Асямолова.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 12
 Chickenpox Work performed : student group MS-113 D Asyamolova Olga.
Chickenpox Work performed : student group MS-113 D Asyamolova Olga.
 Table of contents 1)the definition of the disease; 2) epidemiology; 3) pathogenesis; 4) course of illness; 5) symptoms; 6)complications of the disease; 7)nursing; 8)treatment;
Table of contents 1)the definition of the disease; 2) epidemiology; 3) pathogenesis; 4) course of illness; 5) symptoms; 6)complications of the disease; 7)nursing; 8)treatment;
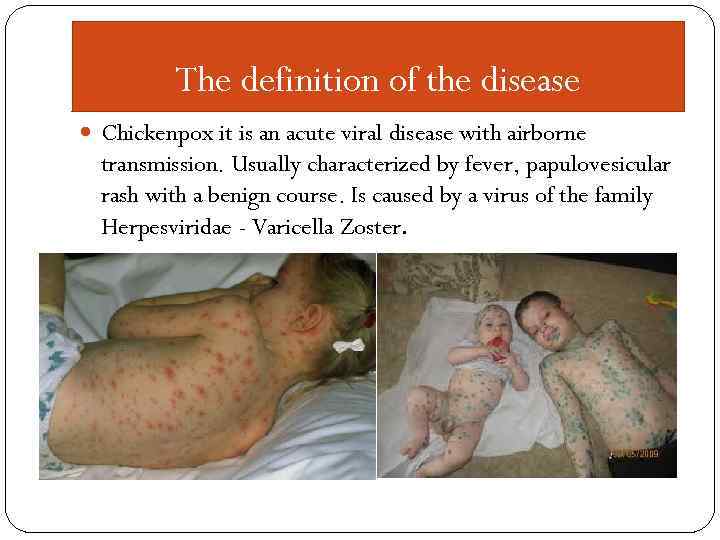 The definition of the disease Chickenpox it is an acute viral disease with airborne transmission. Usually characterized by fever, papulovesicular rash with a benign course. Is caused by a virus of the family Herpesviridae - Varicella Zoster.
The definition of the disease Chickenpox it is an acute viral disease with airborne transmission. Usually characterized by fever, papulovesicular rash with a benign course. Is caused by a virus of the family Herpesviridae - Varicella Zoster.
 Epidemiology The source of infection is a sick man, representing the epidemic danger from the end of the incubation period and prior to the lapse of the crusts. The pathogen is spread by airborne droplets. Ill mostly children aged 6 months to 7 years. Adults suffer chickenpox rare because usually carry it even in childhood. In patients with severe immunodeficiency different etiology (in the rare case when HIV infection and in patients after organ transplantation; often acclimatization, and decreased immunity caused by severe stress) possible reinfection.
Epidemiology The source of infection is a sick man, representing the epidemic danger from the end of the incubation period and prior to the lapse of the crusts. The pathogen is spread by airborne droplets. Ill mostly children aged 6 months to 7 years. Adults suffer chickenpox rare because usually carry it even in childhood. In patients with severe immunodeficiency different etiology (in the rare case when HIV infection and in patients after organ transplantation; often acclimatization, and decreased immunity caused by severe stress) possible reinfection.
 Pathogenesis The virus enters the body through the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and is embedded in the epithelial cells of the mucosa. The virus then enters the blood and is fixed in the skin, causing the surface layer of the pathological process: limited expansion of capillaries (spot), serous edema (papule), peeling of the epidermis (vesicles). Due to the propagation of the virus and allergic response of the body arise fever and other common non-specific symptoms of infection. After an illness occurs a strong immunity.
Pathogenesis The virus enters the body through the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and is embedded in the epithelial cells of the mucosa. The virus then enters the blood and is fixed in the skin, causing the surface layer of the pathological process: limited expansion of capillaries (spot), serous edema (papule), peeling of the epidermis (vesicles). Due to the propagation of the virus and allergic response of the body arise fever and other common non-specific symptoms of infection. After an illness occurs a strong immunity.
 Course of illness During varicella distinguish the following periods: incubation, prodromal period, periods of eruptions and the formation of crusts. The incubation period for patients aged 30 years is 11 -21 day, up to 30 years 13 -17 days (average 14). Prodromal period occurs within 1 -2 days before the rash (in some cases prodromal period is absent and the disease manifests rash). Prodromal phenomena in children may not be expressed. In adults prodromal phenomena are more frequent and heavier flow (headache, low back pain, fever). Period rash most babies flows without much disturbance of the General condition, fever coincides with the mass of the rash, the rash appears Tacloban, so the fever may have a wave like character. In adults, the rash is often massive, accompanied by fever, General toxic effects severe itching.
Course of illness During varicella distinguish the following periods: incubation, prodromal period, periods of eruptions and the formation of crusts. The incubation period for patients aged 30 years is 11 -21 day, up to 30 years 13 -17 days (average 14). Prodromal period occurs within 1 -2 days before the rash (in some cases prodromal period is absent and the disease manifests rash). Prodromal phenomena in children may not be expressed. In adults prodromal phenomena are more frequent and heavier flow (headache, low back pain, fever). Period rash most babies flows without much disturbance of the General condition, fever coincides with the mass of the rash, the rash appears Tacloban, so the fever may have a wave like character. In adults, the rash is often massive, accompanied by fever, General toxic effects severe itching.
 The resulting rash looks pink spots the size of 2 -4 mm, which in a few hours turn into papules, some of which, in turn, becomes the vesicles. Vesicles chamber, surrounded by a ring of hyperemia. After 1 -3 days they dry up, forming a surface crust is dark red or brown color, which fall on the 2 -3 rd week. As the rash appears again, the rash is polymorphic in nature, that is, in a limited area can be seen at the same time spots, papules, vesicles, and crusts. Simultaneously with skin rash, mucous membranes appears enanthema. It's the bubbles that quickly marirosa, turning into a sore with a yellowish-gray bottom, surrounded by a red rim. Often enanthema limited to 1 -3 items. Heals enanthema within 1 -2 days. Febrile period lasts 2 -5 days, sometimes up to 8 -10 days (if the rash is very heavy and prolonged). The rash can last from 2 to 5 days and up to 7 -9 days. Usually chickenpox occurs benign, but with the development of bullous, or hemorrhagic gangrenous form of the disease and possible complications such as encephalitis, myocarditis, pyoderma, lymphadenitis. Chickenpox in pregnant women is not considered by doctors as an indication for abortion. When infected with chickenpox during pregnancy up to 14 weeks, the risk to the fetus is 0. 4 %, while infection in the period from 14 to 20 weeks - no more than 2 %. After 20 weeks for a child there is virtually no risk. Treatment of specific immunoglobulin during pregnancy dramatically reduces even this very small risk to the unborn child.
The resulting rash looks pink spots the size of 2 -4 mm, which in a few hours turn into papules, some of which, in turn, becomes the vesicles. Vesicles chamber, surrounded by a ring of hyperemia. After 1 -3 days they dry up, forming a surface crust is dark red or brown color, which fall on the 2 -3 rd week. As the rash appears again, the rash is polymorphic in nature, that is, in a limited area can be seen at the same time spots, papules, vesicles, and crusts. Simultaneously with skin rash, mucous membranes appears enanthema. It's the bubbles that quickly marirosa, turning into a sore with a yellowish-gray bottom, surrounded by a red rim. Often enanthema limited to 1 -3 items. Heals enanthema within 1 -2 days. Febrile period lasts 2 -5 days, sometimes up to 8 -10 days (if the rash is very heavy and prolonged). The rash can last from 2 to 5 days and up to 7 -9 days. Usually chickenpox occurs benign, but with the development of bullous, or hemorrhagic gangrenous form of the disease and possible complications such as encephalitis, myocarditis, pyoderma, lymphadenitis. Chickenpox in pregnant women is not considered by doctors as an indication for abortion. When infected with chickenpox during pregnancy up to 14 weeks, the risk to the fetus is 0. 4 %, while infection in the period from 14 to 20 weeks - no more than 2 %. After 20 weeks for a child there is virtually no risk. Treatment of specific immunoglobulin during pregnancy dramatically reduces even this very small risk to the unborn child.
 Symptoms The most characteristic symptom is an itchy rash. The day before the rash is slightly raised temperature, deteriorating General condition, appetite vanishes. Within 24 hours on the trunk and scalp appear small reddish-pink spots that turn into blisters filled with clear content. The contents of the bubbles becomes cloudy, they revealed, then they are formed crust. Rashes can move on the face, sometimes on hands and feet. Within 3 -4 days there are new lesions. Sometimes the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes, genitals, there are small sores.
Symptoms The most characteristic symptom is an itchy rash. The day before the rash is slightly raised temperature, deteriorating General condition, appetite vanishes. Within 24 hours on the trunk and scalp appear small reddish-pink spots that turn into blisters filled with clear content. The contents of the bubbles becomes cloudy, they revealed, then they are formed crust. Rashes can move on the face, sometimes on hands and feet. Within 3 -4 days there are new lesions. Sometimes the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes, genitals, there are small sores.
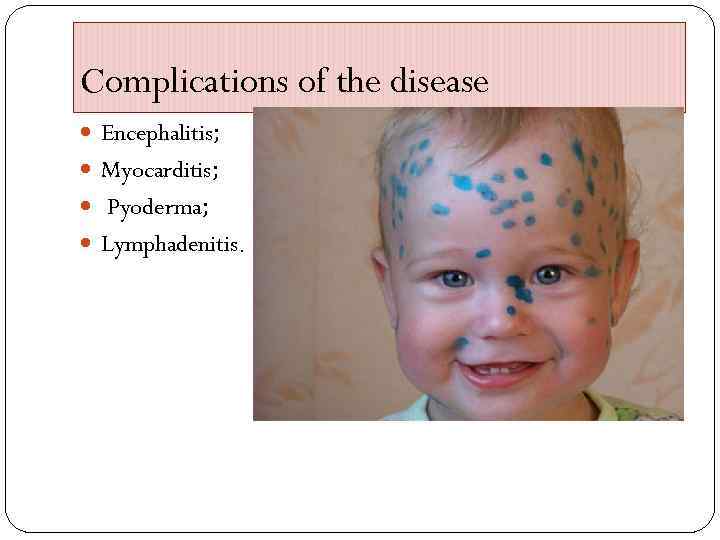 Complications of the disease Encephalitis; Myocarditis; Pyoderma; Lymphadenitis.
Complications of the disease Encephalitis; Myocarditis; Pyoderma; Lymphadenitis.
 Nursing If your child is sick with chickenpox: 1)make sure that it does not RUB the skin. Because itching can be irresistible; 2) briefly podstawie baby nails or put his hands mittens; 3) Ask your doctor to prescribe a medicine that relieves itching; 4) To prevent infection of the skin, make sure that the child was clean all the time. With the emergence of strong and painful skin or burning sensation, immediately contact your doctor. These symptoms may indicate a serious secondary infection. 5)Aspirin patients chickenpox can lead to the development of a very dangerous Raynaud's syndrome. 6)Instead of aspirin, if necessary, give your child tylenol or other medication that contains acetaminophen). Or ask your doctor to prescribe you another safe cure.
Nursing If your child is sick with chickenpox: 1)make sure that it does not RUB the skin. Because itching can be irresistible; 2) briefly podstawie baby nails or put his hands mittens; 3) Ask your doctor to prescribe a medicine that relieves itching; 4) To prevent infection of the skin, make sure that the child was clean all the time. With the emergence of strong and painful skin or burning sensation, immediately contact your doctor. These symptoms may indicate a serious secondary infection. 5)Aspirin patients chickenpox can lead to the development of a very dangerous Raynaud's syndrome. 6)Instead of aspirin, if necessary, give your child tylenol or other medication that contains acetaminophen). Or ask your doctor to prescribe you another safe cure.
 Treatment 1)Bed rest throughout the febrile period; 2) The use of interferon reduces (sometimes prevents podsypanina, reduces the number of complications; 3) The use of interferon reduces (sometimes prevents podsypanina, reduces the number of complications; 4) The use of ultraviolet irradiation can be shown to accelerate the fall of peel; 5) To reduce the temperature widely used paracetamol.
Treatment 1)Bed rest throughout the febrile period; 2) The use of interferon reduces (sometimes prevents podsypanina, reduces the number of complications; 3) The use of interferon reduces (sometimes prevents podsypanina, reduces the number of complications; 4) The use of ultraviolet irradiation can be shown to accelerate the fall of peel; 5) To reduce the temperature widely used paracetamol.



