bf1f892d7a0e60ad4db08de65704d73c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

Chinese Migration in a Globalizing World Leo Suryadinata

Two latest waves of Chinese migrations o The 19 th century and early 20 th century o The end of the 20 th century onward o Reasons for migration o Pull factors in mainland China and push factors outside China o Some differences in these factors over the two periods

Differences between two waves of migrants o Destinations (Developing and Developed countries); o Sources of migrants; o Qualities of migrants o Luodi shenggeng, Luoye guigeng, or Transnational?

Types of New Chinese Migrants o Chinese overseas students and their families/Professionals o Ordinary migrants to join family members o Investors/Businessmen o Workers (including illegal workers)

In Developed Countries o According to Prof. Zhuang Guotu, there are o o about 4 millions new Chinese migrants 3 -3. 5 millions went to developed countries; of which over 2 million went to USA Earlier migrants came from Taiwan, HK; many were students and investors New migrants from China form the largest new Chinese migrant population The presence of large new Chinese migrants is linked to state policy in developed countries.

USA (in thousand) o Year o 1961 o 1970 o 1980 o 1990 o 2006 Chinese Pop. No. 237, 292 435, 062 812, 178 1, 645, 472 2, 879, 636 3, 565, 458 % of US pop 0. 13 0. 20 0. 35 0. 65 1. 02 1. 19

Australia (in Thousand) o Year pop o 1961 o 1976 o 1986 o 2001 o 2006 Chinese pop. no. % of Aussie 23, 568 26, 198 36, 638 196, 347 556, 560 669, 890 0. 22 0. 21 0. 27 1. 30 2. 97 2. 64

New Zealand (in thousand) o Year o 1980 s o 1990 o 1996 o 2001 o 2006 Chinese pop. no 19, 000 40, 000 81, 390 105, 057 147, 570 % of NZ pop. 0. 6 1. 1 2. 0 3. 6
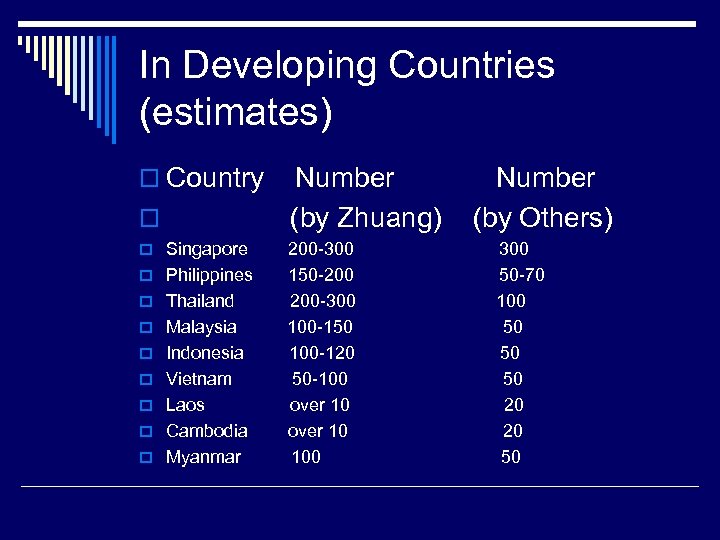
In Developing Countries (estimates) o Country o o Singapore o Philippines o Thailand o Malaysia o Indonesia o Vietnam o Laos o Cambodia o Myanmar Number (by Zhuang) 200 -300 150 -200 200 -300 100 -150 100 -120 50 -100 over 10 100 Number (by Others) 300 50 -70 100 50 50 50 20 20 50

Two kinds of states & Chinese migration o The nature of the states affects migration o Migrant states welcome migrants o Indigenous states reject migrants o US, Canada, Australia and New Zealand are migrant states o In SEA, only Singapore is a migrant state; legal Chinese migration to other states is difficult.
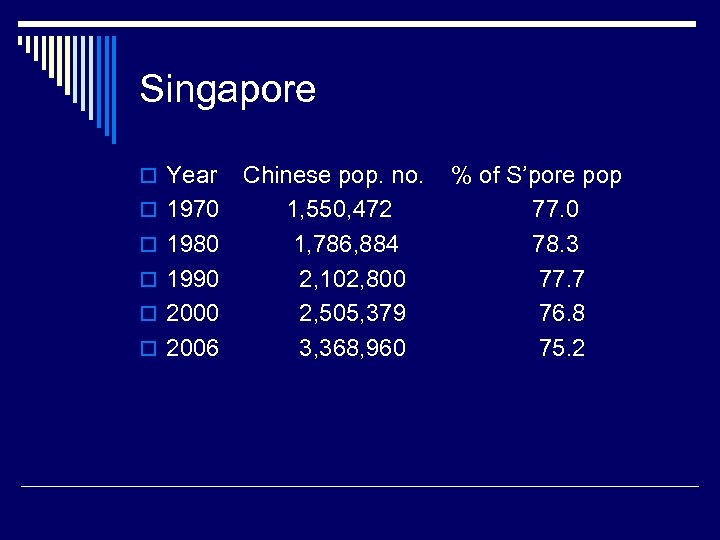
Singapore o Year o 1970 o 1980 o 1990 o 2006 Chinese pop. no. 1, 550, 472 1, 786, 884 2, 102, 800 2, 505, 379 3, 368, 960 % of S’pore pop 77. 0 78. 3 77. 7 76. 8 75. 2

Malaysia o Year Chinese pop. no. o 1970 o 1980 o 1991 o 2000 o 2005 3, 719, 000 4, 415, 000 4, 945, 000 5, 692, 000 6, 000 % of Malaysian pop 35. 6 32. 1 26. 4 24. 4 23. 3
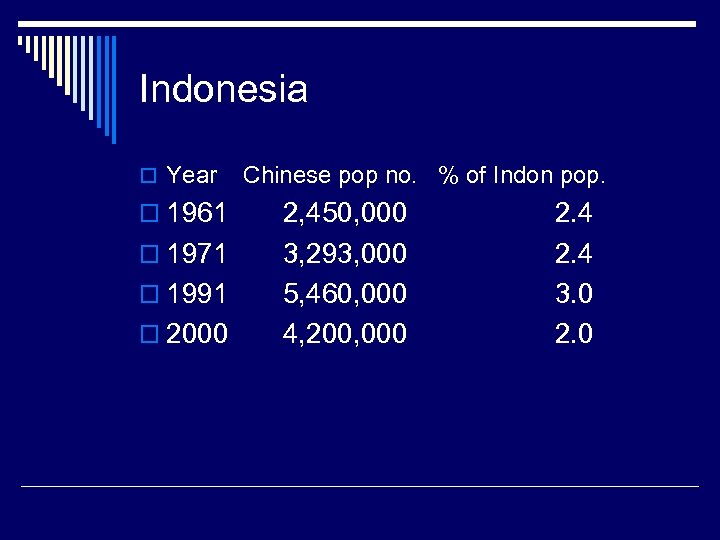
Indonesia o Year o 1961 o 1971 o 1991 o 2000 Chinese pop no. % of Indon pop. 2, 450, 000 3, 293, 000 5, 460, 000 4, 200, 000 2. 4 3. 0 2. 0

Concluding remarks o Chinese new migration is part and parcel of global migration o More migrants have gone to developed rather than developing countries o The sources are not confined to mainland China, but Taiwan, HK, & SEA o Different impacts on developed & developing countries

o More foreign-born Chinese than local born-Chinese in developed countries; o More local-born Chinese than foreignborn Chinese in developing countries o Problem of integration still remains?
bf1f892d7a0e60ad4db08de65704d73c.ppt