4afd660d7cc12a3bae0e1b8ff9cf2dc5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69

CHRONOS 7 University of Antwerp September 19, 2006 Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality Sumiyo Nishiguchi Stony Brook University snishigu@ic. sunysb. edu http: //homepage 3. nifty. com/sumiyo_nishiguchi/ CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 1

Abstract past tense marker can be `fake’ i. e. , used without reference to past time in the context of: l The expressing speaker’s surprise l recalling something l seeing the fulfillment of expectations. l CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 2

(1)a. Oh, it was here (all along). b. A, koko-ni {at-ta/#a-ru}. Oh here-LOC be-PAST/be-PRES (Japanese) CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 3
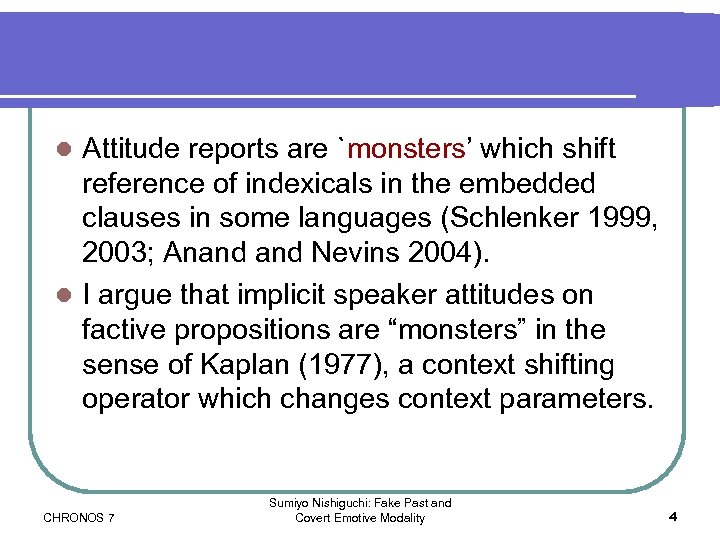
Attitude reports are `monsters’ which shift reference of indexicals in the embedded clauses in some languages (Schlenker 1999, 2003; Anand Nevins 2004). l I argue that implicit speaker attitudes on factive propositions are “monsters” in the sense of Kaplan (1977), a context shifting operator which changes context parameters. l CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 4

l. I base my argument on the mono-clausal fake past construction N. B. The terminology `fake' comes from Iatridou (2000). CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 5
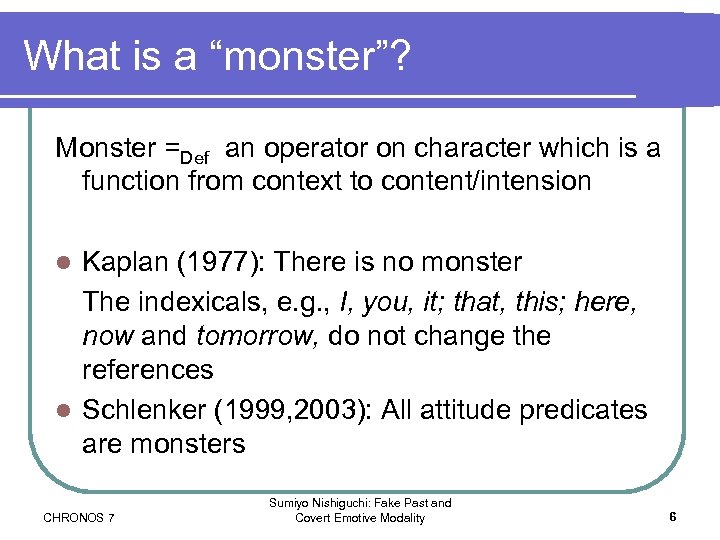
What is a “monster”? Monster =Def an operator on character which is a function from context to content/intension Kaplan (1977): There is no monster The indexicals, e. g. , I, you, it; that, this; here, now and tomorrow, do not change the references l Schlenker (1999, 2003): All attitude predicates are monsters l CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 6

Monster supporters: l Schlenker (1999, 2003): l l Attitude verbs quantify over contexts of thought or of speech. Attitude predicates are monsters that shift the references of indexicals. As evidence, Amharic first person pronoun shifts its reference into third person under attitude verbs Anand Nevins (2004): l CHRONOS 7 In Zazaki, the verb vano (say) shifts indexicals I, you, here and yesterday in its scope. Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 7

Strengthening limited evidence for monsters l All supporting arguments for monsters have been based on the indexical shift in embedded context under attitude predicates. l You need to have monsters in nonembedded contexts. CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 8

Mono-clausal factive sentences l The fake past construction is factive simple sentences (not embedded under attitude predicates) and temporal and parameter shifts. l I argue that speaker's emotion (surprise) -bouletic (in view of what I want) and epistemic speculative modality (in view of what I know, Kratzer 1991)- is a context shifting operator. CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 9
![Slave embedded clauses: (2) …say… […you…] I Fake past simple sentences: (3) COVERT MODAL Slave embedded clauses: (2) …say… […you…] I Fake past simple sentences: (3) COVERT MODAL](https://present5.com/presentation/4afd660d7cc12a3bae0e1b8ff9cf2dc5/image-10.jpg)
Slave embedded clauses: (2) …say… […you…] I Fake past simple sentences: (3) COVERT MODAL [ …PAST…] PRES CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 10
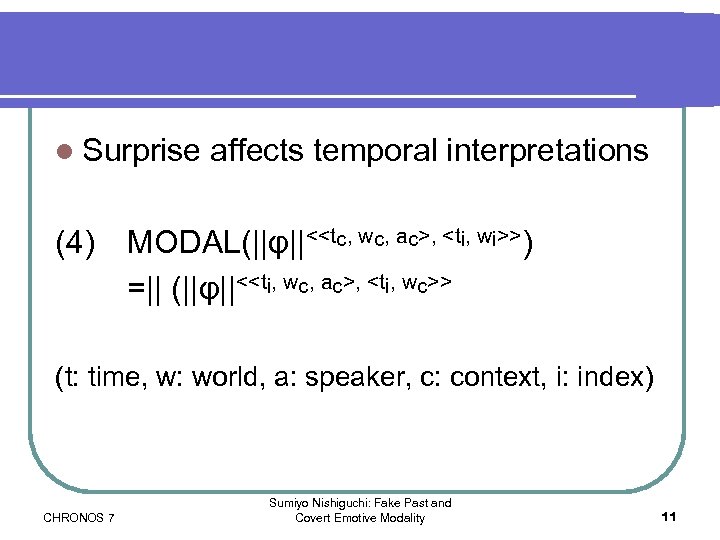
l Surprise (4) affects temporal interpretations MODAL(||φ||<<tc, wc, ac>, <ti, wi>>) =|| (||φ||<<ti, wc, ac>, <ti, wc>> (t: time, w: world, a: speaker, c: context, i: index) CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 11
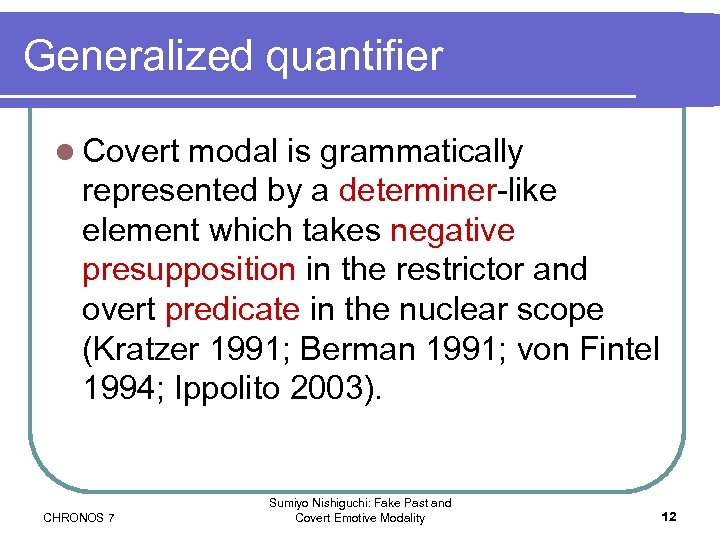
Generalized quantifier l Covert modal is grammatically represented by a determiner-like element which takes negative presupposition in the restrictor and overt predicate in the nuclear scope (Kratzer 1991; Berman 1991; von Fintel 1994; Ippolito 2003). CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 12

Fake Past CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 13

l The past tense marker can receive non-past interpretation when associated with discovery, fulfillment of expectation, recalling of a plan (Teramura 1984, among others) often as exclamatives. CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 14

Surprise (5)a. Oh, it was here (all along). b. A, koko-ni {at-ta/#a-ru}。 Oh here-LOC be-PAST/be-PRES (Japanese) CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 15

Cross-linguistic phenomena (6)a. Oh, the book was here (all along). b. Chek-i yogi iss-ot-ne. (Korean) book-NOM c. Waragat book here be-PAST-EXC all-a gaa ide. (Dasenach) place at sit-PAST ‘The book was sitting at this place’ CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 16

Recalling the future schedule (7) (8) I had a meeting next Monday. Mintian you-le wanyan. tomorrow have-PERF party ‘I had a party tomorrow’ (Mandarin) CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 17

Mismatched temporal adverbials (9) (10) (11) There was a party tomorrow. Mintian you-le wanyan. (Mandarin) tomorrow have-PERF party `I had a party tomorrow‘ Asu-wa Maria-no tanjobi-dat-ta. (Japanese) tomorrow-TOP Maria-GEN birthday-be-PAST `Tomorrow is Maria's birthday’ Antecedent of counterfactuals can (Ippolito 2003) (12) If it rained tomorrow, I would go shopping. l CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 18

The forgotten information (13) a. b What was your name? (Teramura 1982) Onamae-wa nan-deshi-ta-ka. Name-TOP (14) a. b. Where did you live? Osumai-wa dochira-deshi-ta-ka-ne. residence-TOP CHRONOS 7 what-HON-PAST-Q where-HON-PAST-Q-PAR Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 19

The past tense refers to present, not simple past, with surprise (15)# Oh, the book was here. But it is not here anymore. (16) # A, shinbun-ga koko-ni at-ta. Oh newspaper-NOM here-LOC be-PAST Demo ima-wa mo nai. but now-TOP already NEG `Oh, the newspaper was here. But it's not here anymore' CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 20

Fake Past and Aktionsarten: English: Stative predicates (17) Oh, it was here (all along). * Eventive predicates (18) Oh, the bus {#came/is coming}. CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 21

Stative predicates Japanese/Korean: (19) A, koko-ni Oh here-LOC at-ta/#a-ru. (Japanese) be-PAST/be-PRES `Oh, it was here‘ (20) Chek-i yogi iss-ot-ne. (Korean) book-NOM here be-PAST-EXC `Oh, the was here' CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 22

Eventive predicates (21) Basu-ga ki-ta. (Japanese) bus-NOM come-PAST `The bus is coming‘ CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 23

(22) a. CHRONOS 7 prisho-l. bus b. Avtobus (Russian) come-PAST ‘The bus is coming’ # Avtobus prihodit. bus come-PRES ‘The bus comes’ Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 24

(23) Ya ush-la. (Russian) I go-PAST `I am leaving‘ CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 25

Inchoative Japanese inchoative verbs that bring change of states (24) A, warat-ta. l oh smile-PAST ‘Oh, (the baby) is smiling (=started to smile)’ (25) A, hikoki-ga ton-da. (Japanese) Oh airplane-NOM fly-PAST ‘Oh, the airplane is flying’ CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 26

(26) Shimat-ta. close-PAST ‘Oh, no’ CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 27

Adjectives (individual level) (27) Yo-kat-ta. (Japanese) good-be-PAST ‘Thank goodness’ (when a lost wallet was returned with money) (28) (Ao-to omot-tei-tara) kuro-dat-ta blue-COMP think-PROG-then black-be-PAST ‘(I thought it was blue but) it was black’ CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 28

Achievement verbs l Achievement verbs (Vendler 1967) e. g. , come, arrive at, get wet give non-past interpretations CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 29

*Accomplishment verbs, e. g. , build a house, and draw a circle are unnatural with the nonpast reading: (29) a. #A, Taro-ga ie-o tate-ta. l oh b. house-ACC build-PAST ‘Oh, Taro is building a house’ #A, Taro-ga jukkiro hashit-ta. oh CHRONOS 7 Taro-NOM 10 km ‘Oh, Taro is running 10 km’ Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality run-PAST 30

Typical fake past predicates l Copular stage level predicates CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 31

Pragmatic explanation on aktionsarten l Stative/*eventive -It is more surprising to find existence of something than perceiving events. CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 32

l Achievement/*accomplishment -Normally, surprise is caused by perceiving the momentous events or change of states. Long-term processes would not surprise us instantly. Achievement verbs such as come or become wet surprise us while gradual accomplishment, e. g. , build a house and running ten miles, are not so astonishing naturally. CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 33

Unaccusativity and surprise l Fake past predicates are mostly limited to unaccusative verbs such as be, exist, and come (cf. Kusumoto 2001; Ogihara 2004 for relative clauses). CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 34

Unaccusativity test VP internal numerals associate with the surface subject (mutual c-command in base position) (Miyagawa and Babyonyshev 2004): Transitive verb: (30) *Gakusei-ga [VP hon-o san-nin kat]-ta. l Students-NOM book-ACC `Three students bought a book’ CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 3 -CL buy-PAST 35
![(31)Honi-ga [VPtsukue-no ue-ni ti ni-satsu at]-ta. book-NOM desk-GEN up-LOC 2 -CL be-PAST `There were (31)Honi-ga [VPtsukue-no ue-ni ti ni-satsu at]-ta. book-NOM desk-GEN up-LOC 2 -CL be-PAST `There were](https://present5.com/presentation/4afd660d7cc12a3bae0e1b8ff9cf2dc5/image-36.jpg)
(31)Honi-ga [VPtsukue-no ue-ni ti ni-satsu at]-ta. book-NOM desk-GEN up-LOC 2 -CL be-PAST `There were two books on the desk’ (32)Basu-ga [VP ekimae-ni ti ni-dai ki]-ta. bus-NOM station-front-LOC 2 -CL come-PAST `Two buses came in front of the station’ CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 36

(33) A, warat-ta. oh smile-Past `Oh, (the baby) is smiling’ (33)’ A, [gakuseii-ga butai-de ti san-nin warat]-ta. oh student-NOM stage-LOC 3 -CL smile-PAST `Oh, the three students laughed on the stage’ CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 37

(34) Shimat-t-a. close-PAST-be `Oh, no‘ (34)’ *Gakuseii-ga mae-de ti san-nin shimat-ta. student-NOM front-LOC 3 -CL close-PAST `The three students made a mistake in front’ CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 38

Unaccusativity contributes to surprise Unaccusative verbs 1. Representational verbs be, exist, come 2. Verbs of posture sit… l The nature of unaccusative predicates contributes to surprise l Finding existence and appearance is likely to cause more astonishment than finding transitive predicates CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 39

Puzzle l Why is the past tense used for non-past? (1) Oh, it was here (all along). CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 40

Fake past as a counterfactual morpheme Counterfactual conditional: (35) If it rained tomorrow, I would go to Florida (but it is not likely). l Topic worlds and the actual world differ Simple fake past: (36) There was a mistake (surprisingly). l The actual world is counterfactual to the prospective actual world CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 41

Tense as a shifty indexical l l Tense is a shiftable indexical. What shifts tense? CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 42

Tense resembles pronouns such as he, she, or it, due to its: i) deictic (demonstrative); ii) anaphoric; and, iii) bound variable-like natures (Partee 1973). i) Tense is deictic: (37) I didn't turn off the stove (utterance on the way to work) l The deictic past refers to a definite interval identified from the extra-linguistic content. l CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 43

Shifty pronouns While English pronouns always take the speaker's perspective, Slave and Japanese pronouns take the matrix subject's viewpoint in indirect discourse. (38) a. John told me that I should go home. b. John ? aranila séhdi. (Slave) l John 2 SG. gohome 3 SG. told. 1 SG `John told me to go home' (Rice 1986: 51) CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 44

(39) Yoko-ni omae-ga warui-to iw-are-ta. (Japanese) Yoko-DAT you-NOM bad-COMP say-PASS-PAST `Yoko told me that I was wrong (it was my fault)' CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 45

l In the embedded reports, pronouns are not directly referential in Japanese and Slave, as well as in Amharic, Aghem, Navajo, Zazaki, Russian and Navajo (Lewis 1980, Hyman 1979, Rice 1986, Speas 2000, Schlenker 1999, 2003, Anand Nevins 2004). CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 46

l Such pronominal indexicals have been used to argue against Kaplanian view that indexicals are rigidly specified before the context is derived (Kaplan 1977). Schlenker (1999) and others argue that such changes of references of indexicals are the evidence that indexicals are context dependent, and the attitude predicates are monsterous functions that manipulate the context parameters in embedded clauses. CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 47
Strengthening monster theory l l All the arguments of monster supporters have been based on the data on the embedded clauses. The data on mono-clausal fake past sentences present stronger support for the anti-Kaplanian view. CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 48

Fake past simple sentences give stronger support for monsters l l Being simple sentences, context parameters are not maneuvered by attitude reports but by speaker attitude itself. Overt+covert attitude predicates switch tense. CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 49

Necessary condition: surprise Surprise licenses non-past interpretations of the past tense (Teramura 1984) (40)a. # At-ta. (without surprise, with fake past reading) l exist-PAST `It was here' b. At-ta. (without surprise, with real past reading) exist-PAST `It was here' CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 50

Negative presuppositions (41) (Nai-to omotte-i-ta-ra, ) at-ta. NEG-COMP think-be-PAST-then be-PAST `It was here (surprisingly). ' CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 51

Or, the speaker’s expectation is realized (42) (Kuru-to omotte-i-ta basu-ga yappari) ki-ta. come-COMP think be-PAST bus-NOM as I expected come-PAST `The bus is coming (as expected)’ l l l The speaker doubted or has not been sure if p. The common ground contains both p worlds and non-p worlds Fake past assertions disambiguate the actual world (cf. Stalnaker 2004) CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 52
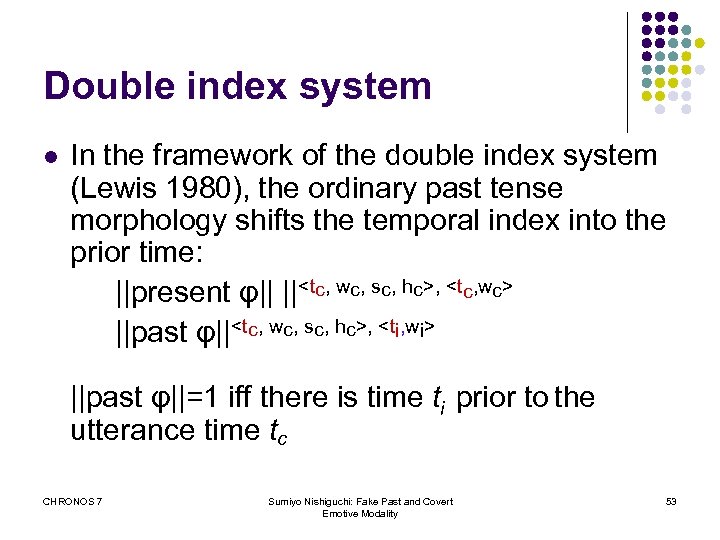
Double index system l In the framework of the double index system (Lewis 1980), the ordinary past tense morphology shifts the temporal index into the prior time: ||present φ|| ||<tc, wc, sc, hc>, <tc, wc> ||past φ||<tc, wc, sc, hc>, <ti, wi> ||past φ||=1 iff there is time ti prior to the utterance time tc CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 53
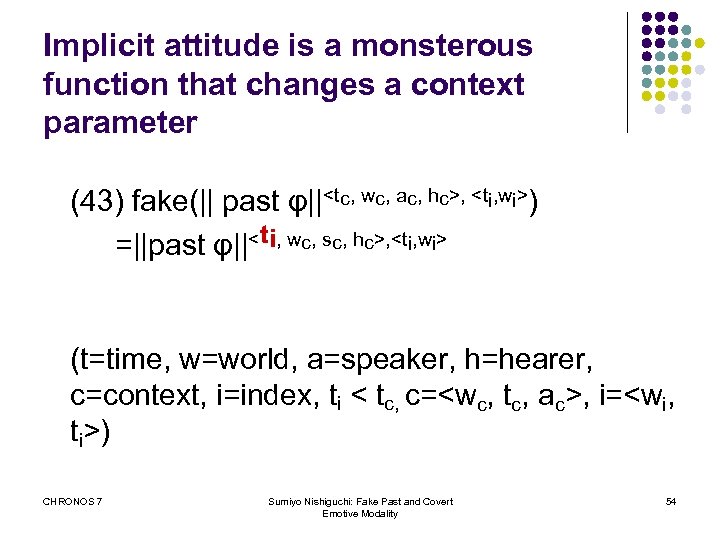
Implicit attitude is a monsterous function that changes a context parameter (43) fake(|| past φ||<tc, wc, ac, hc>, <ti, wi>) =||past φ||<ti, wc, sc, hc>, <ti, wi> (t=time, w=world, a=speaker, h=hearer, c=context, i=index, ti < tc, c=<wc, tc, ac>, i=<wi, ti>) CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 54

Type of the monster Fake tense operator: (44) Where c=<wc, tc, ac>, i=<wi, ti>, ti is prior to tc, c: Dc=Ds×De, s: Ds=Dw×Dt l l Fake: ((c×s)→t) →((c×s)→t) l Fake (||φ||<c, i>)=1 iff ||φ||<c[ti/tc], i>=1 CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 55

The data set is incomplete before the utterance (Veltman 1981) l The speaker does not know enough data but expects that ``the book is not here’’ ``the bus is coming’’ ``tomorrow is not Mary’s birthday’’ l The data set becomes complete by seeing the facts or remembering the facts CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 56

Exp: Expectation function based on the available data (45) Expa(wi)(ti)||φ||wi, tiΛExpa(wc)(tc)||φ||wc, tc ΛKnowa (wc)(tc)||φ||wc, tc (46) Expa(wi)(ti)||~φ||wi, tiΛExpa(wc)(tc)||φ||wc, tc ΛKnowa(wc)(tc)||φ||wc, tc (ti<tc, tc: utterance time, wc: actual world) CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 57

Schema of fake past sentences l l of surprise (negative presupposition) f: While expecting ~f, a finds f and a is glad to find f of fulfillment of expectancy (positive presupposition) f: While expecting f in contrast with ~f, a finds f and a is glad to find f CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 58

Conversational backgrounds: 1. Speculative epistemic necessity/possibility: must/probably/might ¬φ 2. Bouletic modality (in view of what I want): φworlds are ranked higher than ¬ φ worlds CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 59

Conversational backgrounds l l Modal base f (in view of available evidence, speculative epistemic necessity/possibility): must/probably/might ~f: (c×s)→((c×s)→t)→t) Ordering source g (in view of what I want, bouletic modality): ~f worlds are ranked higher than f worlds: (c×s)→((c×s)→t) where Ds=Dw×Dt, Dc=Ds×De CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 60
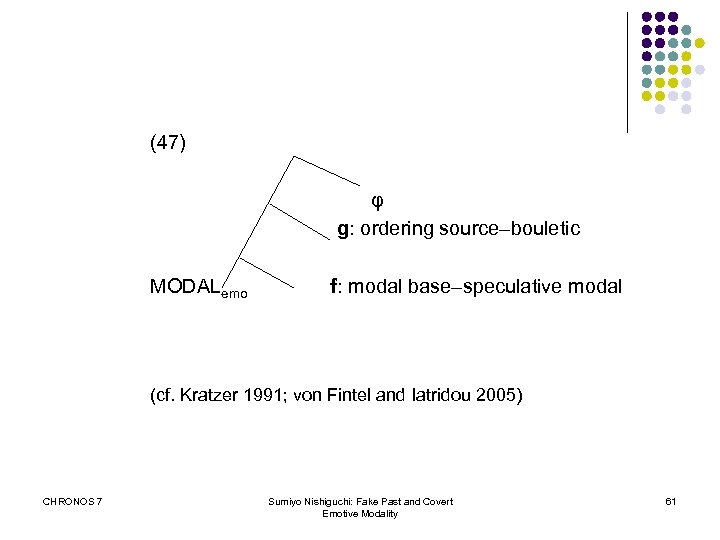
(47) φ g: ordering source–bouletic MODALemo f: modal base–speculative modal (cf. Kratzer 1991; von Fintel and Iatridou 2005) CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 61

(48) ||fake (past)|| (wc)(f)(g)(||φ||) =1 if wc f(wi) w MAXg(wc) : ||φ||(wc)=1, ||past||(wc)(f)(g)(||φ||), otherwise. Where for a given strict partial order <p on worlds, define the selection function maxp that selects the set of <p -best worlds from any set X of worlds: X W: maxp(X)={w X: ¬ w' X: w'<p w} CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 62
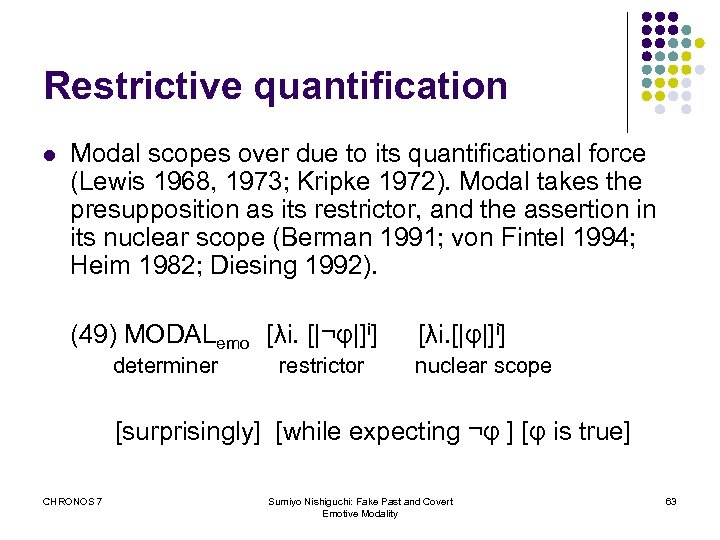
Restrictive quantification l Modal scopes over due to its quantificational force (Lewis 1968, 1973; Kripke 1972). Modal takes the presupposition as its restrictor, and the assertion in its nuclear scope (Berman 1991; von Fintel 1994; Heim 1982; Diesing 1992). (49) MODALemo [λi. [|¬φ|]i] determiner restrictor [λi. [|φ|]i] nuclear scope [surprisingly] [while expecting ¬φ ] [φ is true] CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 63
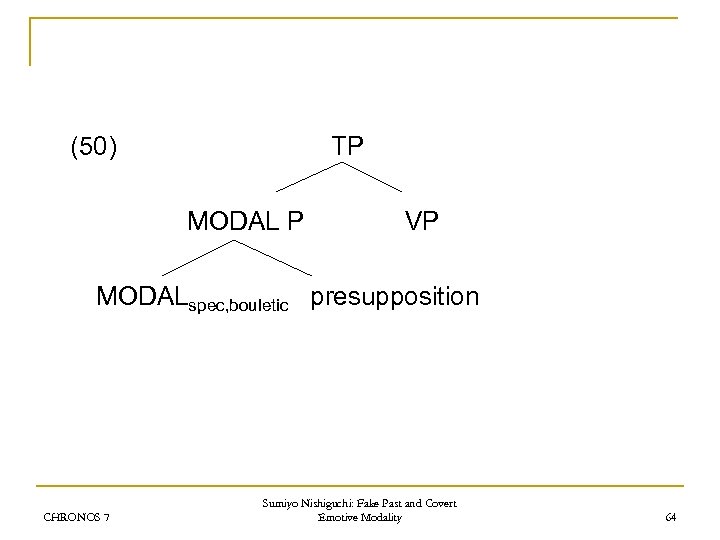
(50) TP MODAL P VP MODALspec, bouletic presupposition CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 64
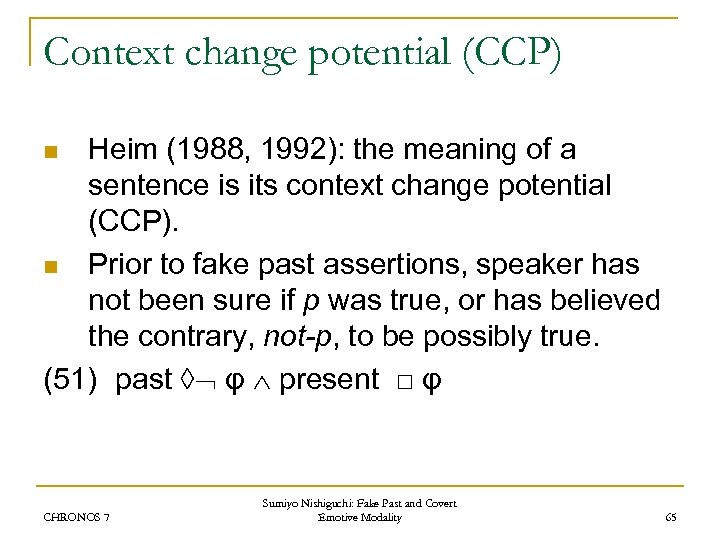
Context change potential (CCP) Heim (1988, 1992): the meaning of a sentence is its context change potential (CCP). n Prior to fake past assertions, speaker has not been sure if p was true, or has believed the contrary, not-p, to be possibly true. (51) past ◊ φ present □ φ n CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 65

n Fake past utterances q q change the context by eliminating not-p and adds p. disambiguate the actual world. (52) CCP of fake past sentences: for any context c, LF f, c + fake past φ =c - Believe(a, φ) + Believe(a, φ) CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 66

Or, q extract disbelief on p and adds belief on p. If speaker has strongly believed the contrary, negation takes narrower scope than Believe. (53) c – Believe (a, φ) + Believe (a, φ) CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 67

Conclusion Surprise and implicit speaker attitudes affect temporal interpretations of factive, unaccusative, and typically stative predicates. The mono-clausal fake past sentences show that covert emotive modality interacting with bouletic and epistemic speculative modality is the monster. CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 68

Modal functions as a determiner-like element taking presuppositions in the restrictor Fake past assertions update contexts CHRONOS 7 Sumiyo Nishiguchi: Fake Past and Covert Emotive Modality 69
4afd660d7cc12a3bae0e1b8ff9cf2dc5.ppt