 Chemistry Lecture #4 Volodimir Vreshch Ivano-Frankivsk
Chemistry Lecture #4 Volodimir Vreshch Ivano-Frankivsk
 1 Plane Introduction Chemical kinetics and - basic principles Speed of chemical reaction Mass action law Influence of different factors for reaction speed Conclusions
1 Plane Introduction Chemical kinetics and - basic principles Speed of chemical reaction Mass action law Influence of different factors for reaction speed Conclusions
 Chemical kinetics 2 Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the study of rates of chemical processes. Homogenous reaction is a reaction in which reactants and products stay in the same phase 2 SO 2 (gas) + O 2 (gas) → 2 SO 3(gas) Heterogonous reaction is a reaction in which reactants and products stay in different same phase 2 Н 2 O (gas) + 2 S (solid) → 2 H 2 S (gas)+ O 2 (gas)
Chemical kinetics 2 Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the study of rates of chemical processes. Homogenous reaction is a reaction in which reactants and products stay in the same phase 2 SO 2 (gas) + O 2 (gas) → 2 SO 3(gas) Heterogonous reaction is a reaction in which reactants and products stay in different same phase 2 Н 2 O (gas) + 2 S (solid) → 2 H 2 S (gas)+ O 2 (gas)
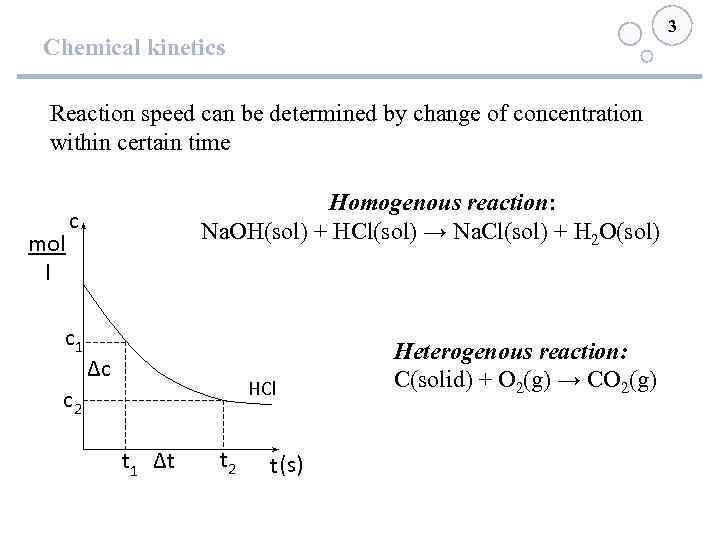 3 Chemical kinetics Reaction speed can be determined by change of concentration within certain time mol l Homogenous reaction: Na. OH(sol) + HCl(sol) → Na. Cl(sol) + H 2 O(sol) с с1 ∆с HCl с2 t 1 ∆t t 2 t (s) Heterogenous reaction: С(solid) + О 2(g) → СО 2(g)
3 Chemical kinetics Reaction speed can be determined by change of concentration within certain time mol l Homogenous reaction: Na. OH(sol) + HCl(sol) → Na. Cl(sol) + H 2 O(sol) с с1 ∆с HCl с2 t 1 ∆t t 2 t (s) Heterogenous reaction: С(solid) + О 2(g) → СО 2(g)
 Chemical kinetics Reaction speed depends on -Nature of reactants - Temperature and pressure - Concentration - Catalyst 4
Chemical kinetics Reaction speed depends on -Nature of reactants - Temperature and pressure - Concentration - Catalyst 4
 5 Chemical kinetics Mass action law When two reactants, A and B, react together at a given temperature in a "substitution reaction, " the affinity, or chemical force between them, is proportional to the active masses, [A] and [B], each raised to a particular power Homogenous reaction: N 2 (gas) + 3 H 2 (gas) → 2 NH 3 (gas) υ = k[N 2][H 2]3 k – reaction speed constant. Heterogeneous reaction: S (solid) + O 2 (gas) → SO 2 (gas) υ = k[О 2]
5 Chemical kinetics Mass action law When two reactants, A and B, react together at a given temperature in a "substitution reaction, " the affinity, or chemical force between them, is proportional to the active masses, [A] and [B], each raised to a particular power Homogenous reaction: N 2 (gas) + 3 H 2 (gas) → 2 NH 3 (gas) υ = k[N 2][H 2]3 k – reaction speed constant. Heterogeneous reaction: S (solid) + O 2 (gas) → SO 2 (gas) υ = k[О 2]
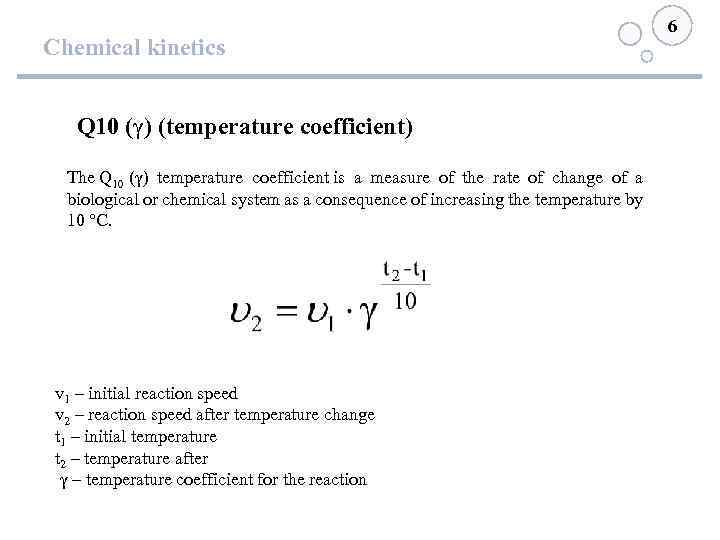 Chemical kinetics Q 10 (γ) (temperature coefficient) The Q 10 (γ) temperature coefficient is a measure of the rate of change of a biological or chemical system as a consequence of increasing the temperature by 10 °C. v 1 – initial reaction speed v 2 – reaction speed after temperature change t 1 – initial temperature t 2 – temperature after γ – temperature coefficient for the reaction 6
Chemical kinetics Q 10 (γ) (temperature coefficient) The Q 10 (γ) temperature coefficient is a measure of the rate of change of a biological or chemical system as a consequence of increasing the temperature by 10 °C. v 1 – initial reaction speed v 2 – reaction speed after temperature change t 1 – initial temperature t 2 – temperature after γ – temperature coefficient for the reaction 6
![7 Chemical kinetics System energy Activation energy – [АK]* Eакт ∆Н < 0 (ecsotermic 7 Chemical kinetics System energy Activation energy – [АK]* Eакт ∆Н < 0 (ecsotermic](https://present5.com/presentation/150785993_417189255/image-8.jpg) 7 Chemical kinetics System energy Activation energy – [АK]* Eакт ∆Н < 0 (ecsotermic reaction) ∆H reaction coordinate (interatomic distance)
7 Chemical kinetics System energy Activation energy – [АK]* Eакт ∆Н < 0 (ecsotermic reaction) ∆H reaction coordinate (interatomic distance)
 Chemical kinetics Chemical equilibrium Non reversible reaction: 2 KCl. O 3 → 2 KCl + 3 O 2↑ Reversible reaction: N 2 + 3 H 2 ↔ 2 NH 3 + Q (–∆Н) A reversible reaction is a chemical reaction that results in an equilibrium mixture of reactants and products. 8
Chemical kinetics Chemical equilibrium Non reversible reaction: 2 KCl. O 3 → 2 KCl + 3 O 2↑ Reversible reaction: N 2 + 3 H 2 ↔ 2 NH 3 + Q (–∆Н) A reversible reaction is a chemical reaction that results in an equilibrium mixture of reactants and products. 8
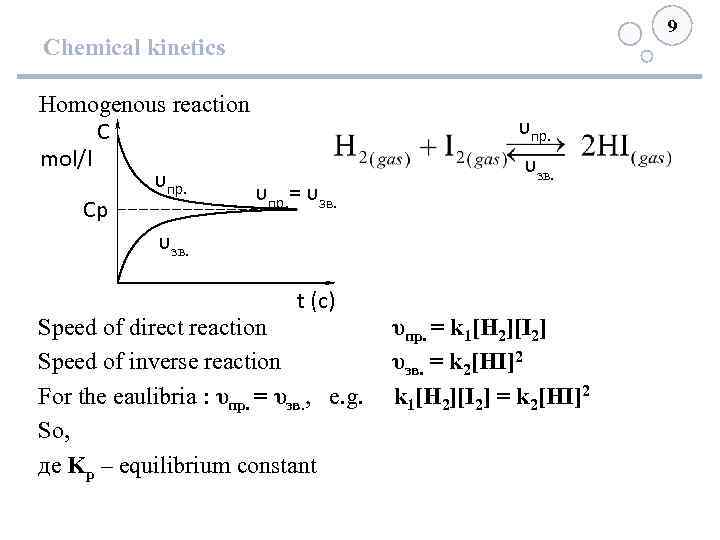 9 Chemical kinetics Homogenous reaction С mol/l υпр. = υзв. Ср υзв. υпр. υзв. t (с) Speed of direct reaction υпр. = k 1[H 2][I 2] Speed of inverse reaction υзв. = k 2[HI]2 For the eaulibria : υпр. = υзв. , e. g. k 1[H 2][I 2] = k 2[HI]2 So, де Kр – equilibrium constant
9 Chemical kinetics Homogenous reaction С mol/l υпр. = υзв. Ср υзв. υпр. υзв. t (с) Speed of direct reaction υпр. = k 1[H 2][I 2] Speed of inverse reaction υзв. = k 2[HI]2 For the eaulibria : υпр. = υзв. , e. g. k 1[H 2][I 2] = k 2[HI]2 So, де Kр – equilibrium constant
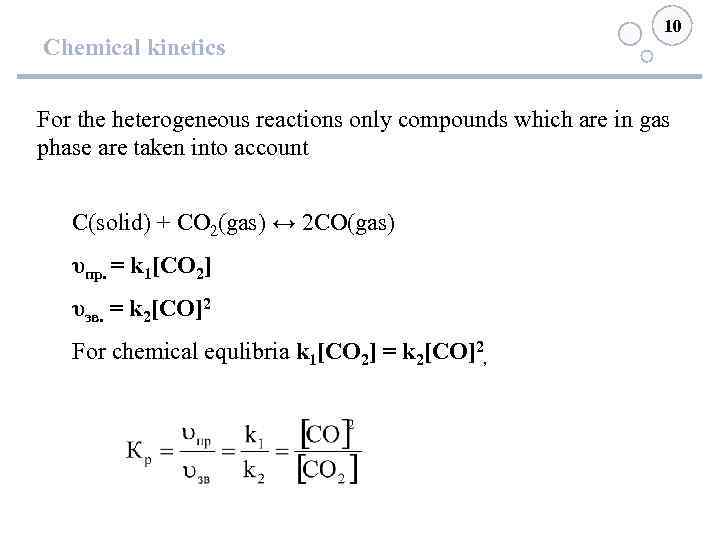 10 Chemical kinetics For the heterogeneous reactions only compounds which are in gas phase are taken into account С(solid) + СО 2(gas) ↔ 2 СО(gas) υпр. = k 1[СО 2] υзв. = k 2[СО]2 For chemical equlibria k 1[СО 2] = k 2[СО]2,
10 Chemical kinetics For the heterogeneous reactions only compounds which are in gas phase are taken into account С(solid) + СО 2(gas) ↔ 2 СО(gas) υпр. = k 1[СО 2] υзв. = k 2[СО]2 For chemical equlibria k 1[СО 2] = k 2[СО]2,
 Chemical kinetics 11 Le Chatelier principle If a chemical system at equilibrium experiences a change in concentration, temperature, volume, or partial pressure, then the equilibrium shifts to counteract the imposed change and a new equilibrium is established.
Chemical kinetics 11 Le Chatelier principle If a chemical system at equilibrium experiences a change in concentration, temperature, volume, or partial pressure, then the equilibrium shifts to counteract the imposed change and a new equilibrium is established.