7975bd8a35f9c0758a5ee2e20e9c6a6c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

Chat with the Lab: Mobilizing Informix Dynamic Server Enterprise Data April 12, 2006 Jerry Keesee, Director of the Informix Lab Anita Chung, chunga@us. ibm. com Jacques Roy, jacquesr@us. ibm. com © 2006 IBM Corporation

Enterprise Mobility Delivers ROI Now Increase Productivity Same personnel, more requests completed In 2004. . . 625 M WW Cell phone shipments 11. 7 M PDAs will be sold 30 M total hotspot users 50% business laptops will have Wi. Fi Customer Loyalty & Retention Less customer churn with value-added services Generate Additional Revenue More time with customers Increase Profitability New business models, higher margins © 2006 IBM Corporation 2

At the right time (any time) IDS Delivered to the right source The Right Information Using the appropriate technology © 2006 IBM Corporation At the right place (every place) 3

Overview Mobile database and synchronization solution that easily integrates into existing IT environments § Reliable and secure access to enterprise information anywhere, any time for mobile workforce § A ~250 KB zero admin data store that can be easily synchronized with DB 2, IDS and other JDBC compliant enterprise data sources Benefits • Increase Employee Productivity • Improve Profitability • Reduce Costs § Multi-platform synchronization server Support § A scalable solution that readily integrates with a portfolio of wireless offerings from IBM and your existing IT investments § Robust, high performance and on demand information management capability to mobile environment § Best of breed mobile client support § Three flexible licensing options to choose from “ © 2006 IBM Corporation Outlet Explorer, powered by DB 2 Everyplace, improves the efficiency of field-based sales representatives by at least 50 percent. But the real benefit is the quality and reliability of the information that is now easily accessible, which can lead to increased profits. —Wolfram Ernst, Managing Director and Co-founder, LEAD 4
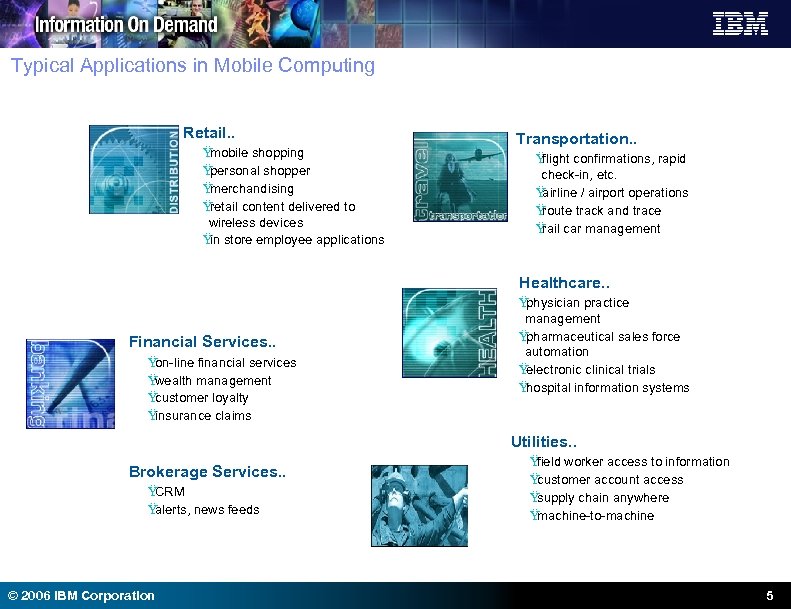
Typical Applications in Mobile Computing Retail. . Ÿ mobile shopping Ÿ personal shopper Ÿ merchandising Ÿ retail content delivered to wireless devices Ÿ store employee applications in Transportation. . Ÿ flight confirmations, rapid check-in, etc. Ÿ airline / airport operations Ÿ route track and trace Ÿ car management rail Healthcare. . Financial Services. . Ÿ on-line financial services Ÿ wealth management Ÿ customer loyalty Ÿ insurance claims Ÿ physician practice management Ÿ pharmaceutical sales force automation Ÿ electronic clinical trials Ÿ hospital information systems Utilities. . Brokerage Services. . Ÿ CRM Ÿ alerts, news feeds © 2006 IBM Corporation Ÿ field worker access to information Ÿ customer account access Ÿ supply chain anywhere Ÿ machine-to-machine 5

Considerations When Exploiting Enterprise Mobility § Who needs Access? § Which devices? § Is there connectivity available? § What application/information is needed on-site? § How do I manage these devices? § What level of security is required? § How do I connect across different network protocols? © 2006 IBM Corporation 6
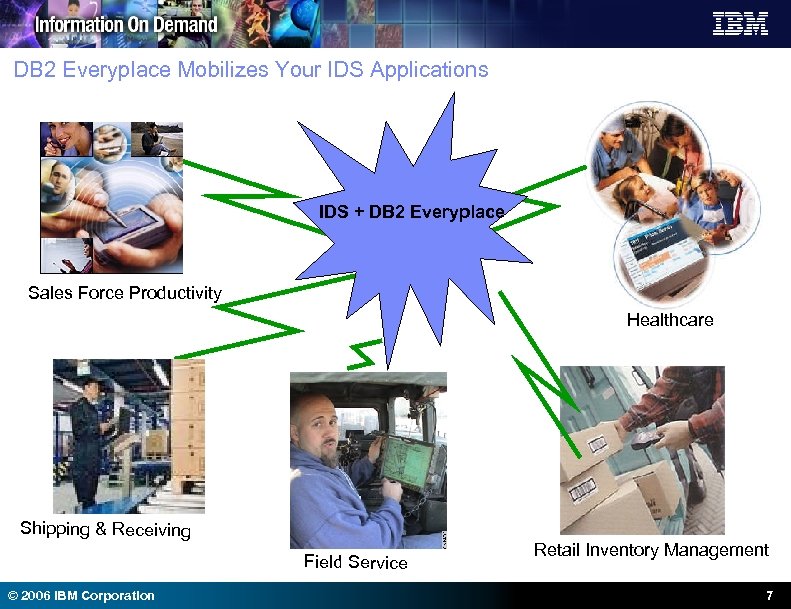
DB 2 Everyplace Mobilizes Your IDS Applications IDS + DB 2 Everyplace Sales Force Productivity Healthcare Shipping & Receiving Field Service © 2006 IBM Corporation Retail Inventory Management 7
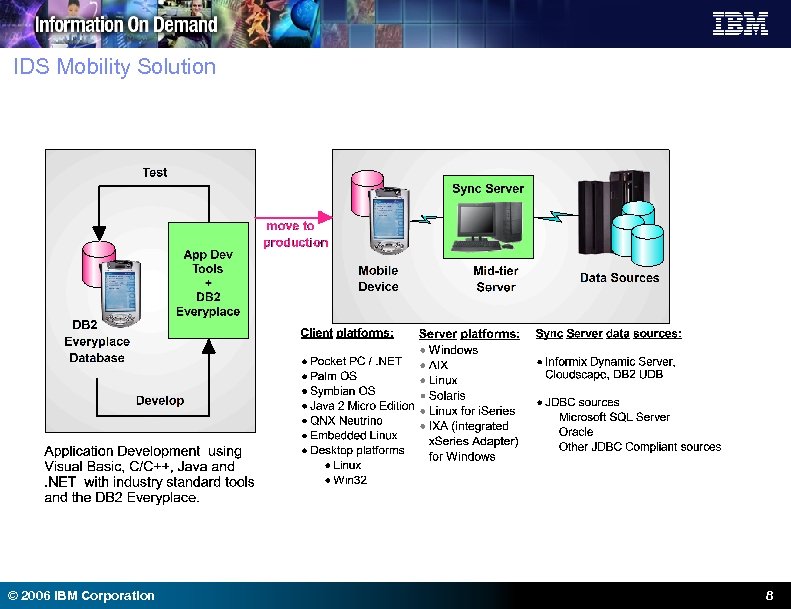
IDS Mobility Solution © 2006 IBM Corporation 8

DB 2 Everyplace V 8. 2 § Lay the foundation for enterprise mobility on demand } } Complete mobile relational database and synchronization solution Best of breed mobile platform support Reliable and secure enterprise data access right from your palm Complements a wide range of IBM wireless and information management software § Offer rapid return of investment } Integrated, open and scalable mobile application development made easy Zero administration, ultra small footprint mobile data base } Ship in three editions to meet the needs of enterprises of all sizes and ISV/OEM—Database Edition, Express Edition, Enterprise Edition § Free trial download available at: } http: //www 14. software. ibm. com/webapp/download/product. jsp? s=p&id=JPEN 4 HNW 2 H } http: //www-306. ibm. com/software/data/db 2/everyplace/index. html © 2006 IBM Corporation 9

Application Development Freedom § C/C++ § JDBC §. net languages § Web Services § App. Forge § Metrowerks § Eclipse § WSAD § WSDD § Platform Flexibility © 2006 IBM Corporation 10

Scalable On Demand § As business grows, so can the underlying mobile database and synchronization infrastructure… } Start with DB 2 Everyplace Express } Upgrade transparently to DB 2 Everyplace Enterprise Edition } With a Simple license key change © 2006 IBM Corporation 11
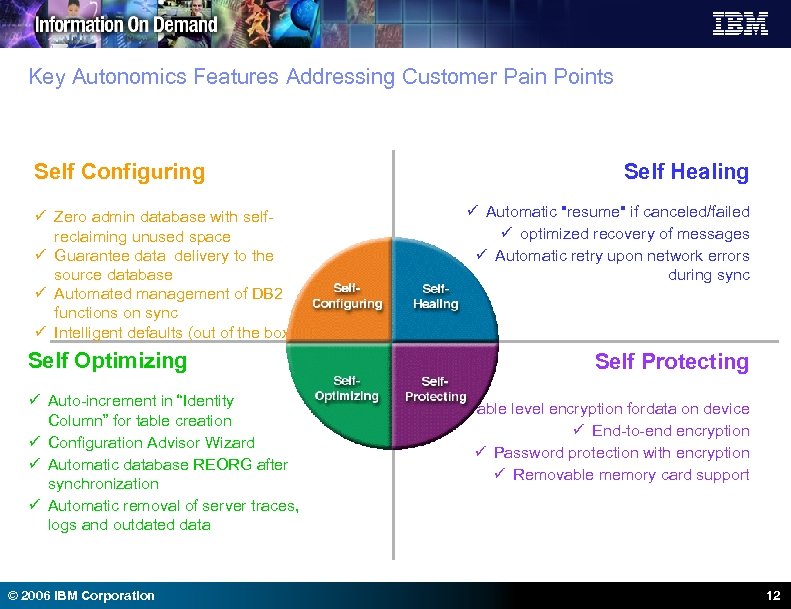
Key Autonomics Features Addressing Customer Pain Points Self Configuring ü Zero admin database with selfreclaiming unused space ü Guarantee data delivery to the source database ü Automated management of DB 2 functions on sync ü Intelligent defaults (out of the box) Self Optimizing ü Auto-increment in “Identity Column” for table creation ü Configuration Advisor Wizard ü Automatic database REORG after synchronization ü Automatic removal of server traces, logs and outdated data © 2006 IBM Corporation Self Healing ü Automatic "resume" if canceled/failed ü optimized recovery of messages ü Automatic retry upon network errors during sync Self Protecting ü Table level encryption fordata on device ü End-to-end encryption ü Password protection with encryption ü Removable memory card support 12

Reference: CEMIG Where they started: § Legacy driven processes § Expensive dedicated satellite link § Technicians returning to operational bases for new orders How they changed: § Implemented DB 2 Everyplace to connect field technicians to IDS database with service request data § Dispatch service orders to 500 mobile users who are with equipped with handheld devices What they are achieving: § Improve responsiveness to service outages § Improve customer satisfaction § Achieve measurable ROI of US$600, 000 per year © 2006 IBM Corporation 13

IDS Mobility Components Component Description Database Engine High performance data store for managing and using data on mobile and embedded devices Sync Client Sync client to communicate with the server using an httpbased synchronization protocol. Sync Server Mobile user management and synchronization of enterprise data with mobile and embedded devices DB 2 Everyplace is a small footprint relational database and synchronization server for mobile computing and embedded devices. © 2006 IBM Corporation 14
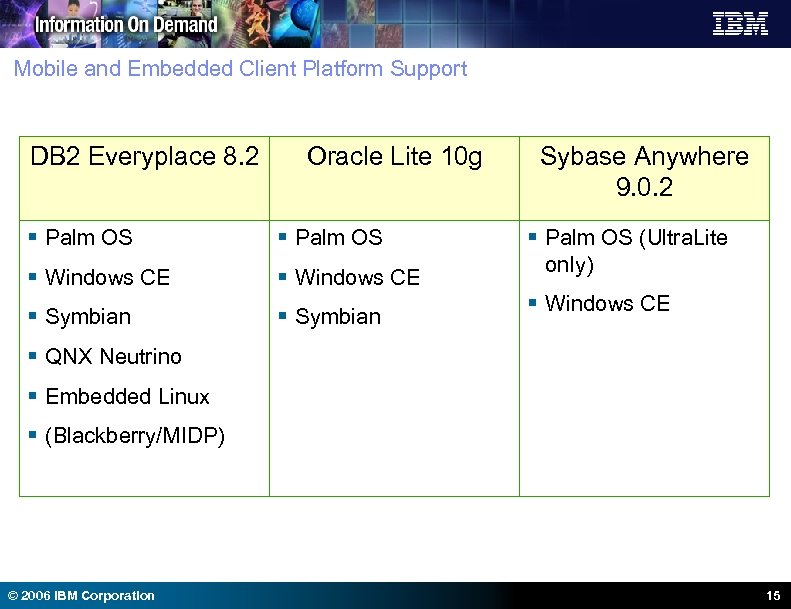
Mobile and Embedded Client Platform Support DB 2 Everyplace 8. 2 Oracle Lite 10 g § Palm OS § Windows CE § Symbian Sybase Anywhere 9. 0. 2 § Palm OS (Ultra. Lite only) § Windows CE § QNX Neutrino § Embedded Linux § (Blackberry/MIDP) © 2006 IBM Corporation 15
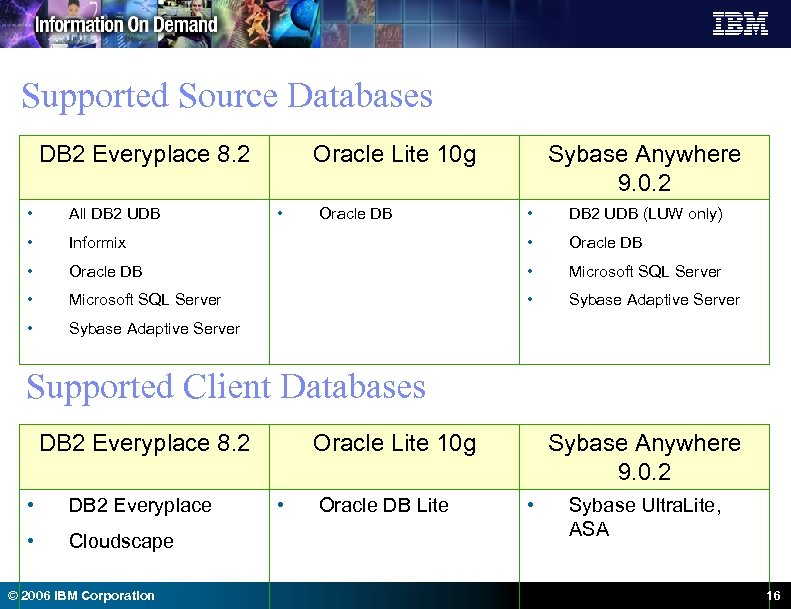
Supported Source Databases DB 2 Everyplace 8. 2 • All DB 2 UDB • Oracle Lite 10 g • Sybase Anywhere 9. 0. 2 • DB 2 UDB (LUW only) Informix • Oracle DB • Microsoft SQL Server • Sybase Adaptive Server Oracle DB Supported Client Databases DB 2 Everyplace 8. 2 • DB 2 Everyplace • Cloudscape © 2006 IBM Corporation Oracle Lite 10 g • Oracle DB Lite Sybase Anywhere 9. 0. 2 • Sybase Ultra. Lite, ASA 16

Enterprise Mobility Solution for IDS Mobile Device Sync Server Data Source HTTP/HTTPS JDBC Synchronize Replicate § Database Engine §DB 2 Everyplace §Cloud. Scape § Sync Client API § Mobile Application © 2006 IBM Corporation § DB 2 Everyplace Sync Server § Control DB § Mirror DB § Sync Server Servlet § WAS/Embedded WAS § Mobile Device Administration Console § Informix Dynamic Server 17
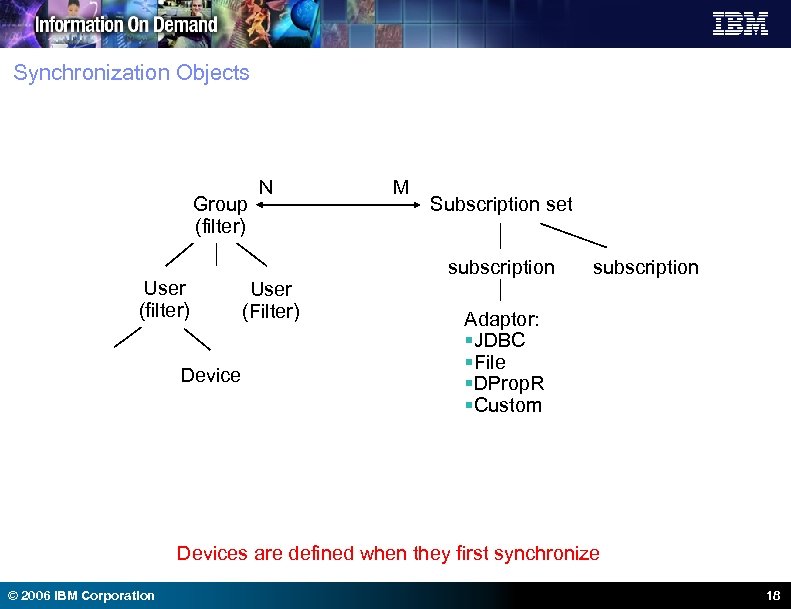
Synchronization Objects Group (filter) User (filter) Device N M Subscription set subscription User (Filter) subscription Adaptor: §JDBC §File §DProp. R §Custom Devices are defined when they first synchronize © 2006 IBM Corporation 18
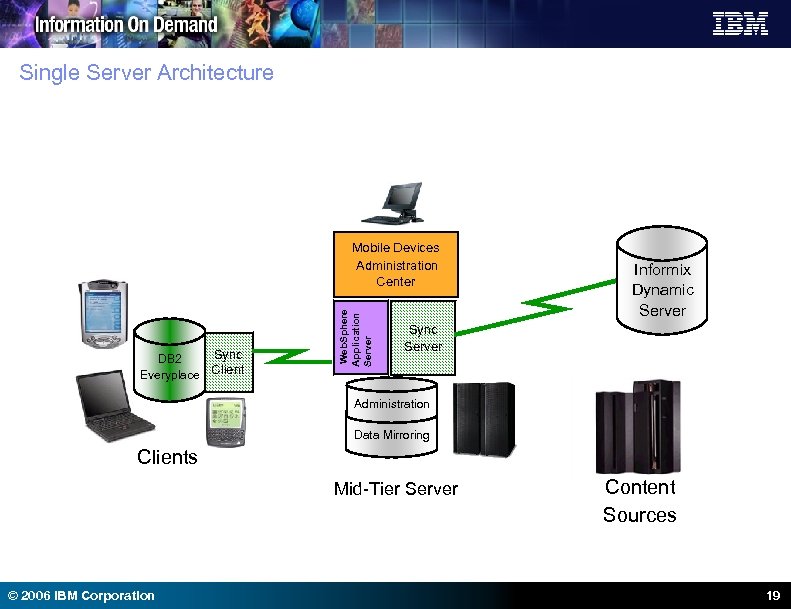
Single Server Architecture Sync DB 2 Everyplace Client Web. Sphere Application Server Mobile Devices Administration Center Informix Dynamic Server Sync Server Administration Data Mirroring Clients Mid-Tier Server © 2006 IBM Corporation Content Sources 19
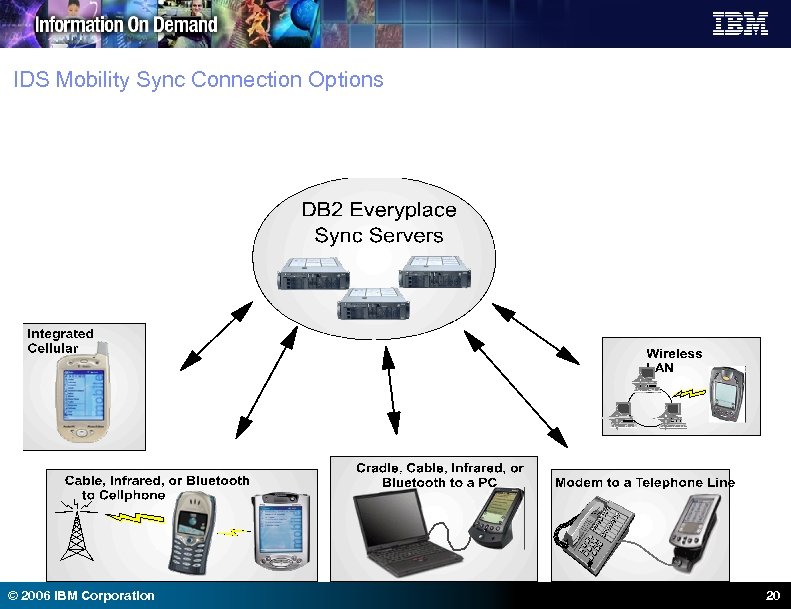
IDS Mobility Sync Connection Options © 2006 IBM Corporation 20
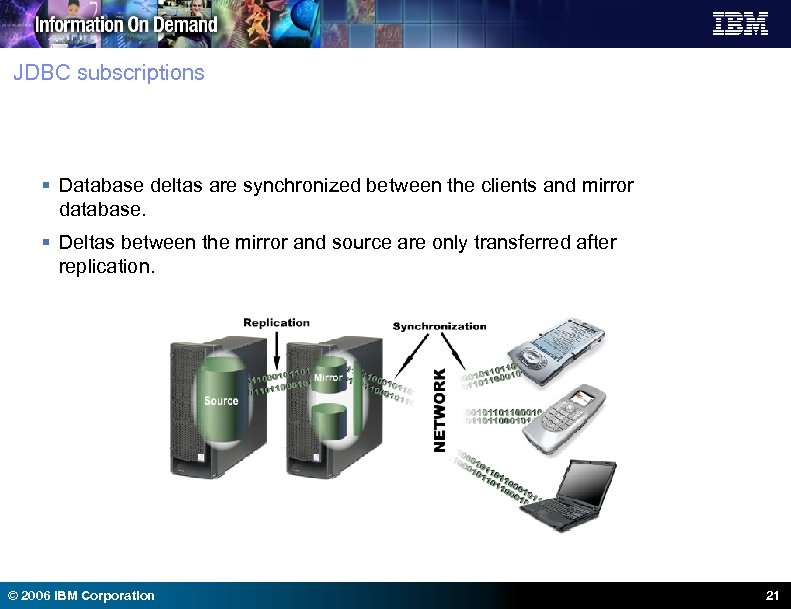
JDBC subscriptions § Database deltas are synchronized between the clients and mirror database. § Deltas between the mirror and source are only transferred after replication. © 2006 IBM Corporation 21

DB 2 Everyplace Subscriptions for IDS § A replication subscription provides specifications for how the information in a source system (an enterprise server) is to be synchronized with a target system (the mobile device). § JDBC subscriptions provide users with access to data in source tables on a data source with a JDBC interface, including Oracle, DB 2, Microsoft SQL Server, Informix, Sybase, and Lotus Domino. § Upload subscriptions only allows the user to directly insert rows into a table on a source database. Related tables on the mobile devices are not refreshed during synchronization. § File subscriptions allow replication of any type of file stored at the source server and are not bi-directional. §. © 2006 IBM Corporation 22

Sync Server § DB 2 Everyplace uses several metadata tables to maintain information about its internal structure. § The performance of relational databases will typically decline as tables grow unless they are periodically reorganized. § Customer data should reside in backend servers on separate systems from the DB 2 Everyplace system for maximum performance. © 2006 IBM Corporation 23

Sync Server and Client Overview § Centralized administration § Mobile Devices Administration Center GUI (MDAC) § Zero administration on devices § Manage table definitions, constraints, and indexes § Vertical and horizontal partitioning of data § Control distribution of data, files, and applications § Grouping of subscriptions § Access control for device users based on privileges © 2006 IBM Corporation 24

Sync Server and Client Overview § Message protocol utilizes WAP binary XML for compression § Automatic upgrade distribution of database and sync client engine software without user intervention § Security § Authentication § MD 5 authentication for standalone § LDAP authentication with WEA § Communication data encryption § 56 -bit and 128 -bit DES for standalone § SSL with WEA § Local data encryption on devices setup through central administration © 2006 IBM Corporation 25

Custom Logic § Allows application to customize behavior of synchronization and replication. § Custom Logic provides a mechanism for: § Real-time synchronization and replication § Primary key substitution § Customize conflict resolution § Callbacks available for: § start/end of database replication § start/end of table replication or synchronization § changed row of table during replication or synchronization. Javadocs § API documentation available in: § $DSYINSTDIR/doc/lang/javadoc/Custom. Logic © 2006 IBM Corporation 26
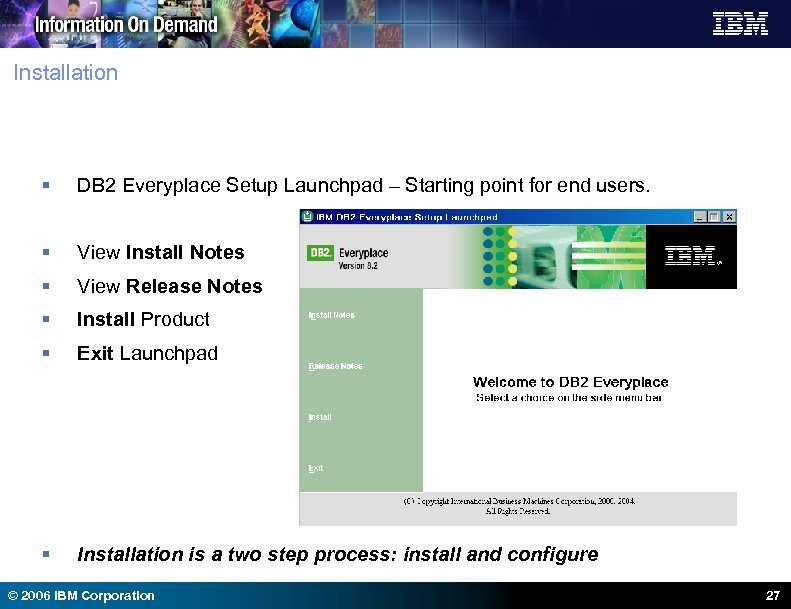
Installation § DB 2 Everyplace Setup Launchpad – Starting point for end users. § View Install Notes § View Release Notes § Install Product § Exit Launchpad § Installation is a two step process: install and configure © 2006 IBM Corporation 27
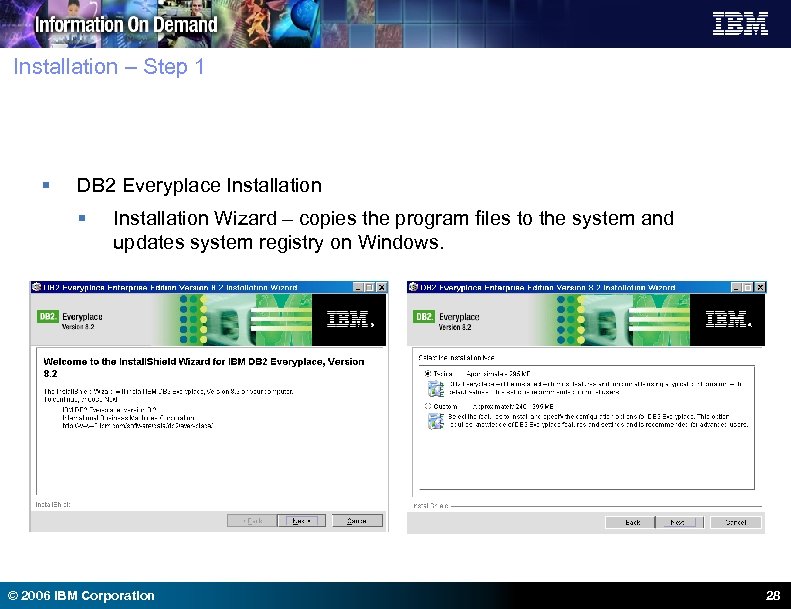
Installation – Step 1 § DB 2 Everyplace Installation § Installation Wizard – copies the program files to the system and updates system registry on Windows. © 2006 IBM Corporation 28
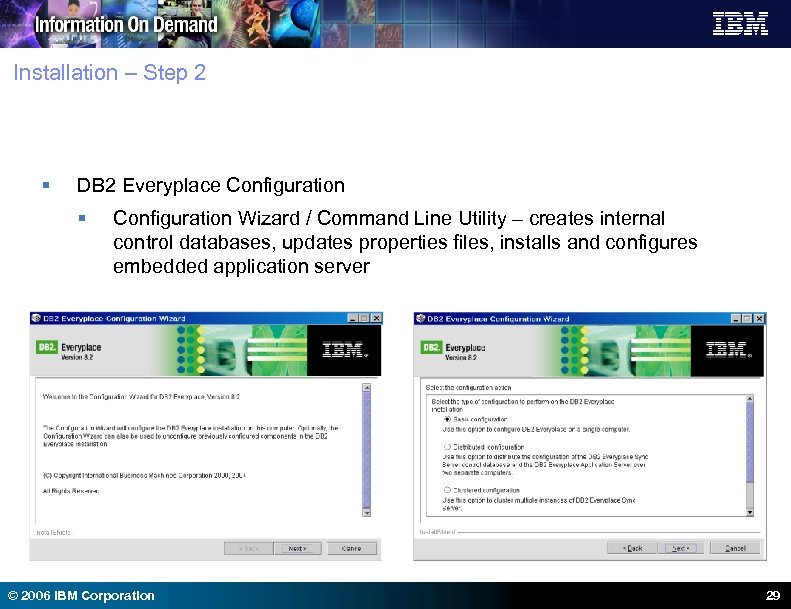
Installation – Step 2 § DB 2 Everyplace Configuration § Configuration Wizard / Command Line Utility – creates internal control databases, updates properties files, installs and configures embedded application server © 2006 IBM Corporation 29

DB 2 Everyplace Directory Structure DB 2 Everyplace Clients clientapisample C_API, Java_API, NMP <platform> Products for client platforms database, nmpinstall, sync config doc jvm jre license log prt release Server Sync Server component Uninstaller was_install Web. Sphere Application Server component © 2006 IBM Corporation 30

Best Practice § DB 2 e } Create indices for the most common queries } Minimize the number of records needed on the client (filter) } Synchronize often when you make client changes § Subscriptions } } Subscriptions with different replication needs should go to different mirrors Include as many tables as possible in a subscription Use long replication cycle Use upload subscriptions if possible for performance § Inserts directly on the source } Minimize the use of complex filters © 2006 IBM Corporation 31

Best Practice (continue) § Design solution with no or minimum conflicts § Try to separate static and dynamic data in your design § Client communication } Adjust the timeout value for the client (default 30 sec) } Increase HTTP I/O timeout on WAS and HTTP Server (default 5 sec, use 30 -60 sec) © 2006 IBM Corporation 32

Why Mobilizing IDS Data? Immediate Availability of Data Minimized Cost Increased Productivity Improved Responsiveness Increased Effectiveness © 2006 IBM Corporation 33
References § IDS Mobility on Demand: http: //www-306. ibm. com/software/data/informix/ids/mobility/ § DB 2 Everyplace external website: http: //www. ibm. com/software/data/db 2/everyplace § DB 2 Everyplace library: http: //www-306. ibm. com/software/data/db 2/everyplace/library. html § DB 2 Everyplace forum: http: //server 6. kepnet. com/cgi-bin/db 2 www/db 2 everyplaceforum. mac/main § DB 2 Everyplace documentation § IBM DB 2 Everyplace Sync Server Administration Guide § IBM DB 2 Everyplace Installation and User’s Guide © 2006 IBM Corporation 34
Get Mobilized Now – Leverage your existing Informix Dynamic Server based applications to mobilize your workforce – Purchase Informix Dynamic Server v 10. 0 or Upgrade to IDS v 10. 0 – Contact your local IBM Sales Representative or Business Partner for the latest offers – Or log on to www. ibm. com/informix/ids /mobility for more information © 2006 IBM Corporation 35

www. ibm. com/informix/ids/mobility © 2006 IBM Corporation 36
7975bd8a35f9c0758a5ee2e20e9c6a6c.ppt