4179668ee9b3c2729d800719fd01c3ff.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Chris Rizoz: Carrier Phase-Based GNSS: a university research agenda Chris Rizos Satellite Navigation & Positioning (SNAP) Group, School of Surveying & Spatial Information Systems The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia Civil GPS Service Interface Committee Meeting 10 -11 February 2003, Melbourne, Australia

Overview u. GPS R&D: The Big Picture u. University GPS Research Topics u. The Australian Scene: CRC & NICTA u. Directions in SNAP Research Civil GPS Service Committee Meeting 10 -11 February 2003, Melbourne, Victoria

GPS: Space-Based Positioning System of Unequalled Versatility • Geodetic technique -- accurate, low-cost, portable, massive ground infrastructure • Surveying tool -- valuable addition to the surveyor's toolkit • Navigation technology -- affordable, ubiquitous, impacting on all marine-air-land navigation practice • Consumer electronics -- alter society's view of the world & influence the mobile services provided through wireless technologies

First civilian GPS (geodetic) receivers, early 1980 s First Australian GPS control survey, state of South Australia 1985

Evolution of the User Segment u 1980 s: military, surveying & geodesy u 1990 s: navigation users u 2000 s: consumer electronics, LBS This has influenced the R&D trends… So what have the universities been doing?

Australian University GPS R&D (1) u ‘Geodesy’ the primary driver since the mid-1980 s u Concentrated in depts of surveying/geomatics u Algorithm development… CPH modelling & processing, AR, etc. u Applications focus… geodynamics, reference frame, surveying, “kinematic”, etc. u UNSW, CUT, UM, RMIT, USA, UT, UC, QUT Has uni R&D focus evolved with application trends?

Australian University GPS R&D (2) u Largely CPH-based… PR techniques & apps have been shunned u No hardware developments… EE skills lacking u No navigation technology ‘research culture’… EE depts totally indifferent to GNSS R&D u Industry dominated by SMEs… minor influence on university R&D u Can university R&D capability adapt to new challenges?

Convergence of Developments u Wireless Communications u Mobile Computing u Mobile Positioning u Spatial Database Servers Will the Uni R&D agenda reflect such mainstream technologies/apps, or remain focused on niches? ? ?
GPS: the “slow burn” technology u At heart of convergence of crucial technologies: GPS the core technology u Low-cost, high-performance of GPS u GPS as infrastructure: a vital utility u Next generation GNSS: modernized GPS, Galileo, etc. u Massive potential for new products & services

GPS-Related Research Challenges (1) u Deformation/Geodynamics: u GPS HW/SW systems, coms issues, time series analysis, DIn. SAR/remote sensing, engineering apps, etc. u CGPS: u Bistatic radar imaging, multipath analysis, ground & airborne systems, remote sensing apps, etc. u Base stn QC/ops, coms issues, web apps, scalability, servers, multifunctionality, new services, nonpositioning apps, etc. GPS Meteorology: Ionospheric & tropospheric studies, ground & space-based, interaction with NWM, etc. "Indirect" GPS: Long-Range Kinematic GPS: Ocean buoy positioning, CGPS apps over long distances, coms issues, etc. u GPS/Glonass/Galileo: Observation modelling, new data processing algorithms, multifrequency OTF-AR, QC, new apps, receiver customisation, etc. Civil GPS Service Committee Meeting 10 -11 February 2003, Melbourne, Victoria

GPS-Related Research Challenges (2) u Precise Navigation: u New apps, coms link issues, new instrumentation, new algorithms, etc. u Hazard Monitoring: Volcanoes, landslides, structural integrity, ground subsidence, which technology & processing strategies? u GNSS Augmentations: WAAS, WADGPS, RADGPS, testing & advice on implementation issues u GPS & Internet & Wireless: Internet DGPS, RTK, processing engines, monitoring & control, etc. Multi-Sensor Systems: GPS+INS, LIDAR, CCD+, MEMS integration challenges. u MSS Applications: Mobile mapping, augmented reality, robotics (guidance/control), etc. u New Technologies: Pseudolites, receiver designs, mobilephone positioning, WLAN, etc. u Telegeoinformatics: LBS, GIS, indoor positioning, apps issues, mobile devices & wireless coms. Civil GPS Service Committee Meeting 10 -11 February 2003, Melbourne, Victoria

The Australian Scene u GPS expertise concentrated in surveying/geomatics depts. , not EE. u Applied/practical research is more valued by industry, but CPH-based research provides necessary challenges for academia. u Australian GPS R&D is worldclass (although predominantly focused on CPH-based tech/apps). u Cooperative Research Centre in Spatial Information (CRC-SI) to be established mid-2003. u National ICT Centre-of-Excellence established 2002.

CRC-SI (1) • • Industry, government & university consortium To begin from mid-2003 Seven year funding >$4 m(cash), $10 m(inkind) p. a. Focus on the science & applications of SI Five research programs Seven demonstrator projects Commercialisation, advanced training & technology transfer from CRC to industry & government partners First opportunity for university GNSS R&D agenda to be shaped by industry/users…

CRC-SI (2) • SME consortium • Public sector agencies: Geosciences Australia, DIGO, DITM, Land Victoria, DOLA, Ag. West, etc. • Universities: Univ. of Melbourne, UNSW, Curtin Univ. , Charles Sturt Univ. • Industry contributions: ESRI, Intergraph, Raytheon, and others • Headquarters at Univ. of Melbourne • Research programs headed by university researchers • Demonstrators link research to integrated outcomes

CRC-SI (3) • Integrated Positioning & Mapping Systems Chris Rizos (UNSW) • Metric Imagery as a Spatial Information Source Clive Fraser (UM) • Spatial Information System Design & Spatial Data Infrastructures - Ian Williamson (UM) • Earth Observation for Renewable Natural Resource Management - Tony Milne (UNSW) • Modelling & Visualisation for Spatial Decision Support - Ian Bishop (UM)

NICTA u Recent announcement by Federal Government of ICT ‘centre of excellence’ to NSW-ACT consortium. u Universities: UNSW, ANU, Sydney Univ. u UNSW is lead institution. u Others: ACT, DITM, Lend Lease, . . . u $130 m over 5 years (matched by other funds). u >200 fulltime researchers & lots of graduate students. u Dominated by EE, Telecom Eng. & Comp. Sci. u Challenge: how to encourage R&D into SI Technology & Applications?

Satellite Navigation and Positioning (SNAP) Group u Located within the School of Surveying & SIS, Faculty of Engineering, UNSW. u Largest and most active academic GPS R&D group in Australia. u Specialising in theory, technology and applications of positioning using GPS and other navigation technologies. http: //www. gmat. unsw. edu. au/snap Civil GPS Service Committee Meeting 10 -11 February 2003, Melbourne, Victoria

Project Theme 1 u. Indonesian volcano monitoring u. Singapore building monitoring u. Appin area subsidence monitoring u. Mixed receiver networks u. Integration of GPS & DIn. SAR u. Tectonic & geomorphological interpretation of ground deformation u. Meteorological studies u. Time series analysis

Project Theme 2 u. CPH-based GPS/Glonass/ Galileo positioning u. Stochastic modelling u. Ambiguity resolution & validation u. INS data modelling u. PL data modelling & issues u. Integration of GPS & INS & PL u. Integration of navigation & image sensor systems, & associated HW issues u. Kalman filtering algorithms/SW

Project Theme 3 u. RTK-GPS, single & network-based u. Algorithms for kinematic positioning u. Single-frequency algorithms u. Pseudolite development u. Receiver firmware customisation u. Industrial applications of RTK u. Coms link R&D, incl. Internet, WLAN u. Software-defined receivers u. Embedded processors & RTOS u. GPS Development Kits
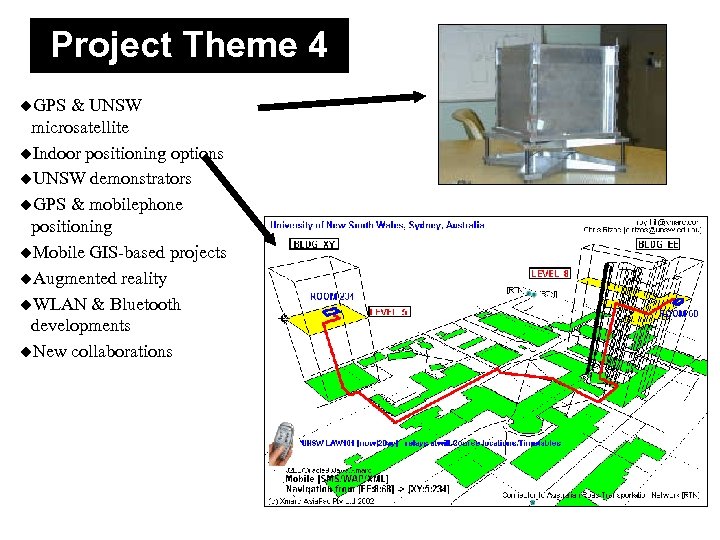
Project Theme 4 u. GPS & UNSW microsatellite u. Indoor positioning options u. UNSW demonstrators u. GPS & mobilephone positioning u. Mobile GIS-based projects u. Augmented reality u. WLAN & Bluetooth developments u. New collaborations
Current SNAP R&D u u u u u GPS+In. SAR deformation monitoring techniques Syd. NET network-based GPS infrastructure & apps Pseudolite(+ other sensors) technology & applications Receiver firmware customisation Low-cost CPH-based positioning systems High performance, CPH-based kinematic positioning systems Indoor positioning concepts & technologies Indirect GPS signals research Stochastic modelling & fundamental research Civil GPS Service Committee Meeting 10 -11 February 2003, Melbourne, Victoria
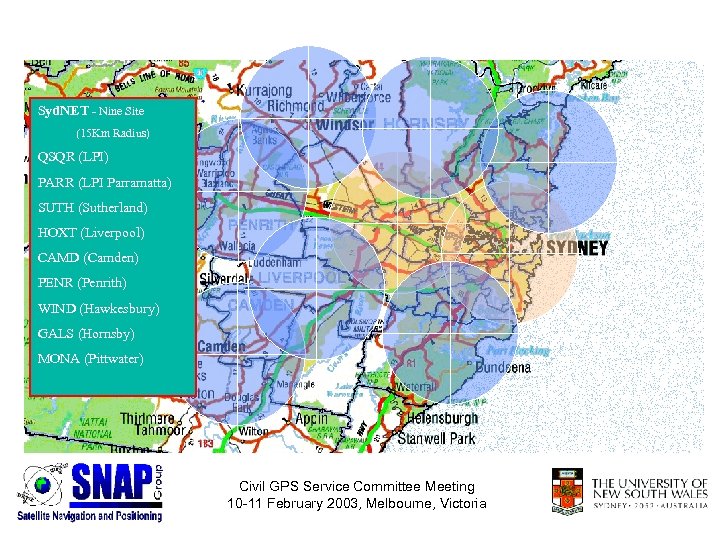
Syd. NET - Nine Site (15 Km Radius) QSQR (LPI) PARR (LPI Parramatta) SUTH (Sutherland) HOXT (Liverpool) CAMD (Camden) PENR (Penrith) WIND (Hawkesbury) GALS (Hornsby) MONA (Pittwater) Civil GPS Service Committee Meeting 10 -11 February 2003, Melbourne, Victoria
Uni R&D… From Geodesy to Telegeoinformatics? u GPS-only algorithm research nearing the end, some new 'lease-of-life' from Galileo & modernized GPS. u Industry wants solutions, hence core CPH competency must be preserved & made available for applications. u Niche (precision) applications are still attractive, but will increasingly involve system or sensor integration. u Telegeoinformatics applications cannot be ignored, being multi-disciplinary in nature, but more HW based. u Days of ‘ivory tower’ R&D at unis are numbered, must seek strategic partnerships for mutual benefit.
4179668ee9b3c2729d800719fd01c3ff.ppt