ангиология - для врачей последиплома.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 73
 Часть 1 Кровеносные сосуды
Часть 1 Кровеносные сосуды
 Структура сосудистой стенки § Стенка сосуда состоит из трех оболочек § Tunica intima – выстлана со стороны просвета сосуда эндотелием § Tunica media – построена из волокон неисчерченной мышечной ткани, миоцитов, чередующихся с эластическими волокнами. Обладает двумя функциями § Сужение– вазоконстрикция § Расширение– вазодилятация § Tunica externa – содержит соединительно тканные волокна
Структура сосудистой стенки § Стенка сосуда состоит из трех оболочек § Tunica intima – выстлана со стороны просвета сосуда эндотелием § Tunica media – построена из волокон неисчерченной мышечной ткани, миоцитов, чередующихся с эластическими волокнами. Обладает двумя функциями § Сужение– вазоконстрикция § Расширение– вазодилятация § Tunica externa – содержит соединительно тканные волокна
 Структура артерий, вен и капилляров
Структура артерий, вен и капилляров
 Типы кровеносных сосудов § § Артерии– несут кровь от сердца Капилляры– маленькие кровеносные сосуды § The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid § Вены– несут кровь к сердцу
Типы кровеносных сосудов § § Артерии– несут кровь от сердца Капилляры– маленькие кровеносные сосуды § The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid § Вены– несут кровь к сердцу
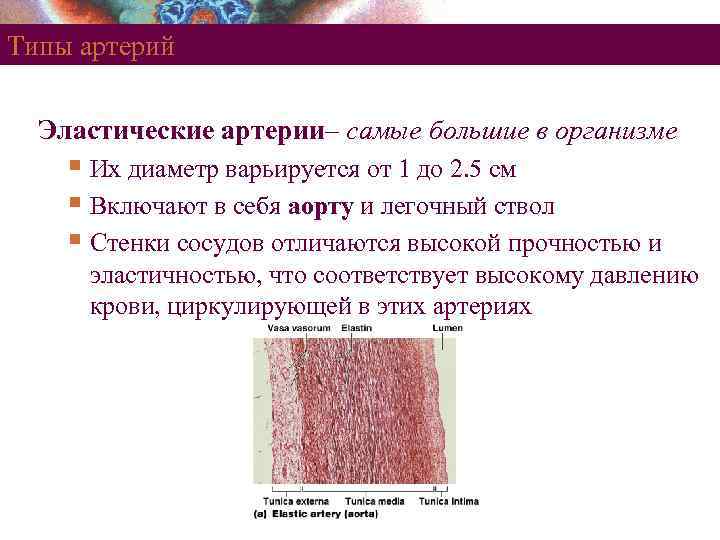 Типы артерий Эластические артерии– самые большие в организме § Их диаметр варьируется от 1 до 2. 5 см § Включают в себя аорту и легочный ствол § Стенки сосудов отличаются высокой прочностью и эластичностью, что соответствует высокому давлению крови, циркулирующей в этих артериях
Типы артерий Эластические артерии– самые большие в организме § Их диаметр варьируется от 1 до 2. 5 см § Включают в себя аорту и легочный ствол § Стенки сосудов отличаются высокой прочностью и эластичностью, что соответствует высокому давлению крови, циркулирующей в этих артериях
 Types of Arteries Артерии мышечно-эластического типа § Lie distal to elastic arteries § Diameters range from 1 cm to 0. 3 mm § Includes most named arteries § Tunica media is thick § Unique features § Internal and external elastic laminae
Types of Arteries Артерии мышечно-эластического типа § Lie distal to elastic arteries § Diameters range from 1 cm to 0. 3 mm § Includes most named arteries § Tunica media is thick § Unique features § Internal and external elastic laminae
 Types of Arteries Артериолы § Характеризуются тонкими стенками § Их диаметр составляет 0. 3 mm -10 µm § Во внутреннем слое слабо выражен подэндотелиальный слой § Диаметр артерриол зависит от § Локальных факторов § Симпатической нервной системы Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 2 c
Types of Arteries Артериолы § Характеризуются тонкими стенками § Их диаметр составляет 0. 3 mm -10 µm § Во внутреннем слое слабо выражен подэндотелиальный слой § Диаметр артерриол зависит от § Локальных факторов § Симпатической нервной системы Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 2 c
 Капилляры § Наименьшие по размеру кровеносные сосуды § Диаметр их насчитывает 8– 10 µm § Красные кровяные тельца свободно циркулируют в одном направлении § Специальные функции § Легкие– oxygen enters blood, carbon dioxide leaves § Тонкий кишечник– receive digested nutrients § Железы внутренней секреции– pick up hormones § Почки– removal of nitrogenous wastes Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Капилляры § Наименьшие по размеру кровеносные сосуды § Диаметр их насчитывает 8– 10 µm § Красные кровяные тельца свободно циркулируют в одном направлении § Специальные функции § Легкие– oxygen enters blood, carbon dioxide leaves § Тонкий кишечник– receive digested nutrients § Железы внутренней секреции– pick up hormones § Почки– removal of nitrogenous wastes Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 RBCs in a Capillary Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 3
RBCs in a Capillary Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 3
 Capillary Beds § § Network of capillaries running through tissues Precapillary sphincters § Regulate the flow of blood to tissues § § Tendons and ligaments – poorly vascularized Epithelia and cartilage – avascular § Receive nutrients from nearby CT PLAY Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure and Function Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Capillary Beds § § Network of capillaries running through tissues Precapillary sphincters § Regulate the flow of blood to tissues § § Tendons and ligaments – poorly vascularized Epithelia and cartilage – avascular § Receive nutrients from nearby CT PLAY Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure and Function Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
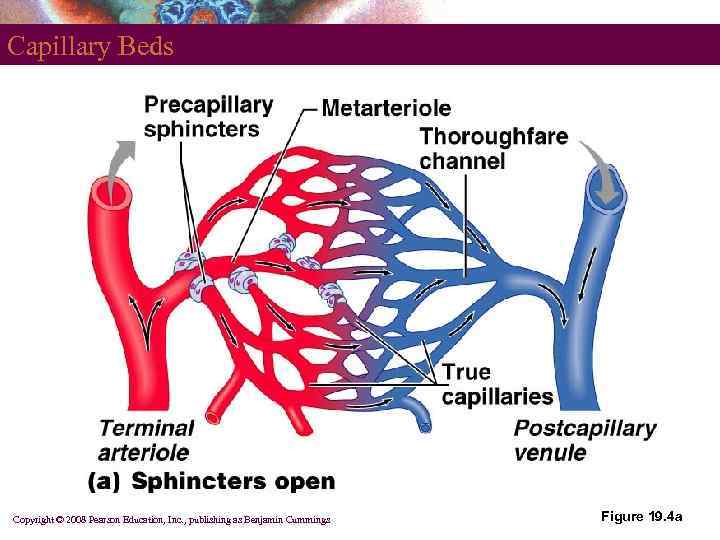 Capillary Beds Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 4 a
Capillary Beds Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 4 a
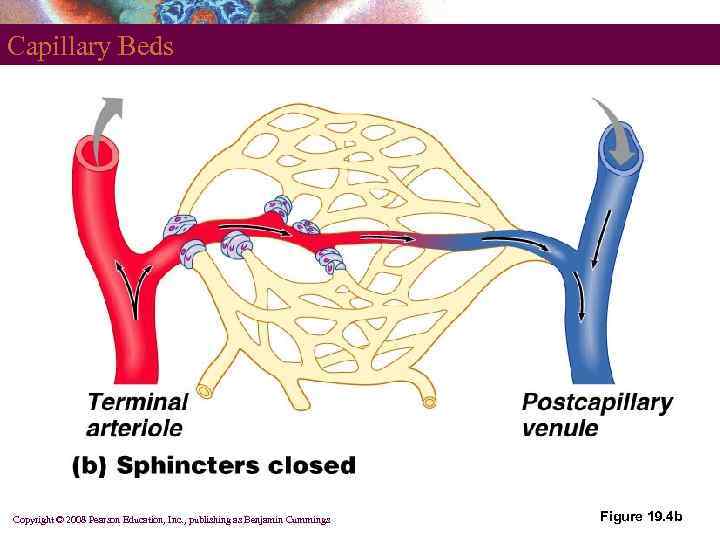 Capillary Beds Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 4 b
Capillary Beds Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 4 b
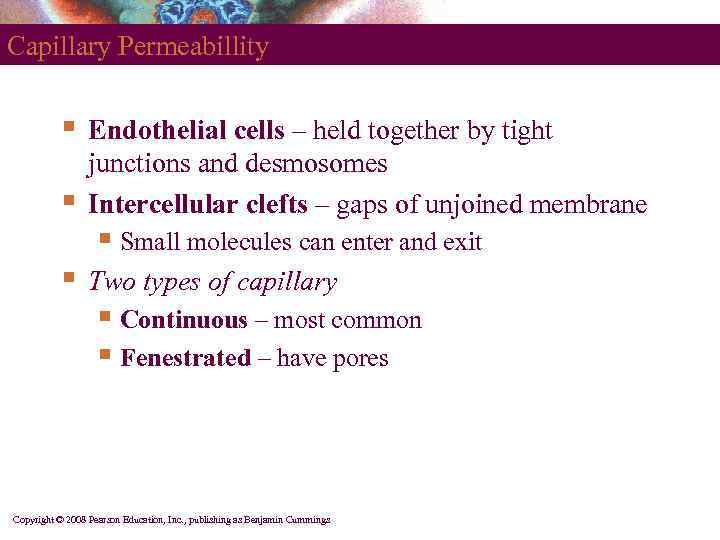 Capillary Permeabillity § § Endothelial cells – held together by tight junctions and desmosomes Intercellular clefts – gaps of unjoined membrane § Small molecules can enter and exit § Two types of capillary § Continuous – most common § Fenestrated – have pores Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Capillary Permeabillity § § Endothelial cells – held together by tight junctions and desmosomes Intercellular clefts – gaps of unjoined membrane § Small molecules can enter and exit § Two types of capillary § Continuous – most common § Fenestrated – have pores Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
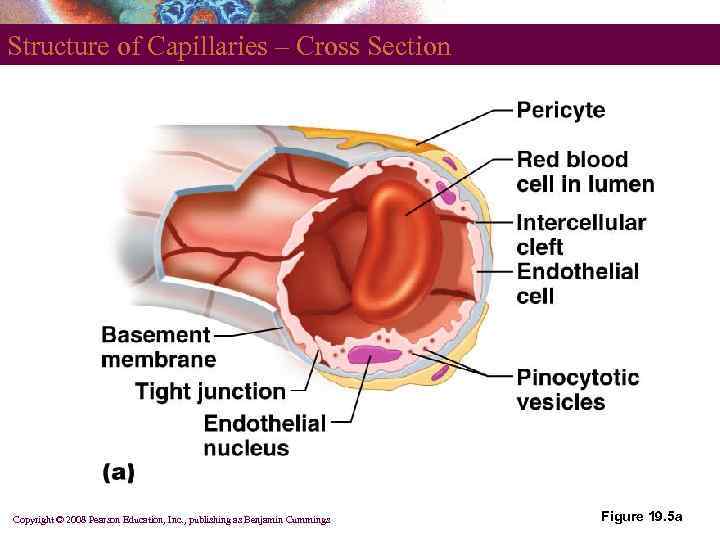 Structure of Capillaries – Cross Section Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 5 a
Structure of Capillaries – Cross Section Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 5 a
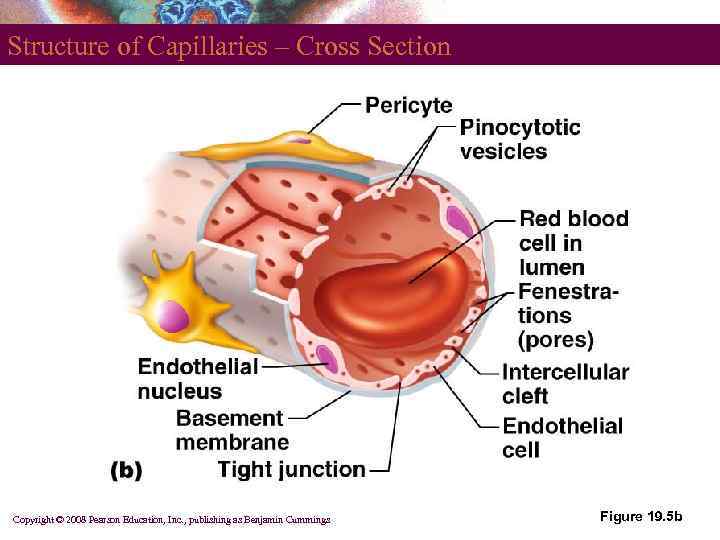 Structure of Capillaries – Cross Section Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 5 b
Structure of Capillaries – Cross Section Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 5 b
 Routes of Capillary Permeability § Four routes into and out of capillaries § Direct diffusion § Through intercellular clefts § Through cytoplasmic vesicles § Through fenestrations Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Routes of Capillary Permeability § Four routes into and out of capillaries § Direct diffusion § Through intercellular clefts § Through cytoplasmic vesicles § Through fenestrations Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
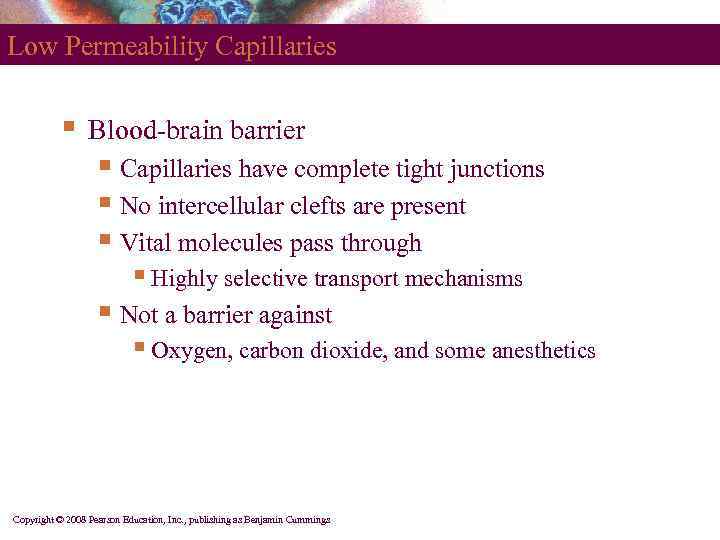 Low Permeability Capillaries § Blood-brain barrier § Capillaries have complete tight junctions § No intercellular clefts are present § Vital molecules pass through § Highly selective transport mechanisms § Not a barrier against § Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and some anesthetics Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Low Permeability Capillaries § Blood-brain barrier § Capillaries have complete tight junctions § No intercellular clefts are present § Vital molecules pass through § Highly selective transport mechanisms § Not a barrier against § Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and some anesthetics Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Sinusoids § Wide, leaky capillaries found in some organs § Usually fenestrated § Intercellular clefts are wide open § Occur in bone marrow and spleen § Sinusoids have a large diameter and twisted course Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Sinusoids § Wide, leaky capillaries found in some organs § Usually fenestrated § Intercellular clefts are wide open § Occur in bone marrow and spleen § Sinusoids have a large diameter and twisted course Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
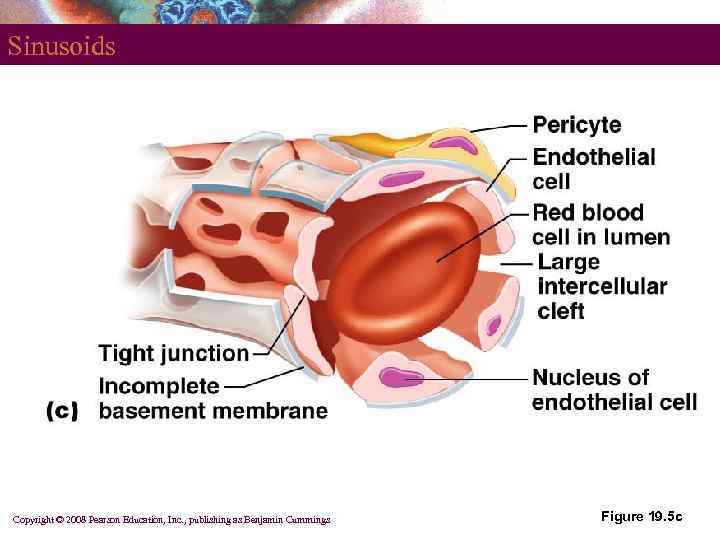 Sinusoids Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 5 c
Sinusoids Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 5 c
 Veins § § § Conduct blood from capillaries toward the heart Blood pressure is much lower than in arteries Smallest veins – called venules § Diameters from 8 – 100 µm § Smallest venules – called postcapillary venules § § Venules join to form veins Tunica externa is the thickest tunic in veins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Veins § § § Conduct blood from capillaries toward the heart Blood pressure is much lower than in arteries Smallest veins – called venules § Diameters from 8 – 100 µm § Smallest venules – called postcapillary venules § § Venules join to form veins Tunica externa is the thickest tunic in veins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
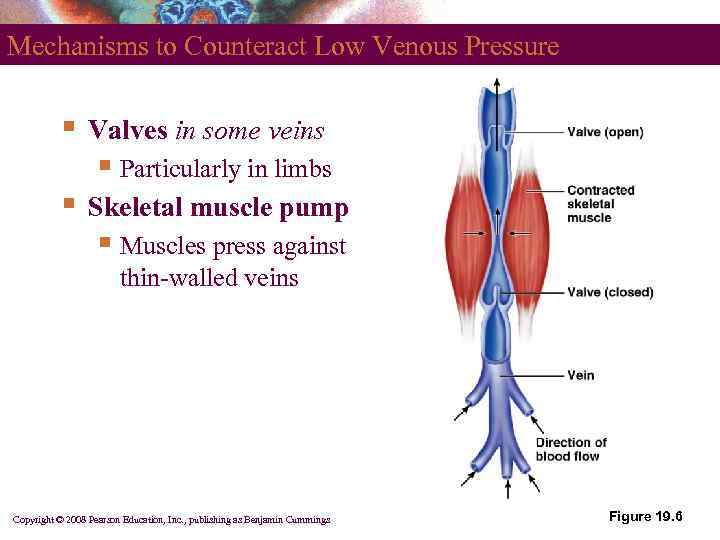 Mechanisms to Counteract Low Venous Pressure § Valves in some veins § Particularly in limbs § Skeletal muscle pump § Muscles press against thin-walled veins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 6
Mechanisms to Counteract Low Venous Pressure § Valves in some veins § Particularly in limbs § Skeletal muscle pump § Muscles press against thin-walled veins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 6
 Vascular Anastomoses § Vessels interconnect to form vascular anastomoses § Organs receive blood from more than one arterial source § Neighboring arteries form arterial anastomoses § Provide collateral channels § Veins anastomose more frequently than arteries Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Vascular Anastomoses § Vessels interconnect to form vascular anastomoses § Organs receive blood from more than one arterial source § Neighboring arteries form arterial anastomoses § Provide collateral channels § Veins anastomose more frequently than arteries Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Vasa Vasorum § Tunica externa of large vessels have § Tiny arteries, capillaries, and veins § Vasa vasorum vessels of vessels § Nourish outer region of large vessels § Inner half of large vessels receive nutrients from luminal blood Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Vasa Vasorum § Tunica externa of large vessels have § Tiny arteries, capillaries, and veins § Vasa vasorum vessels of vessels § Nourish outer region of large vessels § Inner half of large vessels receive nutrients from luminal blood Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Легочный круг кровообращения § Pulmonary trunk leaves the right ventricle § Divides into right and left pulmonary arteries § Superior and inferior pulmonary veins § Carry oxygenated blood into the left atrium Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Легочный круг кровообращения § Pulmonary trunk leaves the right ventricle § Divides into right and left pulmonary arteries § Superior and inferior pulmonary veins § Carry oxygenated blood into the left atrium Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
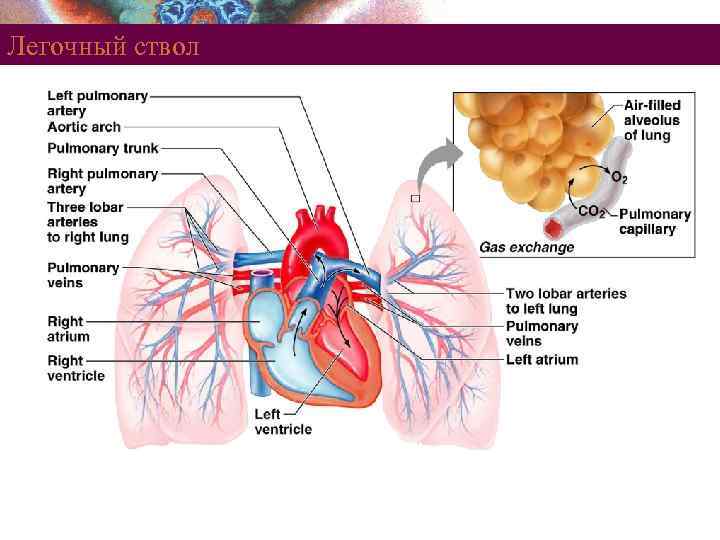 Легочный ствол
Легочный ствол
 Systemic Circulation § Systemic Arteries § Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart § Aorta – largest artery in the body Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Systemic Circulation § Systemic Arteries § Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart § Aorta – largest artery in the body Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
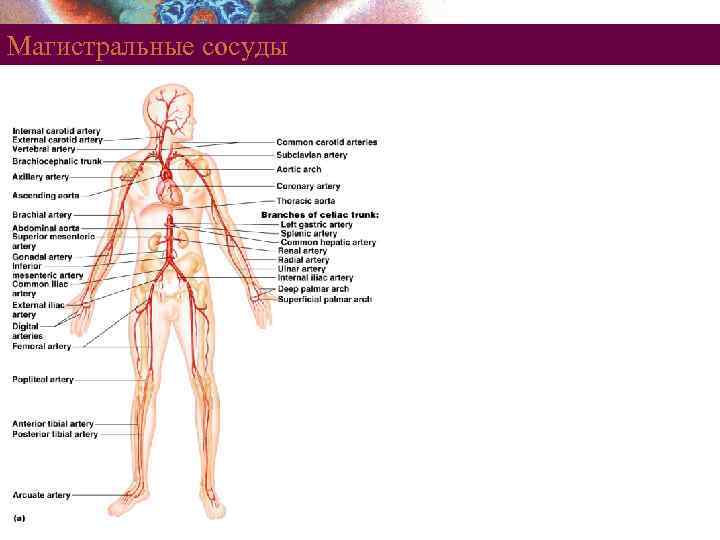 Магистральные сосуды
Магистральные сосуды
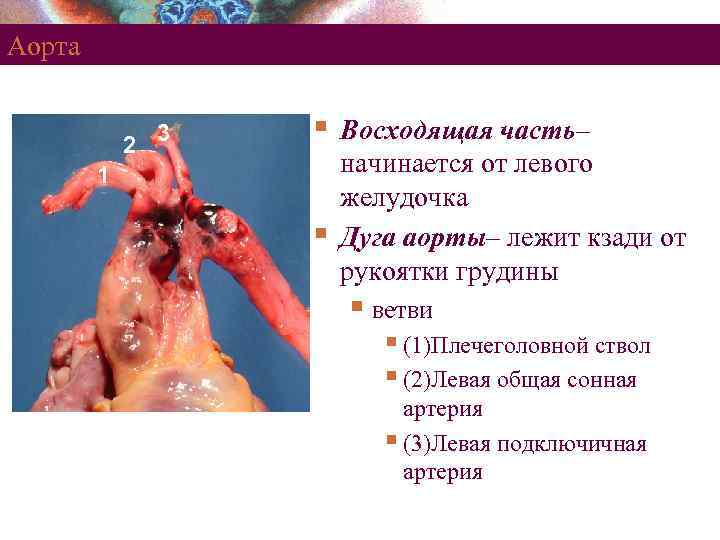 Аорта 2 3 § 1 § Восходящая часть– начинается от левого желудочка Дуга аорты– лежит кзади от рукоятки грудины § ветви § (1)Плечеголовной ствол § (2)Левая общая сонная артерия § (3)Левая подключичная артерия
Аорта 2 3 § 1 § Восходящая часть– начинается от левого желудочка Дуга аорты– лежит кзади от рукоятки грудины § ветви § (1)Плечеголовной ствол § (2)Левая общая сонная артерия § (3)Левая подключичная артерия
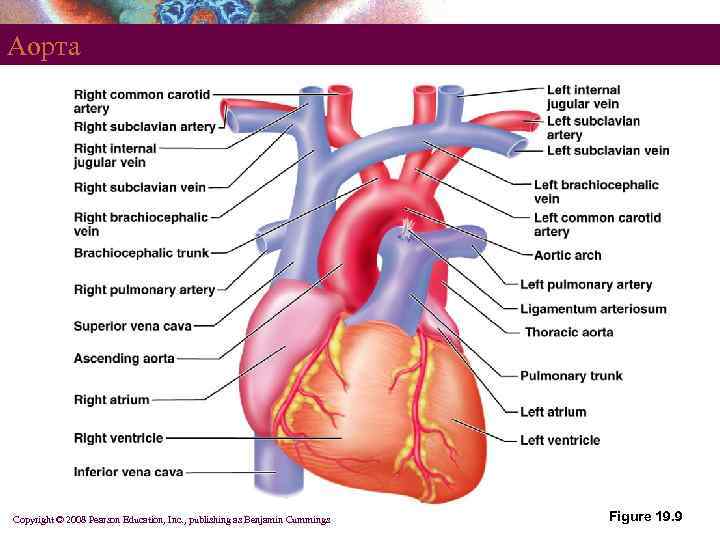 Аорта Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 9
Аорта Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 9
 Аорта § § Descending aorta – continues from the aortic arch § Thoracic aorta – in the region of T 5–T 12 § Abdominal aorta – ends at L 4 Divides into right and left common iliac arteries Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Аорта § § Descending aorta – continues from the aortic arch § Thoracic aorta – in the region of T 5–T 12 § Abdominal aorta – ends at L 4 Divides into right and left common iliac arteries Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 19 HUMAN ANATOMY Power. Point® Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon, University of Alabama, Birmingham PART 2 Blood Vessels fifth edition MARIEB | MALLATT | WILHELM Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
19 HUMAN ANATOMY Power. Point® Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon, University of Alabama, Birmingham PART 2 Blood Vessels fifth edition MARIEB | MALLATT | WILHELM Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
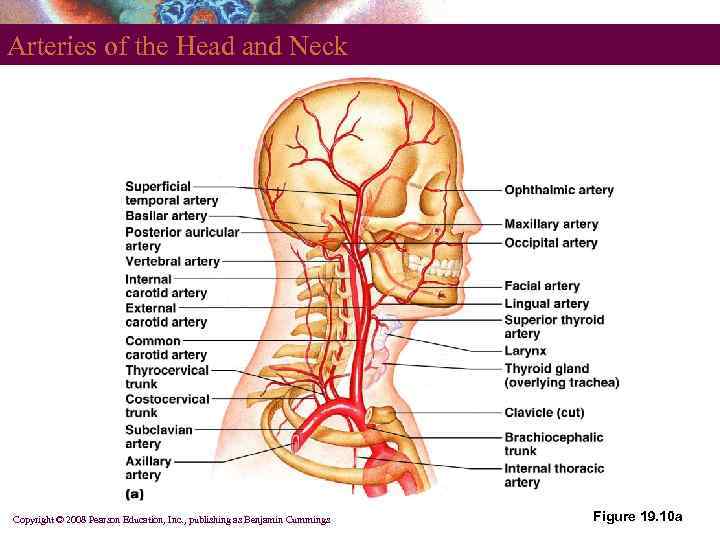 Arteries of the Head and Neck Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 10 a
Arteries of the Head and Neck Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 10 a
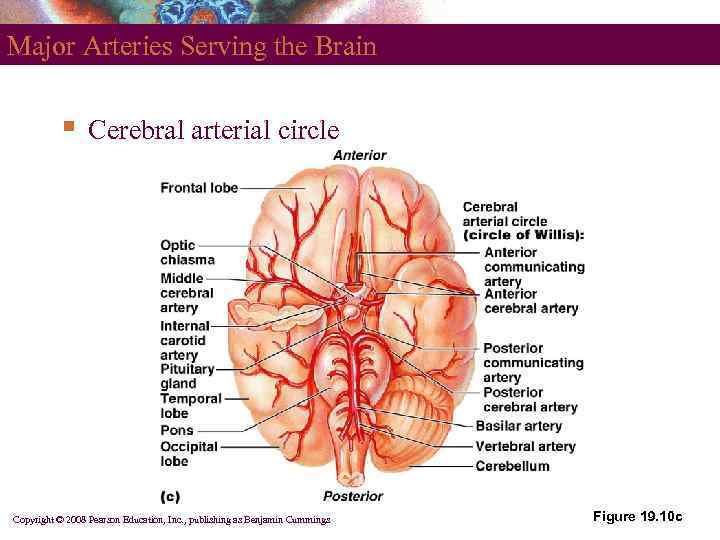 Major Arteries Serving the Brain § Cerebral arterial circle Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 10 c
Major Arteries Serving the Brain § Cerebral arterial circle Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 10 c
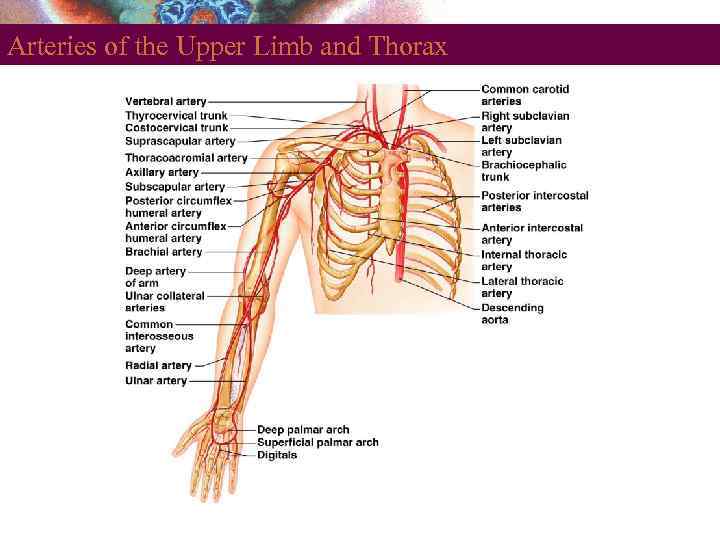 Arteries of the Upper Limb and Thorax
Arteries of the Upper Limb and Thorax
 Arteries of the Abdominal Aorta § § § § Inferior phrenic arteries Celiac trunk Superior mesenteric artery Suprarenal arteries Renal arteries Gonadal (testicular or ovarian) arteries Inferior mesenteric artery Common iliac arteries Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Arteries of the Abdominal Aorta § § § § Inferior phrenic arteries Celiac trunk Superior mesenteric artery Suprarenal arteries Renal arteries Gonadal (testicular or ovarian) arteries Inferior mesenteric artery Common iliac arteries Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
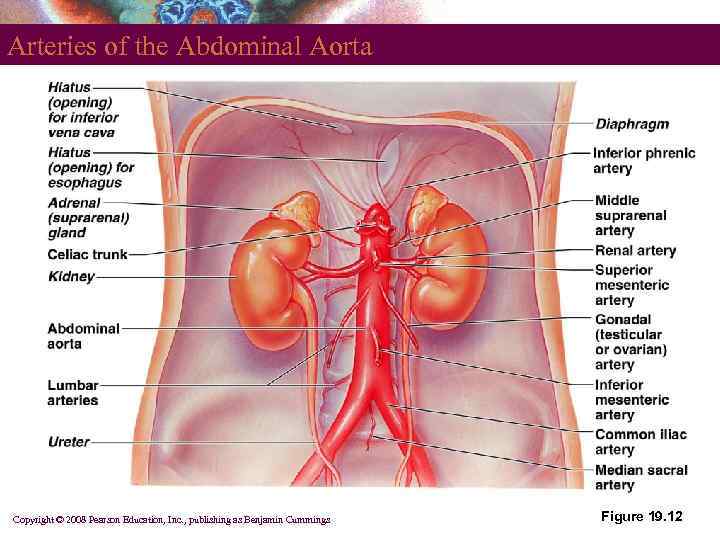 Arteries of the Abdominal Aorta Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 12
Arteries of the Abdominal Aorta Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 12
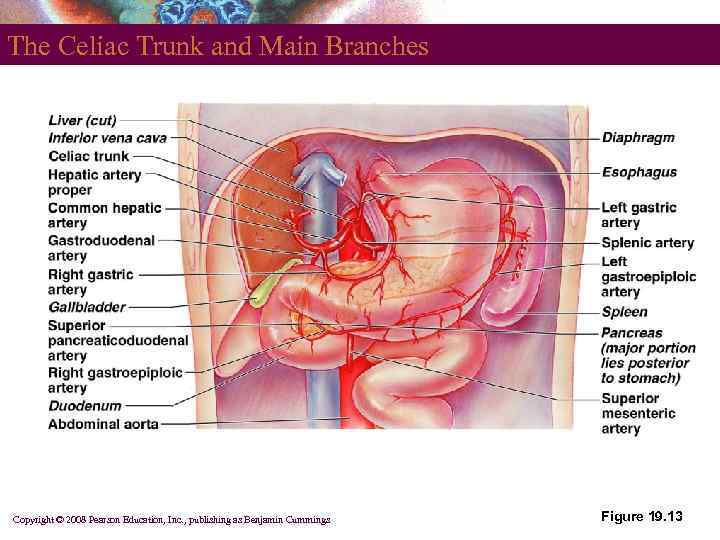 The Celiac Trunk and Main Branches Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 13
The Celiac Trunk and Main Branches Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 13
 19 HUMAN ANATOMY Power. Point® Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon, University of Alabama, Birmingham PART 3 Blood Vessels fifth edition MARIEB | MALLATT | WILHELM Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
19 HUMAN ANATOMY Power. Point® Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon, University of Alabama, Birmingham PART 3 Blood Vessels fifth edition MARIEB | MALLATT | WILHELM Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
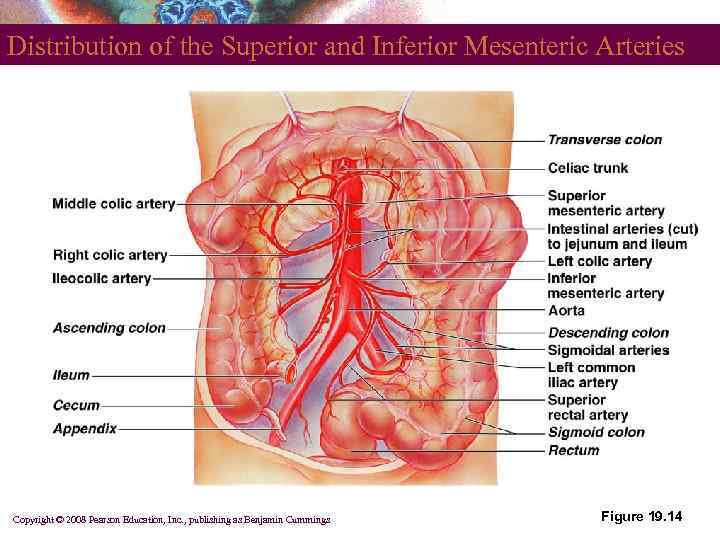 Distribution of the Superior and Inferior Mesenteric Arteries Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 14
Distribution of the Superior and Inferior Mesenteric Arteries Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 14
 Arteries of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs § § § Internal iliac arteries External iliac artery Femoral artery Popliteal artery Anterior tibial artery Posterior tibial artery Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Arteries of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs § § § Internal iliac arteries External iliac artery Femoral artery Popliteal artery Anterior tibial artery Posterior tibial artery Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
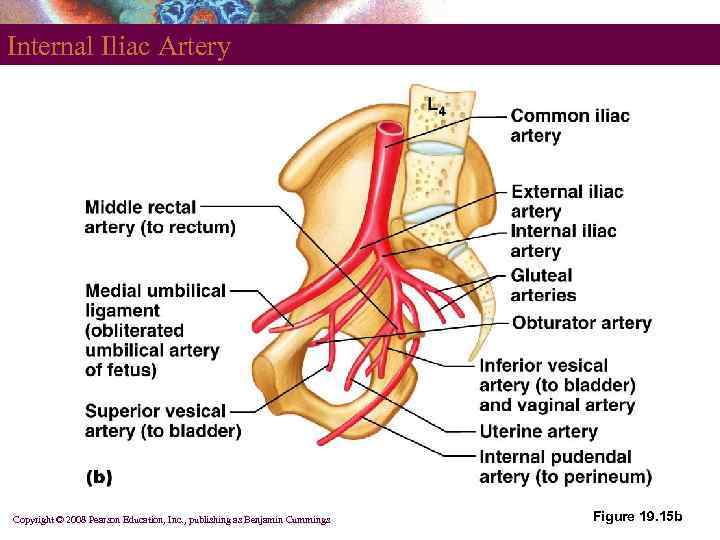 Internal Iliac Artery Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 15 b
Internal Iliac Artery Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 15 b
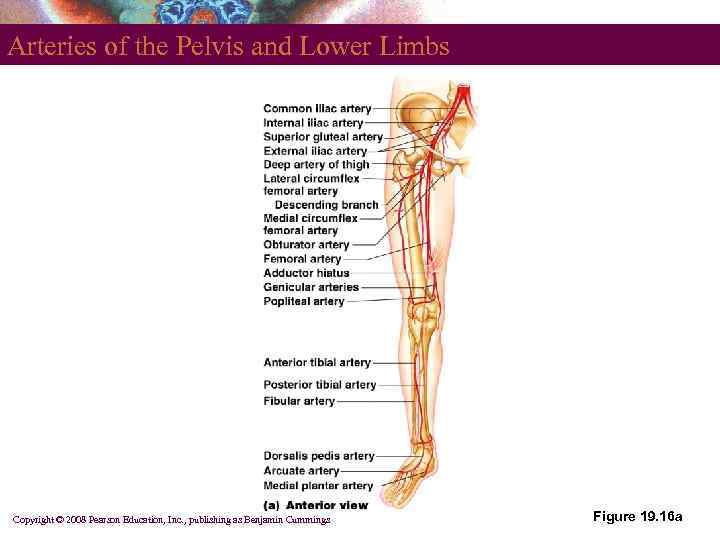 Arteries of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 16 a
Arteries of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 16 a
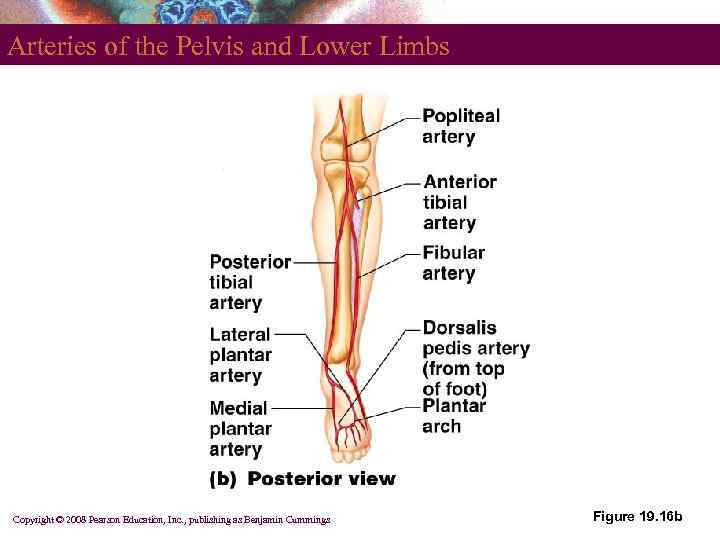 Arteries of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 16 b
Arteries of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 16 b
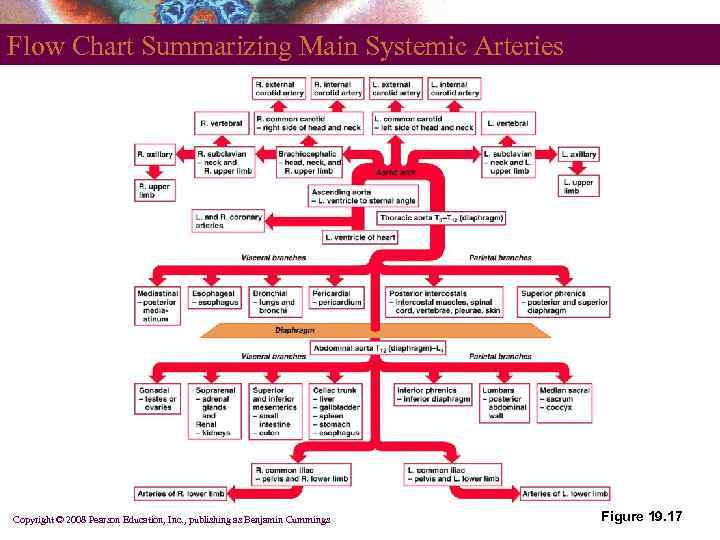 Flow Chart Summarizing Main Systemic Arteries Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 17
Flow Chart Summarizing Main Systemic Arteries Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 17
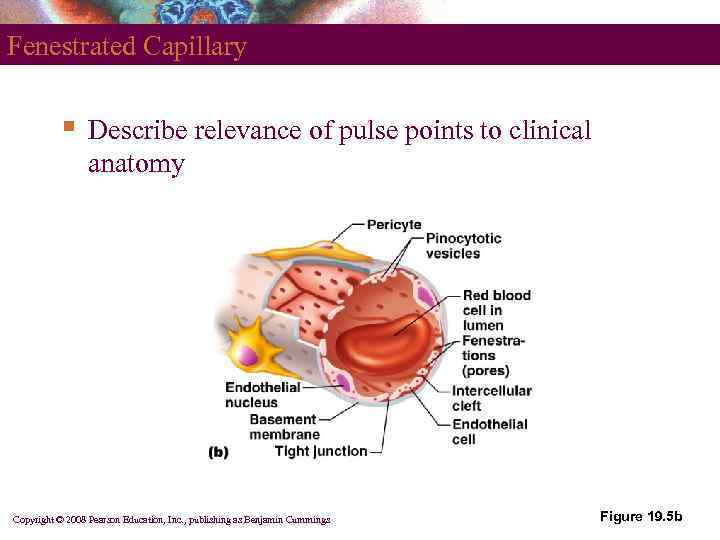 Fenestrated Capillary § Describe relevance of pulse points to clinical anatomy Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 5 b
Fenestrated Capillary § Describe relevance of pulse points to clinical anatomy Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 5 b
 Systemic Veins § § Three major veins enter the right atrium Superficial veins lie just beneath the skin Multivein bundles – venous plexuses Unusual patterns of venous drainage § Dural sinuses § Hepatic portal system Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Systemic Veins § § Three major veins enter the right atrium Superficial veins lie just beneath the skin Multivein bundles – venous plexuses Unusual patterns of venous drainage § Dural sinuses § Hepatic portal system Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Venae Cavae and Tributaries § Superior vena cava § Returns blood from body regions superior to the diaphragm § Inferior vena cava § Returns blood from body regions inferior to the diaphragm § Superior and inferior vena cava § Join the right atrium Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Venae Cavae and Tributaries § Superior vena cava § Returns blood from body regions superior to the diaphragm § Inferior vena cava § Returns blood from body regions inferior to the diaphragm § Superior and inferior vena cava § Join the right atrium Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
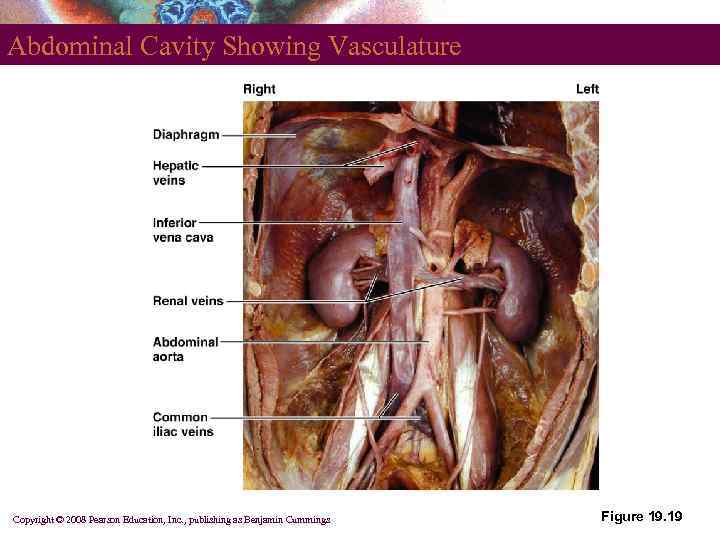 Abdominal Cavity Showing Vasculature Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 19
Abdominal Cavity Showing Vasculature Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 19
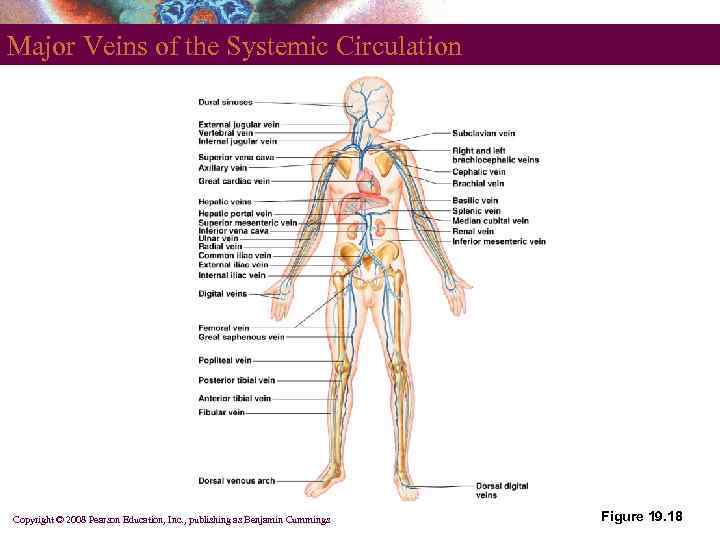 Major Veins of the Systemic Circulation Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 18
Major Veins of the Systemic Circulation Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 18
 19 HUMAN ANATOMY Power. Point® Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon, University of Alabama, Birmingham PART 4 Blood Vessels fifth edition MARIEB | MALLATT | WILHELM Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
19 HUMAN ANATOMY Power. Point® Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon, University of Alabama, Birmingham PART 4 Blood Vessels fifth edition MARIEB | MALLATT | WILHELM Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
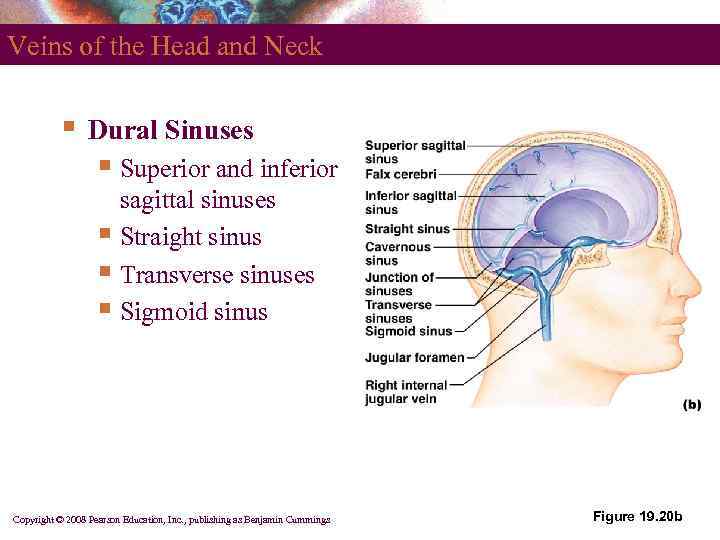 Veins of the Head and Neck § Dural Sinuses § Superior and inferior sagittal sinuses § Straight sinus § Transverse sinuses § Sigmoid sinus Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 20 b
Veins of the Head and Neck § Dural Sinuses § Superior and inferior sagittal sinuses § Straight sinus § Transverse sinuses § Sigmoid sinus Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 20 b
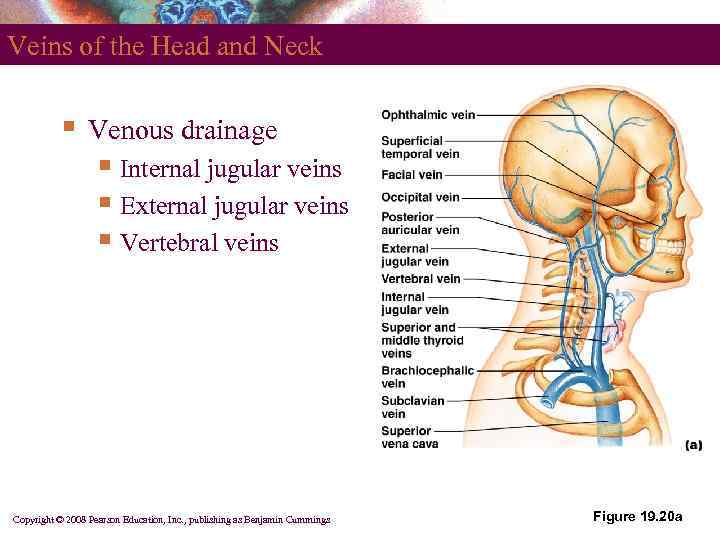 Veins of the Head and Neck § Venous drainage § Internal jugular veins § External jugular veins § Vertebral veins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 20 a
Veins of the Head and Neck § Venous drainage § Internal jugular veins § External jugular veins § Vertebral veins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 20 a
 Veins of the Upper Limbs § Deep Veins § Superficial veins § Follow the paths of companion arteries § Have the same names as the companion arteries § Visible beneath the skin § Cephalic vein § Basilic vein § Median cubital vein § Median vein of the forearm Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Veins of the Upper Limbs § Deep Veins § Superficial veins § Follow the paths of companion arteries § Have the same names as the companion arteries § Visible beneath the skin § Cephalic vein § Basilic vein § Median cubital vein § Median vein of the forearm Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
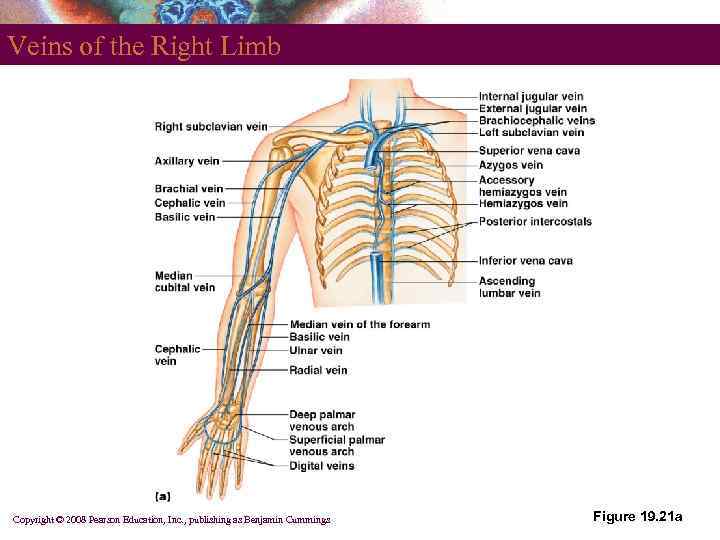 Veins of the Right Limb Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 21 a
Veins of the Right Limb Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 21 a
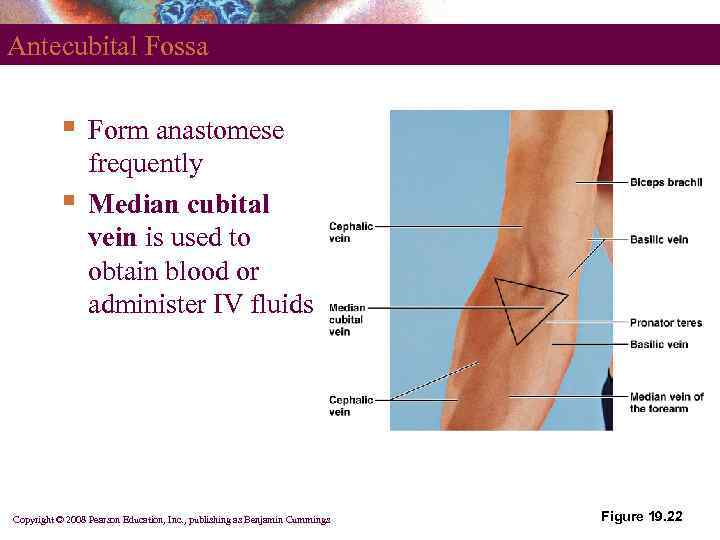 Antecubital Fossa § § Form anastomese frequently Median cubital vein is used to obtain blood or administer IV fluids Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 22
Antecubital Fossa § § Form anastomese frequently Median cubital vein is used to obtain blood or administer IV fluids Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 22
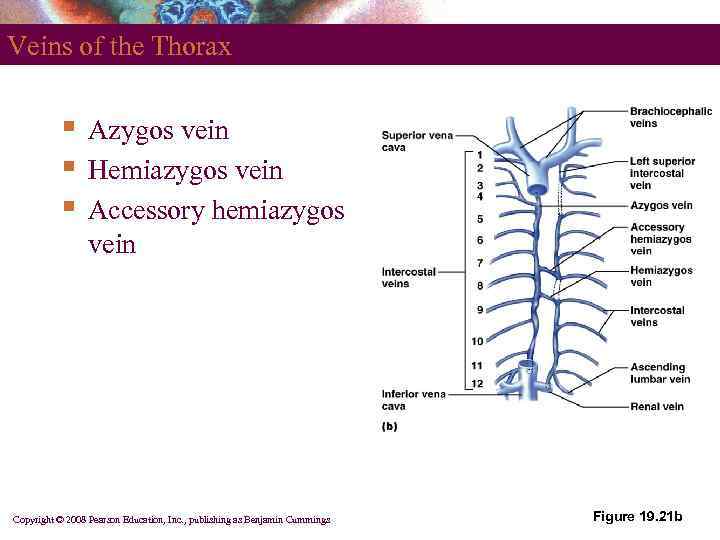 Veins of the Thorax § § § Azygos vein Hemiazygos vein Accessory hemiazygos vein Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 21 b
Veins of the Thorax § § § Azygos vein Hemiazygos vein Accessory hemiazygos vein Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 21 b
 Veins of the Abdomen § § § Lumbar veins Gonadal (testicular or ovarian) veins Renal veins Suprarenal veins Hepatic veins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Veins of the Abdomen § § § Lumbar veins Gonadal (testicular or ovarian) veins Renal veins Suprarenal veins Hepatic veins Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
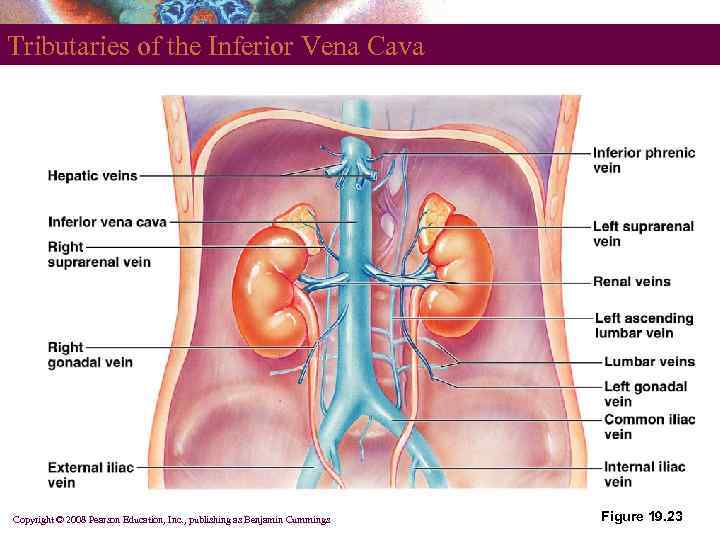 Tributaries of the Inferior Vena Cava Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 23
Tributaries of the Inferior Vena Cava Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 23
 The Hepatic Portal System § § § A specialized part of the vascular circuit Picks up digested nutrients Delivers nutrients to the liver for processing Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
The Hepatic Portal System § § § A specialized part of the vascular circuit Picks up digested nutrients Delivers nutrients to the liver for processing Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
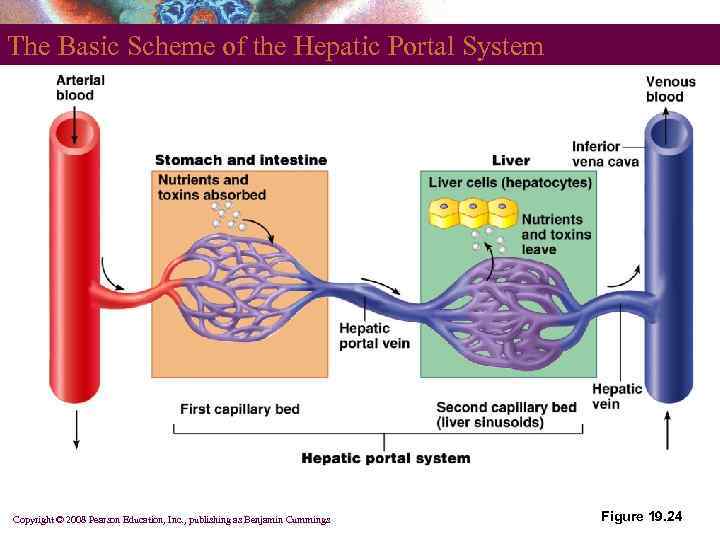 The Basic Scheme of the Hepatic Portal System Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 24
The Basic Scheme of the Hepatic Portal System Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 24
 19 HUMAN ANATOMY Power. Point® Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon, University of Alabama, Birmingham PART 5 Blood Vessels fifth edition MARIEB | MALLATT | WILHELM Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
19 HUMAN ANATOMY Power. Point® Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon, University of Alabama, Birmingham PART 5 Blood Vessels fifth edition MARIEB | MALLATT | WILHELM Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
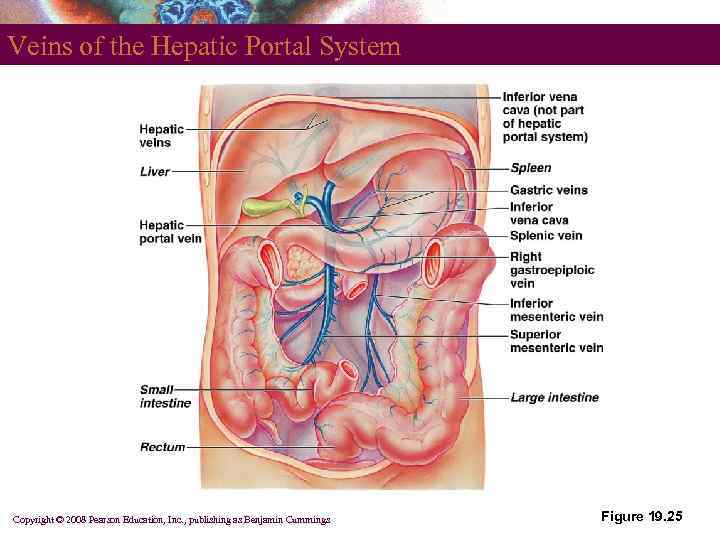 Veins of the Hepatic Portal System Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 25
Veins of the Hepatic Portal System Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 25
 Veins of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs § Deep veins § Share the name of the accompanying artery § Superficial veins § Great saphenous vein empties into the femoral vein § Small saphenous vein empties into the popliteal vein Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Veins of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs § Deep veins § Share the name of the accompanying artery § Superficial veins § Great saphenous vein empties into the femoral vein § Small saphenous vein empties into the popliteal vein Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
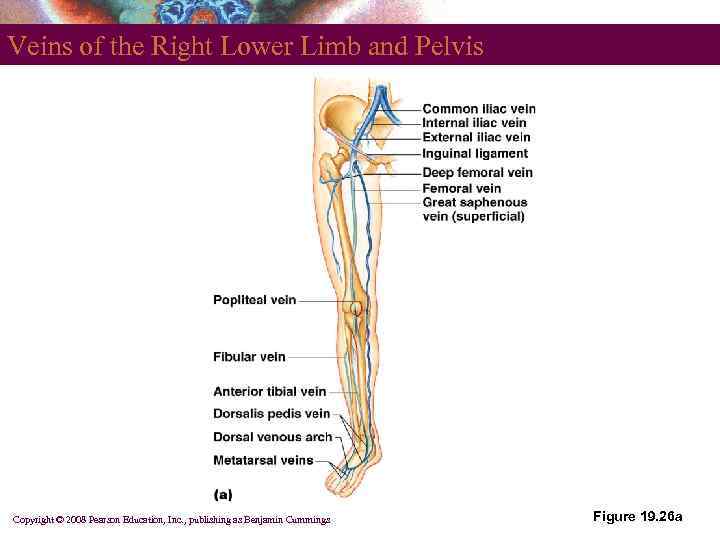 Veins of the Right Lower Limb and Pelvis Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 26 a
Veins of the Right Lower Limb and Pelvis Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 26 a
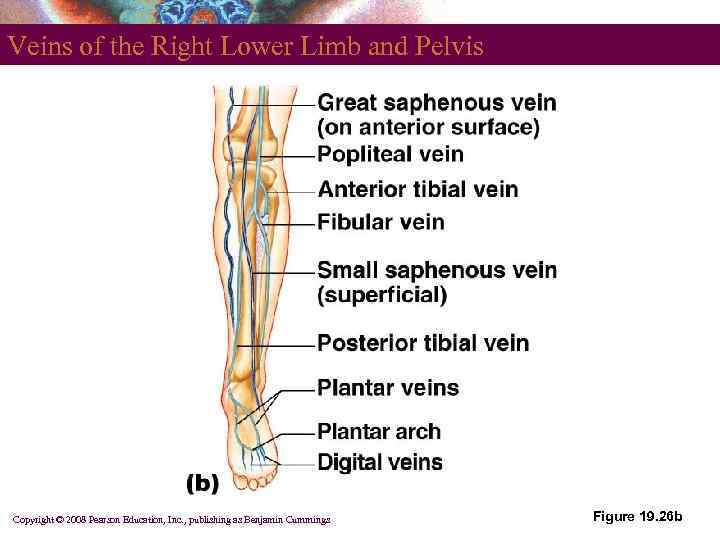 Veins of the Right Lower Limb and Pelvis Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 26 b
Veins of the Right Lower Limb and Pelvis Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 26 b
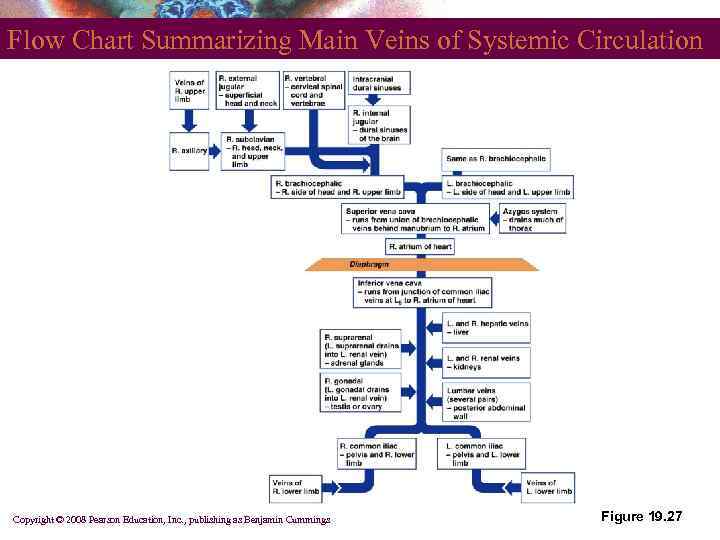 Flow Chart Summarizing Main Veins of Systemic Circulation Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 27
Flow Chart Summarizing Main Veins of Systemic Circulation Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 27
 Disorders of the Blood Vessels § § § Aneurysm Deep vein thrombosis of the lower limb Venous disease Microangiopathy of diabetes Arteriovenous malformation Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Disorders of the Blood Vessels § § § Aneurysm Deep vein thrombosis of the lower limb Venous disease Microangiopathy of diabetes Arteriovenous malformation Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Blood Vessels Throughout Life § Fetal Circulation § All major vessels in place by month three of development § Differences between fetal and postnatal circulation § Fetus must supply blood to the placenta § Very little blood is sent through the pulmonary circuit Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Blood Vessels Throughout Life § Fetal Circulation § All major vessels in place by month three of development § Differences between fetal and postnatal circulation § Fetus must supply blood to the placenta § Very little blood is sent through the pulmonary circuit Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Vessels to and from the Placenta § Umbilical vessels run in the umbilical cord § Paired umbilical arteries § Unpaired umbilical vein § Fetal vessels and structures § Ductus venosus § Ligamentum teres § Ligamentum venosum § Medial umbilical ligaments Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Vessels to and from the Placenta § Umbilical vessels run in the umbilical cord § Paired umbilical arteries § Unpaired umbilical vein § Fetal vessels and structures § Ductus venosus § Ligamentum teres § Ligamentum venosum § Medial umbilical ligaments Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Shunts Away from the Pulmonary Circuit § § Foramen ovale Ductus arteriosus Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Shunts Away from the Pulmonary Circuit § § Foramen ovale Ductus arteriosus Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
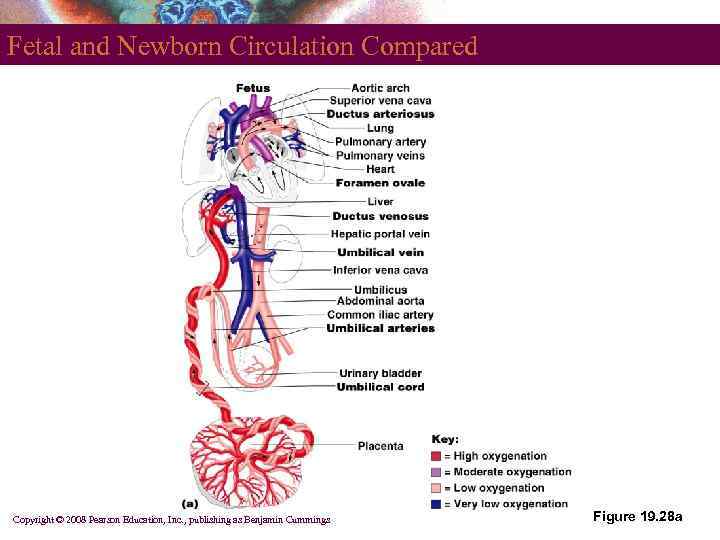 Fetal and Newborn Circulation Compared Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 28 a
Fetal and Newborn Circulation Compared Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 28 a
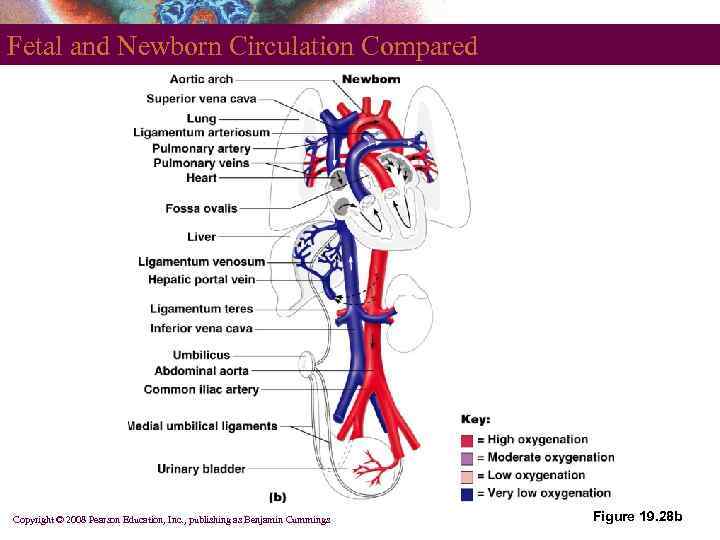 Fetal and Newborn Circulation Compared Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 28 b
Fetal and Newborn Circulation Compared Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings Figure 19. 28 b
 Blood Vessels in Adulthood § Atherosclerosis begins in youth § Consequences evident in middle to old age § Males § More atherosclerosis than females between ages 45 – 65 § Females § Experience heart disease and atherosclerosis later in life Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Blood Vessels in Adulthood § Atherosclerosis begins in youth § Consequences evident in middle to old age § Males § More atherosclerosis than females between ages 45 – 65 § Females § Experience heart disease and atherosclerosis later in life Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. , publishing as Benjamin Cummings


