83359d79707645a251f1459f1029cfcd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Child Protection Transformation Is Change Really Needed in Florida’s Child Welfare System?
Child Protection Transformation Is Change Really Needed in Florida’s Child Welfare System?
 The Reality of Florida’s Current System A child in FL is twice as likely to have an open child abuse investigation Our focus is very incident driven Our assessment process is not comprehensive Child safety is very subjective across the state Our response to unsafe children is inconsistent Florida accepts 8 out of every 10 calls made to the Hotline, creating a CPI investigation 80% of the time ◦ Only Alabama, Texas, and Washington DC have higher percentages
The Reality of Florida’s Current System A child in FL is twice as likely to have an open child abuse investigation Our focus is very incident driven Our assessment process is not comprehensive Child safety is very subjective across the state Our response to unsafe children is inconsistent Florida accepts 8 out of every 10 calls made to the Hotline, creating a CPI investigation 80% of the time ◦ Only Alabama, Texas, and Washington DC have higher percentages
 Why Are We Transforming? Nubia Barahona’s death in 2011 o A thorough case review revealed: Inconsistent, inefficient, and redundant practices throughout the state High recurrence, recidivism, re-investigation rates Technology and system inefficiencies Staff turnover and ineffective training o This case spearheaded the need for “change” in FL
Why Are We Transforming? Nubia Barahona’s death in 2011 o A thorough case review revealed: Inconsistent, inefficient, and redundant practices throughout the state High recurrence, recidivism, re-investigation rates Technology and system inefficiencies Staff turnover and ineffective training o This case spearheaded the need for “change” in FL
 Project Organization Florida Safety Decision Making Methodology (FSDMM) Professionalism Technology Compliance Communication and Change Management
Project Organization Florida Safety Decision Making Methodology (FSDMM) Professionalism Technology Compliance Communication and Change Management
 Project Organization FSDMM: Florida Safety Decision Making Methodology ◦ Major practice reform from Hotline to On-going Services New methodology is considered “Cutting Edge” or a best practice approach for child welfare services A similar safety methodology is used by 20 other states across the country ◦ Improving the quality of our work with families ◦ Standardized agency performance metrics
Project Organization FSDMM: Florida Safety Decision Making Methodology ◦ Major practice reform from Hotline to On-going Services New methodology is considered “Cutting Edge” or a best practice approach for child welfare services A similar safety methodology is used by 20 other states across the country ◦ Improving the quality of our work with families ◦ Standardized agency performance metrics
 Project Organization Professionalism: ◦ ◦ Base salary increases for investigators Career opportunities Development of and compliance with FSDMM Appropriate use of authority
Project Organization Professionalism: ◦ ◦ Base salary increases for investigators Career opportunities Development of and compliance with FSDMM Appropriate use of authority
 Project Organization Technology: ◦ Command Center Transformation at the Hotline ◦ Florida Safe Families Network (FSFN) Updates ◦ Statewide Automated Child Welfare Information System (SACWIS) Compliance ◦ Creating a better system to allow Child Welfare Professionals to be in the field with families and not restricted by timeframes, paperwork, and/or computer work
Project Organization Technology: ◦ Command Center Transformation at the Hotline ◦ Florida Safe Families Network (FSFN) Updates ◦ Statewide Automated Child Welfare Information System (SACWIS) Compliance ◦ Creating a better system to allow Child Welfare Professionals to be in the field with families and not restricted by timeframes, paperwork, and/or computer work
 Project Organization Compliance: ◦ Chapter 39 Revisions ◦ Administrative Code (65 C) Revisions ◦ Operating Procedure Updates **Laws and Rules will all be aligned with the Florida Safety Decision Making Methodology (FSDMM)
Project Organization Compliance: ◦ Chapter 39 Revisions ◦ Administrative Code (65 C) Revisions ◦ Operating Procedure Updates **Laws and Rules will all be aligned with the Florida Safety Decision Making Methodology (FSDMM)
 Project Organization Communication and Change Management: ◦ Ensure delivery of core concepts and project messages to ALL stakeholders including YOU!
Project Organization Communication and Change Management: ◦ Ensure delivery of core concepts and project messages to ALL stakeholders including YOU!
 What is Child Protection Transformation? Multi-year project designed to address identified concerns with Florida’s Child Protection System ◦ Started over 2 years ago with the CPI Initiative ◦ Dependency Judges have been a positive voice for this project ◦ Developed from years of research and other states across the country effectively using safety models in their child welfare systems
What is Child Protection Transformation? Multi-year project designed to address identified concerns with Florida’s Child Protection System ◦ Started over 2 years ago with the CPI Initiative ◦ Dependency Judges have been a positive voice for this project ◦ Developed from years of research and other states across the country effectively using safety models in their child welfare systems
 The Vision of Transformation To work more effectively with families and children toward achieving child safety Florida families deserve to work with highly skilled, trained, knowledgeable professionals to keep children safe, keep families together when possible, with focus on protective capacities and family engagement To help families achieve child safety and self sufficiency even when intervention is necessary
The Vision of Transformation To work more effectively with families and children toward achieving child safety Florida families deserve to work with highly skilled, trained, knowledgeable professionals to keep children safe, keep families together when possible, with focus on protective capacities and family engagement To help families achieve child safety and self sufficiency even when intervention is necessary
 How Is This Accomplished? Introducing a consistently applied safety decision making methodology Professionalizing our Workforce Enhancing our Technology
How Is This Accomplished? Introducing a consistently applied safety decision making methodology Professionalizing our Workforce Enhancing our Technology
 What Will Be Achieve? Improved and permanently changed business practice and consistent safety decision making Reduce re-investigations and re-victimization Systems integration and technology improvements for efficiency Professionalized and stabilized workforce Higher quality casework and better outcomes for children and families Serving the RIGHT families for the RIGHT reasons
What Will Be Achieve? Improved and permanently changed business practice and consistent safety decision making Reduce re-investigations and re-victimization Systems integration and technology improvements for efficiency Professionalized and stabilized workforce Higher quality casework and better outcomes for children and families Serving the RIGHT families for the RIGHT reasons
 Child Protection Transformation Florida Safety Decision Making Methodology Florida Department of Children and Families Copyright 2013 Florida Department of Children & Families
Child Protection Transformation Florida Safety Decision Making Methodology Florida Department of Children and Families Copyright 2013 Florida Department of Children & Families
 800 -96 -ABUSE Hotline-Currently, a very high screen in rate ◦ Process now is VERY intrusive CPI-High recidivism Case Management-High case loads Community Partners-Mandatory reporting Copyright 2013 Florida Department of Children & Families
800 -96 -ABUSE Hotline-Currently, a very high screen in rate ◦ Process now is VERY intrusive CPI-High recidivism Case Management-High case loads Community Partners-Mandatory reporting Copyright 2013 Florida Department of Children & Families
 Definition of Safe and Unsafe SAFE…children are considered safe when there are no present or impending danger threats, or the caregivers’ protective capacities control existing threats UNSAFE… children are vulnerable to present or impending danger threats, and caregivers have insufficient protective capacity to control existing threats.
Definition of Safe and Unsafe SAFE…children are considered safe when there are no present or impending danger threats, or the caregivers’ protective capacities control existing threats UNSAFE… children are vulnerable to present or impending danger threats, and caregivers have insufficient protective capacity to control existing threats.
 Present Danger Immediate Significant Clearly Observable Severe harm Present tense---right now Requires immediate response
Present Danger Immediate Significant Clearly Observable Severe harm Present tense---right now Requires immediate response
 Impending Danger …. not happening at this moment……but a “state of danger” Child is in a position of continual danger
Impending Danger …. not happening at this moment……but a “state of danger” Child is in a position of continual danger
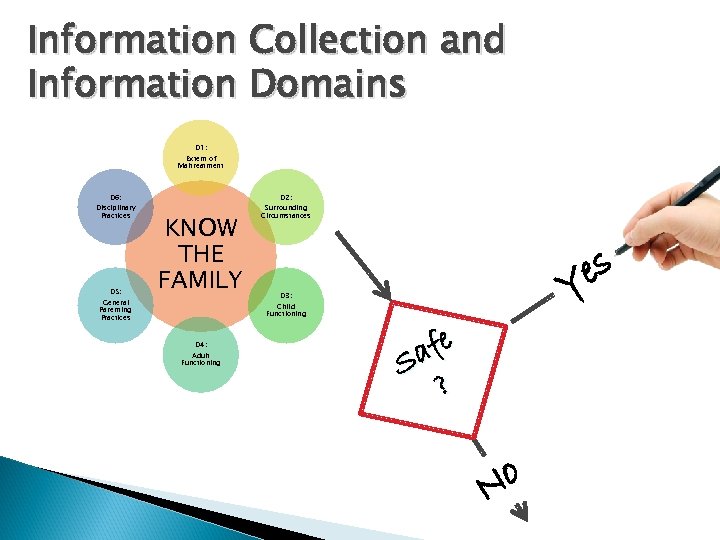 Information Collection and Information Domains D 1: Extent of Maltreatment D 6: Disciplinary Practices D 5: General Parenting Practices D 2: KNOW THE FAMILY Surrounding Circumstances es Y D 3: Child Functioning D 4: Adult Functioning afe S ? o N
Information Collection and Information Domains D 1: Extent of Maltreatment D 6: Disciplinary Practices D 5: General Parenting Practices D 2: KNOW THE FAMILY Surrounding Circumstances es Y D 3: Child Functioning D 4: Adult Functioning afe S ? o N
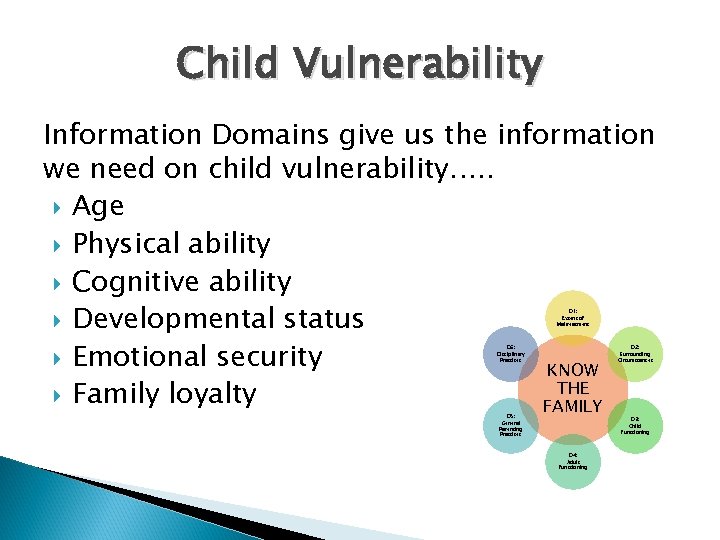 Child Vulnerability Information Domains give us the information we need on child vulnerability…. . Age Physical ability Cognitive ability Developmental status Emotional security KNOW THE Family loyalty FAMILY D 1: Extent of Maltreatment D 6: Disciplinary Practices D 2: Surrounding Circumstances D 5: General Parenting Practices D 3: Child Functioning D 4: Adult Functioning
Child Vulnerability Information Domains give us the information we need on child vulnerability…. . Age Physical ability Cognitive ability Developmental status Emotional security KNOW THE Family loyalty FAMILY D 1: Extent of Maltreatment D 6: Disciplinary Practices D 2: Surrounding Circumstances D 5: General Parenting Practices D 3: Child Functioning D 4: Adult Functioning
 Definition of Protective Capacity…. how a parent thinks, feels, acts…. .
Definition of Protective Capacity…. how a parent thinks, feels, acts…. .
 Protective Capacities Vigilant Protectiveness Cognitive Behavioral Emotional
Protective Capacities Vigilant Protectiveness Cognitive Behavioral Emotional
 Cognitive Protective Capacity Cognitive protective capacity Intellectual knowledge, understanding and perceptions Contribute to protective vigilance reality oriented accurate perception of a child recognition of a child’s needs ability to accurately process and interpret various stimuli • understanding of protective role • intellectually able • understanding and recognizing threats • •
Cognitive Protective Capacity Cognitive protective capacity Intellectual knowledge, understanding and perceptions Contribute to protective vigilance reality oriented accurate perception of a child recognition of a child’s needs ability to accurately process and interpret various stimuli • understanding of protective role • intellectually able • understanding and recognizing threats • •
 Behavioral Protective Capacity Specific action, activity, performance that results in protective vigilance • • • physical capacity and energy ability to set aside own needs adaptive, assertive and responsive takes action impulse control history of being protective
Behavioral Protective Capacity Specific action, activity, performance that results in protective vigilance • • • physical capacity and energy ability to set aside own needs adaptive, assertive and responsive takes action impulse control history of being protective
 Emotional Protective Capacity Emotional protective capacity: Feelings, attitudes and identification with the child that results in protective vigilance • • emotional bond with the child positive attachment with the child love, sensitivity and empathy for the child resiliency stability effectively meets own emotional needs emotional control realizes the child cannot produce gratification and self-esteem for the parent
Emotional Protective Capacity Emotional protective capacity: Feelings, attitudes and identification with the child that results in protective vigilance • • emotional bond with the child positive attachment with the child love, sensitivity and empathy for the child resiliency stability effectively meets own emotional needs emotional control realizes the child cannot produce gratification and self-esteem for the parent
 What is a Safety Plan? Safety plan: actions and services that will temporarily substitute for the lacking parental protective capacity to control the danger threats 26
What is a Safety Plan? Safety plan: actions and services that will temporarily substitute for the lacking parental protective capacity to control the danger threats 26
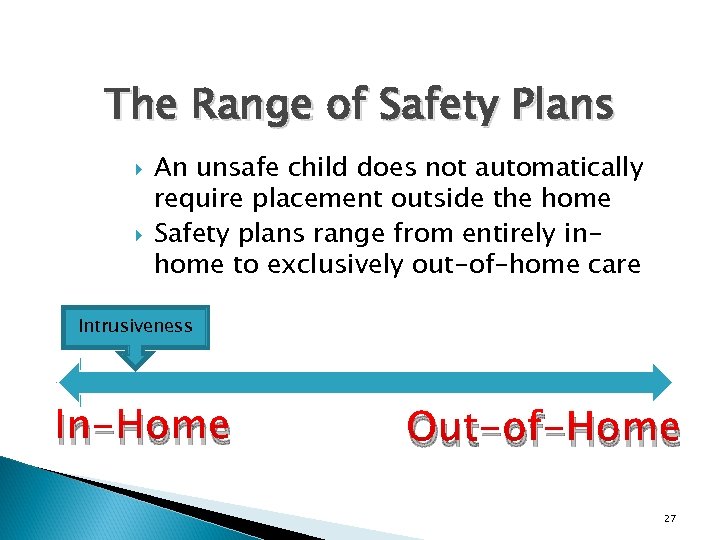 The Range of Safety Plans An unsafe child does not automatically require placement outside the home Safety plans range from entirely inhome to exclusively out-of-home care Intrusiveness In-Home Out-of-Home 27
The Range of Safety Plans An unsafe child does not automatically require placement outside the home Safety plans range from entirely inhome to exclusively out-of-home care Intrusiveness In-Home Out-of-Home 27
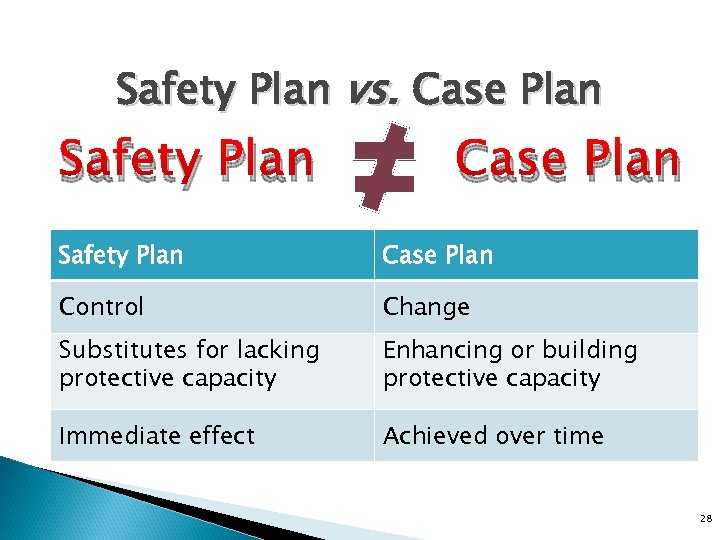 Safety Plan vs. Case Plan Safety Plan Case Plan Control Change Substitutes for lacking protective capacity Enhancing or building protective capacity Immediate effect Achieved over time 28
Safety Plan vs. Case Plan Safety Plan Case Plan Control Change Substitutes for lacking protective capacity Enhancing or building protective capacity Immediate effect Achieved over time 28
 Most families have “Risk Factors” but not all risk factors mean “Services” for those families Safe Children: • provides a measure for identifying families for prevention services. Unsafe children: • case management services
Most families have “Risk Factors” but not all risk factors mean “Services” for those families Safe Children: • provides a measure for identifying families for prevention services. Unsafe children: • case management services
 Ongoing Family Functioning Decisions ü ü ü Are danger threats being managed? How can existing protective capacities – STRENGTHS – be built upon to make changes? What is the relationship between danger threats and the diminished caregiver protective capacities—What Must Change? What are the parents’ perspective or awareness of their caregiver protective capacities? What are the child’s needs and how are the parents meeting or not meeting those needs?
Ongoing Family Functioning Decisions ü ü ü Are danger threats being managed? How can existing protective capacities – STRENGTHS – be built upon to make changes? What is the relationship between danger threats and the diminished caregiver protective capacities—What Must Change? What are the parents’ perspective or awareness of their caregiver protective capacities? What are the child’s needs and how are the parents meeting or not meeting those needs?
 Ongoing Family Functioning Decisions ü ü ü What are the parents ready and willing to work on in the case plan? What are the areas of disagreement in what needs to change? What change strategy (case plan) will be used to assist in enhancing diminished care giver protective capacities?
Ongoing Family Functioning Decisions ü ü ü What are the parents ready and willing to work on in the case plan? What are the areas of disagreement in what needs to change? What change strategy (case plan) will be used to assist in enhancing diminished care giver protective capacities?
 Ongoing Safety Evaluation Can an in-home safety plan replace the out-of-home safety plan? Can we step down the intensity of our intervention?
Ongoing Safety Evaluation Can an in-home safety plan replace the out-of-home safety plan? Can we step down the intensity of our intervention?
 Impact on Internal and External Stakeholders Safety Decision Making Methodology impacts everything: policy, automated system, legal system, quality assurance, staff development. Agency partners – focus on safety services and safety management; includes substance abuse, mental health, domestic violence Legal stakeholders – new constructs, new decision making criteria, new expectations
Impact on Internal and External Stakeholders Safety Decision Making Methodology impacts everything: policy, automated system, legal system, quality assurance, staff development. Agency partners – focus on safety services and safety management; includes substance abuse, mental health, domestic violence Legal stakeholders – new constructs, new decision making criteria, new expectations
 Implementation
Implementation
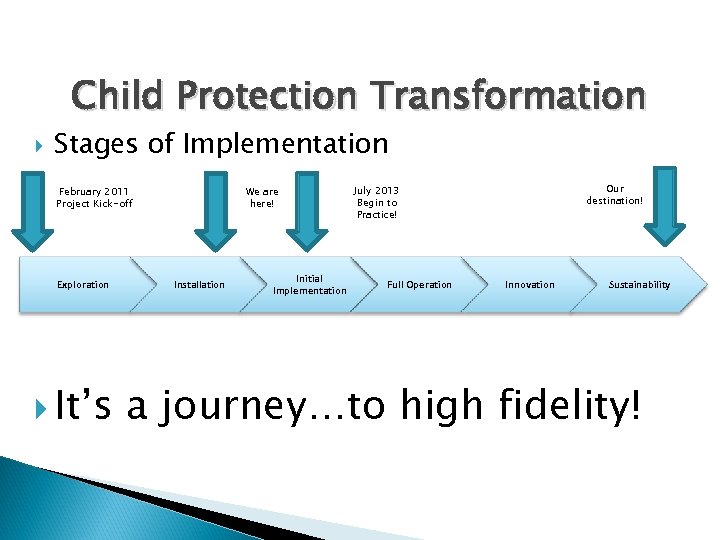 Child Protection Transformation Stages of Implementation February 2011 Project Kick-off Exploration It’s We are here! Installation Initial Implementation Our destination! July 2013 Begin to Practice! Full Operation Innovation Sustainability a journey…to high fidelity!
Child Protection Transformation Stages of Implementation February 2011 Project Kick-off Exploration It’s We are here! Installation Initial Implementation Our destination! July 2013 Begin to Practice! Full Operation Innovation Sustainability a journey…to high fidelity!
 Implementation • • Statewide Implementation Team Sun. Coast Region Training Plans Circuit 6 Training Plans for roll out Capacity Building Super Safety Practice Experts – 42 Safety Practice Experts – 200 Trainer Proficiency Evaluation Process
Implementation • • Statewide Implementation Team Sun. Coast Region Training Plans Circuit 6 Training Plans for roll out Capacity Building Super Safety Practice Experts – 42 Safety Practice Experts – 200 Trainer Proficiency Evaluation Process
 Practice Makes Perfect! Until Then…
Practice Makes Perfect! Until Then…
 Contact Information C P I • Shawna Thomas/Super Safety Practice Expert • sthomas@pascosheriff. org • Trainer, Pasco Sheriff’s Office • Lisa Tobin/Safety Practice Expert • ltobin@pascosheriff. org • Training Supervisor, Pasco Sheriff’s Office • Kristine Fletcher/Safety Practice Expert • kfletcher@pascosheriff. org • Program Manager, Pasco Sheriff’s Office
Contact Information C P I • Shawna Thomas/Super Safety Practice Expert • sthomas@pascosheriff. org • Trainer, Pasco Sheriff’s Office • Lisa Tobin/Safety Practice Expert • ltobin@pascosheriff. org • Training Supervisor, Pasco Sheriff’s Office • Kristine Fletcher/Safety Practice Expert • kfletcher@pascosheriff. org • Program Manager, Pasco Sheriff’s Office
 Questions and Discussion?
Questions and Discussion?


