lecture_7_properties_of_metals.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Chemistry Lecture #8: properties of metals Volodimir Vreshch Ivano-Frankivsk
Chemistry Lecture #8: properties of metals Volodimir Vreshch Ivano-Frankivsk
 1 Plane Introduction Metals general information, metal-metal bond Electrochemical raw General methods of their synthesis Chemical properties of metals Corrosion and their types Conclusions
1 Plane Introduction Metals general information, metal-metal bond Electrochemical raw General methods of their synthesis Chemical properties of metals Corrosion and their types Conclusions
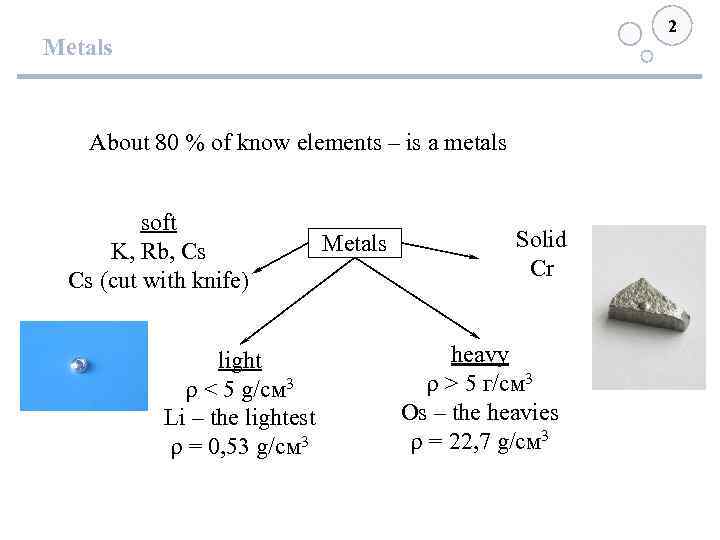 2 Metals About 80 % of know elements – is a metals soft K, Rb, Cs Cs (cut with knife) light ρ < 5 g/см 3 Li – the lightest ρ = 0, 53 g/см 3 Metals Solid Cr heavy ρ > 5 г/см 3 Os – the heavies ρ = 22, 7 g/см 3
2 Metals About 80 % of know elements – is a metals soft K, Rb, Cs Cs (cut with knife) light ρ < 5 g/см 3 Li – the lightest ρ = 0, 53 g/см 3 Metals Solid Cr heavy ρ > 5 г/см 3 Os – the heavies ρ = 22, 7 g/см 3
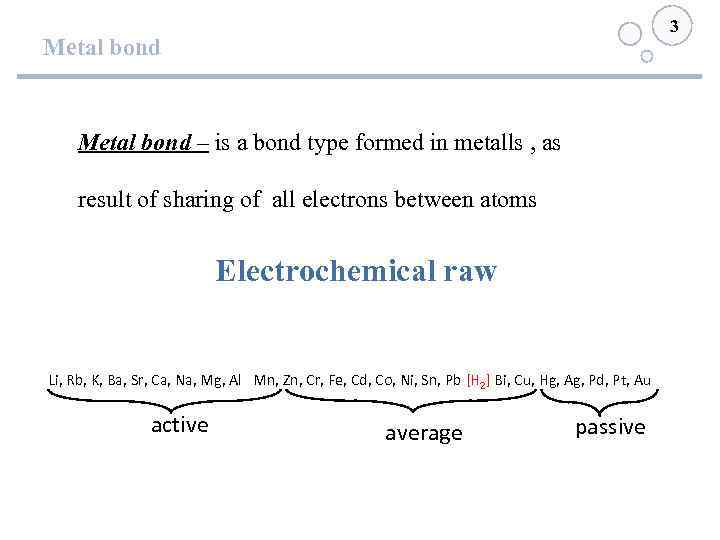 3 Metal bond – is a bond type formed in metalls , as result of sharing of all electrons between atoms Electrochemical raw Li, Rb, K, Ba, Sr, Ca, Na, Mg, Al Mn, Zn, Cr, Fe, Cd, Co, Ni, Sn, Pb [H 2] Bi, Cu, Hg, Ag, Pd, Pt, Au active average passive
3 Metal bond – is a bond type formed in metalls , as result of sharing of all electrons between atoms Electrochemical raw Li, Rb, K, Ba, Sr, Ca, Na, Mg, Al Mn, Zn, Cr, Fe, Cd, Co, Ni, Sn, Pb [H 2] Bi, Cu, Hg, Ag, Pd, Pt, Au active average passive
 4 Metal synthesis - Synthesis from natural sources : Fe. O + C → Fe + CO Fe. O + CO → Fe + CO 2 - When natural sources contains sulfides, first step is usually oxidation with oxygen 2 Zn. S + 3 O 2 → 2 Zn. O + 2 SO 2 Zn. O + C → Zn + CO -Reduction of metal oxides with hydrogen or other reducing agent : Мо. О 3 + 3 Н 2 → Мо + 3 Н 2 О
4 Metal synthesis - Synthesis from natural sources : Fe. O + C → Fe + CO Fe. O + CO → Fe + CO 2 - When natural sources contains sulfides, first step is usually oxidation with oxygen 2 Zn. S + 3 O 2 → 2 Zn. O + 2 SO 2 Zn. O + C → Zn + CO -Reduction of metal oxides with hydrogen or other reducing agent : Мо. О 3 + 3 Н 2 → Мо + 3 Н 2 О
 Metal - synthesis - Metalothermy – Reduction of oxides with more active metal : 3 Fe 3 O 4 + 8 Al → 9 Fe + Al 2 O 3 Ti. Cl 4 + 2 Mg → Ti + Mg. Cl 2 - hydrometallurgy – reduction of metals form their water solution: Cd. SO 4 + Zn → Zn. SO 4 + Cd 5
Metal - synthesis - Metalothermy – Reduction of oxides with more active metal : 3 Fe 3 O 4 + 8 Al → 9 Fe + Al 2 O 3 Ti. Cl 4 + 2 Mg → Ti + Mg. Cl 2 - hydrometallurgy – reduction of metals form their water solution: Cd. SO 4 + Zn → Zn. SO 4 + Cd 5
 Chemical properties 1. Reaction with water with formation of Н 2 from Li to Na 2 Na + 2 Н 2 О → 2 Na. ОН + Н 2↑ form Mg to Pb 2 Al + 3 Н 2 О → Al 2 O 3 + 3 Н 2↑ 2. Reaction of amphoteric metals with hydroxides. Zn + 2 Na. OH + 2 Н 2 О → Na 2[Zn(OH)4] + 2 Н 2↑ More active metals reproduce less active form their solutions Zn + Pb(NO 3)2 → Zn(NO 3)2 + Pb Pb + Zn(NO 3)2 ≠ 6
Chemical properties 1. Reaction with water with formation of Н 2 from Li to Na 2 Na + 2 Н 2 О → 2 Na. ОН + Н 2↑ form Mg to Pb 2 Al + 3 Н 2 О → Al 2 O 3 + 3 Н 2↑ 2. Reaction of amphoteric metals with hydroxides. Zn + 2 Na. OH + 2 Н 2 О → Na 2[Zn(OH)4] + 2 Н 2↑ More active metals reproduce less active form their solutions Zn + Pb(NO 3)2 → Zn(NO 3)2 + Pb Pb + Zn(NO 3)2 ≠ 6
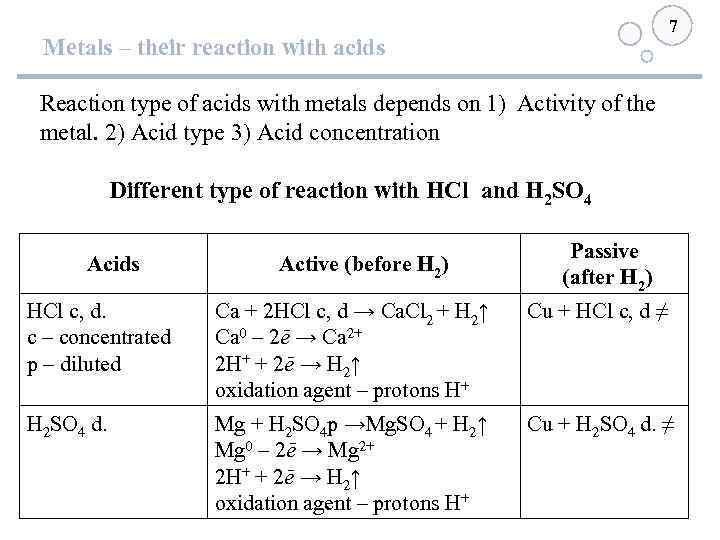 7 Metals – their reaction with acids Reaction type of acids with metals depends on 1) Activity of the metal. 2) Acid type 3) Acid concentration Different type of reaction with HCl and H 2 SO 4 Acids Active (before Н 2) Passive (after Н 2) HCl c, d. c – concentrated р – diluted Са + 2 HCl c, d → Ca. Cl 2 + H 2↑ Ca 0 – 2ē → Ca 2+ 2 H+ + 2ē → Н 2↑ oxidation agent – protons Н+ Сu + HCl c, d ≠ H 2 SO 4 d. Mg + H 2 SO 4 р →Mg. SO 4 + H 2↑ Mg 0 – 2ē → Mg 2+ 2 H+ + 2ē → Н 2↑ oxidation agent – protons Н+ Сu + H 2 SO 4 d. ≠
7 Metals – their reaction with acids Reaction type of acids with metals depends on 1) Activity of the metal. 2) Acid type 3) Acid concentration Different type of reaction with HCl and H 2 SO 4 Acids Active (before Н 2) Passive (after Н 2) HCl c, d. c – concentrated р – diluted Са + 2 HCl c, d → Ca. Cl 2 + H 2↑ Ca 0 – 2ē → Ca 2+ 2 H+ + 2ē → Н 2↑ oxidation agent – protons Н+ Сu + HCl c, d ≠ H 2 SO 4 d. Mg + H 2 SO 4 р →Mg. SO 4 + H 2↑ Mg 0 – 2ē → Mg 2+ 2 H+ + 2ē → Н 2↑ oxidation agent – protons Н+ Сu + H 2 SO 4 d. ≠
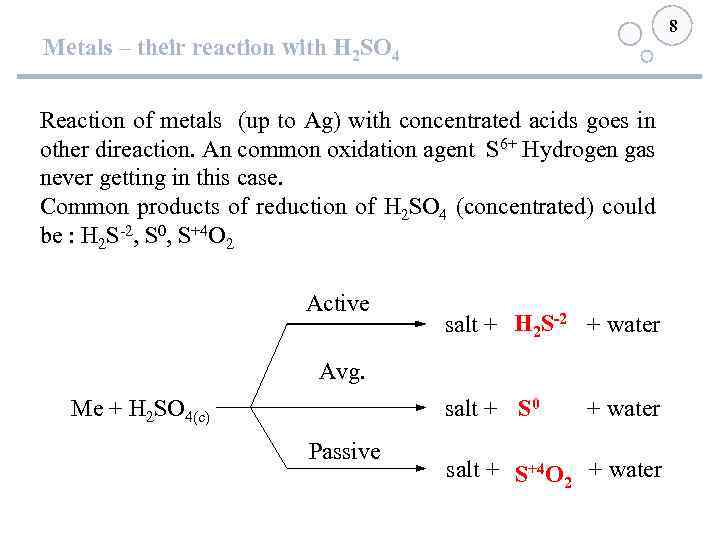 8 Metals – their reaction with H 2 SO 4 Reaction of metals (up to Ag) with concentrated acids goes in other direaction. An common oxidation agent S 6+ Hydrogen gas never getting in this case. Common products of reduction of H 2 SO 4 (concentrated) could be : H 2 S-2, S 0, S+4 O 2 Active H 2 S-2 salt + + water Avg. salt + + water S 0 Me + H 2 SO 4(c) Passive salt + + water S+4 O 2
8 Metals – their reaction with H 2 SO 4 Reaction of metals (up to Ag) with concentrated acids goes in other direaction. An common oxidation agent S 6+ Hydrogen gas never getting in this case. Common products of reduction of H 2 SO 4 (concentrated) could be : H 2 S-2, S 0, S+4 O 2 Active H 2 S-2 salt + + water Avg. salt + + water S 0 Me + H 2 SO 4(c) Passive salt + + water S+4 O 2
 9 Metals With active metals K 0 – 1ē = K+1 S+6 + 8ē = S-2 8 8 1 With average active metals Mn 0 – 2ē = Mn+2 S+6 + 6ē = S 0 6 3 1
9 Metals With active metals K 0 – 1ē = K+1 S+6 + 8ē = S-2 8 8 1 With average active metals Mn 0 – 2ē = Mn+2 S+6 + 6ē = S 0 6 3 1
 10 Metals With passive metals Ag 0 – 1ē = Ag+1 S+6 + 2ē = S+4 2 2 1 Following metals : Fe, Co, Cr, Ni get passivity with H 2 SO 4 (c). Top layer for compounds which cover the metal and this prevent further reaction.
10 Metals With passive metals Ag 0 – 1ē = Ag+1 S+6 + 2ē = S+4 2 2 1 Following metals : Fe, Co, Cr, Ni get passivity with H 2 SO 4 (c). Top layer for compounds which cover the metal and this prevent further reaction.
 Metals – reaction with HNO 3 Me 0 + HNO 3 → metal salt + N+4 O 2 + H 2 O (except Au і Pt) Important!!! Al, Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, Pb – get passivated. Mn 0 – 2ē = Mn+2 N+5 + 1ē = N+4 2 11
Metals – reaction with HNO 3 Me 0 + HNO 3 → metal salt + N+4 O 2 + H 2 O (except Au і Pt) Important!!! Al, Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, Pb – get passivated. Mn 0 – 2ē = Mn+2 N+5 + 1ē = N+4 2 11
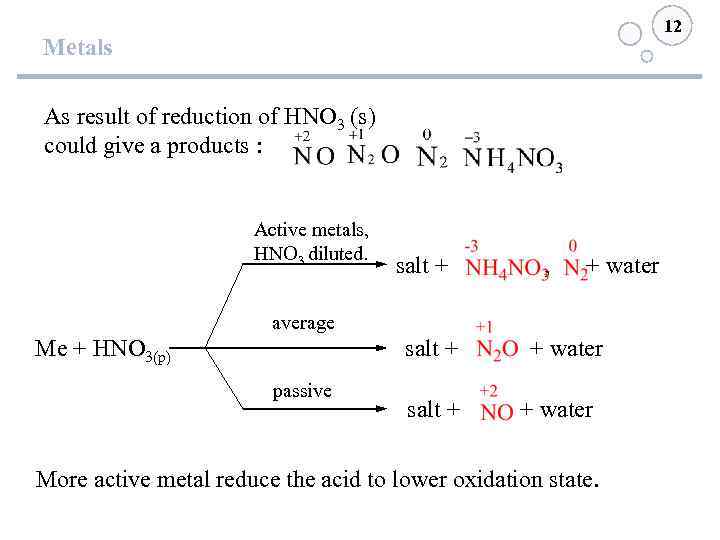 12 Metals As result of reduction of HNO 3 (s) could give a products : Active metals, HNO 3 diluted. salt + , + water average salt + + water Me + HNO 3(р) passive salt + + water More active metal reduce the acid to lower oxidation state.
12 Metals As result of reduction of HNO 3 (s) could give a products : Active metals, HNO 3 diluted. salt + , + water average salt + + water Me + HNO 3(р) passive salt + + water More active metal reduce the acid to lower oxidation state.
 13 Metals Very active metals with very diluted HNO 3 Ba 0 – 2ē = Ba+2 N+5 + 8ē = N-3 8 4 1 Active metals Mg 0 – 2ē = Mg+2 2 N+5 + 10ē = N 20 10 5 1
13 Metals Very active metals with very diluted HNO 3 Ba 0 – 2ē = Ba+2 N+5 + 8ē = N-3 8 4 1 Active metals Mg 0 – 2ē = Mg+2 2 N+5 + 10ē = N 20 10 5 1
 14 Metals of average activity Mn 0 – 2ē = Mn+2 2 N+5 + 8ē = 2 N+1 8 4 1 Passive metals Cu 0 – 2ē = Cu+2 N+5 + 3ē = N+2 6 3 2
14 Metals of average activity Mn 0 – 2ē = Mn+2 2 N+5 + 8ē = 2 N+1 8 4 1 Passive metals Cu 0 – 2ē = Cu+2 N+5 + 3ē = N+2 6 3 2
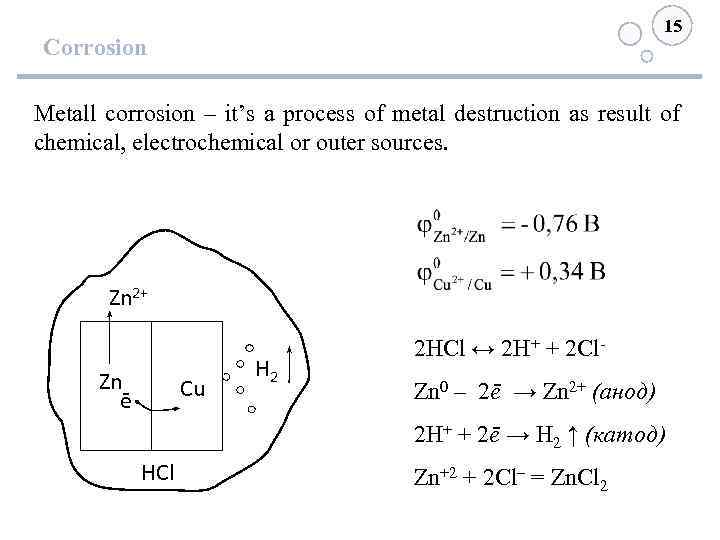 15 Corrosion Metall corrosion – it’s a process of metal destruction as result of chemical, electrochemical or outer sources. Zn 2+ Zn ē Cu H 2 2 HCl ↔ 2 H+ + 2 Cl. Zn 0 – 2ē → Zn 2+ (анод) 2 H+ + 2ē → H 2 ↑ (катод) HCl Zn+2 + 2 Cl– = Zn. Cl 2
15 Corrosion Metall corrosion – it’s a process of metal destruction as result of chemical, electrochemical or outer sources. Zn 2+ Zn ē Cu H 2 2 HCl ↔ 2 H+ + 2 Cl. Zn 0 – 2ē → Zn 2+ (анод) 2 H+ + 2ē → H 2 ↑ (катод) HCl Zn+2 + 2 Cl– = Zn. Cl 2
 Metals Protection from corrosion Chemical: 1. Covering with oils, paintings. 2. Pasivation with some oxidants e. g. (HNO 3(c)). 3. Utilization of corrosion inhibitors Electrochemical : 1. Use of protectors. 16
Metals Protection from corrosion Chemical: 1. Covering with oils, paintings. 2. Pasivation with some oxidants e. g. (HNO 3(c)). 3. Utilization of corrosion inhibitors Electrochemical : 1. Use of protectors. 16


