16fae9b889f097004e552cf5348403cc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 CIM as an Enterprise Tool at Pacifi. Corp Randy Rhodes EMS User Group Conference September 25, 2007
CIM as an Enterprise Tool at Pacifi. Corp Randy Rhodes EMS User Group Conference September 25, 2007
 Agenda – Company Background – Case Studies Close to the Control Center 4 Elsewhere in the Enterprise 4 © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 2 – Pacifi. Corp’s CIM “Scorecard” – Lessons Learned – Future Plans
Agenda – Company Background – Case Studies Close to the Control Center 4 Elsewhere in the Enterprise 4 © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 2 – Pacifi. Corp’s CIM “Scorecard” – Lessons Learned – Future Plans
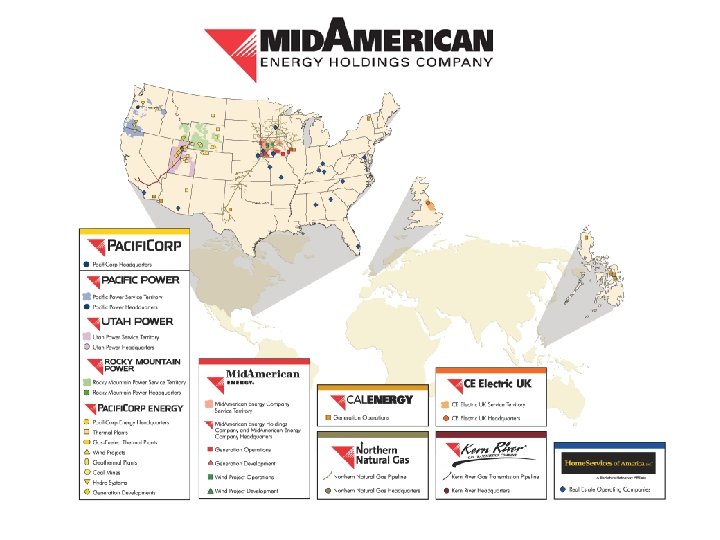
 Key Facts about Pacifi. Corp – Headquarters in Portland, Oregon – 1. 67 million customers in six states – 15, 622 miles of transmission line, 58, 360 miles of distribution line, 900 substations – Three divisions: 4 4 4 Pacific Power – Oregon, Washington and California Rocky Mountain Power – Utah, Wyoming and Idaho Pacifi. Corp Energy – generation and mining – Owned by Mid-American Energy Holdings Company (MEHC) © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 3 • 69 generating plants across West; net capability of 9, 140 MW
Key Facts about Pacifi. Corp – Headquarters in Portland, Oregon – 1. 67 million customers in six states – 15, 622 miles of transmission line, 58, 360 miles of distribution line, 900 substations – Three divisions: 4 4 4 Pacific Power – Oregon, Washington and California Rocky Mountain Power – Utah, Wyoming and Idaho Pacifi. Corp Energy – generation and mining – Owned by Mid-American Energy Holdings Company (MEHC) © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 3 • 69 generating plants across West; net capability of 9, 140 MW
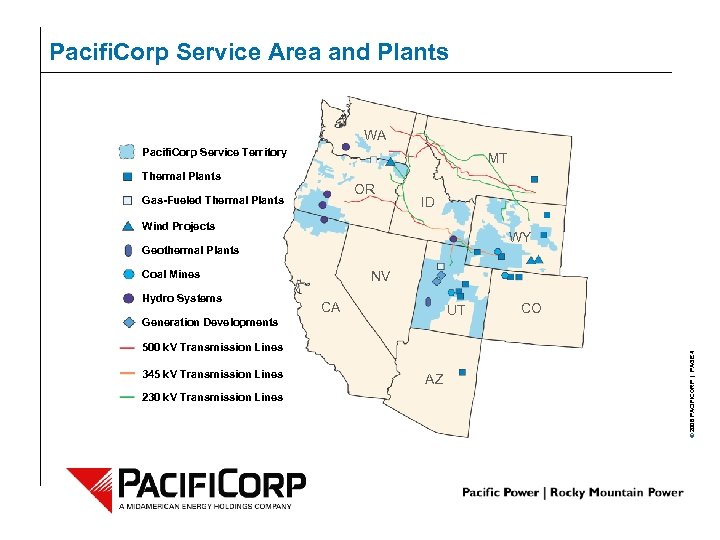 Pacifi. Corp Service Area and Plants WA Pacifi. Corp Service Territory MT Thermal Plants OR Gas-Fueled Thermal Plants ID Wind Projects WY Geothermal Plants NV Hydro Systems CA UT Generation Developments 500 k. V Transmission Lines 345 k. V Transmission Lines 230 k. V Transmission Lines AZ CO © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 4 Coal Mines
Pacifi. Corp Service Area and Plants WA Pacifi. Corp Service Territory MT Thermal Plants OR Gas-Fueled Thermal Plants ID Wind Projects WY Geothermal Plants NV Hydro Systems CA UT Generation Developments 500 k. V Transmission Lines 345 k. V Transmission Lines 230 k. V Transmission Lines AZ CO © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 4 Coal Mines
 CIM is Pacifi. Corp’s Integration Strategy – Pacifi. Corp is successfully using CIM to design both interfaces and databases 4 4 4 CIM was adopted in 1999 as Pacifi. Corp’s application integration standard Used for both messaging and database design for new projects Existing interfaces are reworked when the need arises – CIM-based integration viewed internally as “Best Practice” 4 4 Having a common vocabulary reduces semantic misinterpretation Reusing messages minimizes integration costs Minimal knowledge of internal application designs required – CIM is here to stay 4 4 CIM is standard design practice Pacifi. Corp vendors are getting used to the idea © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 6 4
CIM is Pacifi. Corp’s Integration Strategy – Pacifi. Corp is successfully using CIM to design both interfaces and databases 4 4 4 CIM was adopted in 1999 as Pacifi. Corp’s application integration standard Used for both messaging and database design for new projects Existing interfaces are reworked when the need arises – CIM-based integration viewed internally as “Best Practice” 4 4 Having a common vocabulary reduces semantic misinterpretation Reusing messages minimizes integration costs Minimal knowledge of internal application designs required – CIM is here to stay 4 4 CIM is standard design practice Pacifi. Corp vendors are getting used to the idea © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 6 4
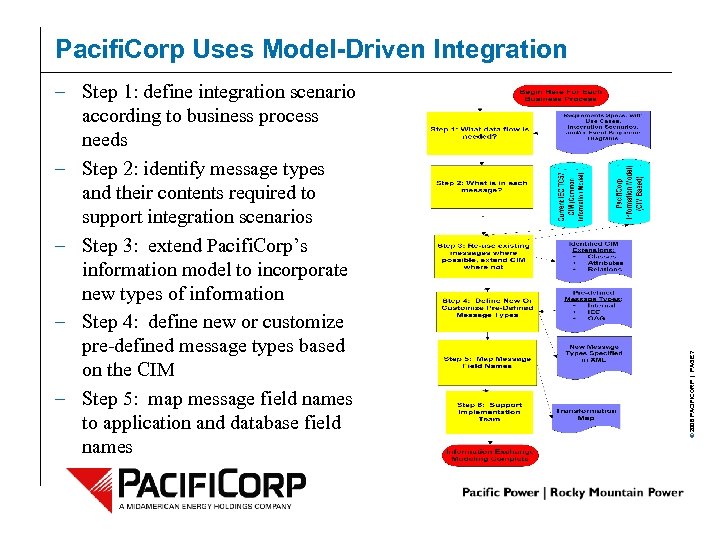 – Step 1: define integration scenario according to business process needs – Step 2: identify message types and their contents required to support integration scenarios – Step 3: extend Pacifi. Corp’s information model to incorporate new types of information – Step 4: define new or customize pre-defined message types based on the CIM – Step 5: map message field names to application and database field names © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 7 Pacifi. Corp Uses Model-Driven Integration
– Step 1: define integration scenario according to business process needs – Step 2: identify message types and their contents required to support integration scenarios – Step 3: extend Pacifi. Corp’s information model to incorporate new types of information – Step 4: define new or customize pre-defined message types based on the CIM – Step 5: map message field names to application and database field names © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 7 Pacifi. Corp Uses Model-Driven Integration
 CIM Implementation Examples – Case Studies Discussed Today 4 4 4 Handling Customer IVR and Outage Calls (ABB CADOPS) Managing Substation and Circuit Load History (OSIsoft PI) Managing EMS Network Model (ABB Network Manager) 4 4 4 Billing Wholesale Transmission Transactions (TWBS) Scheduling Single-Person Work (SPS) Providing Enterprise Reports (Data Warehouse) Trading and Risk Management (K 2) Monitoring Application Activity for SOX (Trip. Wire) Retail Access © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 8 – Other Implementation Examples
CIM Implementation Examples – Case Studies Discussed Today 4 4 4 Handling Customer IVR and Outage Calls (ABB CADOPS) Managing Substation and Circuit Load History (OSIsoft PI) Managing EMS Network Model (ABB Network Manager) 4 4 4 Billing Wholesale Transmission Transactions (TWBS) Scheduling Single-Person Work (SPS) Providing Enterprise Reports (Data Warehouse) Trading and Risk Management (K 2) Monitoring Application Activity for SOX (Trip. Wire) Retail Access © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 8 – Other Implementation Examples
 CIM for Outage-Related Customer Call Handling – Automated Call Handling 4 4 4 Customer account balance check Remote customer meter reading entry Customer outage calls between call center and dispatch applications 4 4 4 Customer phone number recognition between IVR and customer directory Outage detail lookup between IVR and CADOPS Outage detail lookup between GTx and CADOPS Outage creation between IVR, Trouble. UP, and CADOPS All communications between off-site third party provider (TFCC) and Pacifi. Corp are handled through the message bus All IVR steps are stored in IVR log for performance analysis – Much testing around performance and handling of large load © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 9 – Used CIM-based messaging to integrate:
CIM for Outage-Related Customer Call Handling – Automated Call Handling 4 4 4 Customer account balance check Remote customer meter reading entry Customer outage calls between call center and dispatch applications 4 4 4 Customer phone number recognition between IVR and customer directory Outage detail lookup between IVR and CADOPS Outage detail lookup between GTx and CADOPS Outage creation between IVR, Trouble. UP, and CADOPS All communications between off-site third party provider (TFCC) and Pacifi. Corp are handled through the message bus All IVR steps are stored in IVR log for performance analysis – Much testing around performance and handling of large load © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 9 – Used CIM-based messaging to integrate:
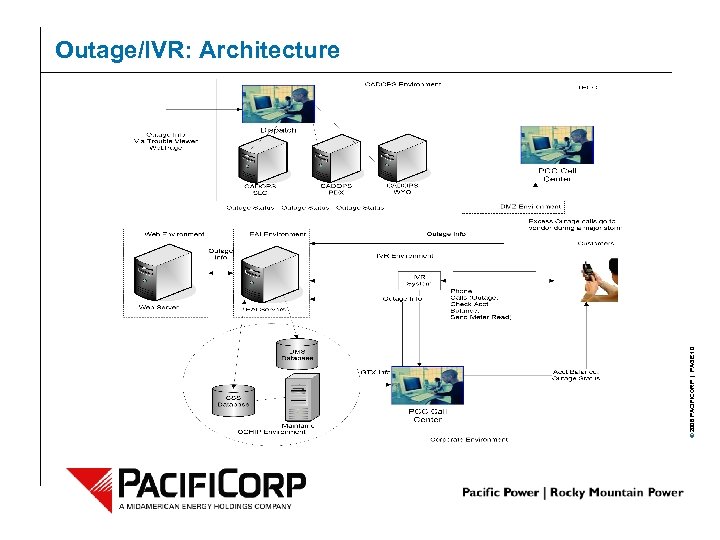 © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 10 Outage/IVR: Architecture
© 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 10 Outage/IVR: Architecture
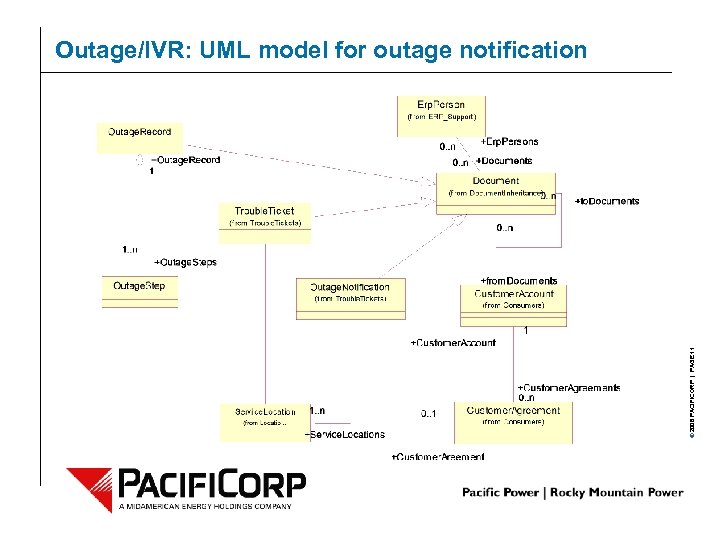 © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 11 Outage/IVR: UML model for outage notification
© 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 11 Outage/IVR: UML model for outage notification
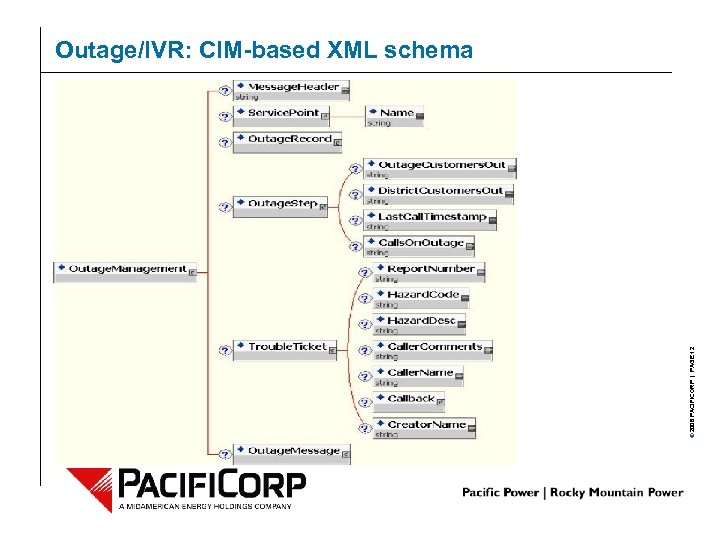 © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 12 Outage/IVR: CIM-based XML schema
© 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 12 Outage/IVR: CIM-based XML schema
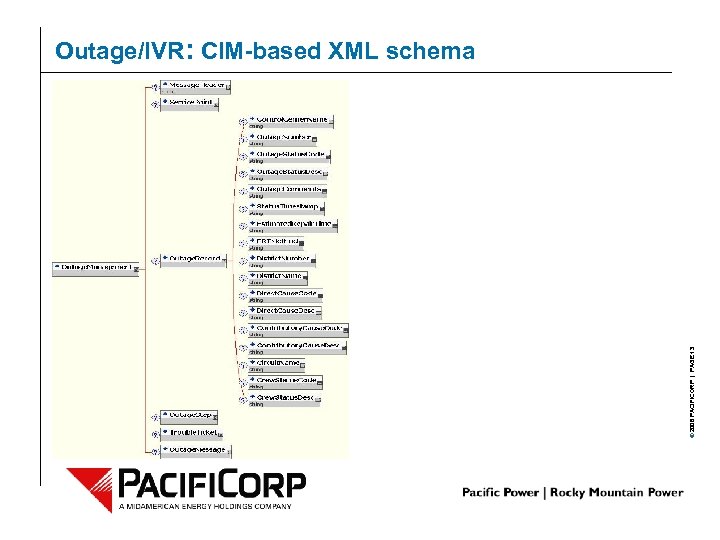 © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 13 Outage/IVR: CIM-based XML schema
© 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 13 Outage/IVR: CIM-based XML schema
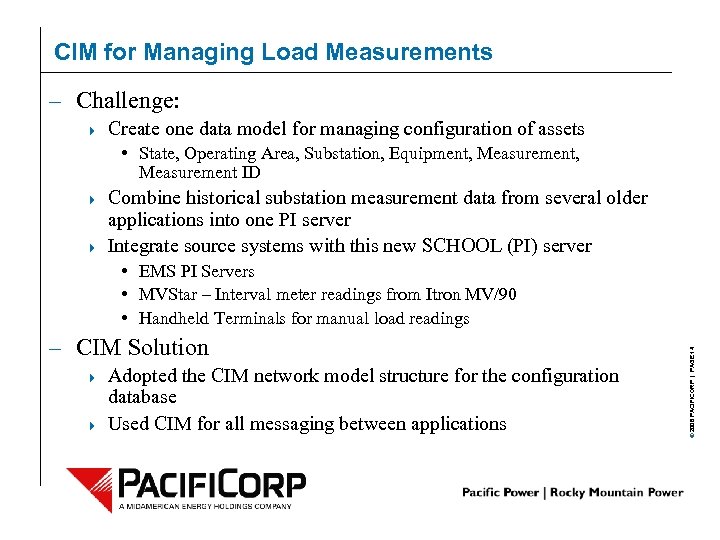 CIM for Managing Load Measurements – Challenge: 4 Create one data model for managing configuration of assets • State, Operating Area, Substation, Equipment, Measurement, Measurement ID 4 4 Combine historical substation measurement data from several older applications into one PI server Integrate source systems with this new SCHOOL (PI) server – CIM Solution 4 4 Adopted the CIM network model structure for the configuration database Used CIM for all messaging between applications © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 14 • EMS PI Servers • MVStar – Interval meter readings from Itron MV/90 • Handheld Terminals for manual load readings
CIM for Managing Load Measurements – Challenge: 4 Create one data model for managing configuration of assets • State, Operating Area, Substation, Equipment, Measurement, Measurement ID 4 4 Combine historical substation measurement data from several older applications into one PI server Integrate source systems with this new SCHOOL (PI) server – CIM Solution 4 4 Adopted the CIM network model structure for the configuration database Used CIM for all messaging between applications © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 14 • EMS PI Servers • MVStar – Interval meter readings from Itron MV/90 • Handheld Terminals for manual load readings
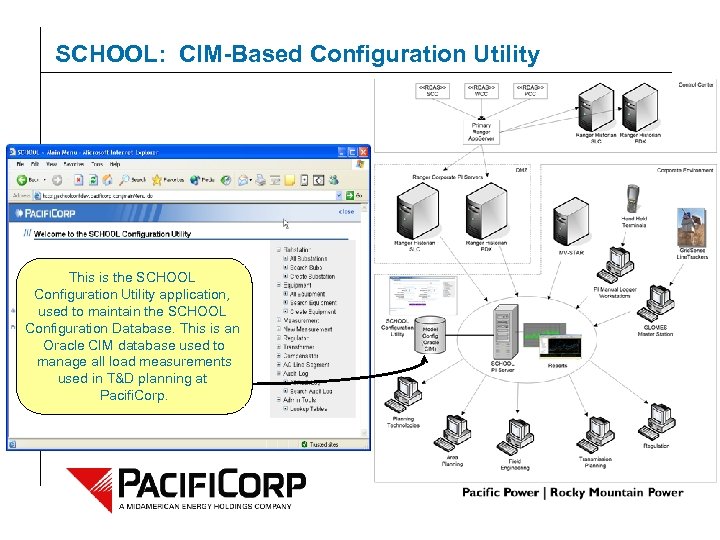 This is the SCHOOL Configuration Utility application, used to maintain the SCHOOL Configuration Database. This is an Oracle CIM database used to manage all load measurements used in T&D planning at Pacifi. Corp. © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 15 SCHOOL: CIM-Based Configuration Utility
This is the SCHOOL Configuration Utility application, used to maintain the SCHOOL Configuration Database. This is an Oracle CIM database used to manage all load measurements used in T&D planning at Pacifi. Corp. © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 15 SCHOOL: CIM-Based Configuration Utility
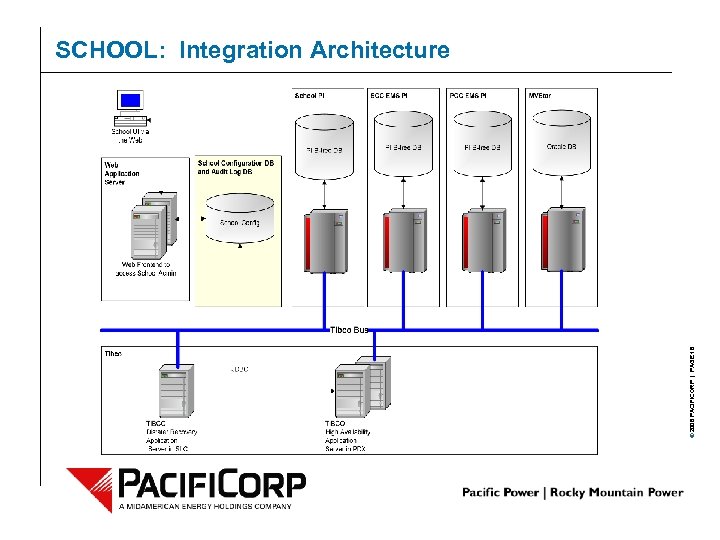 © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 16 SCHOOL: Integration Architecture
© 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 16 SCHOOL: Integration Architecture
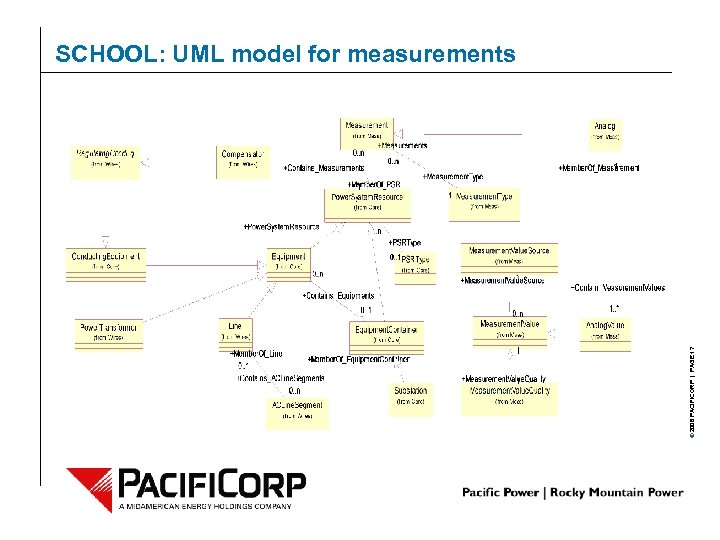 © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 17 SCHOOL: UML model for measurements
© 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 17 SCHOOL: UML model for measurements
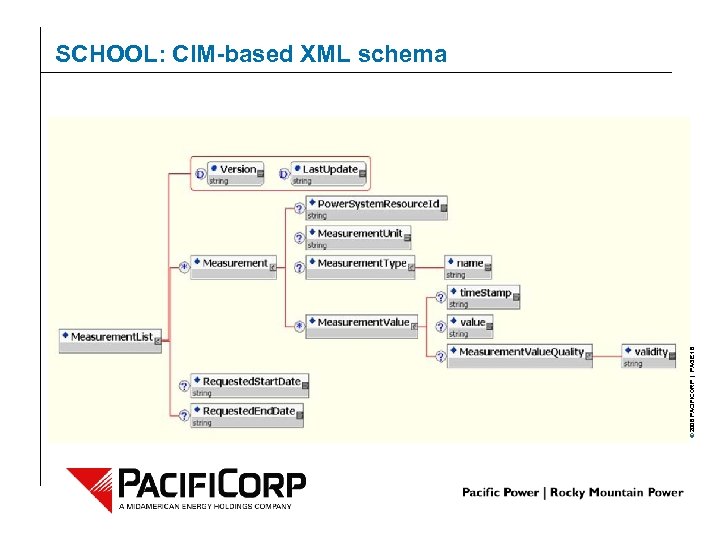 © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 18 SCHOOL: CIM-based XML schema
© 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 18 SCHOOL: CIM-based XML schema
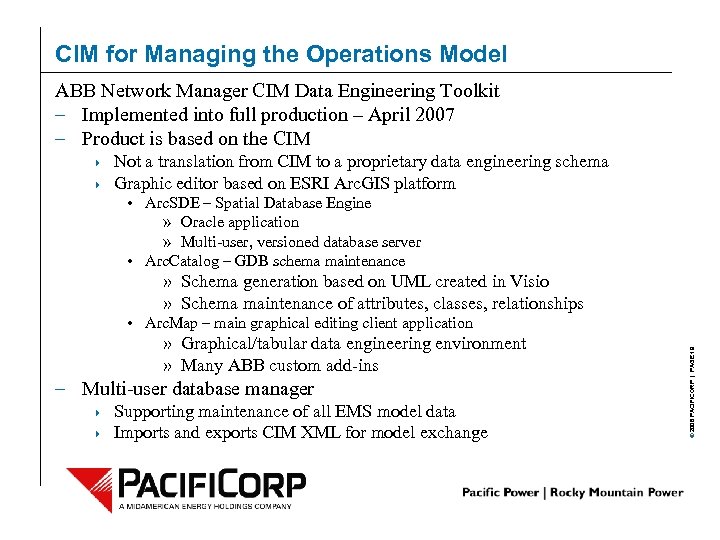 CIM for Managing the Operations Model ABB Network Manager CIM Data Engineering Toolkit – Implemented into full production – April 2007 – Product is based on the CIM 4 4 Not a translation from CIM to a proprietary data engineering schema Graphic editor based on ESRI Arc. GIS platform • Arc. SDE – Spatial Database Engine » Oracle application » Multi-user, versioned database server • Arc. Catalog – GDB schema maintenance » Schema generation based on UML created in Visio » Schema maintenance of attributes, classes, relationships » Graphical/tabular data engineering environment » Many ABB custom add-ins – Multi-user database manager 4 4 Supporting maintenance of all EMS model data Imports and exports CIM XML for model exchange © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 19 • Arc. Map – main graphical editing client application
CIM for Managing the Operations Model ABB Network Manager CIM Data Engineering Toolkit – Implemented into full production – April 2007 – Product is based on the CIM 4 4 Not a translation from CIM to a proprietary data engineering schema Graphic editor based on ESRI Arc. GIS platform • Arc. SDE – Spatial Database Engine » Oracle application » Multi-user, versioned database server • Arc. Catalog – GDB schema maintenance » Schema generation based on UML created in Visio » Schema maintenance of attributes, classes, relationships » Graphical/tabular data engineering environment » Many ABB custom add-ins – Multi-user database manager 4 4 Supporting maintenance of all EMS model data Imports and exports CIM XML for model exchange © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 19 • Arc. Map – main graphical editing client application
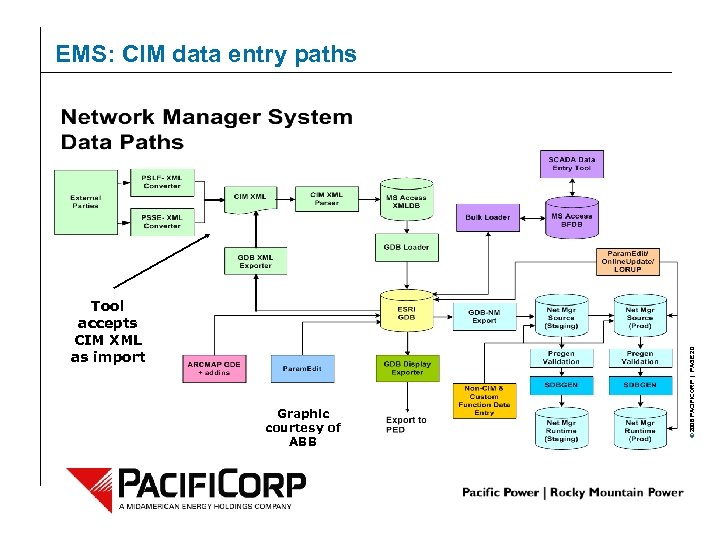 Tool accepts CIM XML as import Graphic courtesy of ABB © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 20 EMS: CIM data entry paths
Tool accepts CIM XML as import Graphic courtesy of ABB © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 20 EMS: CIM data entry paths
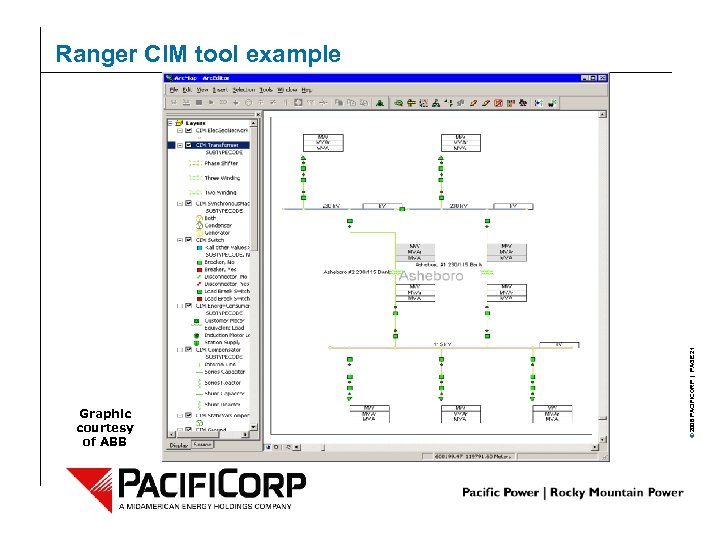 Graphic courtesy of ABB © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 21 Ranger CIM tool example
Graphic courtesy of ABB © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 21 Ranger CIM tool example
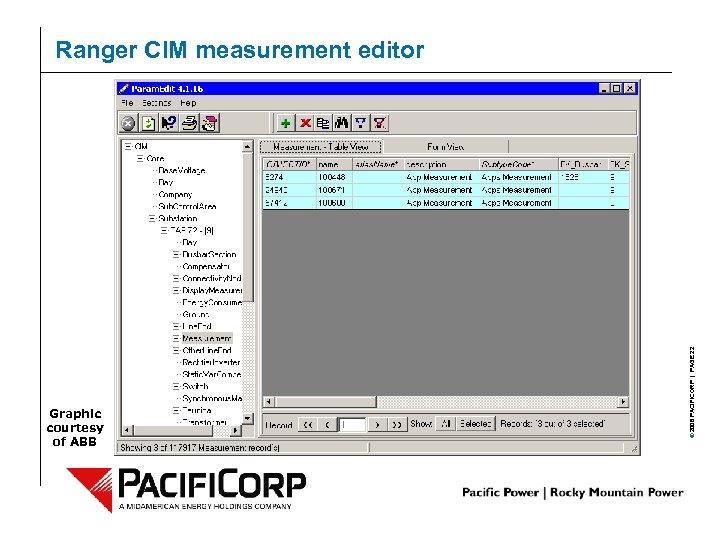 Graphic courtesy of ABB © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 22 Ranger CIM measurement editor
Graphic courtesy of ABB © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 22 Ranger CIM measurement editor
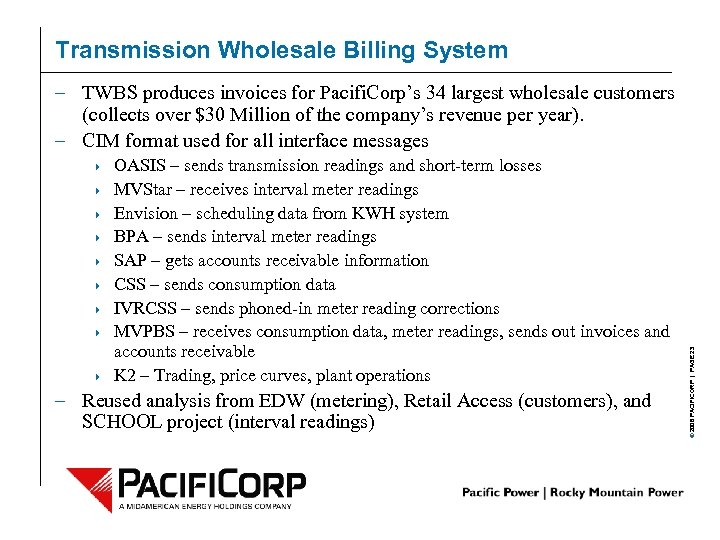 Transmission Wholesale Billing System 4 4 4 4 4 OASIS – sends transmission readings and short-term losses MVStar – receives interval meter readings Envision – scheduling data from KWH system BPA – sends interval meter readings SAP – gets accounts receivable information CSS – sends consumption data IVRCSS – sends phoned-in meter reading corrections MVPBS – receives consumption data, meter readings, sends out invoices and accounts receivable K 2 – Trading, price curves, plant operations – Reused analysis from EDW (metering), Retail Access (customers), and SCHOOL project (interval readings) © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 23 – TWBS produces invoices for Pacifi. Corp’s 34 largest wholesale customers (collects over $30 Million of the company’s revenue per year). – CIM format used for all interface messages
Transmission Wholesale Billing System 4 4 4 4 4 OASIS – sends transmission readings and short-term losses MVStar – receives interval meter readings Envision – scheduling data from KWH system BPA – sends interval meter readings SAP – gets accounts receivable information CSS – sends consumption data IVRCSS – sends phoned-in meter reading corrections MVPBS – receives consumption data, meter readings, sends out invoices and accounts receivable K 2 – Trading, price curves, plant operations – Reused analysis from EDW (metering), Retail Access (customers), and SCHOOL project (interval readings) © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 23 – TWBS produces invoices for Pacifi. Corp’s 34 largest wholesale customers (collects over $30 Million of the company’s revenue per year). – CIM format used for all interface messages
 Single Person Scheduling 4 4 4 Processing time lessened Complexity reduced No reusability © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 24 – A single person scheduling (SPS) system facilitates improved management of short duration, high volume single person work assignments. – CIM attribute names used for data attributes in repository data base – CIM attribute names used for data elements in simplified XML schema – Full CIM XML structure rejected by project
Single Person Scheduling 4 4 4 Processing time lessened Complexity reduced No reusability © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 24 – A single person scheduling (SPS) system facilitates improved management of short duration, high volume single person work assignments. – CIM attribute names used for data attributes in repository data base – CIM attribute names used for data elements in simplified XML schema – Full CIM XML structure rejected by project
 Enterprise Data Warehouse – CIM is the foundation for warehouse data structures – Areas implemented that made particular use of the CIM include the following: 4 4 Customer information from CSS Distribution work management from RCMS Customer metering Project financials © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 25 – Generic CIM names for entities and attributes should make integration with multiple source systems and replacement systems easier – Project issues around dates, other attributes
Enterprise Data Warehouse – CIM is the foundation for warehouse data structures – Areas implemented that made particular use of the CIM include the following: 4 4 Customer information from CSS Distribution work management from RCMS Customer metering Project financials © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 25 – Generic CIM names for entities and attributes should make integration with multiple source systems and replacement systems easier – Project issues around dates, other attributes
 Other Areas – Trading and Risk Management 4 4 Extensions were created for trading applications using both CIM and Financial Products Markup Language (FPML) All new trading application interfaces are designed with CIM and extensions • Forecasting (River, Plant Generation, etc. . . ) • Risk Management (Mark to Market) • Gas Management extensions will be next 4 Change. Audit. Report XSD created to publish changes to operating system and database. © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 26 – SOX
Other Areas – Trading and Risk Management 4 4 Extensions were created for trading applications using both CIM and Financial Products Markup Language (FPML) All new trading application interfaces are designed with CIM and extensions • Forecasting (River, Plant Generation, etc. . . ) • Risk Management (Mark to Market) • Gas Management extensions will be next 4 Change. Audit. Report XSD created to publish changes to operating system and database. © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 26 – SOX
 Retail Access – Oregon’s electric restructuring bill (SB 1149) for investor-owned utilities, implemented March 1, 2002 – Pacifi. Corp used CIM messaging for interfaces between Pacifi. Corp's Customer Information System and Itron interval meter reading system – XML schema developed used explicit structure names rather than repeating groups with type codes © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 27 – Extended CIM structure to include details of customer billing and energy service supplier
Retail Access – Oregon’s electric restructuring bill (SB 1149) for investor-owned utilities, implemented March 1, 2002 – Pacifi. Corp used CIM messaging for interfaces between Pacifi. Corp's Customer Information System and Itron interval meter reading system – XML schema developed used explicit structure names rather than repeating groups with type codes © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 27 – Extended CIM structure to include details of customer billing and energy service supplier
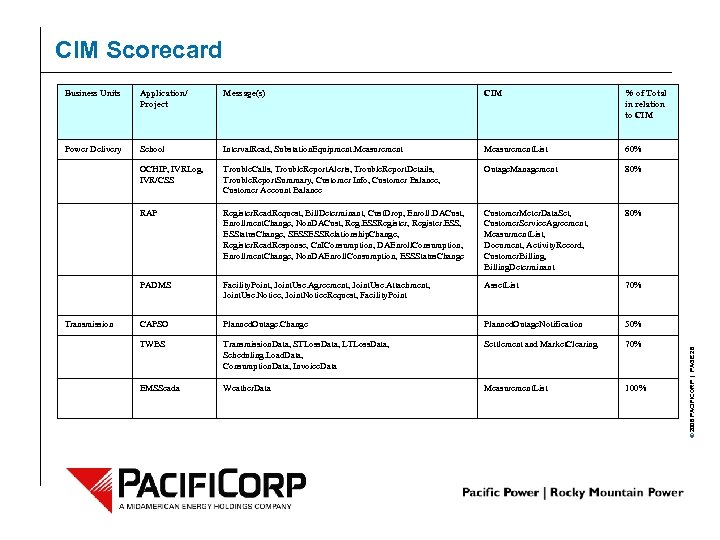 CIM Scorecard Application/ Project Message(s) CIM % of Total in relation to CIM Power Delivery School Interval. Read, Substation. Equipment. Measurement. List 60% OCHIP, IVRLog, IVR/CSS Trouble. Calls, Trouble. Report. Alerts, Trouble. Report. Details, Trouble. Report. Summary, Customer Info, Customer Balance, Customer Account Balance Outage. Management 80% RAP Register. Read. Request, Bill. Determinant, Cust. Drop, Enroll. DACust, Enrollment. Change, Non. DACust, Reg. ESSRegister, Register. ESS, ESStatus. Change, SESSESSRelationship. Change, Register. Read. Response, Cn. IConsumption, DAEnroll. Consumption, Enrollment. Change, Non. DAEnroll. Consumption, ESSStatus. Change Customer. Meter. Data. Set, Customer. Service. Agreement, Measurment. List, Document, Activity. Record, Customer. Billing, Billing. Determinant 80% PADMS Facility. Point, Joint. Use. Agreement, Joint. Use. Attachment, Joint. Use. Notice, Joint. Notice. Request, Facility. Point Asset. List 70% CAPSO Planned. Outage. Change Planned. Outage. Notification 50% TWBS Transmission. Data, STLoss. Data, LTLoss. Data, Scheduling. Load. Data, Consumption. Data, Invoice. Data Settlement and Market. Clearing 70% EMSScada Weather. Data Measurement. List 100% Transmission © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 28 Business Units
CIM Scorecard Application/ Project Message(s) CIM % of Total in relation to CIM Power Delivery School Interval. Read, Substation. Equipment. Measurement. List 60% OCHIP, IVRLog, IVR/CSS Trouble. Calls, Trouble. Report. Alerts, Trouble. Report. Details, Trouble. Report. Summary, Customer Info, Customer Balance, Customer Account Balance Outage. Management 80% RAP Register. Read. Request, Bill. Determinant, Cust. Drop, Enroll. DACust, Enrollment. Change, Non. DACust, Reg. ESSRegister, Register. ESS, ESStatus. Change, SESSESSRelationship. Change, Register. Read. Response, Cn. IConsumption, DAEnroll. Consumption, Enrollment. Change, Non. DAEnroll. Consumption, ESSStatus. Change Customer. Meter. Data. Set, Customer. Service. Agreement, Measurment. List, Document, Activity. Record, Customer. Billing, Billing. Determinant 80% PADMS Facility. Point, Joint. Use. Agreement, Joint. Use. Attachment, Joint. Use. Notice, Joint. Notice. Request, Facility. Point Asset. List 70% CAPSO Planned. Outage. Change Planned. Outage. Notification 50% TWBS Transmission. Data, STLoss. Data, LTLoss. Data, Scheduling. Load. Data, Consumption. Data, Invoice. Data Settlement and Market. Clearing 70% EMSScada Weather. Data Measurement. List 100% Transmission © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 28 Business Units
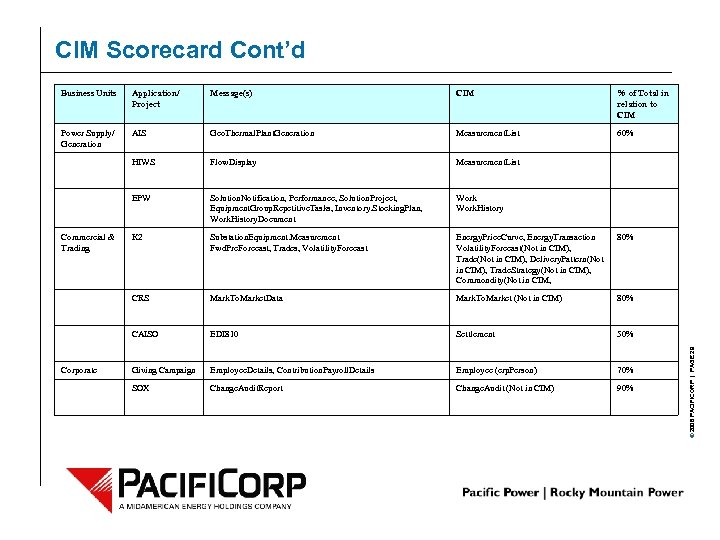 CIM Scorecard Cont’d Application/ Project Message(s) CIM % of Total in relation to CIM Power Supply/ Generation AIS Geo. Thermal. Plant. Generation Measurement. List 60% HIWS Flow. Display Measurement. List EPW Solution. Notification, Performance, Solution. Project, Equipment. Group. Repetitive. Tasks, Inventory. Stocking. Plan, Work. History. Document Work. History K 2 Substation. Equipment. Measurement Fwd. Prc. Forecast, Trades, Volatility. Forecast Energy. Price. Curve, Energy. Transaction Volatility. Forecast(Not in CIM), Trade(Not in CIM), Delivery. Pattern(Not in CIM), Trade. Strategy(Not in CIM), Commondity(Not in CIM, 80% CRS Mark. To. Market. Data Mark. To. Market (Not in CIM) 80% CAISO EDI 810 Settlement 50% Giving Campaign Employee. Details, Contribution. Payroll. Details Employee (erp. Person) 70% SOX Change. Audit. Report Change. Audit (Not in CIM) 90% Commercial & Trading Corporate © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 29 Business Units
CIM Scorecard Cont’d Application/ Project Message(s) CIM % of Total in relation to CIM Power Supply/ Generation AIS Geo. Thermal. Plant. Generation Measurement. List 60% HIWS Flow. Display Measurement. List EPW Solution. Notification, Performance, Solution. Project, Equipment. Group. Repetitive. Tasks, Inventory. Stocking. Plan, Work. History. Document Work. History K 2 Substation. Equipment. Measurement Fwd. Prc. Forecast, Trades, Volatility. Forecast Energy. Price. Curve, Energy. Transaction Volatility. Forecast(Not in CIM), Trade(Not in CIM), Delivery. Pattern(Not in CIM), Trade. Strategy(Not in CIM), Commondity(Not in CIM, 80% CRS Mark. To. Market. Data Mark. To. Market (Not in CIM) 80% CAISO EDI 810 Settlement 50% Giving Campaign Employee. Details, Contribution. Payroll. Details Employee (erp. Person) 70% SOX Change. Audit. Report Change. Audit (Not in CIM) 90% Commercial & Trading Corporate © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 29 Business Units
 – CIM integration works well, especially for Power Delivery – Project work is reduced when the CIM data entities and relationships are mapped before detailed attribute modeling begins – Messages in XSD format are accessible and reusable – Project management: additional data modeling cost of CIM needs to be understood at PM level – Actual savings come from reuse, data clarity, and quality – CIM expertise currently resides in EAI group – Projects need modelers through unit testing – CIM compromises come back to haunt you – Retaining OO-savvy staff is a challenge © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 30 Lessons Learned
– CIM integration works well, especially for Power Delivery – Project work is reduced when the CIM data entities and relationships are mapped before detailed attribute modeling begins – Messages in XSD format are accessible and reusable – Project management: additional data modeling cost of CIM needs to be understood at PM level – Actual savings come from reuse, data clarity, and quality – CIM expertise currently resides in EAI group – Projects need modelers through unit testing – CIM compromises come back to haunt you – Retaining OO-savvy staff is a challenge © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 30 Lessons Learned
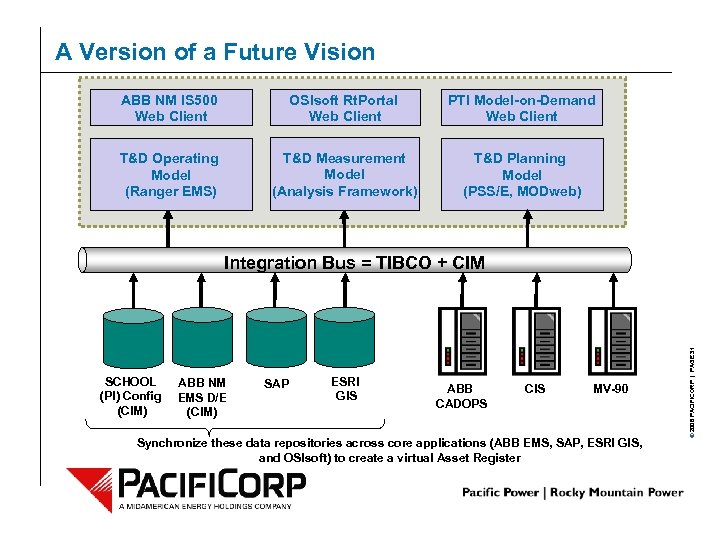 A Version of a Future Vision ABB NM IS 500 Web Client OSIsoft Rt. Portal Web Client PTI Model-on-Demand Web Client T&D Operating Model (Ranger EMS) T&D Measurement Model (Analysis Framework) T&D Planning Model (PSS/E, MODweb) SCHOOL (PI) Config (CIM) ABB NM EMS D/E (CIM) SAP ESRI GIS ABB CADOPS CIS MV-90 Synchronize these data repositories across core applications (ABB EMS, SAP, ESRI GIS, and OSIsoft) to create a virtual Asset Register © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 31 Integration Bus = TIBCO + CIM
A Version of a Future Vision ABB NM IS 500 Web Client OSIsoft Rt. Portal Web Client PTI Model-on-Demand Web Client T&D Operating Model (Ranger EMS) T&D Measurement Model (Analysis Framework) T&D Planning Model (PSS/E, MODweb) SCHOOL (PI) Config (CIM) ABB NM EMS D/E (CIM) SAP ESRI GIS ABB CADOPS CIS MV-90 Synchronize these data repositories across core applications (ABB EMS, SAP, ESRI GIS, and OSIsoft) to create a virtual Asset Register © 2006 PACIFICORP | PAGE 31 Integration Bus = TIBCO + CIM
 Questions? Randy. Rhodes@Pacifi. Corp. com
Questions? Randy. Rhodes@Pacifi. Corp. com


