462af483d5bc88014d1d7121e0369ee4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

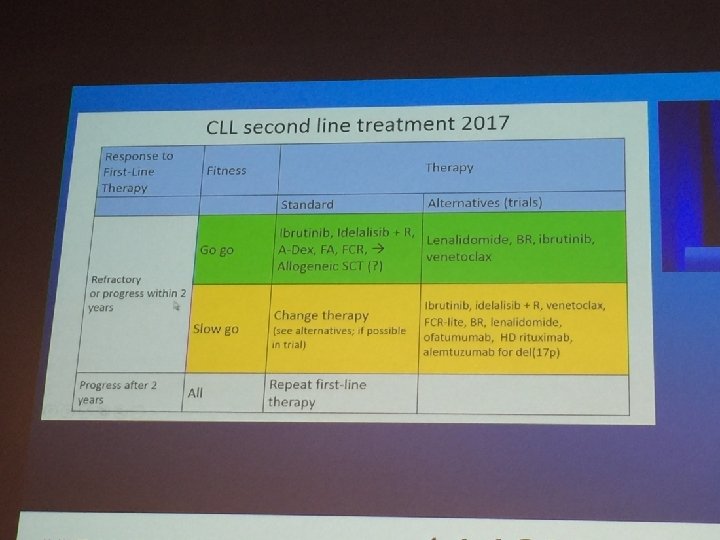
Chemotherapy-free Combinations
Introduction: The depth and durability of response to ibrutinib in patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory (R/R) MCL and high risk CLL is limited. TGR-1202 is a novel oral PI 3 K-δ specific inhibitor designed to have less toxicity than other PI 3 K inhibitors. We hypothesized that combined PI 3 K/BTK blockade with TGR-1202 and ibrutinib would be tolerable and efficacious in R/R MCL and CLL. This is an ongoing phase I/Ib investigator-initiated trial with primary endpoints of recommended phase 2 dose (RP 2 D) and safety/tolerability. Secondary endpoints include ORR and CR rates, PFS, and OS.

Pts receive daily ibrutinib (560 mg MCL, 420 mg CLL) and TGR-1202 doses from 400 mg to 800 mg were evaluated in a standard 3 + 3 design. Pts continue both drugs until progression or unacceptable toxicity. Eligibility criteria: ≥ 1 prior therapy, ECOG PS ≤ 2, and adequate hematologic and organ function. Prior PI 3 K/BTK inhibitors were allowed. Lugano Classification (MCL) and IW-CLL criteria were used to evaluate efficacy.
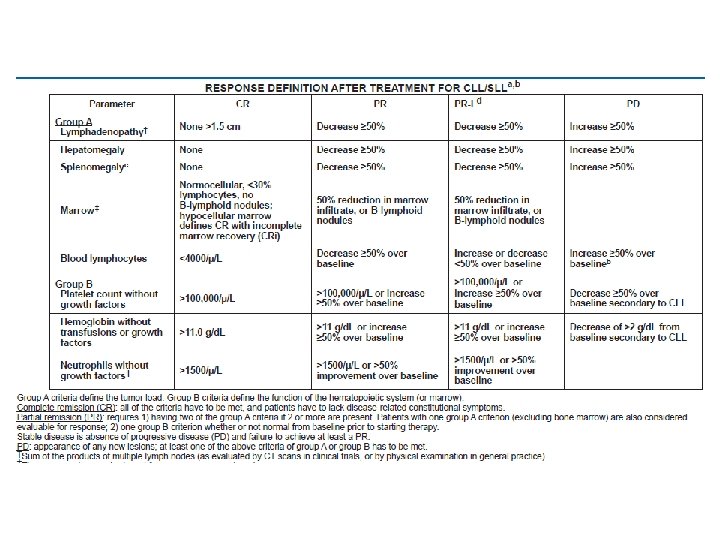
TERMİNOLOJİ Blood. 2008; 111(12): 5446 -56. Relaps: Daha evvelden CR (tam remisyon) ya da PR (kısmi remisyon) elde edilmiş olan hastada 6 ay ya da daha uzun bir zaman sonra progresyon görülmesi. Refrakter hastalık: Tedavi başarısızlığı ya da son tedaviden itibaren ilk 6 ay içinde hastalık progresyonu görülmesi. Tedavi başarısızlığı: Tam ya da kısmi remisyon dışında kalan tüm yanıtlar (stabil hastalık, yanıtsız, progressif hastalık, exitus) tedavi başarısızlığı olarak adlandırılmalıdır.
Results: Thirty-three pts have enrolled on study, including 15 MCL and 18 CLL pts. The median age at enrollment was 67 yrs. (range 48 -83). The median number of prior therapies was 3 for MCL (range 2 -5, including 4 with prior auto. SCT) and 2 for CLL (range 1 -6). In CLL pts, del(17 p) was present in 4/17 (24%), del (11 q) in 7/17 (41%), and unmutated IGHV in 11/17 (65%). In phase I, no DLTs occurred in either arm, and the RP 2 D of TGR-1202 for both MCL and CLL was 800 mg.

In a combined safety analysis of both arms (n = 33), hematologic toxicity included neutropenia (36%, 12% gr 3/4), thrombocytopenia (21%, 3% gr 3), and anemia (21%, 3% gr 3). All grade non-hematologic toxicities in >10% of pts included: nausea (36%, all gr 1/2), fatigue (33%, all gr 1/2), diarrhea (33%, all gr 1/2), and dizziness (24%, all gr 1). Transaminitis (all gr 1) was observed in 7/33 (21%) pts. SAEs included 2 pts each with: gr 3/4 lipase elevation, gr 3 hypophosphatemia, CNS aspergillus infection, and atrial fibrillation, and 1 pt each with: adrenal insufficiency (gr 3), influenza A infection (gr 4), C. difficile infection (gr 4), and sudden death of uncertain cause. Two pts had dose reduction of TGR-1202 (dizziness, nausea), and 3 pts had dosereduction of ibrutinib (atrial fibrillation, palpitations, vitreous hemorrhage).
In CLL, with a median time on study of 11 mo. (range 0. 1 -23. 5 mo. ), the ORR is 89% (16/18), with 1 pt achieving iw. CLL CR, and 1 pt with radiographic CR. The 1 year PFS and OS for MCL are 37% and 52%, and for CLL both are 94%. Conclusions: TGR-1202 plus ibrutinib is well-tolerated in pts with R/R MCL and CLL, with no DLTs observed and a RP 2 D of TGR-1202 800 mg daily. Preliminary efficacy data suggest a high response rate in both diseases. Phase Ib expansion cohorts continue to accrue in this ongoing study (NCT 02268851).

Lymphoma Biology
Stabilizing mutations of NOTCH 1 occur in about 10% of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cases at diagnosis, with a higher frequency in unmutated IGHV (IGHV-UM), immuno-chemorefractory or advanced disease phase CLL, and have been associated with particularly unfavourable prognosis. NOTCH 1 mutations were investigated by NGS. Gene expression profile (GEP) was performed on a one-color 4 x 44 K platform. Validations were performed by QRTPCR, western blotting, flow cytometry. Cell proliferation was evaluated by Cell. Trace assay.

After 48 h culture, NOTCH 1 -mut CLL cells showed increased MYC transcript levels than NOTCH 1 -wt cells. Conclusions: NOTCH 1 mutations in CLL are associated with the overexpression of MYC and MYC-related genes involved in protein biosynthesis including NPM 1.

Novel anti-Lymphoma Strategies

Introduction: The Phase 3 RIAlt. O trial opened in December 2011 to compare ofatumumab plus chlorambucil (O + C) with ofatumumab plus bendamustine (O + B) in patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) considered unfit for FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, rituximab).

A protocol amendment was introduced in September 2014 to investigate the addition of idelalisib (first-in-class inhibitor of the p 110δ isoform of phosphoinositol-3 kinase) or placebo. Review of safety data in January 2016 revealed excessive toxicity due to idelalisib, and recruitment was suspended. All idelalisib/placebo treatment was withdrawn from the trial in March 2016 following safety analysis of idelalisib registration studies and recommendations from Gilead Sciences Ltd and regulatory authorities. Here, we present a preliminary analysis of the cohort of patients in RIAlt. O who received idelalisib or placebo.
Methods: Patients were eligible for inclusion if they had previously untreated CLL requiring treatment by NCI/IWCLL criteria, were considered unfit for FCR and did not have any contraindications to the study drugs. Consenting patients underwent an unblinded 1: 1 randomisation to ofatumumab (300 mg iv day 1 and 1000 mg iv day 8 of cycle 1; 1000 mg iv day 1 of cycle 2 onwards) plus either chlorambucil (10 mg/m 2 day 1 -7, repeated every 28 days for 3 -12 cycles) or bendamustine (70 mg/m 2 iv day 1 -2 for 3 -6 cycles) and a double-blinded 1: 1 randomisation to concurrently administered placebo or idelalisib (150 mg bd for up to 3 years). Co-trimoxazole prophylaxis was recommended. Study drugs were continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS). The post-treatment reporting period for serious adverse events (SAEs) was 6 months for grade 3 -4 infections and 28 days for other events.

Results: 145 patients received idelalisib (73) or placebo (72), with a median idelalisib exposure time of 2. 5 months. As of March 2017, SAEs were reported in 77% of idelalisib-treated patients (81 grade 3 -4 and 8 grade 5) compared to 39% in the placebo group (35 grade 3 -4 and 2 grade 5). The frequency of SAEs in the idelalisib-treated group was similar in both chemotherapy arms. Grade 5 events in this group included sepsis (1), lung infection (3), febrile neutropenia (2), myocardial infarction (1) and sudden death NOS (1).
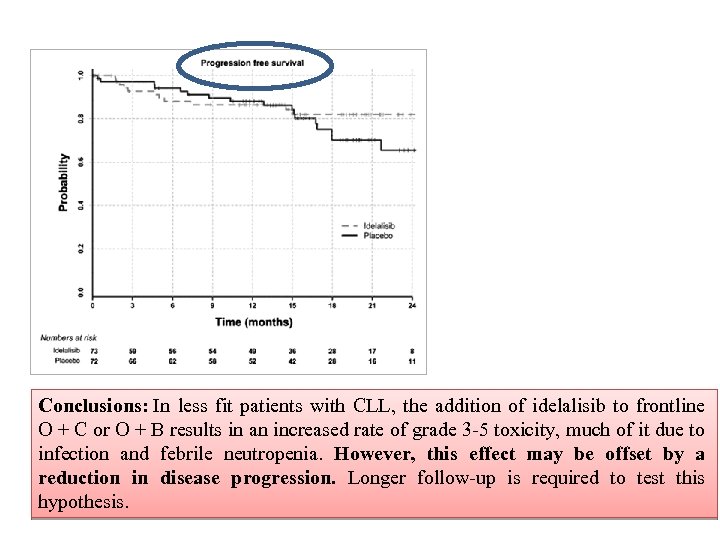
Conclusions: In less fit patients with CLL, the addition of idelalisib to frontline O + C or O + B results in an increased rate of grade 3 -5 toxicity, much of it due to infection and febrile neutropenia. However, this effect may be offset by a reduction in disease progression. Longer follow-up is required to test this hypothesis.

Advances in CLL
BGB-3111 is a potent and irreversible Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, designed to minimize off target inhibition of other TEC- and EGFR-family kinases. BGB-3111 has shown significant activity in a variety of B-cell malignancies, especially CLL/small lymphocytic leukemia (SLL) and Waldenström macroglobulinemia Obinutuzumab (O) is a second-generation anti-CD 20 humanized monoclonal antibody that has increased ADCC activity vs R and is more effective than R when combined with chemotherapy in CLL/SLL and FL.
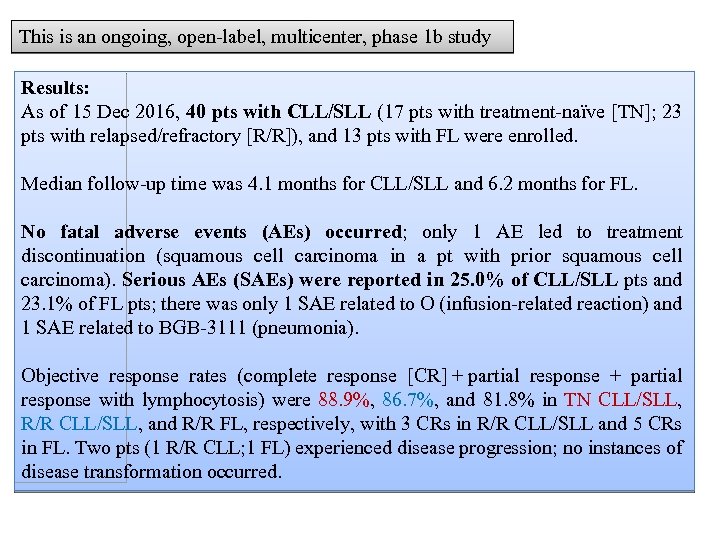
This is an ongoing, open-label, multicenter, phase 1 b study Results: As of 15 Dec 2016, 40 pts with CLL/SLL (17 pts with treatment-naïve [TN]; 23 pts with relapsed/refractory [R/R]), and 13 pts with FL were enrolled. Median follow-up time was 4. 1 months for CLL/SLL and 6. 2 months for FL. No fatal adverse events (AEs) occurred; only 1 AE led to treatment discontinuation (squamous cell carcinoma in a pt with prior squamous cell carcinoma). Serious AEs (SAEs) were reported in 25. 0% of CLL/SLL pts and 23. 1% of FL pts; there was only 1 SAE related to O (infusion-related reaction) and 1 SAE related to BGB-3111 (pneumonia). Objective response rates (complete response [CR] + partial response with lymphocytosis) were 88. 9%, 86. 7%, and 81. 8% in TN CLL/SLL, R/R CLL/SLL, and R/R FL, respectively, with 3 CRs in R/R CLL/SLL and 5 CRs in FL. Two pts (1 R/R CLL; 1 FL) experienced disease progression; no instances of disease transformation occurred.
Ublituximab (UTX) is a novel glycoengineered m. Ab targeting a unique epitope on the CD 20 antigen. TGR-1202 is a next generation, once daily, PI 3 Kδ inhibitor, demonstrating a favorable safety profile compared to prior inhibitors, including in long-term follow up (Burris, 2016). This Ph 1 trial evaluates the safety/efficacy of the triplet combination of a novel anti-CD 20 m. Ab + PI 3 Kδ + BTK inhibitor (ibrutinib) in pts with B-cell malignancies.
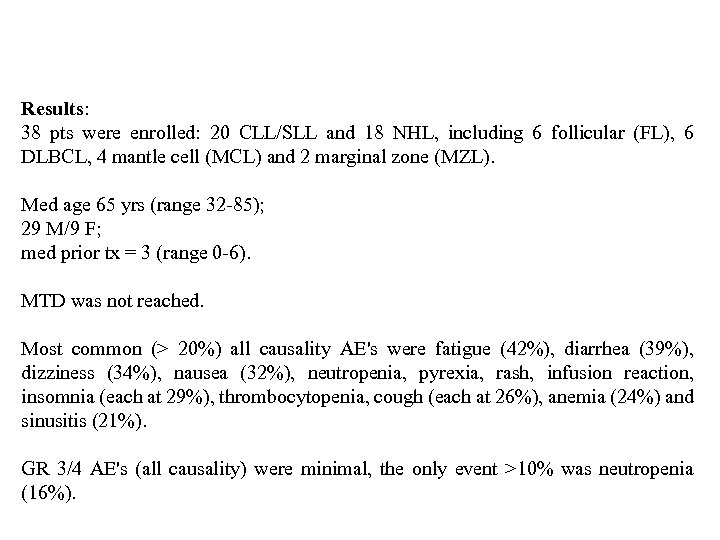
Results: 38 pts were enrolled: 20 CLL/SLL and 18 NHL, including 6 follicular (FL), 6 DLBCL, 4 mantle cell (MCL) and 2 marginal zone (MZL). Med age 65 yrs (range 32 -85); 29 M/9 F; med prior tx = 3 (range 0 -6). MTD was not reached. Most common (> 20%) all causality AE's were fatigue (42%), diarrhea (39%), dizziness (34%), nausea (32%), neutropenia, pyrexia, rash, infusion reaction, insomnia (each at 29%), thrombocytopenia, cough (each at 26%), anemia (24%) and sinusitis (21%). GR 3/4 AE's (all causality) were minimal, the only event >10% was neutropenia (16%).
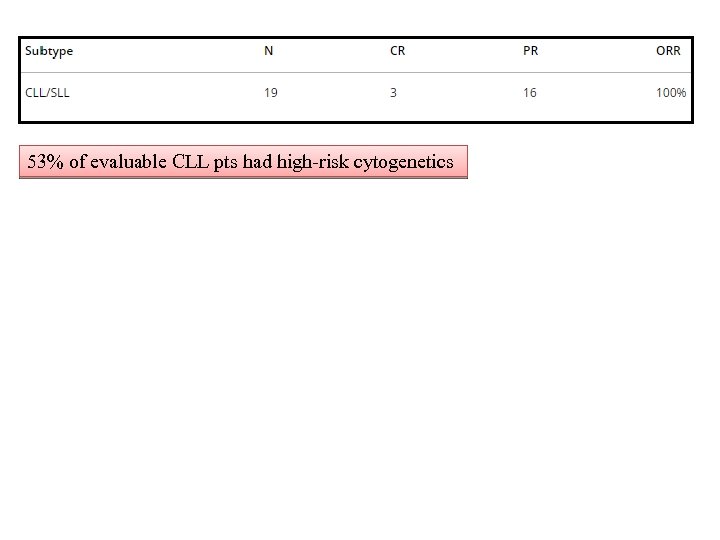
53% of evaluable CLL pts had high-risk cytogenetics
The approval of the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib (IB) has significantly advanced the treatment paradigm for patients (pts) with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), particularly in pts with high-risk cytogenetics who are traditionally less responsive to chemoimmunotherapy. However, among pts with high-risk CLL defined by interruptions in TP 53 (either by mutation or deletion) or loss of chromosome 11 q, outcomes remain inferior with ibrutinib monotherapy, particularly in the relapsed/refractory setting (O'Brien ASH 2016). GENUINE is the first randomized Ph 3 trial conducted assessing the addition of a novel agent to ibrutinib in high-risk rel/ref CLL, and evaluates IB monotherapy vs. UTX + IB.

Methods: Eligible pts with rel/ref CLL and centrally confirmed del 17 p, del 11 q, and/or a TP 53 mutation were randomized 1: 1 to receive IB (420 mg QD) alone or with UTX (900 mg on D 1, 8, 15 of Cycle 1, D 1 of Cycle 2 -6, and Q 3 Cycles thereafter). There was no limit on number of prior therapies. Prior IB exposure was excluded. The primary study endpoint was overall response rate (ORR) per iw. CLL 2008 criteria, with secondary endpoints including CR rate, MRD negativity, PFS, time to response (TTR) and safety.
Results: 126 pts were randomized at sites in the US and Israel, with 117 pts treated (59 on UTX + IB, 58 on IB alone). Median age 67, median of 3 prior therapies (range 1 -8), > 70% of were male. High-risk cytogenetics were relatively balanced between the arms with ~50% having del 17 p. UTX + IB was well tolerated, with infusion reactions the most prevalent AE (44%, GR 3/4 5%). Neutropenia was comparable with the combination (17%, Gr 3/4 7% vs. 10%, Gr 3/4 9%), and other AE's were similar or lower with UTX + IB vs. IB alone (all grades), including fatigue (17% vs. 31%), dizziness (12% vs. 21%), contusion (12% vs. 26%), anemia (10% vs. 16%), and myalgia (9% vs. 14%). At median follow-up of 12 months, best ORR per independent radiology and hematology review for UTX + IB was 80% vs. 47% for IB alone (p < 0. 001). While not powered for secondary endpoints, observed advantages were seen in PFS and radiographic CR rate in the UTX + IB arm. CR and MRD confirmation is ongoing. Conclusions: The addition of UTX to IB demonstrated a superior response rate compared to IB alone without additional clinically significant toxicity.
Introduction: In phase 3 studies, ibrutinib (ibr) was superior to ofatumumab in relapsed/refractory (R/R) CLL/SLL or chlorambucil in treatment (tx)-naïve (TN) CLL/SLL. Ibr + bendamustine/rituximab (BR) was superior to BR in R/R CLL/SLL. Clinical outcomes of pts in these 3 studies were examined to determine the impact of certain prognostic risk factors other than del 17 p.

RESONATE: R/R CLL/SLL, ibr 420 mg/d until progressive disease (PD) or ofatumumab (≤ 24 wk). RESONATE-2: TN CLL/SLL (no del 17 p) ≥ 65 y, ibr 420 mg/d until PD or chlorambucil (≤ 12 cycles). HELIOS: R/R CLL/SLL (no del 17 p), BR (≤ 6 cycles) ± ibr 420 mg/d followed by ibr or placebo until PD.

Data from 3 studies (N = 1238) were pooled to analyze outcomes with/without genomic risk factors IGHV, del 11 q, trisomy 12, or complex karyotype (CK). Results: Median follow-up was 21 mo for both ibr- and comparator-tx pts. In each subgroup, PFS, OS, and response rates were higher in ibr- than comparator-tx pts, regardless of these genomic risk factors.

By univariate analysis in ibr-tx pts, genomic risk factors were not associated with shorter PFS or OS, and del 11 q was associated with a trend of longer PFS and OS. In comparator-tx pts, unmutated (U)-IGHV, del 11 q, and CK were associated with shorter PFS, and U-IGHV and CK with shorter OS. Age ≥ 65 and elevated LDH were associated with shorter OS, and del 11 q with a trend of longer OS. In comparator-tx pts, ≥ 1 prior tx, U-IGHV, del 11 q, CK, male sex, and bulky disease ≥ 5 cm were associated with shorter PFS; CK, male sex, bulky disease ≥ 5 cm, ECOG PS ≥ 1 and elevated LDH were associated with shorter OS.

Conclusions: In UVA and MVA for ibr-tx pts, no clear associations were found for U-IGHV, del 11 q, trisomy 12, and CK with poor outcomes; del 11 q associated with trends of longer PFS and OS in UVA, and longer OS in MVA. In comparator-tx pts, U-IGHV, del 11 q, and CK associated with shorter PFS, OS, and/or lower response rate. Results suggest that risk factors associated with poor outcomes with chemotherapy have less relevance with ibr.



462af483d5bc88014d1d7121e0369ee4.ppt