d76cba891ce41a05176013cdfe401548.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
Chemical Informatics & Cyberinfrastructure Collaboratory Cheminformatics Aspects: HTS Data Analysis & Virtual Screening David J. Wild Visiting Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Informatics djwild@indiana. edu http: //www. informatics. indiana. edu/djwild/ Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 1

About Me • Ph. D. and postdoc in Peter Willett’s Lab (Sheffield) – parallel 2 D and 3 D similarity algorithms. • Postdoc then Senior Scientist at Parke-Davis, Ann Arbor (now Pfizer), researching and developing chemoinformatics tools for bench chemists & modelers. Led collaborations with Tripos and Bioreason for development of HTS analysis software (SAR Navigator, Class. Pharmer) • Left in 2002 to form Wild Ideas Consulting and take up adjunct position at University of Michigan • Visiting Assistant Professor at Indiana since August 2004. Permanent position starting fall 2006. • Now run research group focused on handling large and diverse sources of chemical information. More at http: //www. informatics. indiana. edu/djwild Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 2
“Cheminformatics” contect of CICC proposal • Development of user-centered tools for query, organization, navigation and analysis of large chemical HTS datasets (specifically Pubchem and its subsets), including: – – – Rapid organization of large datasets (cluster analysis) Intuitive interfaces for navigation and analysis Virtual screening Standardization of data exchange formats Data mining of SAR across multiple screens • Or allowing scientists to ask the right questions and have them answered effectively Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 3
Thoughts relating to Pubchem HTS analysis (and more widely applicable) • Scientists’ questions are probably not going to be conceptually complex, but finding the answers can currently be very time consuming and/or complex (for a human) – “which of the 10, 000 hits from this screen are most promising for follow-up? ” – “who else is working on similar chemical structures to these? ” – “are there any compounds in Pubchem (or elsewhere) that might bind to the active site of this protein I just resolved? ” – “do any compounds related to this one exhibit toxic side effects? ” • We need to figure out just what the questions are! (Contextual Inquiry, Use cases) • Answers are often “stale” after a short period of time – questions need to be re-answered as new information is generated • Almost all current systems are passive, and follow the (web) browsing model • Existing approaches do not scale up well Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 4
Use Case Which of these hits should I follow up? • An HTS experiment has produced 10, 000 possible hits out of a screening set of 2 m compounds. A chemist on the project wants to know what the most promising series of compounds for follow-up are, based on: – – – – Series selection BCI cluster analysis Structure-activity relationships lots of methods Chemical and pharmacokinetic properties mitools, chemaxon Compound history g. Nova / Postgre. SQL / Pubchem search Patentability BCI Markush handling software Toxicity Synthetic feasibility + requires visualization tools! Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 5

Use Case Are there any good ligands for my target? • A chemist is working on a project involving a particular protein target, and wants to know: – Any newly published compounds which might fit the protein receptor site g. Nova / Postgre. SQL, Pub. Chem search, FRED Docking – Any published 3 D structures of the protein or of protein-ligand complexes PDB search – Any interactions of compounds with other proteins g. Nova / Postgre. SQL, Pub. Chem search – Any information published on the protein target Journal text search Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 6
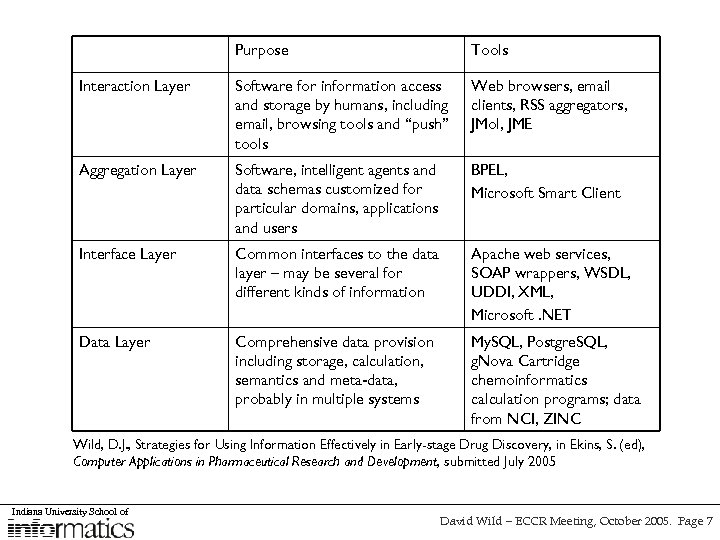
Purpose Tools Interaction Layer Software for information access and storage by humans, including email, browsing tools and “push” tools Web browsers, email clients, RSS aggregators, JMol, JME Aggregation Layer Software, intelligent agents and data schemas customized for particular domains, applications and users BPEL, Microsoft Smart Client Interface Layer Common interfaces to the data layer – may be several for different kinds of information Apache web services, SOAP wrappers, WSDL, UDDI, XML, Microsoft. NET Data Layer Comprehensive data provision including storage, calculation, semantics and meta-data, probably in multiple systems My. SQL, Postgre. SQL, g. Nova Cartridge chemoinformatics calculation programs; data from NCI, ZINC Wild, D. J. , Strategies for Using Information Effectively in Early-stage Drug Discovery, in Ekins, S. (ed), Computer Applications in Pharmaceutical Research and Development, submitted July 2005 Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 7
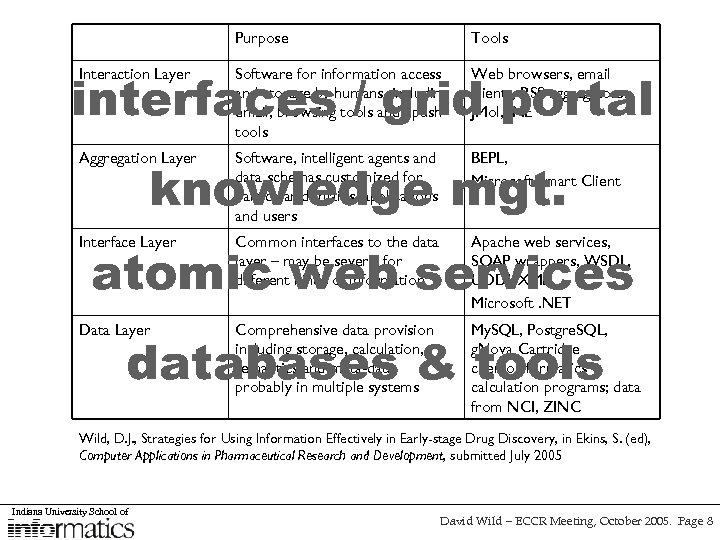
Purpose Tools interfaces / grid portal Interaction Layer Software for information access and storage by humans, including email, browsing tools and “push” tools Web browsers, email clients, RSS aggregators, JMol, JME Aggregation Layer Software, intelligent agents and data schemas customized for particular domains, applications and users BEPL, Microsoft Smart Client Interface Layer Common interfaces to the data layer – may be several for different kinds of information Apache web services, SOAP wrappers, WSDL, UDDI, XML, Microsoft. NET Data Layer Comprehensive data provision including storage, calculation, semantics and meta-data, probably in multiple systems My. SQL, Postgre. SQL, g. Nova Cartridge chemoinformatics calculation programs; data from NCI, ZINC knowledge mgt. atomic web services databases & tools Wild, D. J. , Strategies for Using Information Effectively in Early-stage Drug Discovery, in Ekins, S. (ed), Computer Applications in Pharmaceutical Research and Development, submitted July 2005 Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 8
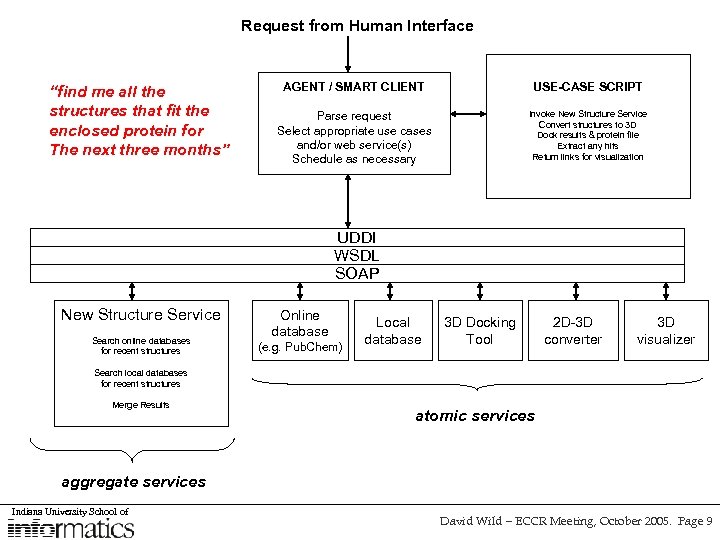
Request from Human Interface “find me all the structures that fit the enclosed protein for The next three months” AGENT / SMART CLIENT USE-CASE SCRIPT Parse request Select appropriate use cases and/or web service(s) Schedule as necessary Invoke New Structure Service Convert structures to 3 D Dock results & protein file Extract any hits Return links for visualization UDDI WSDL SOAP New Structure Service Search online databases for recent structures Online database (e. g. Pub. Chem) Local database 3 D Docking Tool 2 D-3 D converter 3 D visualizer Search local databases for recent structures Merge Results atomic services aggregate services Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 9
Visualization & interface level tools • • No matter how clever the smarts underneath, the overriding factor in usefulness will be the quality of scientists’ interaction with the system Several metaphors in existence for looking at large amounts of 2 D structural information: 2 D plot (SAR Navigator), “spreadsheet” views (Accord, etc), enhanced spreadsheets (Classpharmer, Chem. TK), Kohonen maps, Tree. Maps Contextual Design, Interaction Design (Cooper) and Usability Studies have proven effective in designing the right interfaces for the right people in chemical informatics, and deserve investigation for future use in this project (in collaboration with HCI colleagues on the project) Possibility of multiple interfaces for different people groups (Cooper’s “primary personas”) Don’t assume the browser interface – email / nat. lang. proc ? Start with the basics – – – 2 D chemical structure drawing (input) Visualization of large numbers of chemical structures in 2 D 3 D chemical structure visualization Planning on evaluation of NLP, email, RSS, etc. as well as browser-based interfaces Interface tools will be developed in a grid portal environment using portlet technology Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 10
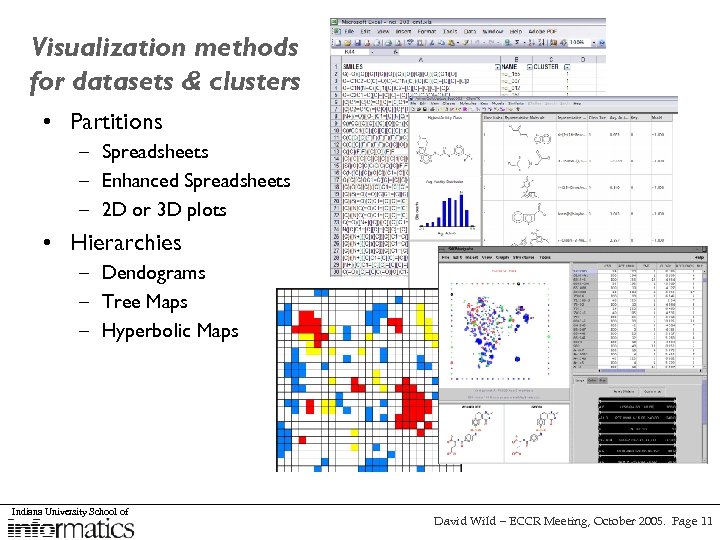
Visualization methods for datasets & clusters • Partitions – Spreadsheets – Enhanced Spreadsheets – 2 D or 3 D plots • Hierarchies – Dendograms – Tree Maps – Hyperbolic Maps Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 11
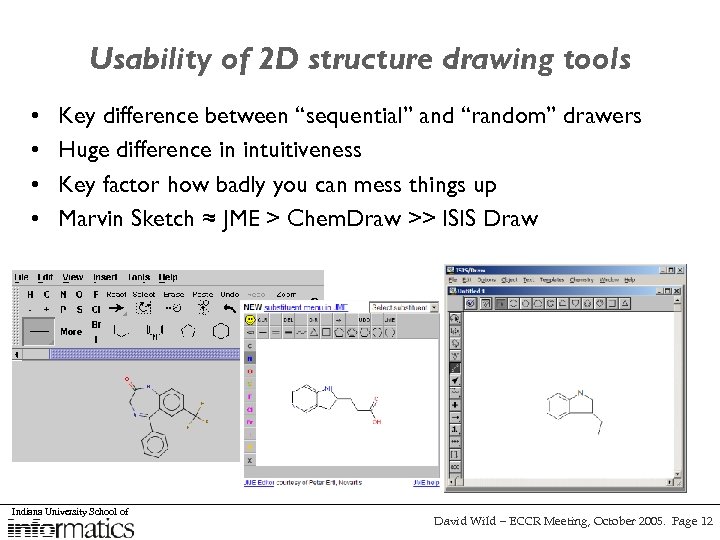
Usability of 2 D structure drawing tools • • Key difference between “sequential” and “random” drawers Huge difference in intuitiveness Key factor how badly you can mess things up Marvin Sketch ≈ JME > Chem. Draw >> ISIS Draw Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 12

Next Steps • • • Develop realistic use-cases based on as much information about potential users as we can muster Work with other members of CICC to define Grid architecture (services required and their interfaces) by integrating requirements of different aspects of Cheminformatics Implement some web services that are likely to be employed in use cases – Rapid dataset search and organization • • Search of Pub. Chem (SOAP interface already exists) Search of local g. Nova / Postgre. SQL database Clustering using BCI (Digital Chemistry) Divisive K-Means BCI Markush searching – Interface tools for navigation and analysis • Integration with Spotfire • Chem. TK (or other spreadsheet-metaphor product) • Develop entirely new interface tools (usability studies) – Virtual Screening • • Indiana University School of Molecular docking with Open. Eye FRED Property calculation with Molinspiration / Chemaxon PDB Search (EMBL) Activity prediction modules (Molinspiration / RP / SVMs etc) David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 13
Supplemental Slides Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 14
Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 15
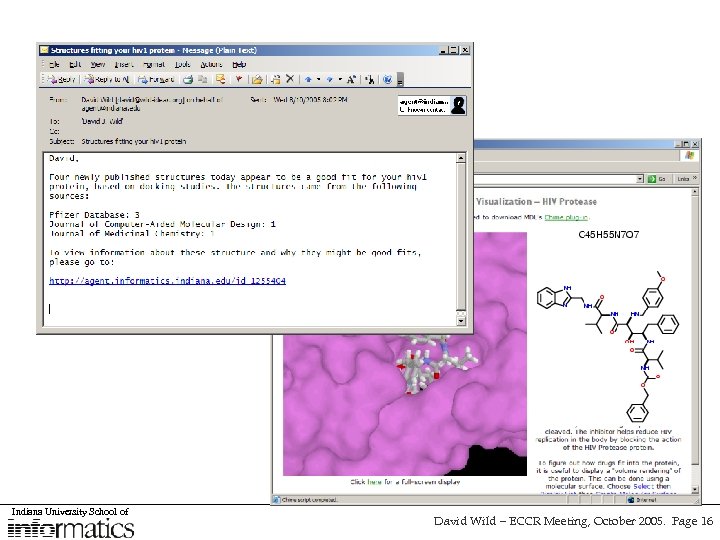
Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 16

Use Case #1 Are there any good ligands for my target? • A chemist is working on a project involving a particular protein target, and wants to know: – Any newly published compounds which might fit the protein receptor site – Any published 3 D structures of the protein or of protein-ligand complexes – Any interactions of compounds with other proteins – Any information published on the protein target Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 17

Use Case #1 Are there any good ligands for my target? • A chemist is working on a project involving a particular protein target, and wants to know: – Any newly published compounds which might fit the protein receptor site g. Nova / Postgre. SQL, Pub. Chem search, FRED Docking – Any published 3 D structures of the protein or of protein-ligand complexes PDB search – Any interactions of compounds with other proteins g. Nova / Postgre. SQL, Pub. Chem search – Any information published on the protein target Journal text search Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 18

Use Case #2 Who else is working on these structures? • A chemist is working on a chemical series for a particular project and wants to know: – If anyone publishes anything using the same or related compounds – Any new compounds added to the corporate collection which are similar or related – If any patents are submitted that might overlap the compounds he is working on – Any pharmacological or toxicological results for those or related compounds – The results for any other projects for which those compounds were screened Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 19
Use Case #2 Who else is working on these structures? • A chemist is working on a chemical series for a particular project and wants to know: – If anyone publishes anything using the same or related compounds ~ Pub. Chem search – Any new compounds added to the corporate collection which are similar or related g. Nova CHORD / Postgre. SQL – If any patents are submitted that might overlap the compounds he is working on ~ BCI Markush handling software – Any pharmacological or toxicological results for those or related compounds g. Nova CHORD / Postgre. SQL, Mi. Toolkit – The results for any other projects for which those compounds were screened g. Nova CHORD / Postgre. SQL, Pub. Chem search Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 20
Use Case - Pubchem Which of these hits should I follow up? • An MLI HTS experiment has produced 10, 000 possible hits out of a screening set of 2 m compounds. A chemist at another laboratory wants to know if there any interesting active series she might want to pursue, based on: – – – Structure-activity relationships Chemical and pharmacokinetic properties Compound history Patentability Toxicity Synthetic feasibility Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 21
Use Case – Pub. Chem Which of these hits should I follow up? • An HTS experiment has produced 10, 000 possible hits out of a screening set of 2 m compounds. A chemist on the project wants to know what the most promising series of compounds for follow-up are, based on: – – – – Series selection BCI cluster analysis Structure-activity relationships lots of methods Chemical and pharmacokinetic properties mitools, chemaxon Compound history g. Nova / Postgre. SQL / Pubchem search Patentability BCI Markush handling software Toxicity Synthetic feasibility + requires visualization tools! Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 22

Cluster Analysis and Chemical Informatics • Used for organizing datasets into chemical series, to build predictive models, or to select representative compounds • Organizational usage has not been as well studies as the other two, but see – Wild, D. J. , Blankley, C. J. Comparison of 2 D Fingerprint Types and Hierarchy Level Selection Methods for Structural Grouping using Wards Clustering, Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences. , 2000, 40, 155 -162. • Essentially helping large datasets become manageable • Methods used: – Jarvis-Patrick and variants • O(N 2), single partition – Ward’s method • Hierarchical, regarded as best, but at least O(N 2) – K-means • < O(N 2), requires set no of clusters, a little “messy” – Sphere-exclusion (Butina) • Fast, simple, similar to JP – Kohonen network • Clusters arranged in 2 D grid, ideal for visualization Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 23
Limitations of Ward’s method for large datasets (>1 m) • Best algorithms have O(N 2) time requirement (RNN) • Requires random access to fingerprints – hence substantial memory requirements (O(N)) • Problem of selection of best partition – can select desired number of clusters • Easily hit 4 GB memory addressing limit on 32 bit machines – Approximately 2 m compounds Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 24
Scaling up clustering methods • Parallelisation – Clustering algorithms can be adapted for multiple processors – Some algorithms more appropriate than others for particular architectures – Ward’s has been parallelized for shared memory machines, but overhead considerable • New methods and algorithms – Divisive (“bisecting”) K-means method – Hierarchical Divisive – Approx. O(Nlog. N) Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 25

Divisive K-means Clustering • New hierarchical divisive method – – – Hierarchy built from top down, instead of bottom up Divide complete dataset into two clusters Continue dividing until all items are singletons Each binary division done using K-means method Originally proposed for document clustering • “Bisecting K-means” – Steinbach, Karypis and Kumar (Univ. Minnesota) http: //wwwusers. cs. umn. edu/~karypis/publications/Papers/PDF/doccluster. pdf – Found to be more effective than agglomerative methods – Forms more uniformly-sized clusters at given level Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 26
BCI Divkmeans • Several options for detailed operation – Selection of next cluster for division – size, variance, diameter – affects selection of partitions from hierarchy, not shape of hierarchy • Options within each K-means division step – – distance measure choice of seeds batch-mode or continuous update of centroids termination criterion • Have developed parallel version for Linux clusters / grids in conjunction with BCI • For more information, see Barnard and Engels talks at: http: //cisrg. shef. ac. uk/shef 2004/conference. htm Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 27
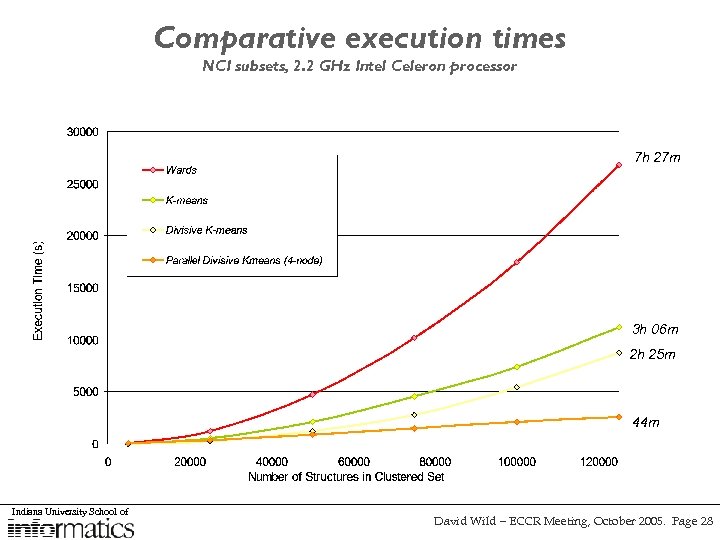
Comparative execution times NCI subsets, 2. 2 GHz Intel Celeron processor 7 h 27 m 3 h 06 m 2 h 25 m 44 m Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 28
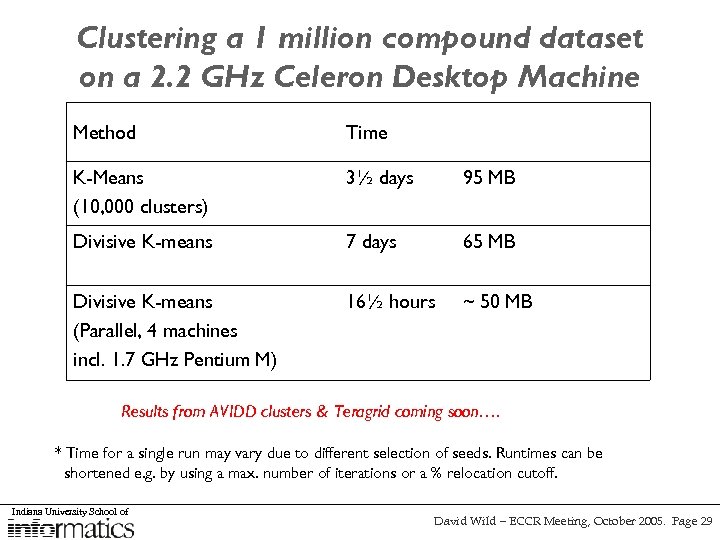
Clustering a 1 million compound dataset on a 2. 2 GHz Celeron Desktop Machine Method Time * Memory Usage K-Means (10, 000 clusters) 3½ days 95 MB Divisive K-means 7 days 65 MB Divisive K-means (Parallel, 4 machines incl. 1. 7 GHz Pentium M) 16½ hours ~ 50 MB Results from AVIDD clusters & Teragrid coming soon…. * Time for a single run may vary due to different selection of seeds. Runtimes can be shortened e. g. by using a max. number of iterations or a % relocation cutoff. Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 29
Divisive Kmeans: Conclusions • Much faster than Ward’s, speed comparable to K-means, suitable for very large datasets (millions) – Time requirements approximately O(N log N) – Current implementation can cluster 1 m compounds in under a week on a low-power desktop PC – Cluster 1 m compounds in a few hours with a 4 -node parallel Linux cluster • Better balance of cluster sizes than Wards or Kmeans • Visual inspection of clusters suggests better assembly of compound series than other methods • Better clustering of actives together than previously-studied methods • Memory requirements minimal • Experiments using AVIDD cluster and Teragrid forthcoming (50+ nodes) Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 30
Visualization & interface level tools • No matter how clever the smarts underneath, the overriding factor in usefulness will be the quality of scientists’ interaction with the system • Contextual Design, Interaction Design (Cooper) and Usability Studies have proven effective in designing the right interfaces for the right people in chemical informatics [collaboration with HCI? ] • Possibility of multiple interfaces for different people groups (Cooper’s “primary personas”) • Don’t assume the browser interface – email / NLP ? • Start with the basics – 2 D chemical structure drawing (input) – Visualization of large numbers of chemical structures in 2 D – 3 D chemical structure visualization • Planning on evaluation of NLP, email, RSS, etc. as well as browser-based interfaces Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 31
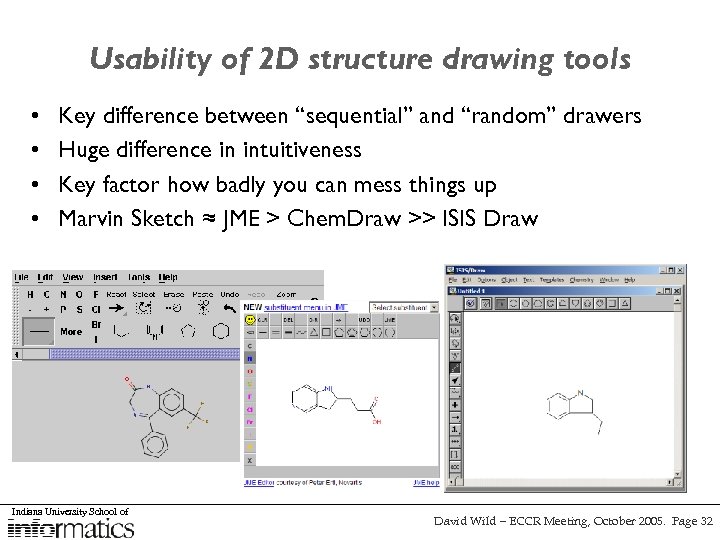
Usability of 2 D structure drawing tools • • Key difference between “sequential” and “random” drawers Huge difference in intuitiveness Key factor how badly you can mess things up Marvin Sketch ≈ JME > Chem. Draw >> ISIS Draw Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 32
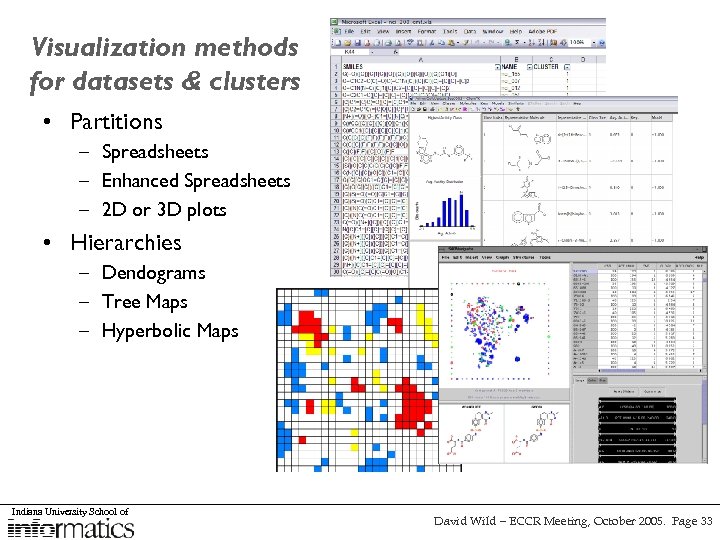
Visualization methods for datasets & clusters • Partitions – Spreadsheets – Enhanced Spreadsheets – 2 D or 3 D plots • Hierarchies – Dendograms – Tree Maps – Hyperbolic Maps Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 33
Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 34
Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 35
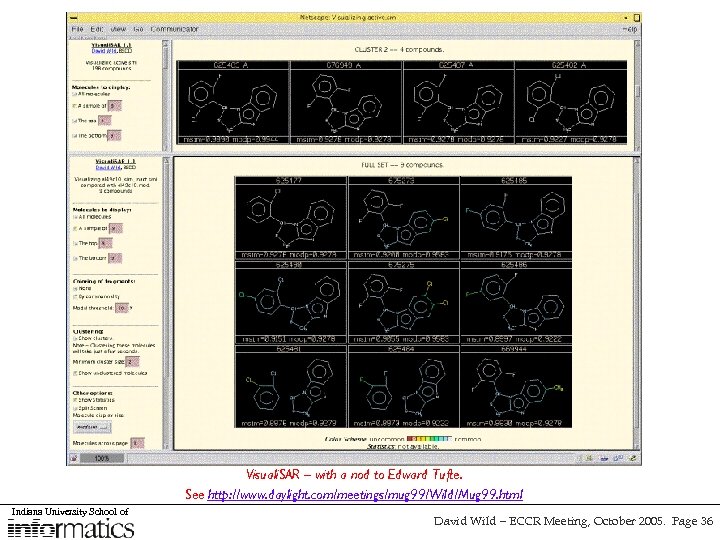
Visuali. SAR – with a nod to Edward Tufte. See http: //www. daylight. com/meetings/mug 99/Wild/Mug 99. html Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 36
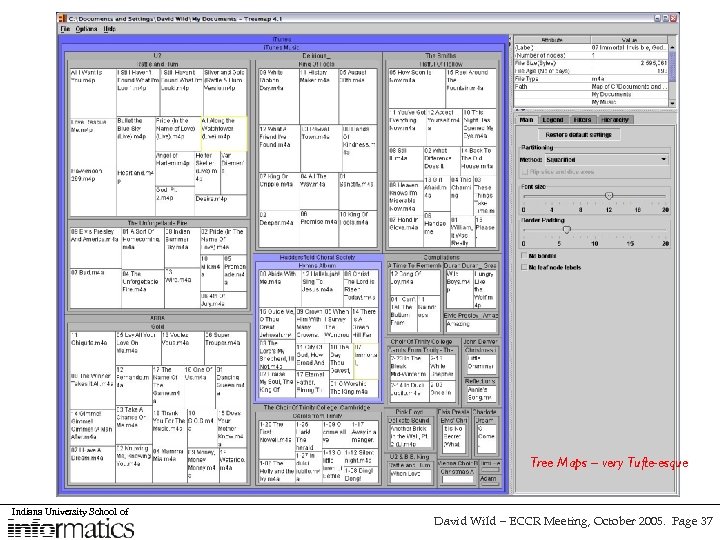
Tree Maps – very Tufte-esque Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 37
External support • ECCR grant ($500, 000) – 20% Co-PI with Fox for development of web services for HTS data organization and visualization – May lead to $5 m/5 years grant for full center • Applied for Microsoft Smart Clients for e. Science grant ($50, 000) – Including Marlon Pierce in the Community Grids lab • Peter Murray-Rust group, Cambridge – offering expertise and assistance with web services • IO-Informatics – provision of Sentient software and consulting • BCI – clustering, structure enumeration & toolkit, consulting • Open. Eye – a range of calculation tools, FRED docking • Molinspiration – Mi. Tools Toolkit • g. Nova – CHORD chemical database system • Possible financial support from company in the UK Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 38

Technology • Perl SOAP: : Lite – Will be used for initial web service development – Doesn’t really implement WSDL & UDDI • Apache Axis & Tomcat – Deploy WSDL for web services • BPEL 4 WS – Business Process Execution Language – For aggregation of web services – http: //www-128. ibm. com/developerworks/library/specification/ws-bpel/ • Microsoft. NET & C# Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 39
Current activities • Core activities – Development of use-cases – Development of initial web services (Perl SOAP: : Lite) – Use of Taverna to prototype use-case scripts • Basic research on future components – Organizing large amounts of chemical information for human consumption • Development of very fast parallel clustering techniques – to be exposed as web services – Selection of interface-level tools for basic interaction • Chemical structure drawing, display • Investigation of email, NLP, RSS, and browser interfaces – Interface-level tools for visualization, navigation and analysis • Cluster and dataset visualization, natural language interfaces) Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 40
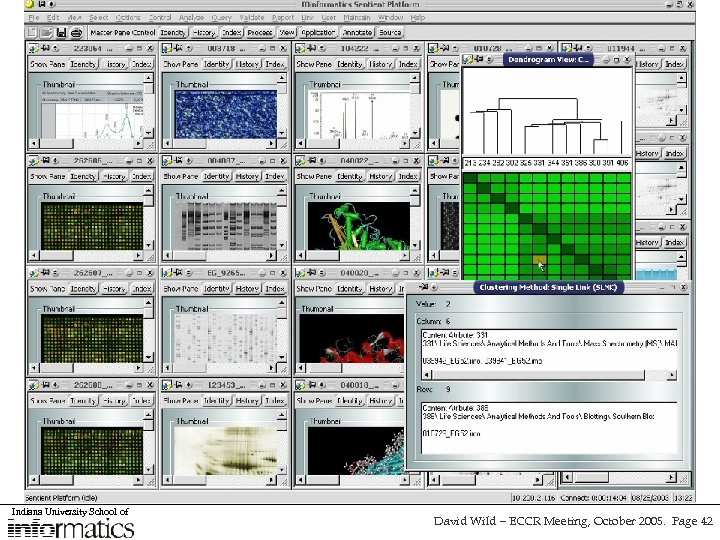
Sentient - an alternative approach to managing heterogenous data sources • Collaboration with IO-Informatics (along with Cornell, and UCSD) for the investigation of service-oriented architectures in life sciences research using Sentient software • Aim to integrate several sources of information relating to Alzheimer’s Disease (brain imaging, morphology, gene expression) so that cross-dataset biomarkers can be identified • Sentient usies Intelligent Multidimensional Objects (IMOs) to define and query data sources and the tools used to access them • Still a browsing approach, but with a layer of coherence and “intelligence” • Hope to expand to include chemistry data • Can also be used as an interface-level tool Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 41
Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 42
Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 43

Conclusions so far • • • Effective exploitation of large volumes and diverse sources of chemical information is a critical problem to solve, with a potential huge impact on the drug discovery process Most information needs of chemists and drug discovery scientists are conceptually straightforward, but complex (for them) to implement All of the technology is now in place to implement may of these information need “use-cases”: the four level model using service-oriented architectures together with smart clients look like a neat way of doing this The aggregation and interface levels offer the most challenges In conjunction with grid computing, rapid and effective organization and visualization of large chemical datasets is feasible in a web service environment Some pieces are missing: – – Chemical structure search of journals (wait for In. Ch. I) Automated patent searching Effective dataset organization Effective interfaces, especially visualization of large numbers of 2 D structures (we’re working on it!) Indiana University School of David Wild – ECCR Meeting, October 2005. Page 44
d76cba891ce41a05176013cdfe401548.ppt