lecture_2_oxides_acid_bases.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Chemistry Lecture #2 Volodimir Vreshch Ivano-Frankivsk
Chemistry Lecture #2 Volodimir Vreshch Ivano-Frankivsk
 1 Plane Introduction Oxides, definition and nomenclature Oxides, classification; and basic reactions Acid and Bases; Nomenclature and classification Acid and Based – main reactions Conclusions
1 Plane Introduction Oxides, definition and nomenclature Oxides, classification; and basic reactions Acid and Bases; Nomenclature and classification Acid and Based – main reactions Conclusions
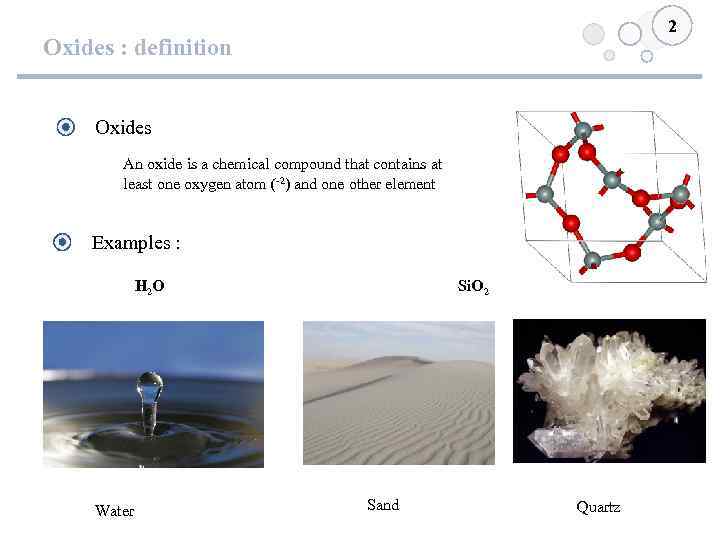 2 Oxides : definition Oxides An oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom (-2) and one other element Examples : H 2 O Water Si. O 2 Sand Quartz
2 Oxides : definition Oxides An oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom (-2) and one other element Examples : H 2 O Water Si. O 2 Sand Quartz
 2 Oxides : oxidation state Oxidation state The formal oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. +1 -2 Li 2 O +3 -2 Exceptions : Al 2 O 3 -1 +1 +2 -2 Ni. O +8 -2 Xe. O 4 +7 -2 Cl 2 O 7 In most cases oxygen have oxidation state -2 Na 2 O 2 +1 -1/2 KO 2 +2 -1 OF 2
2 Oxides : oxidation state Oxidation state The formal oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. +1 -2 Li 2 O +3 -2 Exceptions : Al 2 O 3 -1 +1 +2 -2 Ni. O +8 -2 Xe. O 4 +7 -2 Cl 2 O 7 In most cases oxygen have oxidation state -2 Na 2 O 2 +1 -1/2 KO 2 +2 -1 OF 2
 3 Oxides : nomenclature Nomenclature hemi- 1/2 mono- 1 di- 2 tri- 3 tetra- 4 penta - 5 hexa - 6 hepta - 7 okta - 8 Na 2 O sodium oxide Ca. O calcium oxide Sn. O tin(II) oxide Sn. O 2 tin(IV) oxide Cu 2 O copper(I) oxide Cu. O copper(II) oxide SO 2 sulphur dioxide SO 3 sulphur trioxide NO nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide N 2 O 5 dinitrogen pentoxide Cl 2 O dichlorine oxide Cl 2 O 5 dichlorine pentoxide Cl 2 O 7 dichlorine heptoxide P 2 O 3 diphosphorus trioxide P 2 O 5 diphosphorus pentoxide
3 Oxides : nomenclature Nomenclature hemi- 1/2 mono- 1 di- 2 tri- 3 tetra- 4 penta - 5 hexa - 6 hepta - 7 okta - 8 Na 2 O sodium oxide Ca. O calcium oxide Sn. O tin(II) oxide Sn. O 2 tin(IV) oxide Cu 2 O copper(I) oxide Cu. O copper(II) oxide SO 2 sulphur dioxide SO 3 sulphur trioxide NO nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide N 2 O 5 dinitrogen pentoxide Cl 2 O dichlorine oxide Cl 2 O 5 dichlorine pentoxide Cl 2 O 7 dichlorine heptoxide P 2 O 3 diphosphorus trioxide P 2 O 5 diphosphorus pentoxide
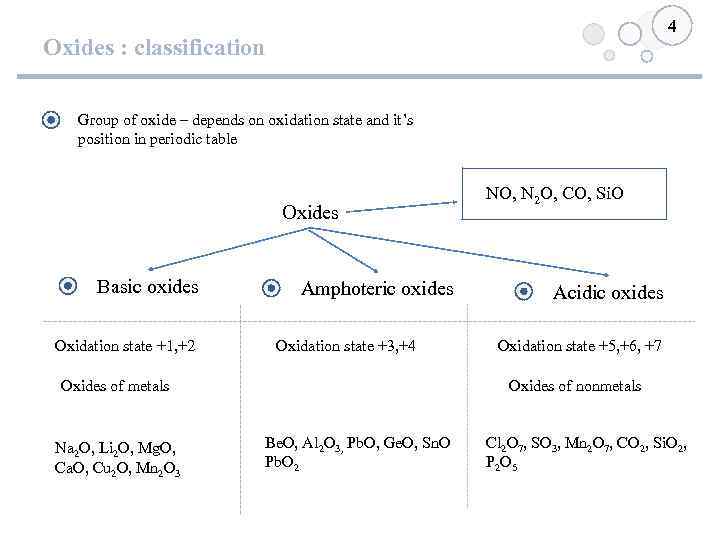 4 Oxides : classification Group of oxide – depends on oxidation state and it’s position in periodic table Oxides Basic oxides Oxidation state +1, +2 Amphoteric oxides Oxidation state +3, +4 Oxides of metals Na 2 O, Li 2 O, Mg. O, Ca. O, Cu 2 O, Mn 2 O 3 NO, N 2 O, CO, Si. O Acidic oxides Oxidation state +5, +6, +7 Oxides of nonmetals Be. O, Al 2 O 3, Pb. O, Ge. O, Sn. O Pb. O 2 Cl 2 O 7, SO 3, Mn 2 O 7, CO 2, Si. O 2, P 2 O 5
4 Oxides : classification Group of oxide – depends on oxidation state and it’s position in periodic table Oxides Basic oxides Oxidation state +1, +2 Amphoteric oxides Oxidation state +3, +4 Oxides of metals Na 2 O, Li 2 O, Mg. O, Ca. O, Cu 2 O, Mn 2 O 3 NO, N 2 O, CO, Si. O Acidic oxides Oxidation state +5, +6, +7 Oxides of nonmetals Be. O, Al 2 O 3, Pb. O, Ge. O, Sn. O Pb. O 2 Cl 2 O 7, SO 3, Mn 2 O 7, CO 2, Si. O 2, P 2 O 5
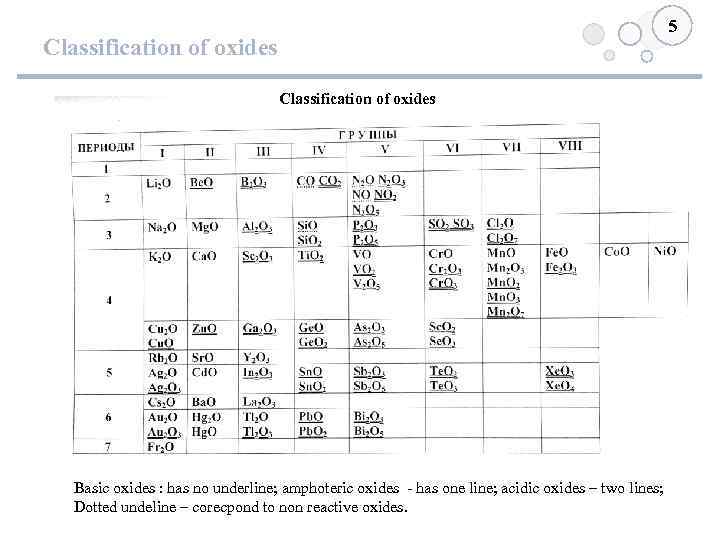 5 Classification of oxides Basic oxides : has no underline; amphoteric oxides - has one line; acidic oxides – two lines; Dotted undeline – corecpond to non reactive oxides.
5 Classification of oxides Basic oxides : has no underline; amphoteric oxides - has one line; acidic oxides – two lines; Dotted undeline – corecpond to non reactive oxides.
 6 Basic oxides Reaction with water Li 2 O + H 2 O → 2 Li. OH Reaction with acidic oxides Li 2 O + SO 3 → Li 2 SO 4 Reaction with acids Li 2 O + 2 HNO 3 → 2 Li. NO 3 + H 2 O Reaction with amphoteric oxides Li 2 O + Al 2 O 3 → 2 Li. Al. O 2 No reaction : Li 2 O + K 2 O →
6 Basic oxides Reaction with water Li 2 O + H 2 O → 2 Li. OH Reaction with acidic oxides Li 2 O + SO 3 → Li 2 SO 4 Reaction with acids Li 2 O + 2 HNO 3 → 2 Li. NO 3 + H 2 O Reaction with amphoteric oxides Li 2 O + Al 2 O 3 → 2 Li. Al. O 2 No reaction : Li 2 O + K 2 O →
 Amphoteric oxides Reaction with bases Al 2 O 3 + 6 Na. OH + 3 H 2 O → 2 Na 3[Al(OH)6] Reaction with acids Al 2 O 3 + 6 HCl → 2 Al. Cl 3+ 3 H 2 O Reaction with acidic oxides Al 2 O 3 + 3 SO 3 → Al 2(SO 4)3 Reaction with amphoteric oxides Al 2 O 3 + K 2 O → 2 KAl. O 2 7
Amphoteric oxides Reaction with bases Al 2 O 3 + 6 Na. OH + 3 H 2 O → 2 Na 3[Al(OH)6] Reaction with acids Al 2 O 3 + 6 HCl → 2 Al. Cl 3+ 3 H 2 O Reaction with acidic oxides Al 2 O 3 + 3 SO 3 → Al 2(SO 4)3 Reaction with amphoteric oxides Al 2 O 3 + K 2 O → 2 KAl. O 2 7
 8 Acidic oxides Reaction with water SO 3 + H 2 O → H 2 SO 4 Reaction with acids SO 3 + Li 2 O → Li 2 SO 4 Reaction with acidic oxides SO 3 + 2 Na. OH → Na 2 SO 4 + H 2 O Reaction with amphoteric oxides Al 2 O 3 + 3 SO 3 → Al 2(SO 4)3 No reaction : SO 3 + CO 2 →
8 Acidic oxides Reaction with water SO 3 + H 2 O → H 2 SO 4 Reaction with acids SO 3 + Li 2 O → Li 2 SO 4 Reaction with acidic oxides SO 3 + 2 Na. OH → Na 2 SO 4 + H 2 O Reaction with amphoteric oxides Al 2 O 3 + 3 SO 3 → Al 2(SO 4)3 No reaction : SO 3 + CO 2 →
 Other examples Ba(OH)2 + H 2 SO 4 → Ba. SO 4↓ + 2 H 2 O Ca(OH)2 + СО 2 → Са. СO 3↓ + H 2 O Na 2 O + H 2 O → 2 Na. OH Вa. O + H 2 O → Вa(OH)2 Mg. O + 2 HNO 3 → Mg(NO 3)2 + H 2 O Ni. O + Cl 2 O 7 → Ni(Cl. O 4)2 Ca. O + Zn. O → Ca. Zn. O 2 Li 2 O + Al 2 O 3 → 2 Li. Al. O 2 SO 2 + H 2 O → H 2 SO 3 N 2 O 5 + H 2 O → 2 HNO 3 Na 2 CO 3 + Si. O 2 → Na 2 Si. O 3 + CO 2↑ Zn. O + HCl → Zn. Cl 2 + H 2 O Fe 2 O 3 + Si. O 2 → Fe 2(Si. O 3)3 Pb. O + Na. OH → Na 2 Pb. O 2 + H 2 O Al 2 O 3 + Mn. O → Mn(Al. O 2)2 9
Other examples Ba(OH)2 + H 2 SO 4 → Ba. SO 4↓ + 2 H 2 O Ca(OH)2 + СО 2 → Са. СO 3↓ + H 2 O Na 2 O + H 2 O → 2 Na. OH Вa. O + H 2 O → Вa(OH)2 Mg. O + 2 HNO 3 → Mg(NO 3)2 + H 2 O Ni. O + Cl 2 O 7 → Ni(Cl. O 4)2 Ca. O + Zn. O → Ca. Zn. O 2 Li 2 O + Al 2 O 3 → 2 Li. Al. O 2 SO 2 + H 2 O → H 2 SO 3 N 2 O 5 + H 2 O → 2 HNO 3 Na 2 CO 3 + Si. O 2 → Na 2 Si. O 3 + CO 2↑ Zn. O + HCl → Zn. Cl 2 + H 2 O Fe 2 O 3 + Si. O 2 → Fe 2(Si. O 3)3 Pb. O + Na. OH → Na 2 Pb. O 2 + H 2 O Al 2 O 3 + Mn. O → Mn(Al. O 2)2 9
 10 Reaction of oxides with water Acids Bases Reaction with water SO 3 + H 2 O → H 2 SO 4 Ca. O + H 2 O → Ca(OH)2 Acid is a substance that, when added to water, increases the concentration of H+ ions in the water Bases is a substance that, when added to water, increases the concentration of OH- ions in the water
10 Reaction of oxides with water Acids Bases Reaction with water SO 3 + H 2 O → H 2 SO 4 Ca. O + H 2 O → Ca(OH)2 Acid is a substance that, when added to water, increases the concentration of H+ ions in the water Bases is a substance that, when added to water, increases the concentration of OH- ions in the water
 11 Acids and bases in real life Phosphoric acid (H 3 PO 4) 18 mg per 100 ml Lemons have 8% of citric acid
11 Acids and bases in real life Phosphoric acid (H 3 PO 4) 18 mg per 100 ml Lemons have 8% of citric acid
 12 Acids and bases in real life Solution of soap in water commonly Give base reaction 50% of Na. OH
12 Acids and bases in real life Solution of soap in water commonly Give base reaction 50% of Na. OH
 13 Nomenclature Acids When the central atom forms only one acid, the suffix -ic is used: hypo- , -ous or per- sufix are used Sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4) HCl. O 3 +V chloric acid Nitric acid (HNO 3) HCl. O 4 +VII perchloric acid Phosphoric acid (H 3 PO 4) HNO 2 +III nitrous acid Chromic acid (H 2 Cr. O 4) HNO 3 +V nitric acid Boric acid (H 3 BO 3) H 2 SO 3 +IV sulphurous acid Acetic acid (CH 3 COOH) H 2 SO 4 +VI sulphuric acid Formic acid (HCOOH) Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
13 Nomenclature Acids When the central atom forms only one acid, the suffix -ic is used: hypo- , -ous or per- sufix are used Sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4) HCl. O 3 +V chloric acid Nitric acid (HNO 3) HCl. O 4 +VII perchloric acid Phosphoric acid (H 3 PO 4) HNO 2 +III nitrous acid Chromic acid (H 2 Cr. O 4) HNO 3 +V nitric acid Boric acid (H 3 BO 3) H 2 SO 3 +IV sulphurous acid Acetic acid (CH 3 COOH) H 2 SO 4 +VI sulphuric acid Formic acid (HCOOH) Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
 Common reactions of acids Reaction with bases H 2 SO 4 + 2 Na. OH → Na 2 SO 4 + 2 H 2 O Reaction with basic or amphoteric oxides Ca. O + HCl → Ca. Cl 2 + H 2 O Reaction with metals Mg + HCl → Mg. Cl 2 + H 2↑ Reaction with another metal salts Ca. CO 3 + HCl → Ca. Cl 2 + H 2 O + CO 2 ↑ 14
Common reactions of acids Reaction with bases H 2 SO 4 + 2 Na. OH → Na 2 SO 4 + 2 H 2 O Reaction with basic or amphoteric oxides Ca. O + HCl → Ca. Cl 2 + H 2 O Reaction with metals Mg + HCl → Mg. Cl 2 + H 2↑ Reaction with another metal salts Ca. CO 3 + HCl → Ca. Cl 2 + H 2 O + CO 2 ↑ 14
 15 Bases common reaction Nomenclature Reaction with acids 2 Na. OH + H 2 SO 4 → Na 2 SO 4 + 2 H 2 O Reaction with acidic oxides Al(OH)3 + SO 3 → Al 2(SO 4)3 + H 2 O KOH – Potassium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 Calcium hydroxide Reaction with amphoteric hydroxide Zn(OH)2 + 2 Na. OH → Na 2 Zn. O 2 + 2 H 2 O
15 Bases common reaction Nomenclature Reaction with acids 2 Na. OH + H 2 SO 4 → Na 2 SO 4 + 2 H 2 O Reaction with acidic oxides Al(OH)3 + SO 3 → Al 2(SO 4)3 + H 2 O KOH – Potassium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 Calcium hydroxide Reaction with amphoteric hydroxide Zn(OH)2 + 2 Na. OH → Na 2 Zn. O 2 + 2 H 2 O
 Amphoteric oxides Reaction with basic oxides Cr(OH)3 + K 2 O → 2 KCr. O 2 + 3 H 2 O Reaction with acidic oxides Zn(OH)2 + SO 3 → Zn. SO 4 + H 2 O 16
Amphoteric oxides Reaction with basic oxides Cr(OH)3 + K 2 O → 2 KCr. O 2 + 3 H 2 O Reaction with acidic oxides Zn(OH)2 + SO 3 → Zn. SO 4 + H 2 O 16
 Reactions done during lab. works S + O 2 → SO 3 P + O 2 → P 2 O 5 SO 3 + H 2 O → H 2 SO 4 P 2 O 5 + H 2 O → H 3 PO 4 Ca. O + H 2 O → Ca(OH)2 Mg. O + HCl → Ca. Cl 2 + H 2 O Ni. O + HCl → Ni. Cl 2 + H 2 O Pb. O + HCl → Pb. Cl 2 Ca. CO 3+ HCl → Ca. Cl 2 + H 2 O + CO 2 ↑ 17
Reactions done during lab. works S + O 2 → SO 3 P + O 2 → P 2 O 5 SO 3 + H 2 O → H 2 SO 4 P 2 O 5 + H 2 O → H 3 PO 4 Ca. O + H 2 O → Ca(OH)2 Mg. O + HCl → Ca. Cl 2 + H 2 O Ni. O + HCl → Ni. Cl 2 + H 2 O Pb. O + HCl → Pb. Cl 2 Ca. CO 3+ HCl → Ca. Cl 2 + H 2 O + CO 2 ↑ 17
 18 Must to remember: Oxides can be devide by 3 classes Basic oxides, amphoteric, and acidic oxides Acid is a compound which increase concentration of H+ in solution. It react with bases with formation of water Na. OH + HCl → Na. Cl + H 2 O
18 Must to remember: Oxides can be devide by 3 classes Basic oxides, amphoteric, and acidic oxides Acid is a compound which increase concentration of H+ in solution. It react with bases with formation of water Na. OH + HCl → Na. Cl + H 2 O
 19 Please, be prepared for the test Questions for the Test #1 : Determinate oxidation state in oxides, and provide with names Classification, difference in behave Reaction of oxides with : water, acids, bases, another oxides Questions for the Test #2 : Write formula of acids and bases; and salts; nomenclature Reaction of acids with : bases, oxides, another salts, metals Reaction of bases with : acids, oxides
19 Please, be prepared for the test Questions for the Test #1 : Determinate oxidation state in oxides, and provide with names Classification, difference in behave Reaction of oxides with : water, acids, bases, another oxides Questions for the Test #2 : Write formula of acids and bases; and salts; nomenclature Reaction of acids with : bases, oxides, another salts, metals Reaction of bases with : acids, oxides


