6a4fd26eda67c7054f6083aa752e37d7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Circular Augmented Rotational Trajectory (CART) Shape Recognition & Curvature Estimation Presentation for 3 IA 2007 Russel Ahmed Apu & Dr. Marina Gavrilova Department of Computer Science University of Calgary
Circular Augmented Rotational Trajectory (CART) Shape Recognition & Curvature Estimation Presentation for 3 IA 2007 Russel Ahmed Apu & Dr. Marina Gavrilova Department of Computer Science University of Calgary
 Brief Outline o o o Motivation Shape Representation Problems with current approach o Proposed Approach (CART) R-Space Representation o Experimental Results o
Brief Outline o o o Motivation Shape Representation Problems with current approach o Proposed Approach (CART) R-Space Representation o Experimental Results o
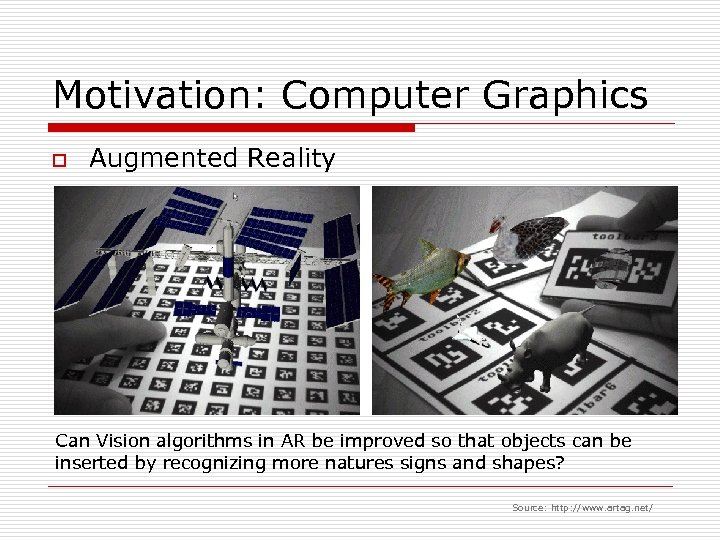 Motivation: Computer Graphics o Augmented Reality Can Vision algorithms in AR be improved so that objects can be inserted by recognizing more natures signs and shapes? Source: http: //www. artag. net/
Motivation: Computer Graphics o Augmented Reality Can Vision algorithms in AR be improved so that objects can be inserted by recognizing more natures signs and shapes? Source: http: //www. artag. net/
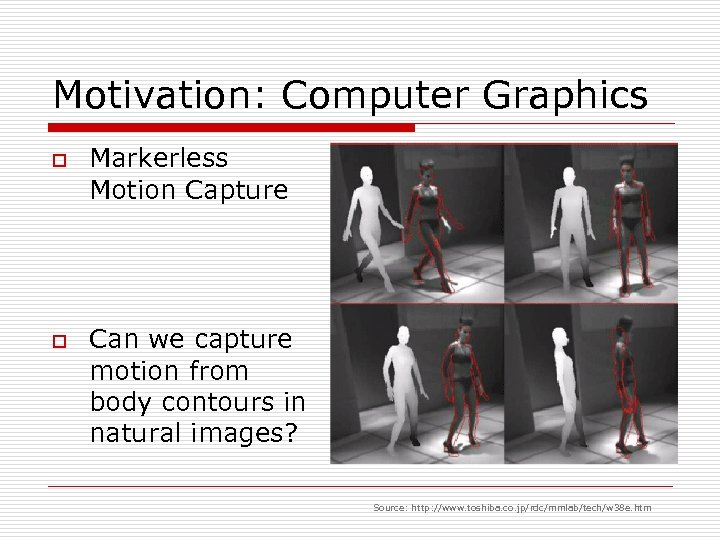 Motivation: Computer Graphics o o Markerless Motion Capture Can we capture motion from body contours in natural images? Source: http: //www. toshiba. co. jp/rdc/mmlab/tech/w 38 e. htm
Motivation: Computer Graphics o o Markerless Motion Capture Can we capture motion from body contours in natural images? Source: http: //www. toshiba. co. jp/rdc/mmlab/tech/w 38 e. htm
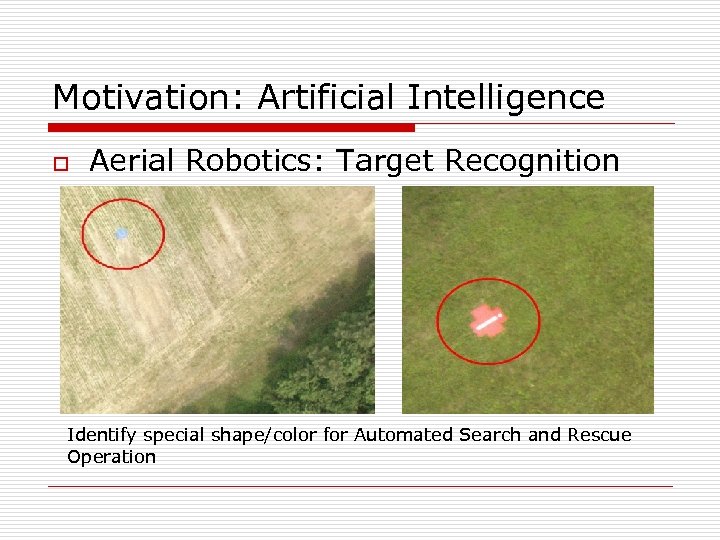 Motivation: Artificial Intelligence o Aerial Robotics: Target Recognition Identify special shape/color for Automated Search and Rescue Operation
Motivation: Artificial Intelligence o Aerial Robotics: Target Recognition Identify special shape/color for Automated Search and Rescue Operation
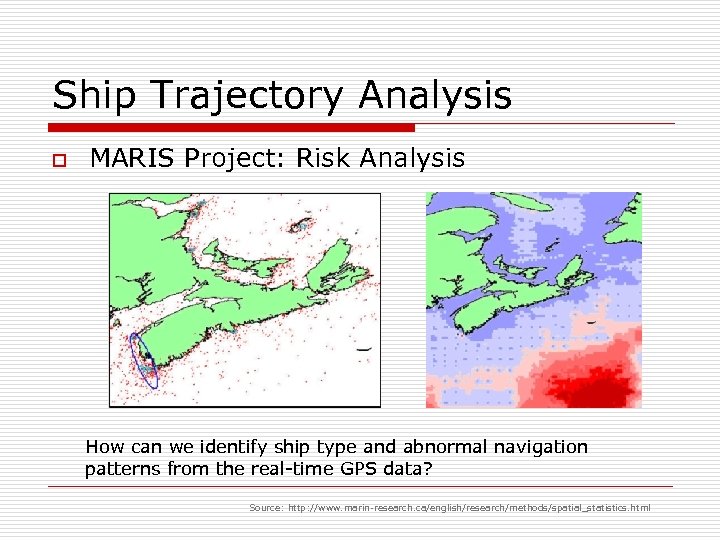 Ship Trajectory Analysis o MARIS Project: Risk Analysis How can we identify ship type and abnormal navigation patterns from the real-time GPS data? Source: http: //www. marin-research. ca/english/research/methods/spatial_statistics. html
Ship Trajectory Analysis o MARIS Project: Risk Analysis How can we identify ship type and abnormal navigation patterns from the real-time GPS data? Source: http: //www. marin-research. ca/english/research/methods/spatial_statistics. html
 Key Problems in the area o o o Extraction of Shapes/contours: n From noisy image with texture & clutters n Overlapped, broken, faded & occluded n Widely varying scale, rotation & transformation Representation & Interpretation of Shapes, Regions & Contours n Vector representation is much better than Raster (pixels) for interpretation n Contour Models: Spline, points, lines or graphs n Detection of invariant feature points Analysis & matching of Shapes n Shape matching and classification for distorted, transformed and often incomplete contour n Detecting geometric properties in shapes despite local noise
Key Problems in the area o o o Extraction of Shapes/contours: n From noisy image with texture & clutters n Overlapped, broken, faded & occluded n Widely varying scale, rotation & transformation Representation & Interpretation of Shapes, Regions & Contours n Vector representation is much better than Raster (pixels) for interpretation n Contour Models: Spline, points, lines or graphs n Detection of invariant feature points Analysis & matching of Shapes n Shape matching and classification for distorted, transformed and often incomplete contour n Detecting geometric properties in shapes despite local noise
 Current Approaches o Active Contour (i. e. Snakes) o Edge Detectors o Segmentation o Normalized-Cuts (and it’s variants) o Corner Detector (I. e. Sift) o Kalman Filter (For noisy contours) o Gausian filters, Haugh Transform etc.
Current Approaches o Active Contour (i. e. Snakes) o Edge Detectors o Segmentation o Normalized-Cuts (and it’s variants) o Corner Detector (I. e. Sift) o Kalman Filter (For noisy contours) o Gausian filters, Haugh Transform etc.
 Problem Complexity… o o o o Very difficult to extract shapes n Object Contour ≠Edges Effective methods are Computationally extensive Some methods such as Active Contour have erratic convergence Loss of detail in Kalman filter, Edge detector, Haugh transform etc. Others: Does not work well to “Classify” shapes Unable to cope with scale, rotation & distortion Unable to detect geometric signatures
Problem Complexity… o o o o Very difficult to extract shapes n Object Contour ≠Edges Effective methods are Computationally extensive Some methods such as Active Contour have erratic convergence Loss of detail in Kalman filter, Edge detector, Haugh transform etc. Others: Does not work well to “Classify” shapes Unable to cope with scale, rotation & distortion Unable to detect geometric signatures
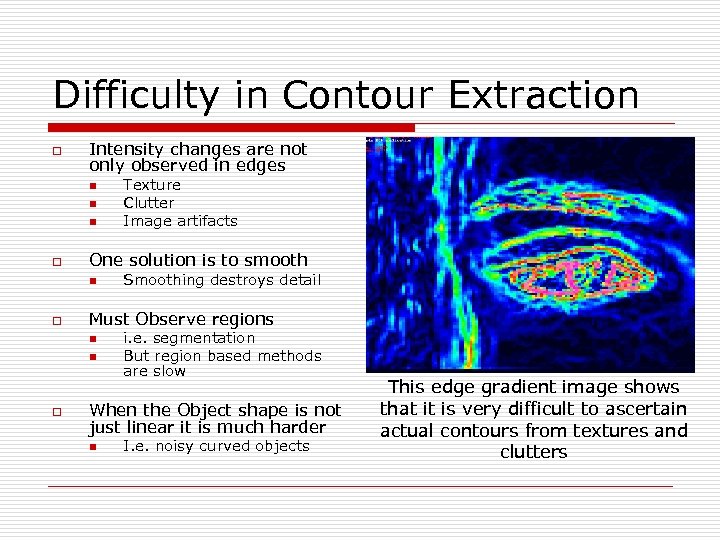 Difficulty in Contour Extraction o Intensity changes are not only observed in edges n n n o One solution is to smooth n o Smoothing destroys detail Must Observe regions n n o Texture Clutter Image artifacts i. e. segmentation But region based methods are slow When the Object shape is not just linear it is much harder n I. e. noisy curved objects This edge gradient image shows that it is very difficult to ascertain actual contours from textures and clutters
Difficulty in Contour Extraction o Intensity changes are not only observed in edges n n n o One solution is to smooth n o Smoothing destroys detail Must Observe regions n n o Texture Clutter Image artifacts i. e. segmentation But region based methods are slow When the Object shape is not just linear it is much harder n I. e. noisy curved objects This edge gradient image shows that it is very difficult to ascertain actual contours from textures and clutters
 Problem with current approaches o Active Contour (i. e. Snakes), Segmentation, Corner Detection are very slow to converge n Not practical in most applications such as Augmented Reality o Edge detection is neither robust nor sufficient o Haugh transform is only good for Straight line Features
Problem with current approaches o Active Contour (i. e. Snakes), Segmentation, Corner Detection are very slow to converge n Not practical in most applications such as Augmented Reality o Edge detection is neither robust nor sufficient o Haugh transform is only good for Straight line Features
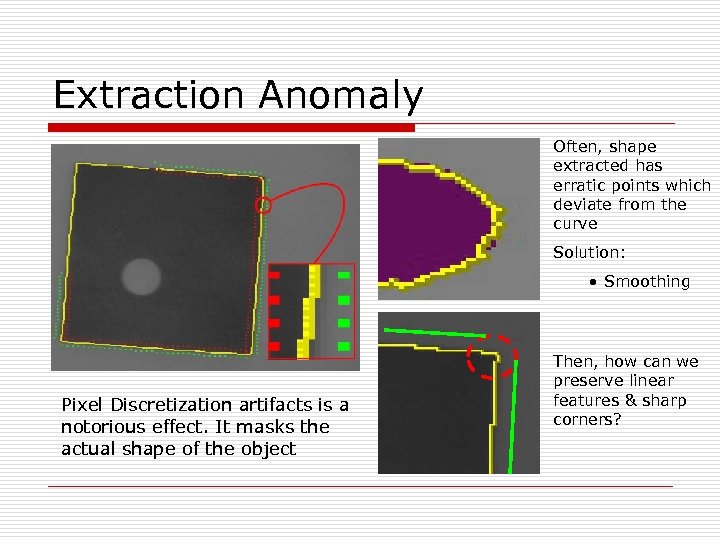 Extraction Anomaly Often, shape extracted has erratic points which deviate from the curve Solution: • Smoothing Pixel Discretization artifacts is a notorious effect. It masks the actual shape of the object Then, how can we preserve linear features & sharp corners?
Extraction Anomaly Often, shape extracted has erratic points which deviate from the curve Solution: • Smoothing Pixel Discretization artifacts is a notorious effect. It masks the actual shape of the object Then, how can we preserve linear features & sharp corners?
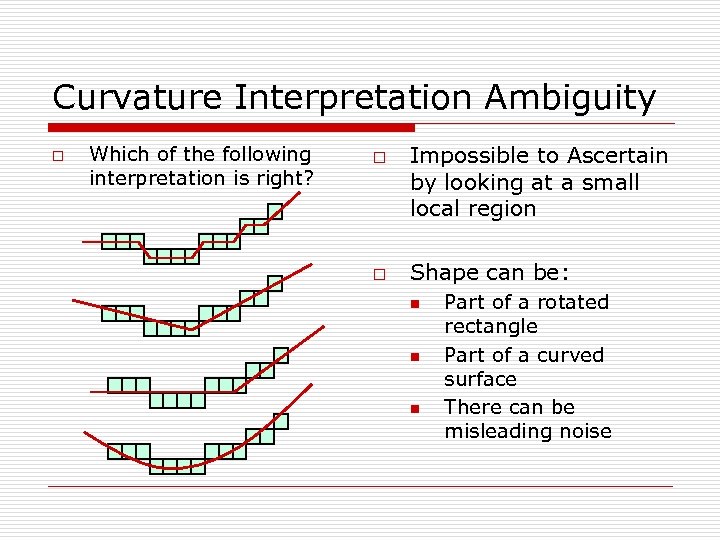 Curvature Interpretation Ambiguity o Which of the following interpretation is right? o o Impossible to Ascertain by looking at a small local region Shape can be: n n n Part of a rotated rectangle Part of a curved surface There can be misleading noise
Curvature Interpretation Ambiguity o Which of the following interpretation is right? o o Impossible to Ascertain by looking at a small local region Shape can be: n n n Part of a rotated rectangle Part of a curved surface There can be misleading noise
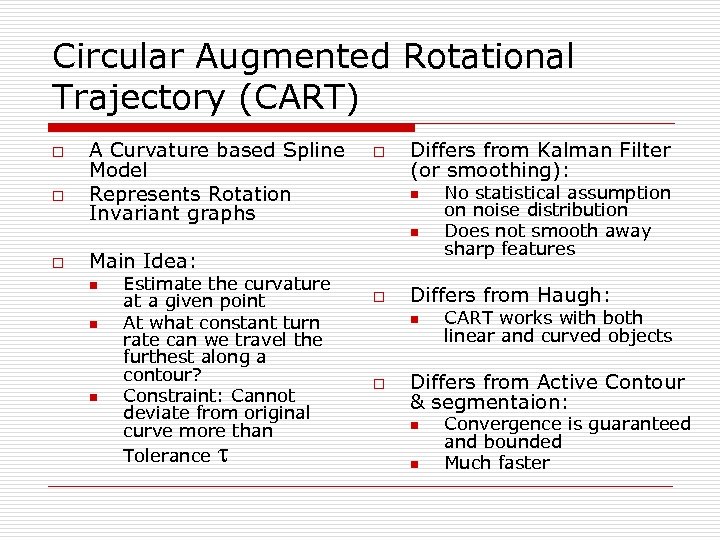 Circular Augmented Rotational Trajectory (CART) o o A Curvature based Spline Model Represents Rotation Invariant graphs o Differs from Kalman Filter (or smoothing): n n o Main Idea: n n n Estimate the curvature at a given point At what constant turn rate can we travel the furthest along a contour? Constraint: Cannot deviate from original curve more than Tolerance o Differs from Haugh: n o No statistical assumption on noise distribution Does not smooth away sharp features CART works with both linear and curved objects Differs from Active Contour & segmentaion: n n Convergence is guaranteed and bounded Much faster
Circular Augmented Rotational Trajectory (CART) o o A Curvature based Spline Model Represents Rotation Invariant graphs o Differs from Kalman Filter (or smoothing): n n o Main Idea: n n n Estimate the curvature at a given point At what constant turn rate can we travel the furthest along a contour? Constraint: Cannot deviate from original curve more than Tolerance o Differs from Haugh: n o No statistical assumption on noise distribution Does not smooth away sharp features CART works with both linear and curved objects Differs from Active Contour & segmentaion: n n Convergence is guaranteed and bounded Much faster
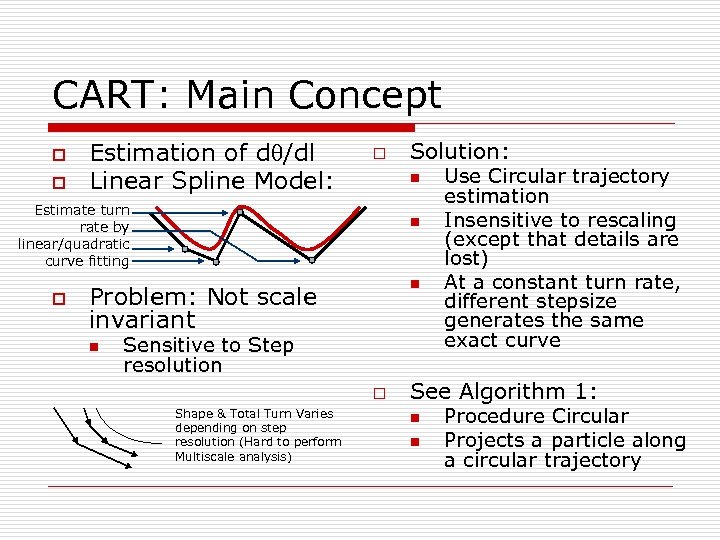 CART: Main Concept o o Estimation of d /dl Linear Spline Model: o n Estimate turn rate by linear/quadratic curve fitting o n n Problem: Not scale invariant n Solution: Sensitive to Step resolution o Shape & Total Turn Varies depending on step resolution (Hard to perform Multiscale analysis) Use Circular trajectory estimation Insensitive to rescaling (except that details are lost) At a constant turn rate, different stepsize generates the same exact curve See Algorithm 1: n n Procedure Circular Projects a particle along a circular trajectory
CART: Main Concept o o Estimation of d /dl Linear Spline Model: o n Estimate turn rate by linear/quadratic curve fitting o n n Problem: Not scale invariant n Solution: Sensitive to Step resolution o Shape & Total Turn Varies depending on step resolution (Hard to perform Multiscale analysis) Use Circular trajectory estimation Insensitive to rescaling (except that details are lost) At a constant turn rate, different stepsize generates the same exact curve See Algorithm 1: n n Procedure Circular Projects a particle along a circular trajectory
 Rotation Estimation o Define A Score n n o o o Score=
Rotation Estimation o Define A Score n n o o o Score=
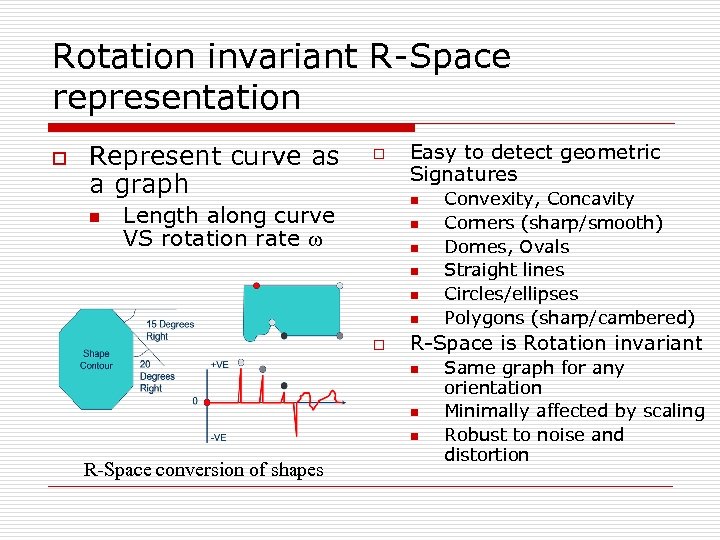 Rotation invariant R-Space representation o Represent curve as a graph n o Easy to detect geometric Signatures n Length along curve VS rotation rate n n n o R-Space is Rotation invariant n n n R-Space conversion of shapes Convexity, Concavity Corners (sharp/smooth) Domes, Ovals Straight lines Circles/ellipses Polygons (sharp/cambered) Same graph for any orientation Minimally affected by scaling Robust to noise and distortion
Rotation invariant R-Space representation o Represent curve as a graph n o Easy to detect geometric Signatures n Length along curve VS rotation rate n n n o R-Space is Rotation invariant n n n R-Space conversion of shapes Convexity, Concavity Corners (sharp/smooth) Domes, Ovals Straight lines Circles/ellipses Polygons (sharp/cambered) Same graph for any orientation Minimally affected by scaling Robust to noise and distortion
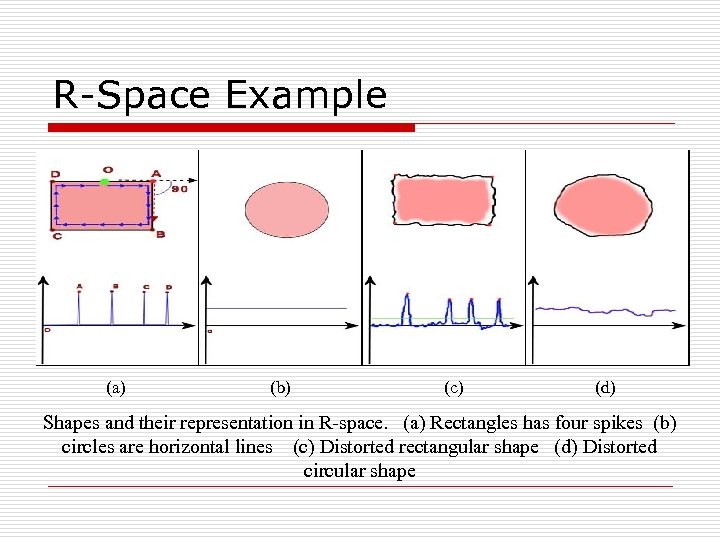 R-Space Example (a) (b) (c) (d) Shapes and their representation in R-space. (a) Rectangles has four spikes (b) circles are horizontal lines (c) Distorted rectangular shape (d) Distorted circular shape
R-Space Example (a) (b) (c) (d) Shapes and their representation in R-space. (a) Rectangles has four spikes (b) circles are horizontal lines (c) Distorted rectangular shape (d) Distorted circular shape
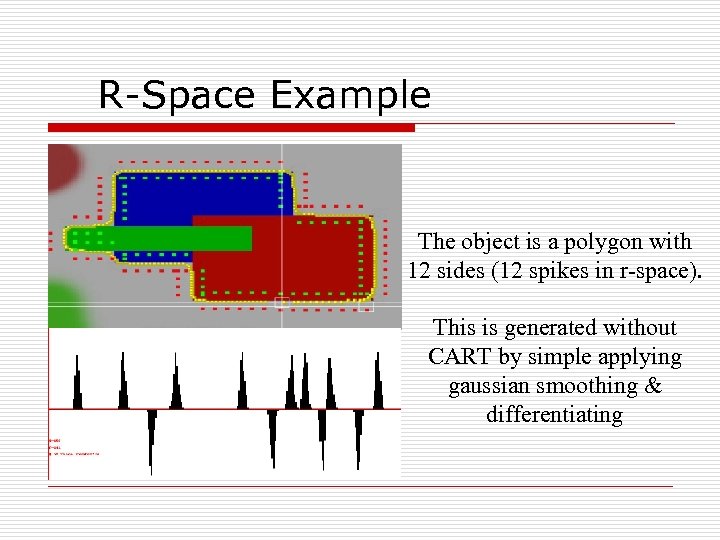 R-Space Example The object is a polygon with 12 sides (12 spikes in r-space). This is generated without CART by simple applying gaussian smoothing & differentiating
R-Space Example The object is a polygon with 12 sides (12 spikes in r-space). This is generated without CART by simple applying gaussian smoothing & differentiating
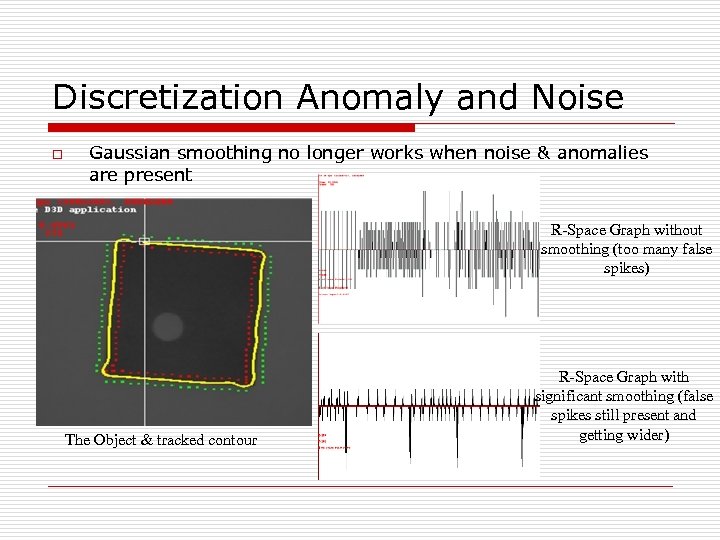 Discretization Anomaly and Noise o Gaussian smoothing no longer works when noise & anomalies are present R-Space Graph without smoothing (too many false spikes) The Object & tracked contour R-Space Graph with significant smoothing (false spikes still present and getting wider)
Discretization Anomaly and Noise o Gaussian smoothing no longer works when noise & anomalies are present R-Space Graph without smoothing (too many false spikes) The Object & tracked contour R-Space Graph with significant smoothing (false spikes still present and getting wider)
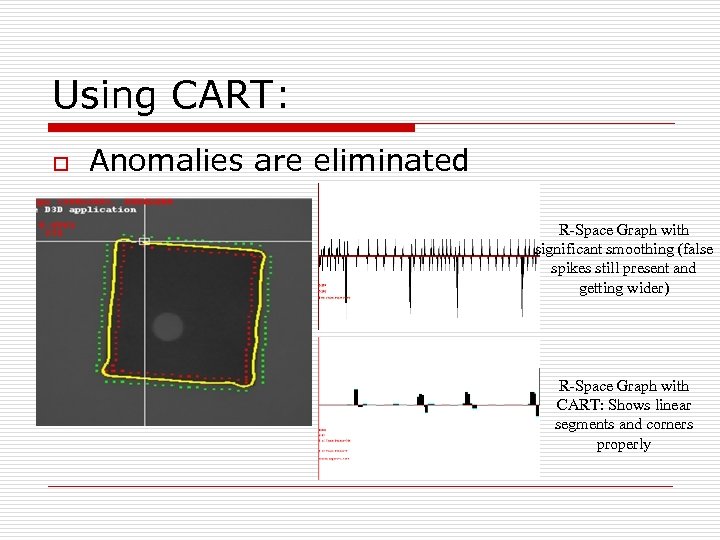 Using CART: o Anomalies are eliminated R-Space Graph with significant smoothing (false spikes still present and getting wider) R-Space Graph with CART: Shows linear segments and corners properly
Using CART: o Anomalies are eliminated R-Space Graph with significant smoothing (false spikes still present and getting wider) R-Space Graph with CART: Shows linear segments and corners properly
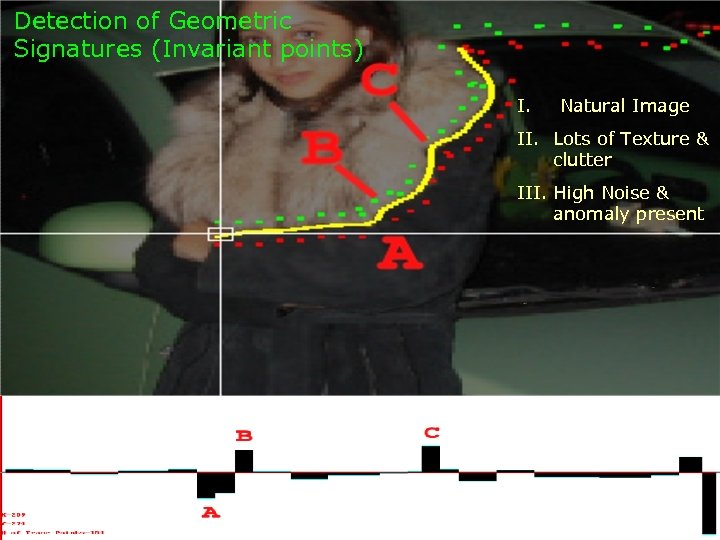 Detection of Geometric Signatures (Invariant points) I. Natural Image II. Lots of Texture & clutter III. High Noise & anomaly present
Detection of Geometric Signatures (Invariant points) I. Natural Image II. Lots of Texture & clutter III. High Noise & anomaly present
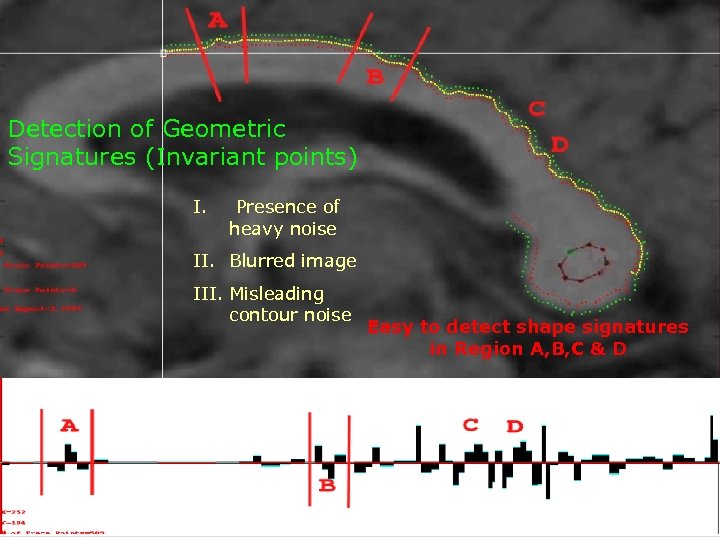 Detection of Geometric Signatures (Invariant points) I. Presence of heavy noise II. Blurred image III. Misleading contour noise Easy to detect shape signatures in Region A, B, C & D
Detection of Geometric Signatures (Invariant points) I. Presence of heavy noise II. Blurred image III. Misleading contour noise Easy to detect shape signatures in Region A, B, C & D
 Conclusion o o o o CART is simple and easy to implement Very efficient and fast compared to other methods Robust convergence & result Robust to Noise & discretization error Allow detection of Corners and other unique geometric signatures Allow Geometric analysis (Convexity, linearity, global curvature etc. ) Invariant to rotation and scaling Minimally affected by other distortions & transformations
Conclusion o o o o CART is simple and easy to implement Very efficient and fast compared to other methods Robust convergence & result Robust to Noise & discretization error Allow detection of Corners and other unique geometric signatures Allow Geometric analysis (Convexity, linearity, global curvature etc. ) Invariant to rotation and scaling Minimally affected by other distortions & transformations
 Thank you : ) Questions & inquiries?
Thank you : ) Questions & inquiries?


