 Characterizing Cells
Characterizing Cells
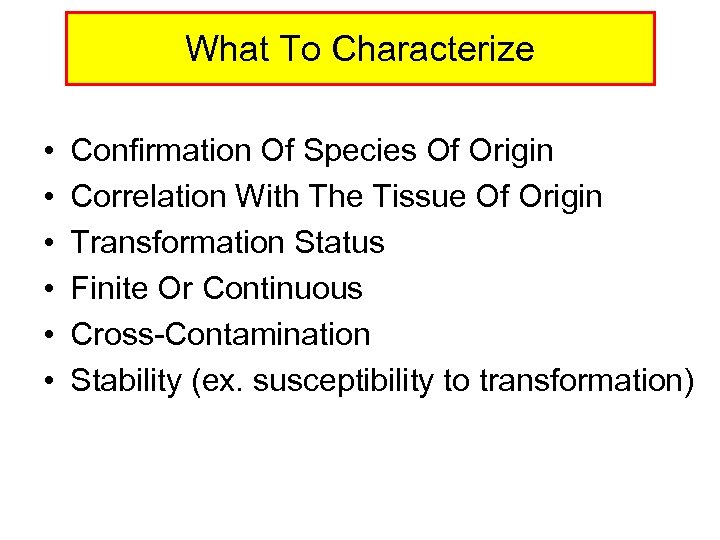 What To Characterize • • • Confirmation Of Species Of Origin Correlation With The Tissue Of Origin Transformation Status Finite Or Continuous Cross-Contamination Stability (ex. susceptibility to transformation)
What To Characterize • • • Confirmation Of Species Of Origin Correlation With The Tissue Of Origin Transformation Status Finite Or Continuous Cross-Contamination Stability (ex. susceptibility to transformation)
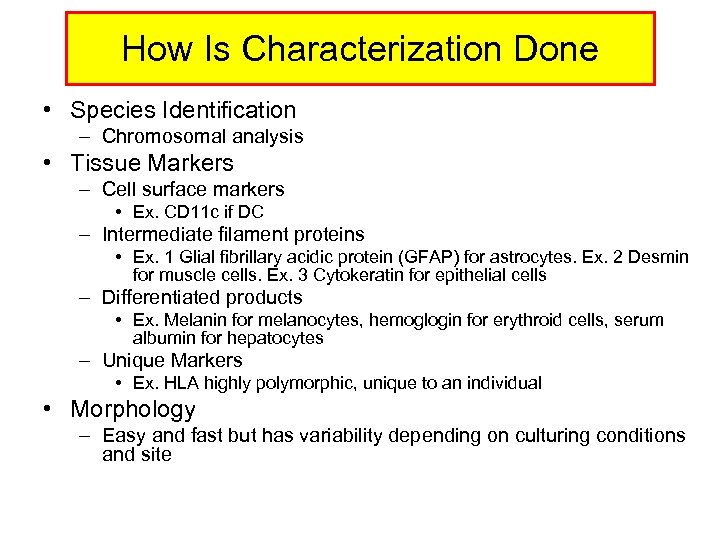 How Is Characterization Done • Species Identification – Chromosomal analysis • Tissue Markers – Cell surface markers • Ex. CD 11 c if DC – Intermediate filament proteins • Ex. 1 Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) for astrocytes. Ex. 2 Desmin for muscle cells. Ex. 3 Cytokeratin for epithelial cells – Differentiated products • Ex. Melanin for melanocytes, hemoglogin for erythroid cells, serum albumin for hepatocytes – Unique Markers • Ex. HLA highly polymorphic, unique to an individual • Morphology – Easy and fast but has variability depending on culturing conditions and site
How Is Characterization Done • Species Identification – Chromosomal analysis • Tissue Markers – Cell surface markers • Ex. CD 11 c if DC – Intermediate filament proteins • Ex. 1 Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) for astrocytes. Ex. 2 Desmin for muscle cells. Ex. 3 Cytokeratin for epithelial cells – Differentiated products • Ex. Melanin for melanocytes, hemoglogin for erythroid cells, serum albumin for hepatocytes – Unique Markers • Ex. HLA highly polymorphic, unique to an individual • Morphology – Easy and fast but has variability depending on culturing conditions and site
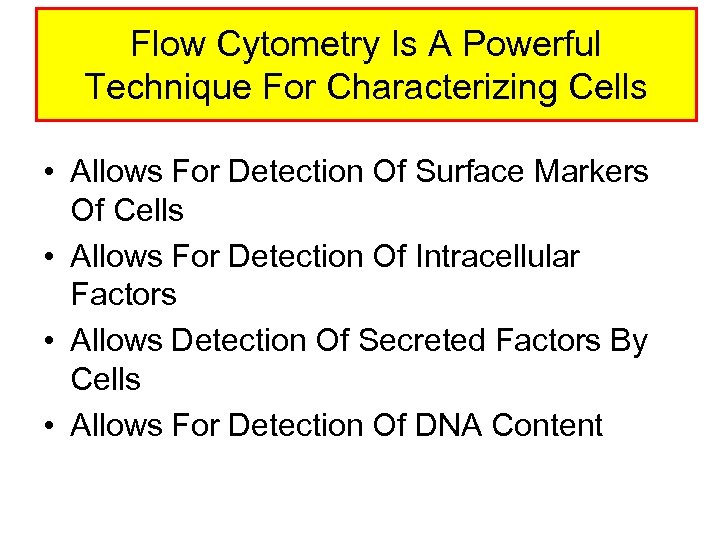 Flow Cytometry Is A Powerful Technique For Characterizing Cells • Allows For Detection Of Surface Markers Of Cells • Allows For Detection Of Intracellular Factors • Allows Detection Of Secreted Factors By Cells • Allows For Detection Of DNA Content
Flow Cytometry Is A Powerful Technique For Characterizing Cells • Allows For Detection Of Surface Markers Of Cells • Allows For Detection Of Intracellular Factors • Allows Detection Of Secreted Factors By Cells • Allows For Detection Of DNA Content
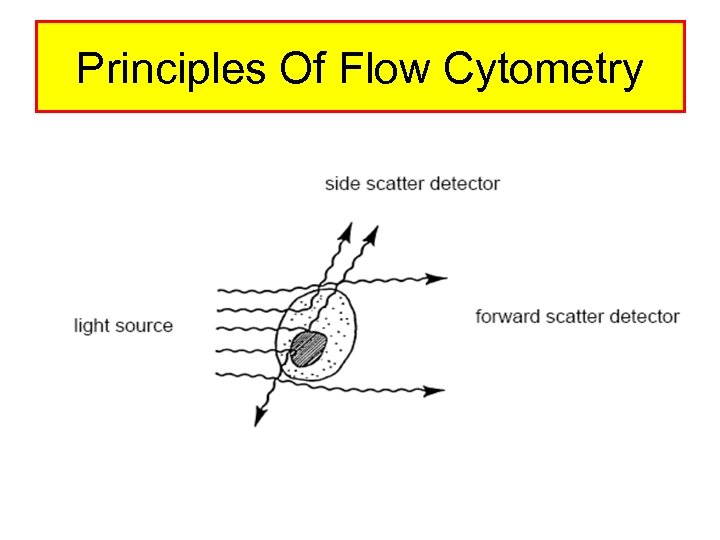 Principles Of Flow Cytometry
Principles Of Flow Cytometry
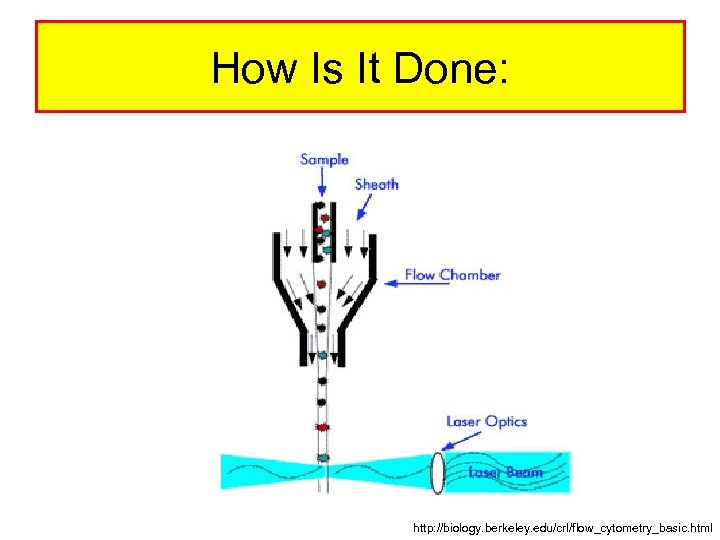 How Is It Done: http: //biology. berkeley. edu/crl/flow_cytometry_basic. html
How Is It Done: http: //biology. berkeley. edu/crl/flow_cytometry_basic. html
 Limitations With Light Scattering • • Some Information Can Be Obtained FSC Correlates With Cell Size SSC Correlates With Internal Complexity To Distinguish Between 2 Cell types – A. Size Has To Be Different OR – B. Internal Complexity i. e amount of granules • If These Two Parameters Are The Same, Then No Distinction Can Be Made • See The Following Figure
Limitations With Light Scattering • • Some Information Can Be Obtained FSC Correlates With Cell Size SSC Correlates With Internal Complexity To Distinguish Between 2 Cell types – A. Size Has To Be Different OR – B. Internal Complexity i. e amount of granules • If These Two Parameters Are The Same, Then No Distinction Can Be Made • See The Following Figure
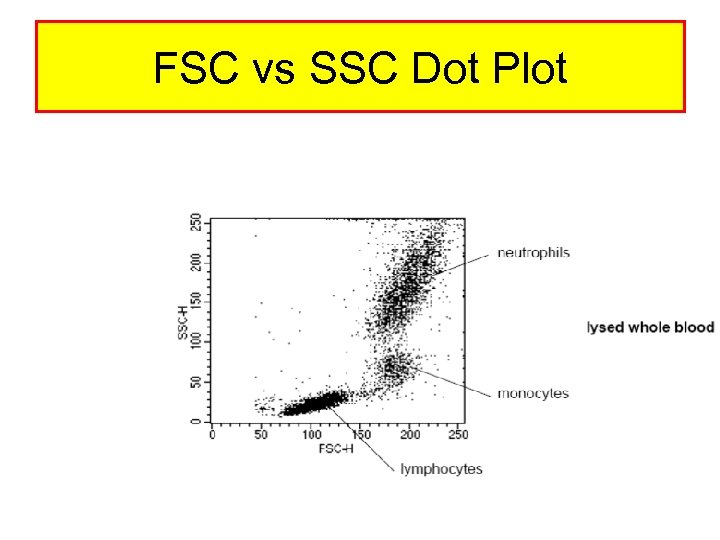 FSC vs SSC Dot Plot
FSC vs SSC Dot Plot
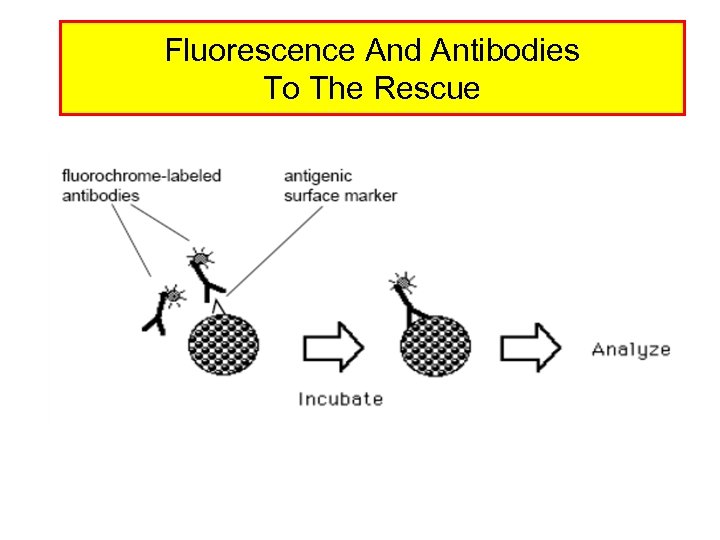 Fluorescence And Antibodies To The Rescue
Fluorescence And Antibodies To The Rescue
 Fluorescent Dyes And Antibodies • Fluorochromes Are Molecules That Emit Fluorescence Upon Excitation With Light – – Ex. FITC (Fluorescein Isothiocyanate) PE (Phycoerythrin) Per. CP (Peridinin Chlorophyll Protein) APC (Allophycocyanin) • Some Fluorochromes Are Proteins, Some Are Small Organic Compounds – Ex. PE (Phycoerythrin)-Protein – Ex. FITC (Fluorescein Isothiocyanate)
Fluorescent Dyes And Antibodies • Fluorochromes Are Molecules That Emit Fluorescence Upon Excitation With Light – – Ex. FITC (Fluorescein Isothiocyanate) PE (Phycoerythrin) Per. CP (Peridinin Chlorophyll Protein) APC (Allophycocyanin) • Some Fluorochromes Are Proteins, Some Are Small Organic Compounds – Ex. PE (Phycoerythrin)-Protein – Ex. FITC (Fluorescein Isothiocyanate)
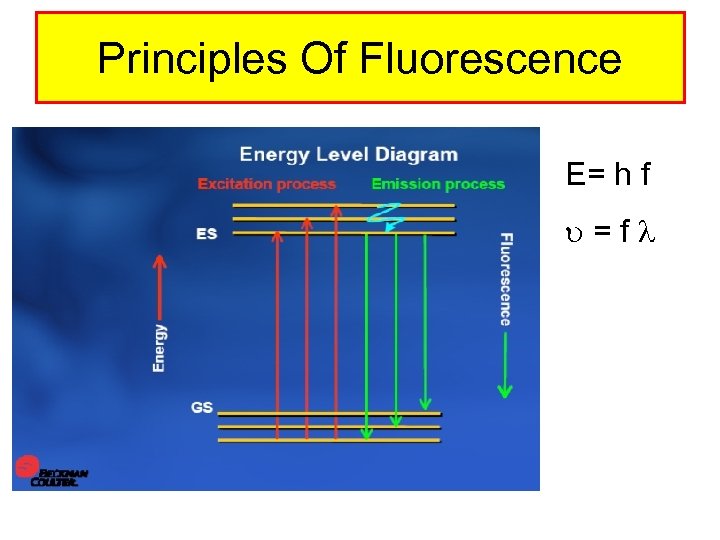 Principles Of Fluorescence E= h f =f
Principles Of Fluorescence E= h f =f
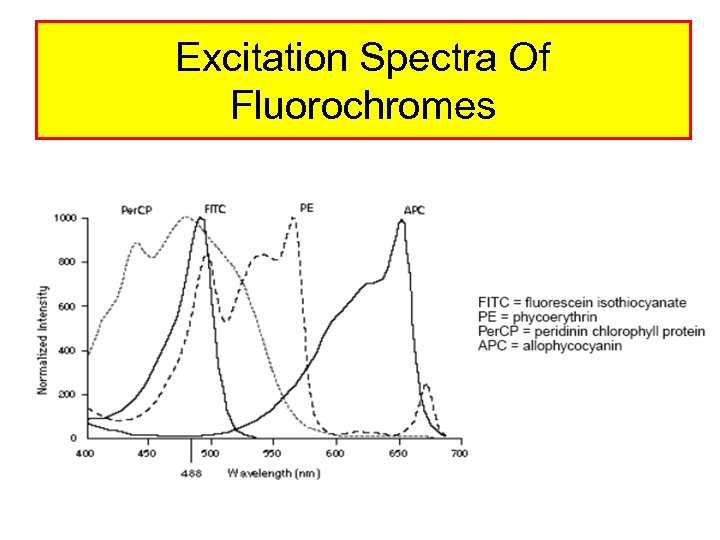 Excitation Spectra Of Fluorochromes
Excitation Spectra Of Fluorochromes
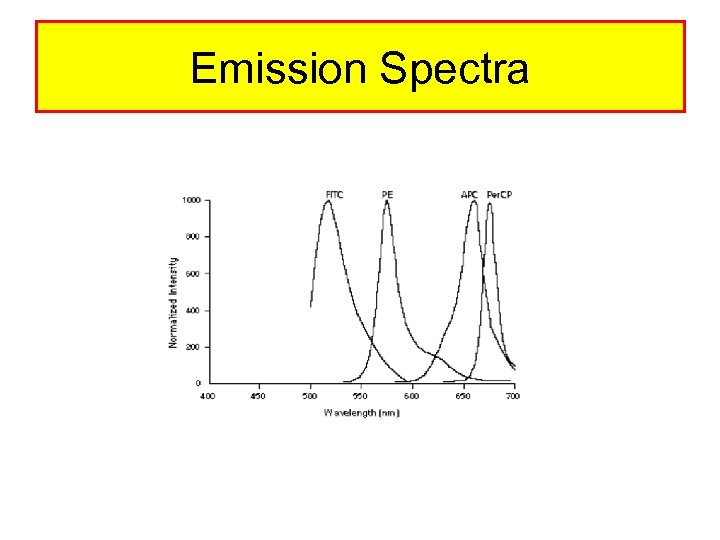 Emission Spectra
Emission Spectra
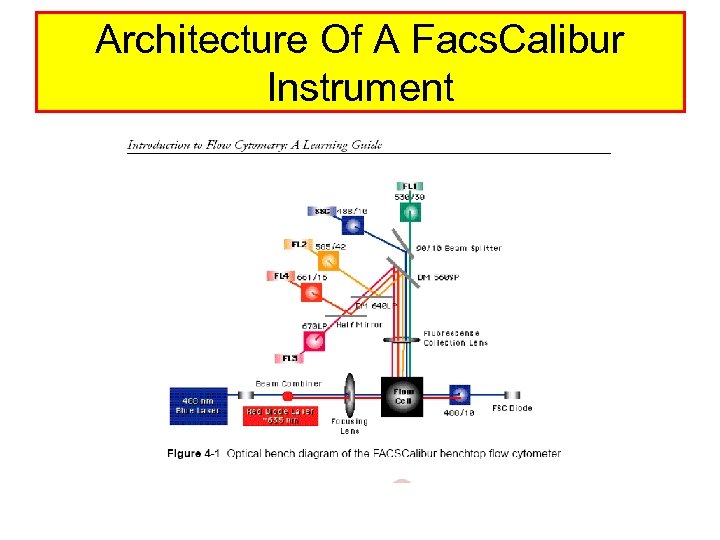 Architecture Of A Facs. Calibur Instrument
Architecture Of A Facs. Calibur Instrument
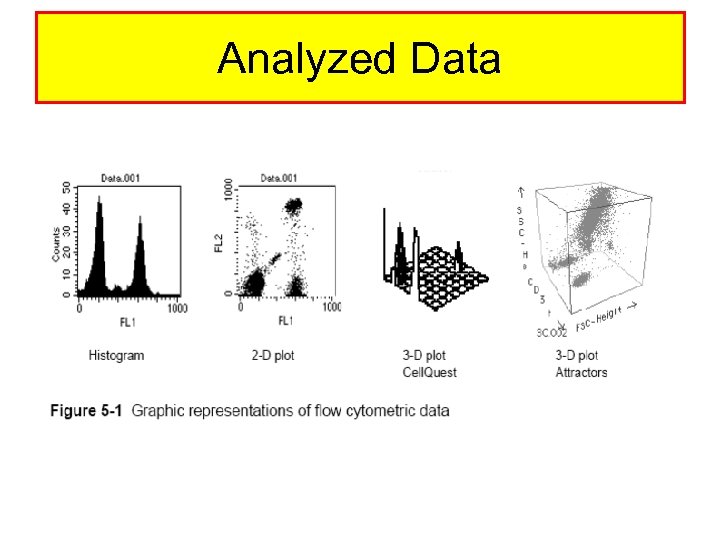 Analyzed Data
Analyzed Data
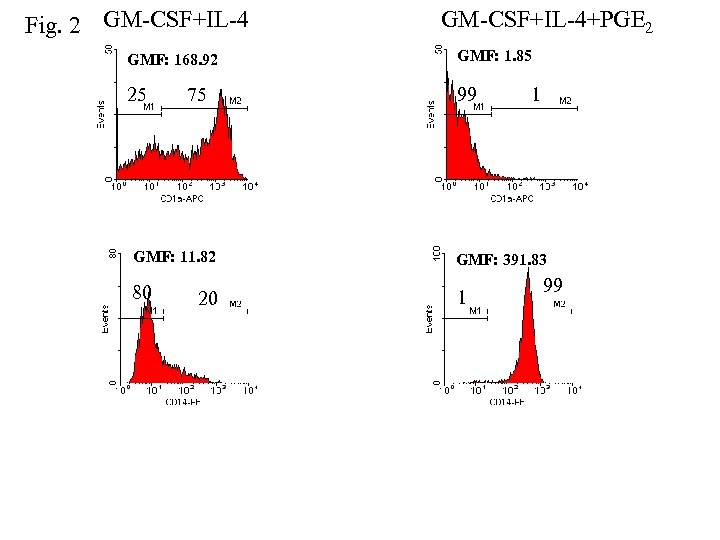 Fig. 2 GM-CSF+IL-4+PGE 2 GMF: 168. 92 GMF: 1. 85 25 99 75 1 GMF: 11. 82 GMF: 391. 83 80 1 20 99
Fig. 2 GM-CSF+IL-4+PGE 2 GMF: 168. 92 GMF: 1. 85 25 99 75 1 GMF: 11. 82 GMF: 391. 83 80 1 20 99
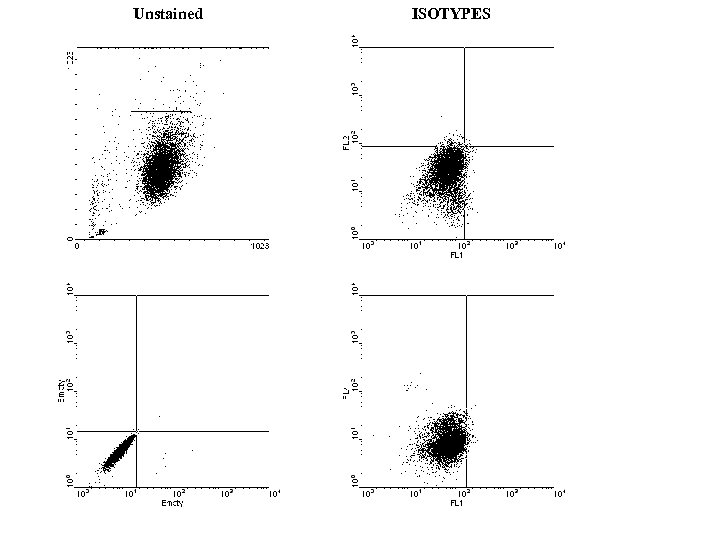 Unstained ISOTYPES
Unstained ISOTYPES
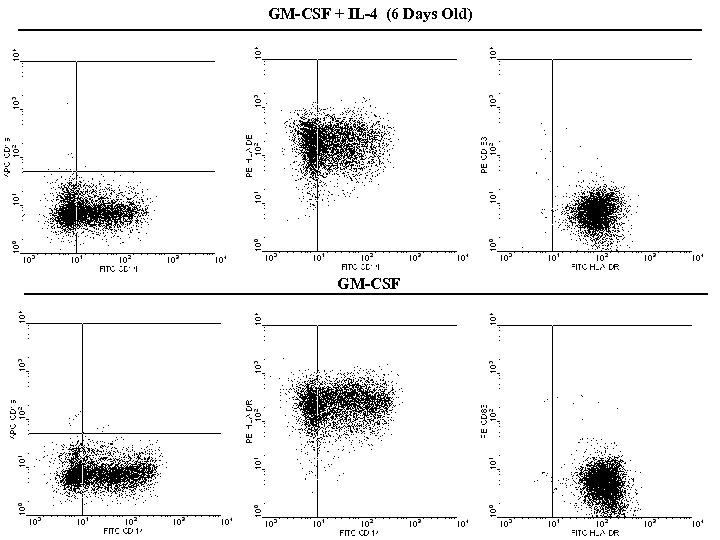 GM-CSF + IL-4 (6 Days Old) GM-CSF
GM-CSF + IL-4 (6 Days Old) GM-CSF