To provide leadership and support to its members and Affiliates to advance the capacity of a Standards-driven Information and Referral industry that brings people and services together. " (www. airs. org)
What is AIRS? ¡ AIRS mission: “To provide leadership and support to its members and Affiliates to advance the capacity of a Standards-driven Information and Referral industry that brings people and services together. " (www. airs. org)
 I&R and the Aging Network – Ao. A, NASUA, NAAAA ¡ Administration on Aging funds: l l Eldercare Locator National Aging Information and Referral Support Center ¡ Annual Aging I&R Symposium-AIRS National Conference ¡ National AIRS Board of Directors ¡ Collaborated with AIRS to establish a specialized I&R Certification for the Aging Network
I&R and the Aging Network – Ao. A, NASUA, NAAAA ¡ Administration on Aging funds: l l Eldercare Locator National Aging Information and Referral Support Center ¡ Annual Aging I&R Symposium-AIRS National Conference ¡ National AIRS Board of Directors ¡ Collaborated with AIRS to establish a specialized I&R Certification for the Aging Network
 Principles of the AIRS Certification Program ¡ AIRS has prepared a four page handout summarizing certification for all candidates. Also the CIRS-A application, and study outlines are available at www. airs. org
Principles of the AIRS Certification Program ¡ AIRS has prepared a four page handout summarizing certification for all candidates. Also the CIRS-A application, and study outlines are available at www. airs. org
 History of Older Americans Act Information and Referral (CIRS-A) 1921 human service I&Rs ¡ More important in 1960 s & 1970 s ¡ Older Americans Act 1965 ¡ 1973 – OAA mandated I&R – through AAAs ¡ 1990 – Ao. A launched its two-pronged National I&R Initiative: l Eldercare Locator l National I&R Support Center ¡
History of Older Americans Act Information and Referral (CIRS-A) 1921 human service I&Rs ¡ More important in 1960 s & 1970 s ¡ Older Americans Act 1965 ¡ 1973 – OAA mandated I&R – through AAAs ¡ 1990 – Ao. A launched its two-pronged National I&R Initiative: l Eldercare Locator l National I&R Support Center ¡
 Tenants ¡ I&R Bill of Rights ¡ Philosophy of Information and Referral ¡ Main Functions of an Information and Referral Service ¡ Services for Older Adults and/or their Caregivers ¡ Services for the Community
Tenants ¡ I&R Bill of Rights ¡ Philosophy of Information and Referral ¡ Main Functions of an Information and Referral Service ¡ Services for Older Adults and/or their Caregivers ¡ Services for the Community
 AIRS Information & Referral Bill of Rights ¡ ¡ ¡ Accurate and comprehensive information Anonymous and/or confidential Inquirer’s personal value system Respect and sensitivity Barrier-free access to information ¡ ¡ Self-determination Appropriate level of support in obtaining services Empowered to the extent possible Access most appropriate service in community
AIRS Information & Referral Bill of Rights ¡ ¡ ¡ Accurate and comprehensive information Anonymous and/or confidential Inquirer’s personal value system Respect and sensitivity Barrier-free access to information ¡ ¡ Self-determination Appropriate level of support in obtaining services Empowered to the extent possible Access most appropriate service in community
 Philosophy of Information & Referral ¡ ¡ Understand inquirers situation Immediate and appropriate information, crisis emergency Empower not solve Help prioritize needs Help identify resources ¡ Do not overwhelm or provide too few options ¡ Advocate ¡ Follow up ¡
Philosophy of Information & Referral ¡ ¡ Understand inquirers situation Immediate and appropriate information, crisis emergency Empower not solve Help prioritize needs Help identify resources ¡ Do not overwhelm or provide too few options ¡ Advocate ¡ Follow up ¡
 Main Functions of Information and Referral Service ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Database Easy access Provide I&R for human services Problem solving assistance/advocacy Follow up Gaps for community planners, funding Develop cooperative relations (coordinated systems), integrated service delivery and education activities
Main Functions of Information and Referral Service ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Database Easy access Provide I&R for human services Problem solving assistance/advocacy Follow up Gaps for community planners, funding Develop cooperative relations (coordinated systems), integrated service delivery and education activities
 AIRS Standards For Professional Information And Referral Version 5. 2 Revised May, 2007 ¡ We need to start with the Standards ¡ To apply the relationship of the Standards to the skills and techniques of I&R Services ¡ The Standards are the foundation of AIRS accreditation ¡ And an excellent training tool!
AIRS Standards For Professional Information And Referral Version 5. 2 Revised May, 2007 ¡ We need to start with the Standards ¡ To apply the relationship of the Standards to the skills and techniques of I&R Services ¡ The Standards are the foundation of AIRS accreditation ¡ And an excellent training tool!
 The Standards begin with: l Introduction l Information and Referral Bill of Rights l Philosophy of Information and Referral l Please highlight important contents of the Standards as these are reviewed
The Standards begin with: l Introduction l Information and Referral Bill of Rights l Philosophy of Information and Referral l Please highlight important contents of the Standards as these are reviewed
 The Standards are grouped in six categories: ¡ I. Service Delivery ¡ II. Resource Database ¡ III. Reports and Measures ¡ IV. Cooperative Relationships ¡ V. Organizational Requirements ¡ VI. Disaster Preparedness
The Standards are grouped in six categories: ¡ I. Service Delivery ¡ II. Resource Database ¡ III. Reports and Measures ¡ IV. Cooperative Relationships ¡ V. Organizational Requirements ¡ VI. Disaster Preparedness
 I. Service Delivery ¡ Standard 1: Information Provision ¡ Standard 2: Referral Process ¡ Standard 3: Advocacy/ Intervention ¡ Standard 4: Crisis Intervention ¡ Standard 5: Follow-up
I. Service Delivery ¡ Standard 1: Information Provision ¡ Standard 2: Referral Process ¡ Standard 3: Advocacy/ Intervention ¡ Standard 4: Crisis Intervention ¡ Standard 5: Follow-up
 II. Resource Database Standard 6: Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria ¡ Standard 7: Data Elements ¡ Standard 8: Classification System (Taxonomy) ¡ Standard 9: Indexing the Resource Database/Search Methods ¡ Standard 10: Database Maintenance ¡
II. Resource Database Standard 6: Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria ¡ Standard 7: Data Elements ¡ Standard 8: Classification System (Taxonomy) ¡ Standard 9: Indexing the Resource Database/Search Methods ¡ Standard 10: Database Maintenance ¡
 III. Reports and Measures ¡ Standard 11: Inquirer Data Collection ¡ Standard 12: Data Analysis and Reporting
III. Reports and Measures ¡ Standard 11: Inquirer Data Collection ¡ Standard 12: Data Analysis and Reporting
 IV. Cooperative Relationships ¡ ¡ Standard 13: Cooperative Relationships within the Local I&R System Standard 14: Cooperative Relationships within the Local Service Delivery System Standard 15: Cooperative Relationships Among Local, State or Provincial, Regional, National, and International I&R Providers Standard 16: Participation in State or Provincial, Regional, National, and International I&R Associations
IV. Cooperative Relationships ¡ ¡ Standard 13: Cooperative Relationships within the Local I&R System Standard 14: Cooperative Relationships within the Local Service Delivery System Standard 15: Cooperative Relationships Among Local, State or Provincial, Regional, National, and International I&R Providers Standard 16: Participation in State or Provincial, Regional, National, and International I&R Associations
 V. Organizational Requirements ¡ Standard 17: Governance ¡ Standard 18: Personnel Administration ¡ Standard 19: Staff Training ¡ Standard 20: Promotion and Outreach
V. Organizational Requirements ¡ Standard 17: Governance ¡ Standard 18: Personnel Administration ¡ Standard 19: Staff Training ¡ Standard 20: Promotion and Outreach
 VI. Disaster Preparedness ¡ Standard 21: Emergency Operations and Business Contingency Plan ¡ Standard 22: Pre- and Post. Disaster Database ¡ Standard 24: Disaster-Related I&R Service Delivery
VI. Disaster Preparedness ¡ Standard 21: Emergency Operations and Business Contingency Plan ¡ Standard 22: Pre- and Post. Disaster Database ¡ Standard 24: Disaster-Related I&R Service Delivery
 VI. Disaster Preparedness ¡ Standard 25: Disaster-Related Inquirer Data Collection/Reports ¡ Standard 26: Disaster-Related Technology Requirements ¡ Standard 27: Disaster Training and Exercise (These are the newest Standards)
VI. Disaster Preparedness ¡ Standard 25: Disaster-Related Inquirer Data Collection/Reports ¡ Standard 26: Disaster-Related Technology Requirements ¡ Standard 27: Disaster Training and Exercise (These are the newest Standards)
 Wrap-up. I&R Professional Standards ¡ ¡ The Standards are an excellent training tool How do the Standards relate to each chapter of the ABC’? How do the Standards relate to CIRSA Competencies? What do the Standards say as we review all of the training materials?
Wrap-up. I&R Professional Standards ¡ ¡ The Standards are an excellent training tool How do the Standards relate to each chapter of the ABC’? How do the Standards relate to CIRSA Competencies? What do the Standards say as we review all of the training materials?
 ABCs Of I&R – Methodology for the 21 sections ¡ Learning concepts and objectives ¡ Section components ¡ Introductory exercises ¡ What the AIRS Standards say ¡ What you need to know ¡ Sample Test Questions
ABCs Of I&R – Methodology for the 21 sections ¡ Learning concepts and objectives ¡ Section components ¡ Introductory exercises ¡ What the AIRS Standards say ¡ What you need to know ¡ Sample Test Questions
 1. The Nature of Information and Referral ¡ What is I&R? ¡ What are the I&R Standards? ¡ Roles of an I&R ¡ Characteristics of an I&R ¡ Information and Referral Bill of Rights ¡ Principles of Information and Referral
1. The Nature of Information and Referral ¡ What is I&R? ¡ What are the I&R Standards? ¡ Roles of an I&R ¡ Characteristics of an I&R ¡ Information and Referral Bill of Rights ¡ Principles of Information and Referral
 Section 2: From Greeting to Closure – The I&R Process Overview of the 5 main stages of the I&R process ¡ Contact ¡ Assessment ¡ Clarification ¡ Information and Referral Giving ¡ Closure
Section 2: From Greeting to Closure – The I&R Process Overview of the 5 main stages of the I&R process ¡ Contact ¡ Assessment ¡ Clarification ¡ Information and Referral Giving ¡ Closure
 Section 3: Empowerment and Advocacy ¡ Empowerment ¡ Advocacy ¡ Individual advocacy ¡ When to advocate ¡ Examples of advocacy ¡ System advocacy
Section 3: Empowerment and Advocacy ¡ Empowerment ¡ Advocacy ¡ Individual advocacy ¡ When to advocate ¡ Examples of advocacy ¡ System advocacy
 Section 4: Follow-up ¡ Reasons for follow-up ¡ Types of follow-up ¡ Follow-up outcomes ¡ Follow-up methods and processes ¡ Outline for potential follow-up
Section 4: Follow-up ¡ Reasons for follow-up ¡ Types of follow-up ¡ Follow-up outcomes ¡ Follow-up methods and processes ¡ Outline for potential follow-up
 Section 5: Crisis Intervention ¡ Role of I&R in a crisis ¡ Handling an immediate crisis ¡ Types of crises ¡ Defusing and handling a crisis situation ¡ Elements of a suicide risk assessment
Section 5: Crisis Intervention ¡ Role of I&R in a crisis ¡ Handling an immediate crisis ¡ Types of crises ¡ Defusing and handling a crisis situation ¡ Elements of a suicide risk assessment
 Section 6: Confidentiality ¡ Confidentiality in I&R ¡ Explicit permission ¡ Reporting of abuse ¡ Confidentiality and endangerment ¡ Relevance of information
Section 6: Confidentiality ¡ Confidentiality in I&R ¡ Explicit permission ¡ Reporting of abuse ¡ Confidentiality and endangerment ¡ Relevance of information
 Section 7: Values, Self-Awareness and Self-Determination ¡ Values and perceptions ¡ Self-awareness ¡ Self-determination ¡ Withholding judgment
Section 7: Values, Self-Awareness and Self-Determination ¡ Values and perceptions ¡ Self-awareness ¡ Self-determination ¡ Withholding judgment
 Section 8: Responding Effectively to “Challenging” Inquirers ¡ Challenging people ¡ Techniques to defuse anger ¡ Mental health calls and “constant callers” ¡ Setting boundaries ¡ Face-to-face interviews
Section 8: Responding Effectively to “Challenging” Inquirers ¡ Challenging people ¡ Techniques to defuse anger ¡ Mental health calls and “constant callers” ¡ Setting boundaries ¡ Face-to-face interviews
 Section 9: Using the Resource Database for I&R Referrals ¡ Nature of a resource database ¡ Structure of a resource database ¡ Searching a resource database ¡ Sharing information with inquirers ¡ Additional considerations when working with resource databases ¡ Other information resources
Section 9: Using the Resource Database for I&R Referrals ¡ Nature of a resource database ¡ Structure of a resource database ¡ Searching a resource database ¡ Sharing information with inquirers ¡ Additional considerations when working with resource databases ¡ Other information resources
 Section 10: Special Populations. Serving Diverse Communities ¡ The meaning of diversity ¡ Diversity awareness ¡ Serving people from diverse communities
Section 10: Special Populations. Serving Diverse Communities ¡ The meaning of diversity ¡ Diversity awareness ¡ Serving people from diverse communities
 Section 11: Special Populations. Serving People with Addictions ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Characteristics of substance abuse Alcoholism and drug addictions Effects of addictions on families Referral options for people with addictions Methadone maintenance Concurrent disorders, co-occurring disorders and dual diagnosis Problem gambling/gambling addictions
Section 11: Special Populations. Serving People with Addictions ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Characteristics of substance abuse Alcoholism and drug addictions Effects of addictions on families Referral options for people with addictions Methadone maintenance Concurrent disorders, co-occurring disorders and dual diagnosis Problem gambling/gambling addictions
 Section 12: Specials Populations. Serving Older Adults ¡ Definitions of “older” and “elderly” ¡ The aging process ¡ Overcoming barriers to communications ¡ Specific services for older adults ¡ Elder abuse
Section 12: Specials Populations. Serving Older Adults ¡ Definitions of “older” and “elderly” ¡ The aging process ¡ Overcoming barriers to communications ¡ Specific services for older adults ¡ Elder abuse
 Section 13: Special Populations. Serving Young People ¡ Serving young people ¡ Youth issues ¡ At-risk youth ¡ Runaway youth ¡ Emancipation
Section 13: Special Populations. Serving Young People ¡ Serving young people ¡ Youth issues ¡ At-risk youth ¡ Runaway youth ¡ Emancipation
 Section 14: Special Populations. Serving People with Mental Illness ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Nature and types of mental illnesses Depression Bipolar disorder Schizophrenia Anxiety disorders Services available for people with mental illnesses Communicating with people concerning mental illness Consumer/survivors
Section 14: Special Populations. Serving People with Mental Illness ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Nature and types of mental illnesses Depression Bipolar disorder Schizophrenia Anxiety disorders Services available for people with mental illnesses Communicating with people concerning mental illness Consumer/survivors
 Section 15: Special Populations. Serving Military Personnel and their Families ¡ Needs of military personnel and their families ¡ Deployment issues ¡ Emotional cycle of separation ¡ Basic structure of military family support services
Section 15: Special Populations. Serving Military Personnel and their Families ¡ Needs of military personnel and their families ¡ Deployment issues ¡ Emotional cycle of separation ¡ Basic structure of military family support services
 Section 17: Resource Database. Overview ¡ Function and contents of an I&R resource database ¡ Database users ¡ Database products ¡ Functions of a Resource Specialist ¡ Skills of a Resource Specialist
Section 17: Resource Database. Overview ¡ Function and contents of an I&R resource database ¡ Database users ¡ Database products ¡ Functions of a Resource Specialist ¡ Skills of a Resource Specialist
 Section 18: Resource Database. Inclusion and Exclusion Policy ¡ ¡ ¡ Nature of inclusion and exclusion criteria Advantages of having a formally documented inclusion/exclusion policy Inclusion Exclusion The gray areas Managing the inclusion/exclusion policy
Section 18: Resource Database. Inclusion and Exclusion Policy ¡ ¡ ¡ Nature of inclusion and exclusion criteria Advantages of having a formally documented inclusion/exclusion policy Inclusion Exclusion The gray areas Managing the inclusion/exclusion policy
 Section 19: Resource Database. Data Structure of a resource database ¡ Organizations, sites and services/programs ¡ Primary and secondary services ¡ AIRS mandatory, recommended and optional data elements ¡ Types of data elements ¡ Advantages of a style guide. ¡
Section 19: Resource Database. Data Structure of a resource database ¡ Organizations, sites and services/programs ¡ Primary and secondary services ¡ AIRS mandatory, recommended and optional data elements ¡ Types of data elements ¡ Advantages of a style guide. ¡
 Section 20: Resource Database. Classification Systems and Taxonomy ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Organizing and indexing resource databases Indexing by organization name Indexing by geographic area Service indexing Structure and strengths of the AIRS/INFO LINE Taxonomy Basic principles of Taxonomy indexing Customizing the Taxonomy Keyword lists
Section 20: Resource Database. Classification Systems and Taxonomy ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Organizing and indexing resource databases Indexing by organization name Indexing by geographic area Service indexing Structure and strengths of the AIRS/INFO LINE Taxonomy Basic principles of Taxonomy indexing Customizing the Taxonomy Keyword lists
 Section 21: Resource Database Maintenance ¡ Data maintenance standards ¡ Annual updating processes ¡ Interim updating processes ¡ Gathering information on a new agency ¡ Managing the updating process ¡ Database security
Section 21: Resource Database Maintenance ¡ Data maintenance standards ¡ Annual updating processes ¡ Interim updating processes ¡ Gathering information on a new agency ¡ Managing the updating process ¡ Database security
 Summary of ABCs, Introduction to the CIRS-A Competencies ¡ ¡ ¡ The ABC’s incorporates the I&R Standards with skills, techniques procedures and provides the formal language and structure of I&R The CIRS-A Competencies combines both the I&R Standards and the ABC’s with knowledge of services for older adults The National I&R Support Center expanded the CIRS Competencies with an Aging Specialty
Summary of ABCs, Introduction to the CIRS-A Competencies ¡ ¡ ¡ The ABC’s incorporates the I&R Standards with skills, techniques procedures and provides the formal language and structure of I&R The CIRS-A Competencies combines both the I&R Standards and the ABC’s with knowledge of services for older adults The National I&R Support Center expanded the CIRS Competencies with an Aging Specialty
 CRIS-A Study Guide ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Tenents of I&R Older Americans Act I&R AIRS Mission Philosophy of I&A I&R Bill of Rights Main Functions for I&R Services for older adults and their caregivers Services for the community
CRIS-A Study Guide ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Tenents of I&R Older Americans Act I&R AIRS Mission Philosophy of I&A I&R Bill of Rights Main Functions for I&R Services for older adults and their caregivers Services for the community
 CRIS-A Study Guide ¡ A. General knowledge of I&A ¡ B. Demonstrated I&R skills and abilities ¡ C. Attitudes and work related behaviors for the Aging Network
CRIS-A Study Guide ¡ A. General knowledge of I&A ¡ B. Demonstrated I&R skills and abilities ¡ C. Attitudes and work related behaviors for the Aging Network
 Online Resource Guide for Developing Aging Competence for I&R/A Specialists (17 Chapters) (page 1 of 2) ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ 1. Aging 2. Aging Network 3. Federal Laws & Programs 4. Elder Rights & Resources 5. Employment & Older Workers 6. Family Caregiving & Kinship 7. Health Care & Aging 8. Health Promotion/ disease prevention
Online Resource Guide for Developing Aging Competence for I&R/A Specialists (17 Chapters) (page 1 of 2) ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ 1. Aging 2. Aging Network 3. Federal Laws & Programs 4. Elder Rights & Resources 5. Employment & Older Workers 6. Family Caregiving & Kinship 7. Health Care & Aging 8. Health Promotion/ disease prevention
 NASUA – Online Resource Guide continued (page 2 of 2) 9. Home & Community Based Services ¡ 10. Income Security/Retirement ¡ 11. Long Term Care/Nursing Homes ¡ 12. Mental Health & Aging ¡ 13. Multicultural Aging ¡ 14. Nutrition ¡ 15. Older volunteers ¡ 16. Senior Housing Options ¡ 17. Transportation & Mobility ¡
NASUA – Online Resource Guide continued (page 2 of 2) 9. Home & Community Based Services ¡ 10. Income Security/Retirement ¡ 11. Long Term Care/Nursing Homes ¡ 12. Mental Health & Aging ¡ 13. Multicultural Aging ¡ 14. Nutrition ¡ 15. Older volunteers ¡ 16. Senior Housing Options ¡ 17. Transportation & Mobility ¡
 Information and Assistance Skills Building The Information & Referral Interview: Models to Remember Norman L. Maas ▪Two Basic Models ▸ ▸ ▸ Basic advice on how to approach the referral interview Basic principles for the crisis intervention model for I&R provision And an overview of active listening
Information and Assistance Skills Building The Information & Referral Interview: Models to Remember Norman L. Maas ▪Two Basic Models ▸ ▸ ▸ Basic advice on how to approach the referral interview Basic principles for the crisis intervention model for I&R provision And an overview of active listening
 What goes into interviewing? The counseling model for the referral interview ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Understanding people How we are all different The importance of feelings Feelings in times of upset and change The mix of feelings Learning to know yourself The importance of each person
What goes into interviewing? The counseling model for the referral interview ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Understanding people How we are all different The importance of feelings Feelings in times of upset and change The mix of feelings Learning to know yourself The importance of each person
 The importance of each person Will come through with the. . . Attentiveness with which you listen ▪ Sensitivity with which you ask questions ▪ Respect with which you treat confidence ▪ Restraint you use in imposing your views on others ▪ Care you take to avoid disappointments and ill-founded statement and promises ▪
The importance of each person Will come through with the. . . Attentiveness with which you listen ▪ Sensitivity with which you ask questions ▪ Respect with which you treat confidence ▪ Restraint you use in imposing your views on others ▪ Care you take to avoid disappointments and ill-founded statement and promises ▪
 What takes place in an interview? At the beginning– discomfort ▪ Putting fears to rest ▪ Information giving: a few general comments ▪ Knowing enough about the person’s problem ▪ A person’s right not to tell you everything ▪ Knowing the resource file ▪
What takes place in an interview? At the beginning– discomfort ▪ Putting fears to rest ▪ Information giving: a few general comments ▪ Knowing enough about the person’s problem ▪ A person’s right not to tell you everything ▪ Knowing the resource file ▪
 What takes place in an interview? ▪ ▪ ▪ Letting people tell you in their own way: good listening pays off Giving information that is useful and relevant to the person Making sure people understand When people get angry Ending the interview
What takes place in an interview? ▪ ▪ ▪ Letting people tell you in their own way: good listening pays off Giving information that is useful and relevant to the person Making sure people understand When people get angry Ending the interview
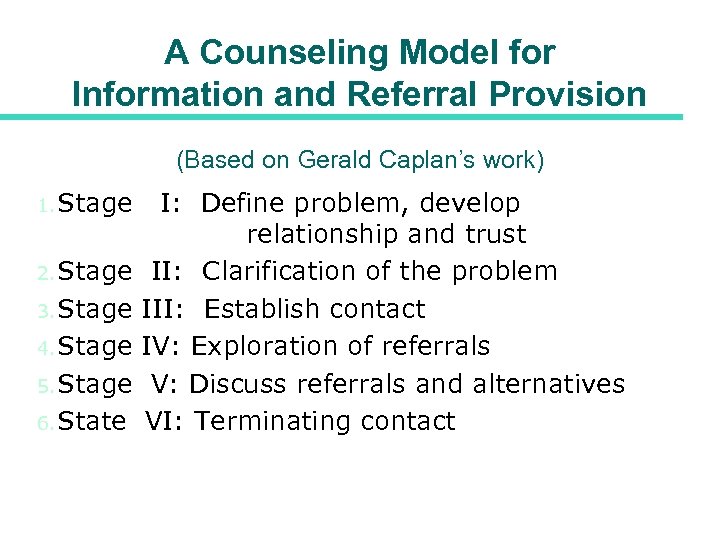 A Counseling Model for Information and Referral Provision (Based on Gerald Caplan’s work) 1. Stage I: Define problem, develop relationship and trust 2. Stage II: Clarification of the problem 3. Stage III: Establish contact 4. Stage IV: Exploration of referrals 5. Stage V: Discuss referrals and alternatives 6. State VI: Terminating contact
A Counseling Model for Information and Referral Provision (Based on Gerald Caplan’s work) 1. Stage I: Define problem, develop relationship and trust 2. Stage II: Clarification of the problem 3. Stage III: Establish contact 4. Stage IV: Exploration of referrals 5. Stage V: Discuss referrals and alternatives 6. State VI: Terminating contact
 Basic Helping Skills ▪ ▪ ▪ Confronting Attitude Attending Reflecting Paraphrasing ▪ ▪ Reflecting feelings Summarizing Focusing Questioning
Basic Helping Skills ▪ ▪ ▪ Confronting Attitude Attending Reflecting Paraphrasing ▪ ▪ Reflecting feelings Summarizing Focusing Questioning
 The referral process Interaction between two people considering involvement of a third party ▪ ▪ ▪ Resource Ring 1. What has client tried so far? 2. What else thought of doing? 3. Assistance from family - friends? 4. Happened before? How handled then?
The referral process Interaction between two people considering involvement of a third party ▪ ▪ ▪ Resource Ring 1. What has client tried so far? 2. What else thought of doing? 3. Assistance from family - friends? 4. Happened before? How handled then?
 The Resource Ring Feelings of the client ▪ ▪ ▪ Frustration Rejection Guilt Anxiety Special fears
The Resource Ring Feelings of the client ▪ ▪ ▪ Frustration Rejection Guilt Anxiety Special fears
 Basic principles in making a referral (page 1 of 2) ▪ ▪ ▪ 1. Let client describe problem-feelings Clarify, move slowly 2. Gather information needed 3. Decide upon referral, discuss with staff 4. Avoid confusing client (1 or 2 referrals) 5. Do not discuss another agency’s fees
Basic principles in making a referral (page 1 of 2) ▪ ▪ ▪ 1. Let client describe problem-feelings Clarify, move slowly 2. Gather information needed 3. Decide upon referral, discuss with staff 4. Avoid confusing client (1 or 2 referrals) 5. Do not discuss another agency’s fees
 Basic principles in making a referral (page 2 of 2) 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Encourage caller to take initiative Have client write down information Give caller realistic information-limits Counseling referral Client may refuse counseling referral
Basic principles in making a referral (page 2 of 2) 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Encourage caller to take initiative Have client write down information Give caller realistic information-limits Counseling referral Client may refuse counseling referral
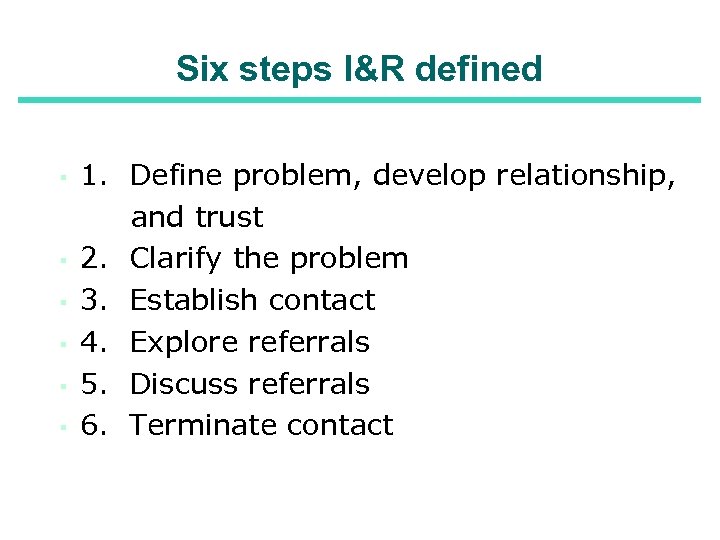 Six steps I&R defined ▪ ▪ ▪ 1. Define problem, develop relationship, and trust 2. Clarify the problem 3. Establish contact 4. Explore referrals 5. Discuss referrals 6. Terminate contact
Six steps I&R defined ▪ ▪ ▪ 1. Define problem, develop relationship, and trust 2. Clarify the problem 3. Establish contact 4. Explore referrals 5. Discuss referrals 6. Terminate contact
 From Common Ground Crisis Center 10 reasons for failures in communication 1. Pre-judgment ▪ 2. Jump to conclusions ▪ 3. Assume ▪ 4. Closed mind ▪ 5. Lack of attention ▪ 6. Wishful hearing ▪ 7. Different ▪ meanings ▪ 8. Talk too much ▪ 9. Lack empathy 10. Fear ▪
From Common Ground Crisis Center 10 reasons for failures in communication 1. Pre-judgment ▪ 2. Jump to conclusions ▪ 3. Assume ▪ 4. Closed mind ▪ 5. Lack of attention ▪ 6. Wishful hearing ▪ 7. Different ▪ meanings ▪ 8. Talk too much ▪ 9. Lack empathy 10. Fear ▪
 You are now ready ¡ Thanks for your hard work ¡ We know you will do well on the CIRS-A exam ¡ Please complete the training evaluation
You are now ready ¡ Thanks for your hard work ¡ We know you will do well on the CIRS-A exam ¡ Please complete the training evaluation
 Good I&A is performed by people who: ▪ ▪ 1. View the client with respect and dignity 2. Believe in self help 3. Work from good referral models 4. Take the time to find out what the client really is trying to resolve and help them explore ways to resolve or address their real problems (Refer to page 53)
Good I&A is performed by people who: ▪ ▪ 1. View the client with respect and dignity 2. Believe in self help 3. Work from good referral models 4. Take the time to find out what the client really is trying to resolve and help them explore ways to resolve or address their real problems (Refer to page 53)
 Active Listening ¡ Four cornerstones l Listening to feelings l Giving feedback l Being non-judgmental l Developing empathy
Active Listening ¡ Four cornerstones l Listening to feelings l Giving feedback l Being non-judgmental l Developing empathy
 Incorporate 8 specific Active Listening Skills Emotional labeling ¡ Reflecting ¡ Paraphrasing ¡ Effective pause ¡ Open-ended questions ¡ “I” message ¡ Consensual Validation ¡
Incorporate 8 specific Active Listening Skills Emotional labeling ¡ Reflecting ¡ Paraphrasing ¡ Effective pause ¡ Open-ended questions ¡ “I” message ¡ Consensual Validation ¡
 Patience and other noble qualities Some helpful phrases Pages 50 - 53 ▪ ▪ ▪ Some good open-ended questions “I” message from-- “I” feel (emotion) when you (behave) because (reason) Values Clarification (clarifying responses) Good termination statements ▸ ▸ ▸ For “normal” callers For “manipulative” callers For “abusive or angry” callers
Patience and other noble qualities Some helpful phrases Pages 50 - 53 ▪ ▪ ▪ Some good open-ended questions “I” message from-- “I” feel (emotion) when you (behave) because (reason) Values Clarification (clarifying responses) Good termination statements ▸ ▸ ▸ For “normal” callers For “manipulative” callers For “abusive or angry” callers
 Ten Basic Rules for Good I&A Listening (Page 53) ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Don’t be judgmental Don’t give personal information to callers Don’t talk about I&A calls or callers outside of I&A Don’t accept responsibility for a caller’s Action Don’t do anything for callers that they can do for themselves
Ten Basic Rules for Good I&A Listening (Page 53) ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Don’t be judgmental Don’t give personal information to callers Don’t talk about I&A calls or callers outside of I&A Don’t accept responsibility for a caller’s Action Don’t do anything for callers that they can do for themselves
 Ten Basic Rules for Good I&A Listening continued (Page 53) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Don’t hesitate to set firm limits on callers when it is needed Don’t leave the I&A room upset by a call or a caller - talk it out with designated staff Do terminate immediately when it is called for DO NOT use active listening skill on every call Do use the staff as your support system
Ten Basic Rules for Good I&A Listening continued (Page 53) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Don’t hesitate to set firm limits on callers when it is needed Don’t leave the I&A room upset by a call or a caller - talk it out with designated staff Do terminate immediately when it is called for DO NOT use active listening skill on every call Do use the staff as your support system
 10 Most Often Overlooked Benefits Make sure callers know about all services ▪ Medicaid ▪ Food Stamps ▪ ▪ ▪ Pharmacy Assistance Property Tax Relief Veterans Benefits ▪ Health Insurance Counseling ▪ State Veterans Benefits ▪ Weatherization ▪ Nutrition Services ▪ SSI
10 Most Often Overlooked Benefits Make sure callers know about all services ▪ Medicaid ▪ Food Stamps ▪ ▪ ▪ Pharmacy Assistance Property Tax Relief Veterans Benefits ▪ Health Insurance Counseling ▪ State Veterans Benefits ▪ Weatherization ▪ Nutrition Services ▪ SSI
 Thanks for participating ¡ ¡ All the materials needed for the CIRS-A exam have been reviewed and you are now ready for the CIRS -A certification exam. Thanks for the hard work.
Thanks for participating ¡ ¡ All the materials needed for the CIRS-A exam have been reviewed and you are now ready for the CIRS -A certification exam. Thanks for the hard work.


