18e0606332e47f3cdf97806933563879.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Chronic disease self management – a systematic review of proactive telephone applications Carly Muller Dean Schillinger Division of General Internal Medicine San Francisco General Hospital University of California San Francisco
Chronic disease self management – a systematic review of proactive telephone applications Carly Muller Dean Schillinger Division of General Internal Medicine San Francisco General Hospital University of California San Francisco
 Introduction u Chronic disease leads mortality and morbidity u Significant potential to reduce the burden u Current system can’t meet long term needs
Introduction u Chronic disease leads mortality and morbidity u Significant potential to reduce the burden u Current system can’t meet long term needs
 Proactive telephone support 1. Questions and information 2. Received and Reviewed by patient 4. Received and reviewed by Health Professional or automated system 3. Response by patient
Proactive telephone support 1. Questions and information 2. Received and Reviewed by patient 4. Received and reviewed by Health Professional or automated system 3. Response by patient
 RE-AIM u Reach u Effectiveness u Adoption u Implementation u Maintenance
RE-AIM u Reach u Effectiveness u Adoption u Implementation u Maintenance
 Overall objective Undertake a systematic literature of proactive use of the telephone to assist chronic disease self management to: 1. develop a conceptual schema 2. understand their effectiveness 3. understand population-level reach
Overall objective Undertake a systematic literature of proactive use of the telephone to assist chronic disease self management to: 1. develop a conceptual schema 2. understand their effectiveness 3. understand population-level reach
 Inclusion/Exclusion Inclusions u All ages u individuals with one or more chronic diseases u PROACTIVE telephone self management applications Exclusions u Telephone solely for data collection interviews or solely for data shunting u Intervention groups comprising 10 or fewer participants u Articles in languages other than English
Inclusion/Exclusion Inclusions u All ages u individuals with one or more chronic diseases u PROACTIVE telephone self management applications Exclusions u Telephone solely for data collection interviews or solely for data shunting u Intervention groups comprising 10 or fewer participants u Articles in languages other than English
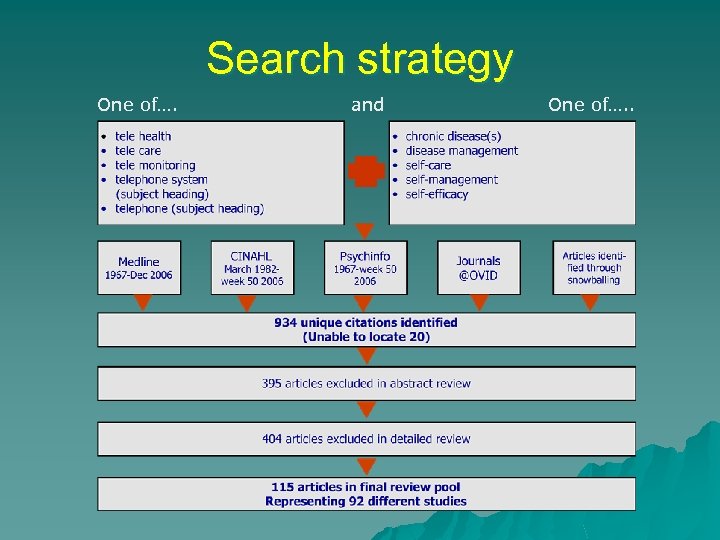 Search strategy One of…. and + One of…. .
Search strategy One of…. and + One of…. .
 Overall intervention description u 115 articles covering 92 studies. u Median intervention sample size = 77 u Median intervention duration = 4 months (range 1 day to 2 years). u 82% US of studies were conducted in the
Overall intervention description u 115 articles covering 92 studies. u Median intervention sample size = 77 u Median intervention duration = 4 months (range 1 day to 2 years). u 82% US of studies were conducted in the
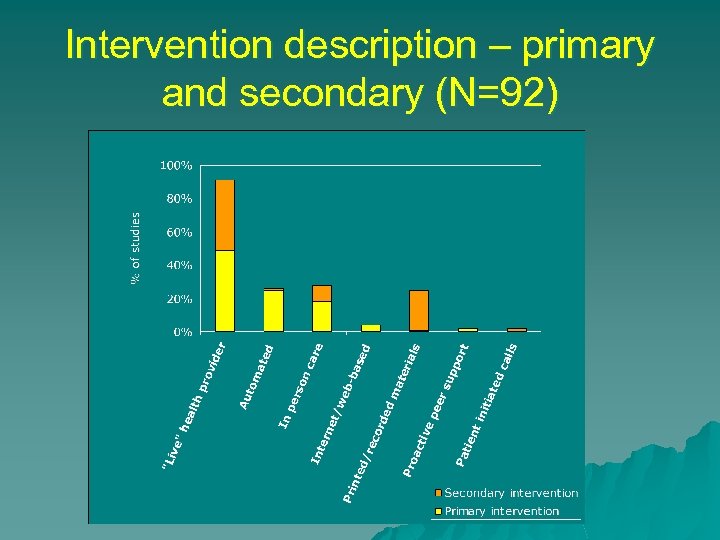 Intervention description – primary and secondary (N=92)
Intervention description – primary and secondary (N=92)
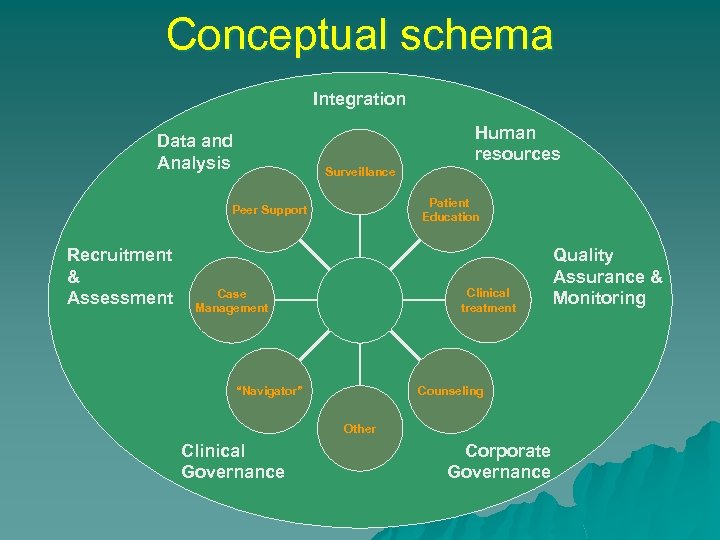 Conceptual schema Integration Human resources Data and Analysis Surveillance Patient Education Peer Support Recruitment & Assessment Clinical treatment Case Management Counseling “Navigator” Other Clinical Governance Corporate Governance Quality Assurance & Monitoring
Conceptual schema Integration Human resources Data and Analysis Surveillance Patient Education Peer Support Recruitment & Assessment Clinical treatment Case Management Counseling “Navigator” Other Clinical Governance Corporate Governance Quality Assurance & Monitoring
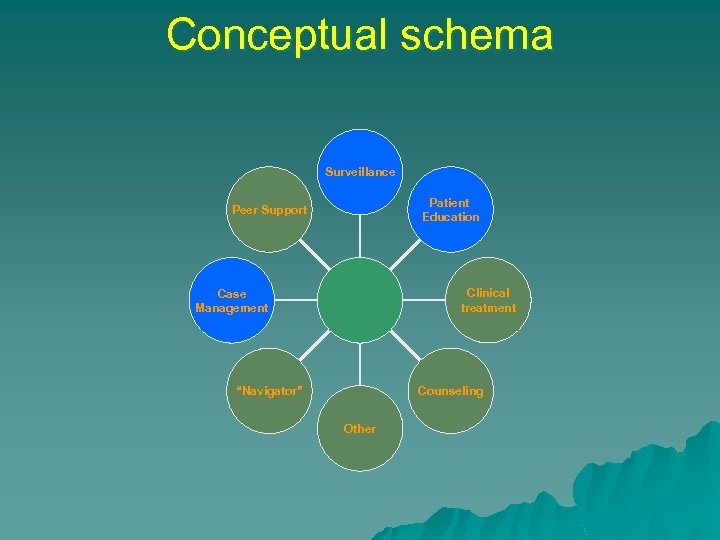 Conceptual schema Surveillance Patient Education Peer Support Clinical treatment Case Management Counseling “Navigator” Other
Conceptual schema Surveillance Patient Education Peer Support Clinical treatment Case Management Counseling “Navigator” Other
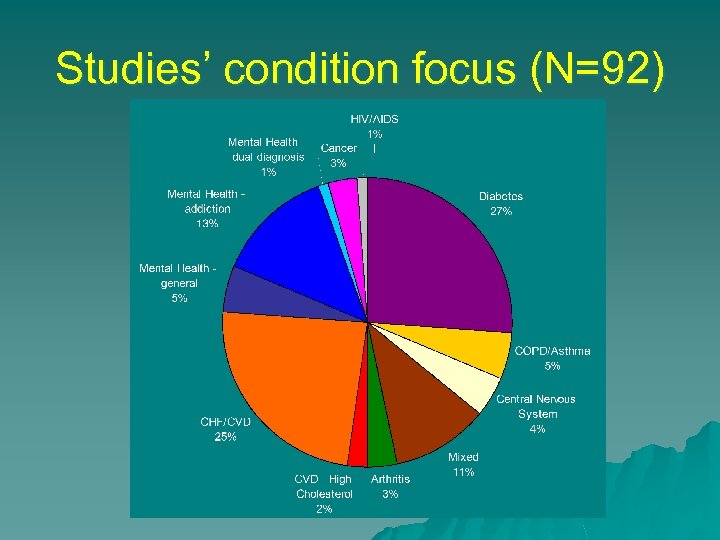 Studies’ condition focus (N=92)
Studies’ condition focus (N=92)
 Effectiveness (N=75) u Comparison groups – 37% multiple interventions, – 51% passive “usual care” – 12% active “usual care” u u 351 different health outcome measures Categories: access, self-efficacy, knowledge, behavior, functional outcomes, physiologic outcomes, clinical guidelines, hospital utilization, ED utilization, medical office visits, costs and other healthcare utilization
Effectiveness (N=75) u Comparison groups – 37% multiple interventions, – 51% passive “usual care” – 12% active “usual care” u u 351 different health outcome measures Categories: access, self-efficacy, knowledge, behavior, functional outcomes, physiologic outcomes, clinical guidelines, hospital utilization, ED utilization, medical office visits, costs and other healthcare utilization
 Effectiveness (N=75) u Comparison groups – 37% multiple interventions, – 51% passive “usual care” – 12% active “usual care” u u 351 different health outcome measures Categories: access, self-efficacy, knowledge, behavior, functional outcomes, physiologic outcomes, clinical guidelines, hospital utilization, ED utilization, medical office visits, costs and other healthcare utilization
Effectiveness (N=75) u Comparison groups – 37% multiple interventions, – 51% passive “usual care” – 12% active “usual care” u u 351 different health outcome measures Categories: access, self-efficacy, knowledge, behavior, functional outcomes, physiologic outcomes, clinical guidelines, hospital utilization, ED utilization, medical office visits, costs and other healthcare utilization
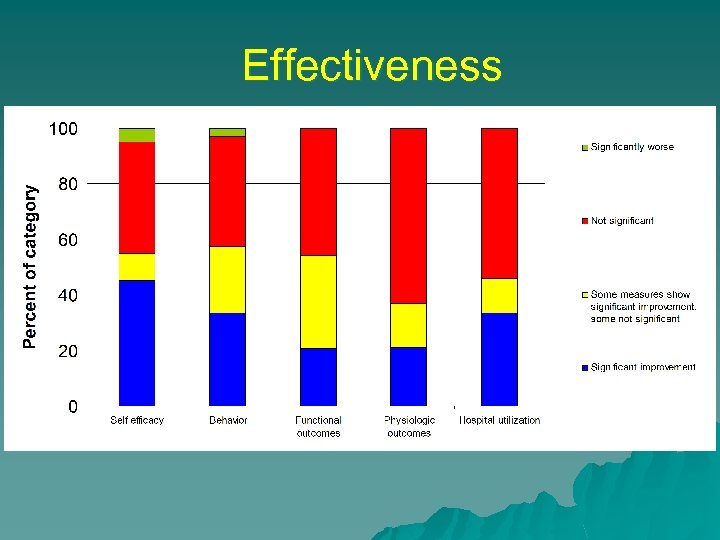 Effectiveness
Effectiveness
 Maintenance of effect
Maintenance of effect
 Representativeness u u u Only 7% of articles sampled from a real world setting Median sample size at intervention completion was only 77 Population vs sample characteristics?
Representativeness u u u Only 7% of articles sampled from a real world setting Median sample size at intervention completion was only 77 Population vs sample characteristics?
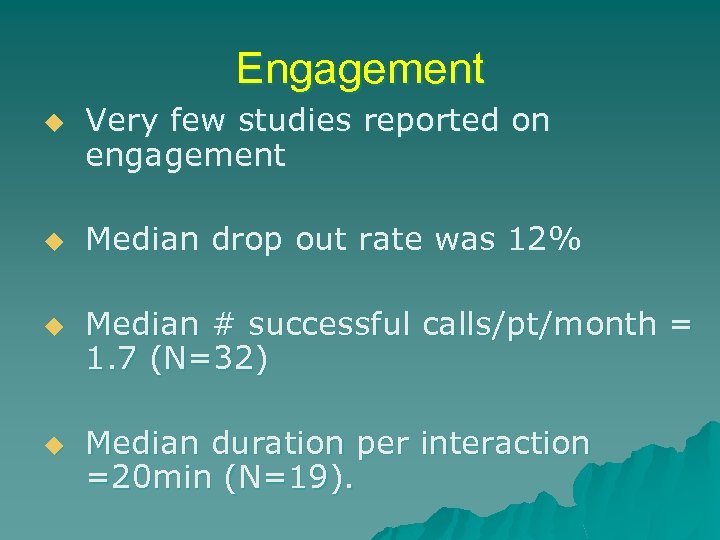 Engagement u u Very few studies reported on engagement Median drop out rate was 12% Median # successful calls/pt/month = 1. 7 (N=32) Median duration per interaction =20 min (N=19).
Engagement u u Very few studies reported on engagement Median drop out rate was 12% Median # successful calls/pt/month = 1. 7 (N=32) Median duration per interaction =20 min (N=19).
 Limitations u Potential for publication bias not evaluated u English u No language only combined measure of effect size as a meta-analysis was not undertaken
Limitations u Potential for publication bias not evaluated u English u No language only combined measure of effect size as a meta-analysis was not undertaken
 Conclusions u Evidence insufficiently robust u Potentially these services may deliver superior - or at the very least equivalent – outcomes u Focus on patient outcomes
Conclusions u Evidence insufficiently robust u Potentially these services may deliver superior - or at the very least equivalent – outcomes u Focus on patient outcomes
 Policy implications Rigorous and larger scale pilots: u$ u Robust specifications u Targeting u Appropriate u Data financing model collection and analysis
Policy implications Rigorous and larger scale pilots: u$ u Robust specifications u Targeting u Appropriate u Data financing model collection and analysis
 Thank-you This work would not have been possible without the support of The Commonwealth Fund Assoc Prof Dean Schillinger Prof Andy Bindman Department of Internal Medicine San Francisco General Hospital University of California San Francisco Primary Health Branch Victorian Department of Human Services, Australia
Thank-you This work would not have been possible without the support of The Commonwealth Fund Assoc Prof Dean Schillinger Prof Andy Bindman Department of Internal Medicine San Francisco General Hospital University of California San Francisco Primary Health Branch Victorian Department of Human Services, Australia
 Research implications Future studies should ensure: u Key information is included to allow assessment of the generalizability of results u Larger sample sizes u Consistency and reporting on reach and effectiveness measures u Long-term monitoring u Cost effectiveness
Research implications Future studies should ensure: u Key information is included to allow assessment of the generalizability of results u Larger sample sizes u Consistency and reporting on reach and effectiveness measures u Long-term monitoring u Cost effectiveness


