fba77f767182738785548d84153eaaa0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 CHINA IN TANZANIA Prof Dr Dr Claude-Hélène Mayer Dr Christian Martin Boness Symposium “China in Africa. Implications for Management, Implications for Change” Thursday 31 st Oct – Friday 1 st Nov 2013 Rhodes University, Grahamstown, South Africa
CHINA IN TANZANIA Prof Dr Dr Claude-Hélène Mayer Dr Christian Martin Boness Symposium “China in Africa. Implications for Management, Implications for Change” Thursday 31 st Oct – Friday 1 st Nov 2013 Rhodes University, Grahamstown, South Africa
 Contents • China in Tanzania Research 2013 • Research Aim and Objectives • Research Methodology • Ethics • Access to the Field of Research • Research Findings in Organisation 1 • Recommendations
Contents • China in Tanzania Research 2013 • Research Aim and Objectives • Research Methodology • Ethics • Access to the Field of Research • Research Findings in Organisation 1 • Recommendations
 China in Tanzania – Chinas gateway to Africa? „Africa needs a market for its products. Africa needs technology for its development. China is ready to provide all that. What is wrong with that? “ Kikwete, President of Tanzania, July 2013
China in Tanzania – Chinas gateway to Africa? „Africa needs a market for its products. Africa needs technology for its development. China is ready to provide all that. What is wrong with that? “ Kikwete, President of Tanzania, July 2013
 China in Tanzania – Chinas gateway to Africa? • Close ties of Chinese-Tanzanian relations and trade are rooted in common history • A joint team of Kenyan and Chinese archeologists found a 15 th Century Chinese coin • 100 years before the first Europeans reached the region News Africa, 18. 10. 2010
China in Tanzania – Chinas gateway to Africa? • Close ties of Chinese-Tanzanian relations and trade are rooted in common history • A joint team of Kenyan and Chinese archeologists found a 15 th Century Chinese coin • 100 years before the first Europeans reached the region News Africa, 18. 10. 2010
 China in Tanzania – Chinas gateway to Africa? • Chinese-Tanzanian Tanzania. Zambia-Railway project (19681976) • TAZARA links the Southern African regional transport network to East Africa and the rest of the world through the East African seaport of Dar- es. Salaam
China in Tanzania – Chinas gateway to Africa? • Chinese-Tanzanian Tanzania. Zambia-Railway project (19681976) • TAZARA links the Southern African regional transport network to East Africa and the rest of the world through the East African seaport of Dar- es. Salaam
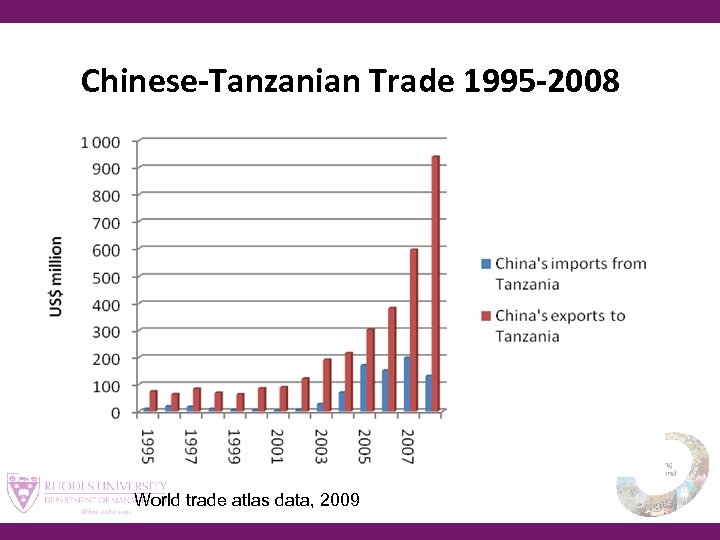 Chinese-Tanzanian Trade 1995 -2008 World trade atlas data, 2009
Chinese-Tanzanian Trade 1995 -2008 World trade atlas data, 2009
 China in Tanzania – Aim of research To better understand the way Chinese organisations are being managed in selected African countries through cross-cultural collaborative research
China in Tanzania – Aim of research To better understand the way Chinese organisations are being managed in selected African countries through cross-cultural collaborative research
 Research methodology • Data collection – Semi-structured interviews (15 questions) – observation • Data analysis: – 5 -step model of content analysis (Terre Blanche, Durrhei & Kelly, 2006) • Limitations of case study design
Research methodology • Data collection – Semi-structured interviews (15 questions) – observation • Data analysis: – 5 -step model of content analysis (Terre Blanche, Durrhei & Kelly, 2006) • Limitations of case study design
 China in Tanzania- Cooperation partners • Rhodes University, Grahamstown, RSA • Middlesex University, London, UK • Nanjing University, Nanjing, China • Ministry of Education and Vocational Training, Dar-es-Salaam • One top executive of a private company
China in Tanzania- Cooperation partners • Rhodes University, Grahamstown, RSA • Middlesex University, London, UK • Nanjing University, Nanjing, China • Ministry of Education and Vocational Training, Dar-es-Salaam • One top executive of a private company
 Research ethics • Informed consent by oral agreement taking in account cross-cultural situation with Chinese, African and European interaction • Chinese organisational consent through access to organisation • Confidentiality and anonymity • Voluntary participation
Research ethics • Informed consent by oral agreement taking in account cross-cultural situation with Chinese, African and European interaction • Chinese organisational consent through access to organisation • Confidentiality and anonymity • Voluntary participation
 Access to organisational fields • Key informants. – Identify counterparts in Tanzanian Government – Embassy of China – Chinese Organization (approached 8) • Organisations: – Industrial sector (1 private and 1 governmental organisation) – Trading (Small Scale Enterprises)
Access to organisational fields • Key informants. – Identify counterparts in Tanzanian Government – Embassy of China – Chinese Organization (approached 8) • Organisations: – Industrial sector (1 private and 1 governmental organisation) – Trading (Small Scale Enterprises)
 Access to organisational fields Research team criteria: • age, cultural background, national background, gender, position in organisation, interdisciplinary approach • for intersubjective validation
Access to organisational fields Research team criteria: • age, cultural background, national background, gender, position in organisation, interdisciplinary approach • for intersubjective validation
 Organisation 1 Large scale enterprise • Type: governmental organisation • Sector: building and construction industry, consultancy services • Products: building and engineering railways, bridges, roads, water supply • Ownership: Chinese • 2000 employees
Organisation 1 Large scale enterprise • Type: governmental organisation • Sector: building and construction industry, consultancy services • Products: building and engineering railways, bridges, roads, water supply • Ownership: Chinese • 2000 employees
 Organisation 1 Large scale enterprise • Number of interviews: 8 • Gender: 3 female, 5 male • Position: 4 manager, 4 staff • Nationality: 5 China, 3 Tanzania • Stay in organization: 3 interviewees less than 12 month, 5 interviewees over 1 year
Organisation 1 Large scale enterprise • Number of interviews: 8 • Gender: 3 female, 5 male • Position: 4 manager, 4 staff • Nationality: 5 China, 3 Tanzania • Stay in organization: 3 interviewees less than 12 month, 5 interviewees over 1 year
 Organisation 2 Large scale enterprise • Type: private international organisation • Sector: Industry, IT • Products: telecommunications and networking equipment • Ownership: Chinese • Approximately 160 employees
Organisation 2 Large scale enterprise • Type: private international organisation • Sector: Industry, IT • Products: telecommunications and networking equipment • Ownership: Chinese • Approximately 160 employees
 Organisation 2 Large scale enterprise • Number of interviews: 16 • Gender: 6 female, 10 male • Postition: 9 manager, 7 staff • Nationality: 6 China, 9 Tanzania, 1 Zambia • Stay in organization: 2 interviewees less 1 year, 14 interviewees more than 1 year
Organisation 2 Large scale enterprise • Number of interviews: 16 • Gender: 6 female, 10 male • Postition: 9 manager, 7 staff • Nationality: 6 China, 9 Tanzania, 1 Zambia • Stay in organization: 2 interviewees less 1 year, 14 interviewees more than 1 year
 Organisations 3 Small scale enterprises • Type: private Chinese retailers • Sector: trade • Products: artificial flowers, housewares • Ownership: Chinese • Location: Kariakoo Sokoni, Dar -es-Salaam, trading spot to entire Tanzania and neighbouring countries • Less than 10 employees
Organisations 3 Small scale enterprises • Type: private Chinese retailers • Sector: trade • Products: artificial flowers, housewares • Ownership: Chinese • Location: Kariakoo Sokoni, Dar -es-Salaam, trading spot to entire Tanzania and neighbouring countries • Less than 10 employees
 Organisations 3 Small scale enterprises • Number of interviews: 4 • Gender: 1 female, 3 male • Position: 4 manager • Nationality: 4 Chinese • Stay in organization: 2 interviewees less than 1 year, 2 interviewees more than 1 year
Organisations 3 Small scale enterprises • Number of interviews: 4 • Gender: 1 female, 3 male • Position: 4 manager • Nationality: 4 Chinese • Stay in organization: 2 interviewees less than 1 year, 2 interviewees more than 1 year
 Biographical data overview on organisations 1 -3 • Total number of interviews: 30 • Gender: 10 female and 20 male persons • Position: 10 employees and 20 managers • Nationality: 15 Chinese, 14 Tanzanians, 1 Zambian • Stay in organization: 7 persons less than 1 year, 23 persons more than 1 year
Biographical data overview on organisations 1 -3 • Total number of interviews: 30 • Gender: 10 female and 20 male persons • Position: 10 employees and 20 managers • Nationality: 15 Chinese, 14 Tanzanians, 1 Zambian • Stay in organization: 7 persons less than 1 year, 23 persons more than 1 year
 Research findings of organisation 1
Research findings of organisation 1
 Biographical data organisation 1 Nationality: 5 Chinese, 3 Tanzanians Gender: 3 Female, 5 Male Stay in Organization: 3 persons less than 1 year, 5 persons more than 1 year
Biographical data organisation 1 Nationality: 5 Chinese, 3 Tanzanians Gender: 3 Female, 5 Male Stay in Organization: 3 persons less than 1 year, 5 persons more than 1 year
 Biographical data organisation 1 • Positions managers • Procurement manager (20 C-M), CH, male • Engineer (21 C-M), CH, male • Senior quantity surveyer (23 CM), TZ, male • Administrator human resources (24 C-M), CH, male
Biographical data organisation 1 • Positions managers • Procurement manager (20 C-M), CH, male • Engineer (21 C-M), CH, male • Senior quantity surveyer (23 CM), TZ, male • Administrator human resources (24 C-M), CH, male
 Biographical data organisation 1 • Positions employees • Personal secretary (17 C-E), TZ, female • Communication employee (18 CE), CH, male • Secretary in trade (19 C-E), CH, female • Logistics and procurement department (22 C-E), TZ, female
Biographical data organisation 1 • Positions employees • Personal secretary (17 C-E), TZ, female • Communication employee (18 CE), CH, male • Secretary in trade (19 C-E), CH, female • Logistics and procurement department (22 C-E), TZ, female
 • “Whether you choose capitalism or socialism it does not matter. What matters is that you have very clear planning for the country like how to develop and that is telling the truth. ” (CHINESE MANAGER 24 C-M IN TANZANIA, 2013)
• “Whether you choose capitalism or socialism it does not matter. What matters is that you have very clear planning for the country like how to develop and that is telling the truth. ” (CHINESE MANAGER 24 C-M IN TANZANIA, 2013)
 Themes in Research 1. Organisation 2. Environment 3. Culture
Themes in Research 1. Organisation 2. Environment 3. Culture
 Theme 1: Organisation - Categories 1. Strategy 2. Structure, Decision Making and Participation 3. Staff and Managers 4. Management Styles 5. Recruitment 6. Qualification and Trainings 7. Knowledge Sharing 8. Working Conditions and Atmosphere 9. Motivation, benefits, rewards
Theme 1: Organisation - Categories 1. Strategy 2. Structure, Decision Making and Participation 3. Staff and Managers 4. Management Styles 5. Recruitment 6. Qualification and Trainings 7. Knowledge Sharing 8. Working Conditions and Atmosphere 9. Motivation, benefits, rewards
 Theme 1: Organisation Category 5: Recruitment, Category 6: Qualification „It is quite difficult to find such higher educated people (i. e. in Tanzania) so sometimes it make us send the people from China to here and that will cost much more than if we had local staff and also some people like us when we come here we can face the difference between the country and we need time to adjust and sometimes maybe they are not quite fit in this environment and they think to go back and every two years they will find a way to go back and two years they may know a little bit and they go back. They keep doing this and this makes it not that efficiency. . . “ Chinese Employee 18 C-E,
Theme 1: Organisation Category 5: Recruitment, Category 6: Qualification „It is quite difficult to find such higher educated people (i. e. in Tanzania) so sometimes it make us send the people from China to here and that will cost much more than if we had local staff and also some people like us when we come here we can face the difference between the country and we need time to adjust and sometimes maybe they are not quite fit in this environment and they think to go back and every two years they will find a way to go back and two years they may know a little bit and they go back. They keep doing this and this makes it not that efficiency. . . “ Chinese Employee 18 C-E,
 Theme 1: Organisation Category 8: Working Conditions „. . . but there is something I want to know; in this company and I can say in most Chinese companies we local people are working for their company without contracts. . . no I do not have a contract. . . I want it, yes. “ Tanzanian Employee 22 C-E
Theme 1: Organisation Category 8: Working Conditions „. . . but there is something I want to know; in this company and I can say in most Chinese companies we local people are working for their company without contracts. . . no I do not have a contract. . . I want it, yes. “ Tanzanian Employee 22 C-E
 Theme 2: Environment - Categories 10. Interaction with Community and Local Organisations 11. Interaction with Government and Trade Unions 12. Benefits for Africa and Tanzania
Theme 2: Environment - Categories 10. Interaction with Community and Local Organisations 11. Interaction with Government and Trade Unions 12. Benefits for Africa and Tanzania
 Theme 2: Environment Category 10: Interaction With Community and Local Organisations „Sometimes they (i. e. Tanzanians) are not honest even first the comes out the big procurement comes out there is more sense and there is a small amount of this order and we just talk on the phone and they told I pay the money to them first and the African people they also want the money first and they say he will give me the materials tomorrow and you just wait and maybe after a while they don’t give you and that is a problem. “ Chinese Manager 20 C-M
Theme 2: Environment Category 10: Interaction With Community and Local Organisations „Sometimes they (i. e. Tanzanians) are not honest even first the comes out the big procurement comes out there is more sense and there is a small amount of this order and we just talk on the phone and they told I pay the money to them first and the African people they also want the money first and they say he will give me the materials tomorrow and you just wait and maybe after a while they don’t give you and that is a problem. “ Chinese Manager 20 C-M
 Theme 2: Environment Category 11: Interaction with Government and Unions „ (Unions). . . they are not available but we have tried our best to make those unions for the sake of our problems but we have not yet succeeded with that because there are several problems that come out and then we fail to solve them because we do not have a union and we are not collected ourselves so it becomes difficult. Tanzanian Manager 23 C-M
Theme 2: Environment Category 11: Interaction with Government and Unions „ (Unions). . . they are not available but we have tried our best to make those unions for the sake of our problems but we have not yet succeeded with that because there are several problems that come out and then we fail to solve them because we do not have a union and we are not collected ourselves so it becomes difficult. Tanzanian Manager 23 C-M
 Theme 3: Culture - Categories 13. Chinese Views on African and Chinese Values 14. Tanzanian Views on African And Chinese Values 15. Compatibility of Chinese Organization in Africa
Theme 3: Culture - Categories 13. Chinese Views on African and Chinese Values 14. Tanzanian Views on African And Chinese Values 15. Compatibility of Chinese Organization in Africa
 Theme 3: Culture Category 13: Chinese Views on African and Chinese Values Oh, a Chinese couple works very hard to buy a big house, but - you know - because they are working very hard they have got to find someone to take care of the house, right? . . . so they find like a house girl to help keep that house clean and whatever. So basically it looks like this young couple works from eight am to midnight everyday and their house girl sitting on the couch playing with the pad. And she sees the sunrise and sundown that is it. Chinese Manager 24 C-M
Theme 3: Culture Category 13: Chinese Views on African and Chinese Values Oh, a Chinese couple works very hard to buy a big house, but - you know - because they are working very hard they have got to find someone to take care of the house, right? . . . so they find like a house girl to help keep that house clean and whatever. So basically it looks like this young couple works from eight am to midnight everyday and their house girl sitting on the couch playing with the pad. And she sees the sunrise and sundown that is it. Chinese Manager 24 C-M
 Theme 3: Culture Category 14: Tanzanian Views on African and Chinese Values „. . . why I am saying they do not match is because you know Chinese they have what they like to do and what they like to be done that is all and you have to follow them. So I think that is the difference. So if they like to do something then you have to do it and you cannot work with them if you want to do things differently. “ Tanzanian Employee 22 C-E
Theme 3: Culture Category 14: Tanzanian Views on African and Chinese Values „. . . why I am saying they do not match is because you know Chinese they have what they like to do and what they like to be done that is all and you have to follow them. So I think that is the difference. So if they like to do something then you have to do it and you cannot work with them if you want to do things differently. “ Tanzanian Employee 22 C-E
 Theme 1: Organisation Overview categories 1 -9 (Tanzanian Manager) Tanzanian Manager (23 C-M - the only one in management) • Participation through management of department • Tanzanian assistant manager (not higher) Tanzanians work from 4 rth level downwards only. • Chinese dominate the management level • Blend of Chinese and Western management style • Tanzanians have weak expertise • Majority of Tanzanians work without contract / written agreement • Chinese have no culture of rewarding and motivation.
Theme 1: Organisation Overview categories 1 -9 (Tanzanian Manager) Tanzanian Manager (23 C-M - the only one in management) • Participation through management of department • Tanzanian assistant manager (not higher) Tanzanians work from 4 rth level downwards only. • Chinese dominate the management level • Blend of Chinese and Western management style • Tanzanians have weak expertise • Majority of Tanzanians work without contract / written agreement • Chinese have no culture of rewarding and motivation.
 Theme 1: Organisation Overview categories 1 -9 (Tanzanian Employees) Tanzanian Employees • No participation • No meetings • No knowledge sharing • No team work • No trainings • Many employees work without written contract • Tz earn monthly salary and normal wages
Theme 1: Organisation Overview categories 1 -9 (Tanzanian Employees) Tanzanian Employees • No participation • No meetings • No knowledge sharing • No team work • No trainings • Many employees work without written contract • Tz earn monthly salary and normal wages
 Theme 2: Environment Overview categories 10 -12 (Chinese Managers) Chinese Managers • Natural Environment: Tanzanian air is not so polluted • Community: Tanzania benefits of local employment and donations of Chinese government (e. g. education) • Benefits for Tanzania: railway, roads development, water supply, rebuilding of Central Railway Line • Sustainability of Chinese projects: TAZARA funds lacking for maintenance (spare parts and technicians)
Theme 2: Environment Overview categories 10 -12 (Chinese Managers) Chinese Managers • Natural Environment: Tanzanian air is not so polluted • Community: Tanzania benefits of local employment and donations of Chinese government (e. g. education) • Benefits for Tanzania: railway, roads development, water supply, rebuilding of Central Railway Line • Sustainability of Chinese projects: TAZARA funds lacking for maintenance (spare parts and technicians)
 Theme 2: Environment Overview categories 10 -12 (Chinese Employees) Chinese Employees • Community: emergency help as part of social responsibility, educational support, no communication with Tanzanians • Benefits for Tanzania: – suggestions, surveys and feasibility studies, infrastructure (harbours, roads, railways) – „Flaw laws“ and (high) need for development aid
Theme 2: Environment Overview categories 10 -12 (Chinese Employees) Chinese Employees • Community: emergency help as part of social responsibility, educational support, no communication with Tanzanians • Benefits for Tanzania: – suggestions, surveys and feasibility studies, infrastructure (harbours, roads, railways) – „Flaw laws“ and (high) need for development aid
 Theme 3: Culture, Category 13 (Chinese) Chinese Views on Self • Chinese value parents • Chinese respect elders • Chinese are not lying • Chinese are truth-telling • Chinese are hard working • Chinese respect Kung Fu Tse • Chinese do not make Tanzanian friends • Chinese entertain complicated relationships
Theme 3: Culture, Category 13 (Chinese) Chinese Views on Self • Chinese value parents • Chinese respect elders • Chinese are not lying • Chinese are truth-telling • Chinese are hard working • Chinese respect Kung Fu Tse • Chinese do not make Tanzanian friends • Chinese entertain complicated relationships
 Theme 3: Culture, Category 13 (Chinese) Chinese Views on Tanzanian Culture • Tanzanians are simple & entertain good relationships • Tanzanians enjoy life, relax and do not stress • Minority of Tanzanians well educated • Tanzanians are open, not worrying about future, respect each other and minorities • Tanzanians work slowly due to tropical heat, otherwise dehydration • Tanzanians are dishonest, unreliable and thiefs (material) • Tanzanians do not control work • In Tanzania personal safety not 100% due to some robberies
Theme 3: Culture, Category 13 (Chinese) Chinese Views on Tanzanian Culture • Tanzanians are simple & entertain good relationships • Tanzanians enjoy life, relax and do not stress • Minority of Tanzanians well educated • Tanzanians are open, not worrying about future, respect each other and minorities • Tanzanians work slowly due to tropical heat, otherwise dehydration • Tanzanians are dishonest, unreliable and thiefs (material) • Tanzanians do not control work • In Tanzania personal safety not 100% due to some robberies
 Theme Culture 3, Category 13 (Chinese) Chinese Ideas for Future Collaboration with Tanzanians • Tanzanians should learn Chinese culture, language, history to understand Chinese performance • Tanzanians should learn following: – Chinese feel pressure, – Chinese save their salaries, – Chinese do not believe in God, have no churches, and are helpful – planning, goal achievment and truth telling, field operation, efficiency, keep deadlines – Han culture is: fast, work hard, high technology, work for 16 hours a day – Chinese culture = a big ball that spins and absorbs all other cultures, mixing them with Chinese culture until it is like one Chinese culture
Theme Culture 3, Category 13 (Chinese) Chinese Ideas for Future Collaboration with Tanzanians • Tanzanians should learn Chinese culture, language, history to understand Chinese performance • Tanzanians should learn following: – Chinese feel pressure, – Chinese save their salaries, – Chinese do not believe in God, have no churches, and are helpful – planning, goal achievment and truth telling, field operation, efficiency, keep deadlines – Han culture is: fast, work hard, high technology, work for 16 hours a day – Chinese culture = a big ball that spins and absorbs all other cultures, mixing them with Chinese culture until it is like one Chinese culture
 Theme 3: Culture, Category 14 (Tanzanians) Tanzanians Views on Self • • Tanzanians have the spirit of hard working Tanzanians are tolerant and peaceful Tanzanians are cooperative Tanzanians are faithful, believing in God
Theme 3: Culture, Category 14 (Tanzanians) Tanzanians Views on Self • • Tanzanians have the spirit of hard working Tanzanians are tolerant and peaceful Tanzanians are cooperative Tanzanians are faithful, believing in God
 Theme 3: Culture, Category 14 (Tanzanians) Tanzanian Views on Chinese Culture • Chinese are fully committed • Chinese are working hard • Chinese are fair • Chinese stick to own lifestyle, are somehow segregative • Chinese blame and complain about African behaviour • Chinese get „poisened“ by bad information on Tanzanians
Theme 3: Culture, Category 14 (Tanzanians) Tanzanian Views on Chinese Culture • Chinese are fully committed • Chinese are working hard • Chinese are fair • Chinese stick to own lifestyle, are somehow segregative • Chinese blame and complain about African behaviour • Chinese get „poisened“ by bad information on Tanzanians
 Theme 3: Culture, Category 14 (Tanzanians) Tanzanian Ideas For Future Collaboration With Chinese • Chinese should learn: – English and Suaheli to make friends – – – history of the last hundred years and local culture African life style, tribal culture, dressing and food habits Respecting Tanzanians believe in God Taking care of nature
Theme 3: Culture, Category 14 (Tanzanians) Tanzanian Ideas For Future Collaboration With Chinese • Chinese should learn: – English and Suaheli to make friends – – – history of the last hundred years and local culture African life style, tribal culture, dressing and food habits Respecting Tanzanians believe in God Taking care of nature
 Summary • Difficulties of accessing Chinese organisations in Tanzania and gaining information • Employees and managers were open talking about challenges • Findings showed 3 themes: – Organisation (9 categories) – Environment and culture (each 3 categories) • Major challenges in terms of organisation: – Difficult working and training conditions for Tanzanian employees – Hardly any interaction with and contact to local communities – Many recreated stereotypes across cultural groups
Summary • Difficulties of accessing Chinese organisations in Tanzania and gaining information • Employees and managers were open talking about challenges • Findings showed 3 themes: – Organisation (9 categories) – Environment and culture (each 3 categories) • Major challenges in terms of organisation: – Difficult working and training conditions for Tanzanian employees – Hardly any interaction with and contact to local communities – Many recreated stereotypes across cultural groups
 General Recommendations • Design consent forms in compliance with intercultural standards and needs • Discuss ethical considerations regarding cross -cultural compatibility • In-depth analysis of data recommended of organisation 1 to 3. • Reflect and manage effects of ILO international law impacting on Chinese African international organisations (contracts, working conditions, trade unions etc. ) • Apply findings in practical work relationships and feedback to organisations highly recommended
General Recommendations • Design consent forms in compliance with intercultural standards and needs • Discuss ethical considerations regarding cross -cultural compatibility • In-depth analysis of data recommended of organisation 1 to 3. • Reflect and manage effects of ILO international law impacting on Chinese African international organisations (contracts, working conditions, trade unions etc. ) • Apply findings in practical work relationships and feedback to organisations highly recommended
 Thank you!
Thank you!


