lecture_3_coord_compounds.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Chemistry Lecture #3 Volodimir Vreshch Ivano-Frankivsk
Chemistry Lecture #3 Volodimir Vreshch Ivano-Frankivsk
 1 Plane Introduction Coordination compounds, deffinition, main principles Nomenclature, classification, and their dissociation Redox reacrions : basic concepts Redox reaction : definition, equation of red-ox reactions Conclusions
1 Plane Introduction Coordination compounds, deffinition, main principles Nomenclature, classification, and their dissociation Redox reacrions : basic concepts Redox reaction : definition, equation of red-ox reactions Conclusions
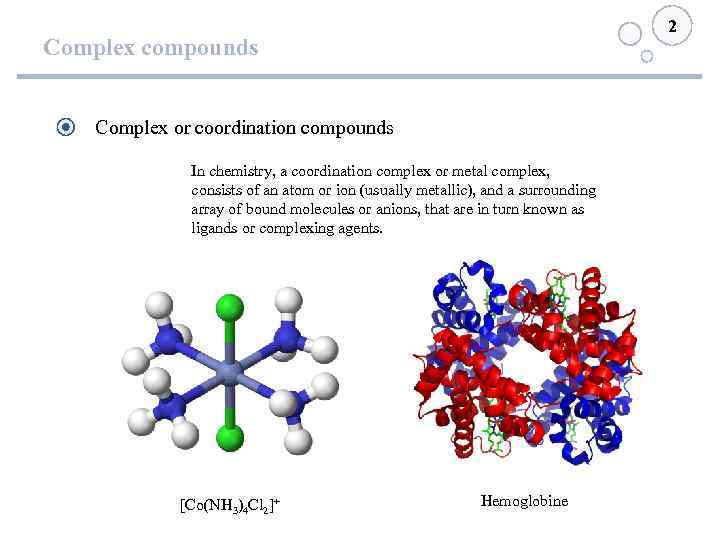 2 Complex compounds Complex or coordination compounds In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex, consists of an atom or ion (usually metallic), and a surrounding array of bound molecules or anions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]+ Hemoglobine
2 Complex compounds Complex or coordination compounds In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex, consists of an atom or ion (usually metallic), and a surrounding array of bound molecules or anions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]+ Hemoglobine
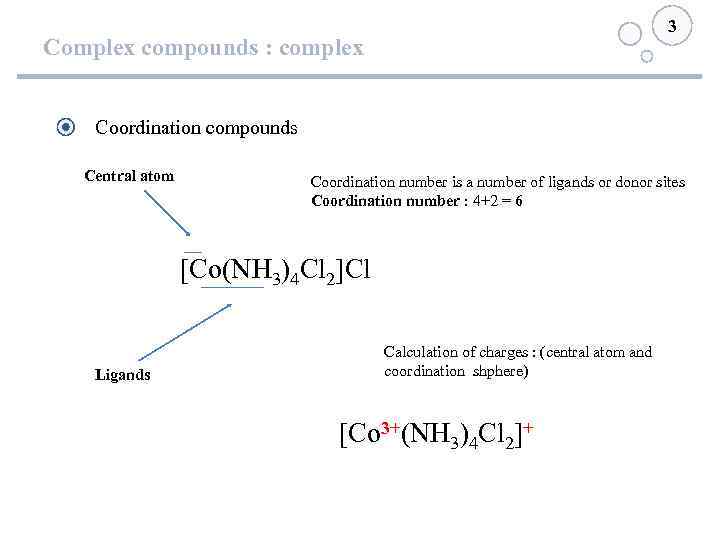 3 Complex compounds : complex Coordination compounds Central atom Coordination number is a number of ligands or donor sites Coordination number : 4+2 = 6 [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Ligands Calculation of charges : (central atom and coordination shphere) [Co 3+(NH 3)4 Cl 2]+
3 Complex compounds : complex Coordination compounds Central atom Coordination number is a number of ligands or donor sites Coordination number : 4+2 = 6 [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Ligands Calculation of charges : (central atom and coordination shphere) [Co 3+(NH 3)4 Cl 2]+
![Complex compounds : nomenclature 4 [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl The basic procedure for naming Complex compounds : nomenclature 4 [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl The basic procedure for naming](https://present5.com/presentation/150785993_417189253/image-5.jpg) Complex compounds : nomenclature 4 [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl The basic procedure for naming a complex: 1. When naming a complex ion, the ligands are named before the metal ion. 2. Write the names of the ligands in the order, -neutral, negative, positive. If there are multiple ligands of the same charge type, they are named in alphabetical order. (Numerical prefixes do not affect the order. ) 3. Multiple occurring monodentate ligands receive a prefix according to the number of occurrences: di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, or hexa. Polydentate ligands (e. g. , ethylenediamine, oxalate) receive bis-, tris-, tetrakis-, etc. 4. Anions end in ido. This replaces the final 'e' when the anion ends with '-ate', e. g. sulfate becomes sulfato. It replaces 'ide': cyanide becomes cyanido. 5. Neutral ligands are given their usual name, with some exceptions: NH 3 becomes ammine; H 2 O becomes aqua or aquo; CO becomes carbonyl; NO becomes nitrosyl. 6. Write the name of the central atom/ion. If the complex is an anion, the central atom's name will end in -ate, and its Latin name will be used if available (except for mercury). If the central atom's oxidation state needs to be specified (when it is one of several possible, or zero), write it as a Roman numeral (or 0) in parentheses. Name cation then anion as separate words (if applicable, as in last example)
Complex compounds : nomenclature 4 [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl The basic procedure for naming a complex: 1. When naming a complex ion, the ligands are named before the metal ion. 2. Write the names of the ligands in the order, -neutral, negative, positive. If there are multiple ligands of the same charge type, they are named in alphabetical order. (Numerical prefixes do not affect the order. ) 3. Multiple occurring monodentate ligands receive a prefix according to the number of occurrences: di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, or hexa. Polydentate ligands (e. g. , ethylenediamine, oxalate) receive bis-, tris-, tetrakis-, etc. 4. Anions end in ido. This replaces the final 'e' when the anion ends with '-ate', e. g. sulfate becomes sulfato. It replaces 'ide': cyanide becomes cyanido. 5. Neutral ligands are given their usual name, with some exceptions: NH 3 becomes ammine; H 2 O becomes aqua or aquo; CO becomes carbonyl; NO becomes nitrosyl. 6. Write the name of the central atom/ion. If the complex is an anion, the central atom's name will end in -ate, and its Latin name will be used if available (except for mercury). If the central atom's oxidation state needs to be specified (when it is one of several possible, or zero), write it as a Roman numeral (or 0) in parentheses. Name cation then anion as separate words (if applicable, as in last example)
![5 Complex compounds : nomenclature [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Anionic Ligands Names Neutral Ligands 5 Complex compounds : nomenclature [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Anionic Ligands Names Neutral Ligands](https://present5.com/presentation/150785993_417189253/image-6.jpg) 5 Complex compounds : nomenclature [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Anionic Ligands Names Neutral Ligands Names Br- bromo NH 3 ammine F- fluoro H 2 O aqua O 2 - oxo NO Nitrosyl OH- Hydroxo CO Carbonyl CN- cyano O 2 dioxygen C 2 O 42 - oxalato N 2 dinitrogen CO 32 - carbonato C 5 H 5 N pyridine CH 3 COO- acetato H 2 NCH 2 NH ethylenediamine 2
5 Complex compounds : nomenclature [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Anionic Ligands Names Neutral Ligands Names Br- bromo NH 3 ammine F- fluoro H 2 O aqua O 2 - oxo NO Nitrosyl OH- Hydroxo CO Carbonyl CN- cyano O 2 dioxygen C 2 O 42 - oxalato N 2 dinitrogen CO 32 - carbonato C 5 H 5 N pyridine CH 3 COO- acetato H 2 NCH 2 NH ethylenediamine 2
![6 Complex compounds : nomenclature [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Number Prefix 1 mono 5 6 Complex compounds : nomenclature [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Number Prefix 1 mono 5](https://present5.com/presentation/150785993_417189253/image-7.jpg) 6 Complex compounds : nomenclature [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Number Prefix 1 mono 5 penta (pentakis) 9 nona (ennea) 2 di (bis) 6 hexa (hexakis) 10 deca 3 tri (tris) 7 hepta 11 undeca 4 tetra (tetrakis) 8 octa 12 dodeca
6 Complex compounds : nomenclature [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Number Prefix 1 mono 5 penta (pentakis) 9 nona (ennea) 2 di (bis) 6 hexa (hexakis) 10 deca 3 tri (tris) 7 hepta 11 undeca 4 tetra (tetrakis) 8 octa 12 dodeca
![Complex compounds : nomenclature [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Name of Metal Name in an Complex compounds : nomenclature [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Name of Metal Name in an](https://present5.com/presentation/150785993_417189253/image-8.jpg) Complex compounds : nomenclature [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Name of Metal Name in an Anionic Complex Iron Ferrate Copper Cuprate Lead Plumbate Silver Argenate Gold Aurate Tin Stannate 7
Complex compounds : nomenclature [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Name of Metal Name in an Anionic Complex Iron Ferrate Copper Cuprate Lead Plumbate Silver Argenate Gold Aurate Tin Stannate 7
![Nomenclature : examples K 2[Ni. Cl 4] potasium tetrachloridonickelate(II) K 3[Cu(NH 3)Cl 5] potasium Nomenclature : examples K 2[Ni. Cl 4] potasium tetrachloridonickelate(II) K 3[Cu(NH 3)Cl 5] potasium](https://present5.com/presentation/150785993_417189253/image-9.jpg) Nomenclature : examples K 2[Ni. Cl 4] potasium tetrachloridonickelate(II) K 3[Cu(NH 3)Cl 5] potasium amminepentachlorocuprate(II) [Co(NH 3)5 Cl]SO 4 pentaamminechloridocobalt(III) sulfate 8
Nomenclature : examples K 2[Ni. Cl 4] potasium tetrachloridonickelate(II) K 3[Cu(NH 3)Cl 5] potasium amminepentachlorocuprate(II) [Co(NH 3)5 Cl]SO 4 pentaamminechloridocobalt(III) sulfate 8
![Complex compounds : dissociation Primary dissociation K 4[Fe(СN)6] 4 K+ + [Fe(СN)6]4 - Secondary Complex compounds : dissociation Primary dissociation K 4[Fe(СN)6] 4 K+ + [Fe(СN)6]4 - Secondary](https://present5.com/presentation/150785993_417189253/image-10.jpg) Complex compounds : dissociation Primary dissociation K 4[Fe(СN)6] 4 K+ + [Fe(СN)6]4 - Secondary dissociation [Fe(СN)6]4 - 6 CN- + Fe 2+ Equilibrium constant can be called instability constant. Smaller K - correspond to more stable compounds 9
Complex compounds : dissociation Primary dissociation K 4[Fe(СN)6] 4 K+ + [Fe(СN)6]4 - Secondary dissociation [Fe(СN)6]4 - 6 CN- + Fe 2+ Equilibrium constant can be called instability constant. Smaller K - correspond to more stable compounds 9
![10 Coordination compounds : calculations Central atom [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Ligands Coordination number 10 Coordination compounds : calculations Central atom [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Ligands Coordination number](https://present5.com/presentation/150785993_417189253/image-11.jpg) 10 Coordination compounds : calculations Central atom [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Ligands Coordination number : 6 Central atom charge : +3 [Co 3+(NH 3)4 Cl 2]+ Coordination sphere charge +1
10 Coordination compounds : calculations Central atom [Co(NH 3)4 Cl 2]Cl Ligands Coordination number : 6 Central atom charge : +3 [Co 3+(NH 3)4 Cl 2]+ Coordination sphere charge +1
 Redox reactions : definition 11 Redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed—that is, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species.
Redox reactions : definition 11 Redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed—that is, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species.
 Redox reactions : in nature A bonfire. Combustion consists of redox reactions. 12
Redox reactions : in nature A bonfire. Combustion consists of redox reactions. 12
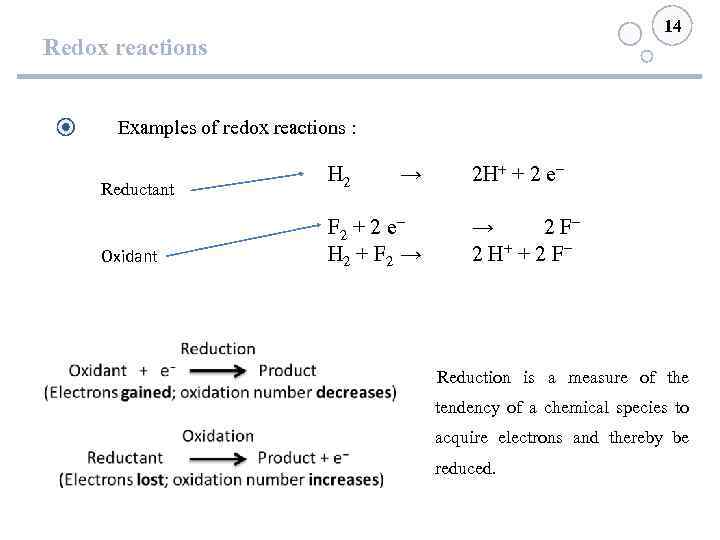 14 Redox reactions Examples of redox reactions : Reductant H 2 → Oxidant F 2 + 2 e− H 2 + F 2 → 2 H+ + 2 e− → 2 F− 2 H+ + 2 F− Reduction is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons and thereby be reduced.
14 Redox reactions Examples of redox reactions : Reductant H 2 → Oxidant F 2 + 2 e− H 2 + F 2 → 2 H+ + 2 e− → 2 F− 2 H+ + 2 F− Reduction is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons and thereby be reduced.
 15 Balancing : step by step Starting conditions : KMn. O 4 + Na 2 SO 3 + H 2 O → Mn. O 2 + Na 2 SO 4 + KOH For a following reaction please, write : a) Oxidation state of elements which change it during the reaction , b) correct coefficients, c) Oxidant and redutant Balancing reactions Example : Step #1: (oxidation states) KMn+7 O 4 + Na 2 S+4 O 3 + H 2 O → Mn+4 O 2 + Na 2 S+6 O 4 + KOH Step #2: (electron balance) Reduction : Mn+7 + 3 e → Mn+4 Oxidation : S+4 + 2 e → S+6 6 2 3
15 Balancing : step by step Starting conditions : KMn. O 4 + Na 2 SO 3 + H 2 O → Mn. O 2 + Na 2 SO 4 + KOH For a following reaction please, write : a) Oxidation state of elements which change it during the reaction , b) correct coefficients, c) Oxidant and redutant Balancing reactions Example : Step #1: (oxidation states) KMn+7 O 4 + Na 2 S+4 O 3 + H 2 O → Mn+4 O 2 + Na 2 S+6 O 4 + KOH Step #2: (electron balance) Reduction : Mn+7 + 3 e → Mn+4 Oxidation : S+4 + 2 e → S+6 6 2 3
 16 Balancing : step by step Step #2: (electron balance) Reduction : Mn+7 + 3 e → Mn+4 6 Oxidation : S+4 + 2 e → S+6 2 3 Step #3: (finding coefficient) 2 KMn+7 O 4 + 3 Na 2 S+4 O 3 + H 2 O → 2 Mn+4 O 2 + 3 Na 2 S+6 O 4 + 2 KOH Step #4 (double check) atoms of oxygen: 18 ← Oxygen → 18
16 Balancing : step by step Step #2: (electron balance) Reduction : Mn+7 + 3 e → Mn+4 6 Oxidation : S+4 + 2 e → S+6 2 3 Step #3: (finding coefficient) 2 KMn+7 O 4 + 3 Na 2 S+4 O 3 + H 2 O → 2 Mn+4 O 2 + 3 Na 2 S+6 O 4 + 2 KOH Step #4 (double check) atoms of oxygen: 18 ← Oxygen → 18
 17 Please, be prepared for the test Questions for the Test #1 : Coordination compounds Questions for the Test #2 : Redox processes
17 Please, be prepared for the test Questions for the Test #1 : Coordination compounds Questions for the Test #2 : Redox processes


