116692b3637f9e71e1b56ea211a950cb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 Characterizing and Defending Against DDo. S Attacks Christos Papadopoulos. . and many others
Characterizing and Defending Against DDo. S Attacks Christos Papadopoulos. . and many others
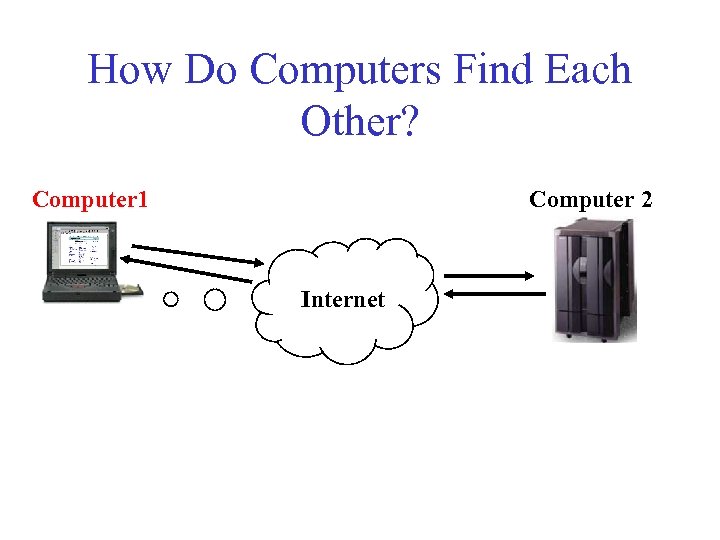 How Do Computers Find Each Other? Computer 1 Computer 2 Internet
How Do Computers Find Each Other? Computer 1 Computer 2 Internet
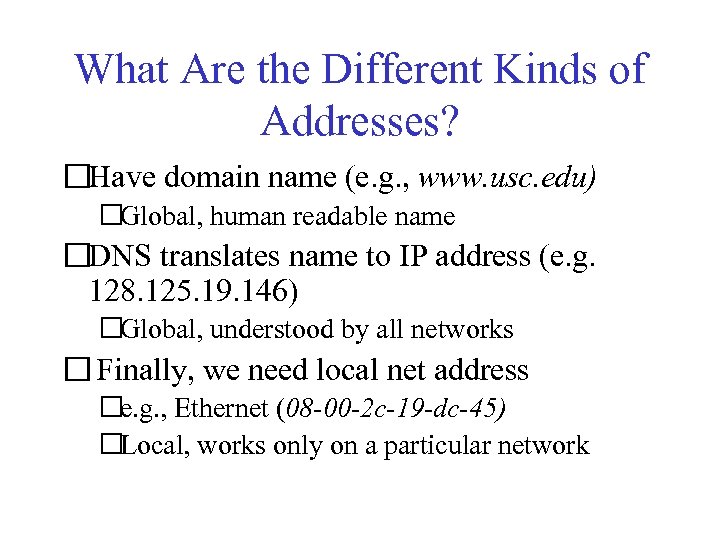 What Are the Different Kinds of Addresses? Have domain name (e. g. , www. usc. edu) Global, human readable name DNS translates name to IP address (e. g. 128. 125. 19. 146) Global, understood by all networks Finally, we need local net address e. g. , Ethernet (08 -00 -2 c-19 -dc-45) Local, works only on a particular network
What Are the Different Kinds of Addresses? Have domain name (e. g. , www. usc. edu) Global, human readable name DNS translates name to IP address (e. g. 128. 125. 19. 146) Global, understood by all networks Finally, we need local net address e. g. , Ethernet (08 -00 -2 c-19 -dc-45) Local, works only on a particular network
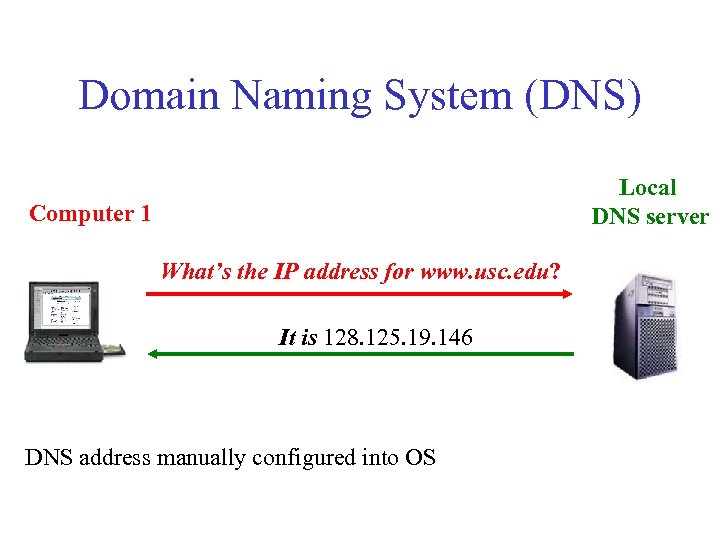 Domain Naming System (DNS) Local DNS server Computer 1 What’s the IP address for www. usc. edu? It is 128. 125. 19. 146 DNS address manually configured into OS
Domain Naming System (DNS) Local DNS server Computer 1 What’s the IP address for www. usc. edu? It is 128. 125. 19. 146 DNS address manually configured into OS
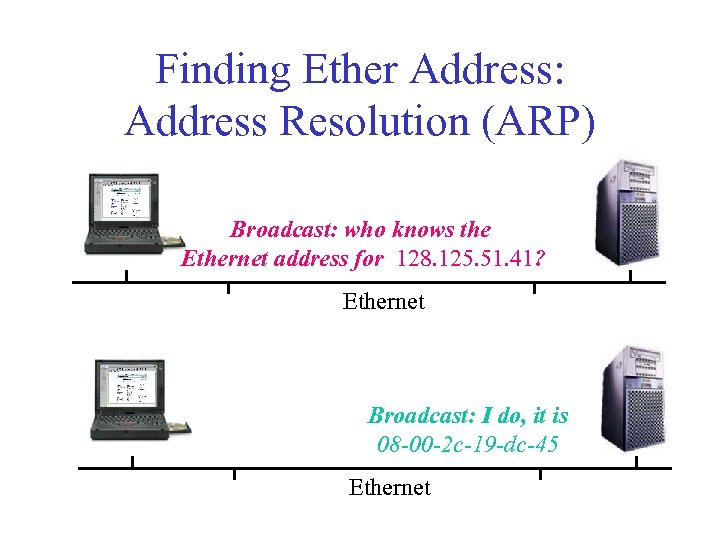 Finding Ether Address: Address Resolution (ARP) Broadcast: who knows the Ethernet address for 128. 125. 51. 41? Ethernet Broadcast: I do, it is 08 -00 -2 c-19 -dc-45 Ethernet
Finding Ether Address: Address Resolution (ARP) Broadcast: who knows the Ethernet address for 128. 125. 51. 41? Ethernet Broadcast: I do, it is 08 -00 -2 c-19 -dc-45 Ethernet
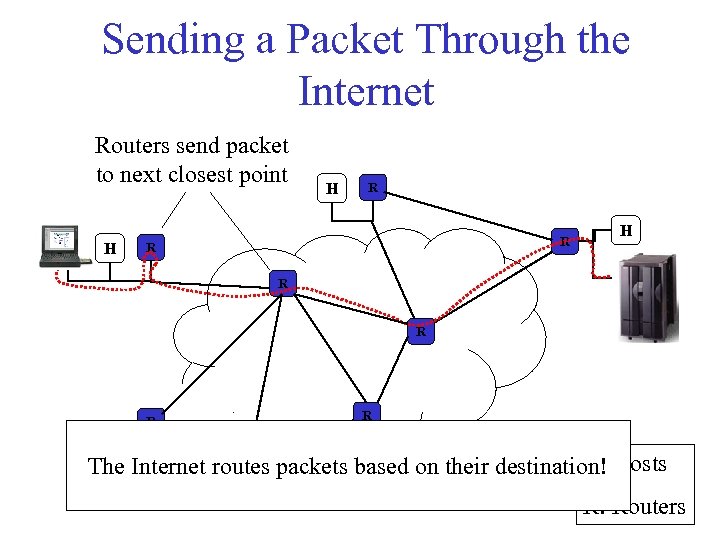 Sending a Packet Through the Internet Routers send packet to next closest point H H H R R R R H: The Internet routes packets based on their destination! Hosts H R: Routers
Sending a Packet Through the Internet Routers send packet to next closest point H H H R R R R H: The Internet routes packets based on their destination! Hosts H R: Routers
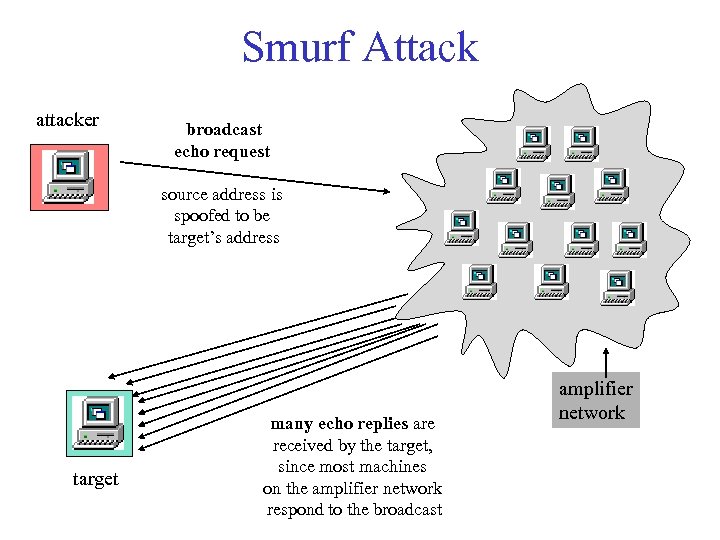 Smurf Attack attacker broadcast echo request source address is spoofed to be target’s address target many echo replies are received by the target, since most machines on the amplifier network respond to the broadcast amplifier network
Smurf Attack attacker broadcast echo request source address is spoofed to be target’s address target many echo replies are received by the target, since most machines on the amplifier network respond to the broadcast amplifier network
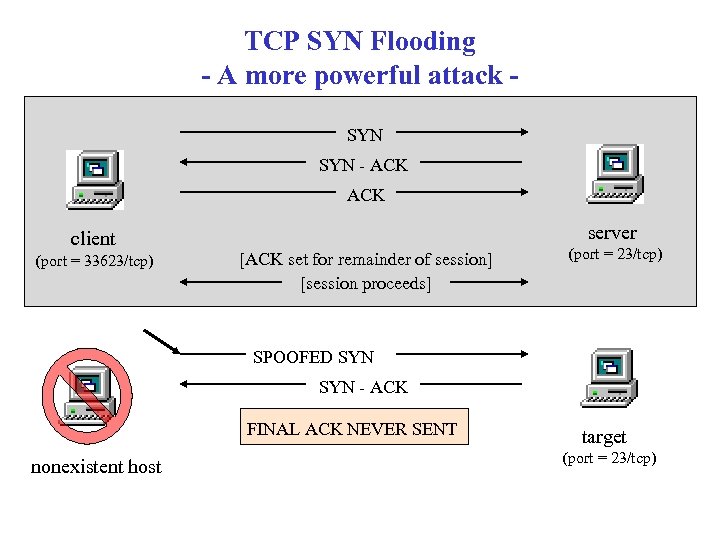 TCP SYN Flooding - A more powerful attack SYN - ACK client (port = 33623/tcp) server [ACK set for remainder of session] [session proceeds] (port = 23/tcp) SPOOFED SYN - ACK FINAL ACK NEVER SENT nonexistent host target (port = 23/tcp)
TCP SYN Flooding - A more powerful attack SYN - ACK client (port = 33623/tcp) server [ACK set for remainder of session] [session proceeds] (port = 23/tcp) SPOOFED SYN - ACK FINAL ACK NEVER SENT nonexistent host target (port = 23/tcp)
 So, What Is DDo. S? Distributed Denial of Service § New, more pernicious type of attack § Many hosts “gang” up to attack another host § Network resource attack: § Bandwidth § State
So, What Is DDo. S? Distributed Denial of Service § New, more pernicious type of attack § Many hosts “gang” up to attack another host § Network resource attack: § Bandwidth § State
 Why Should We Care? § Successfully used to attack prominent sites in the Internet by those with a primitive understanding of internet protocols § It is relatively easy to do, but hard to detect and stop § It is only going to get worse unless we develop adequate protection mechanisms
Why Should We Care? § Successfully used to attack prominent sites in the Internet by those with a primitive understanding of internet protocols § It is relatively easy to do, but hard to detect and stop § It is only going to get worse unless we develop adequate protection mechanisms
 Anatomy of an Attack § Compromise a large set of machines § Install attack tools § Instruct all attack machines to initiate attack against a victim Process highly automated
Anatomy of an Attack § Compromise a large set of machines § Install attack tools § Instruct all attack machines to initiate attack against a victim Process highly automated
 Phase 1: Compromise A (stolen) account is used as repository for attack tools. A scan is performed to identify potential victims. A script is used to compromise the victims.
Phase 1: Compromise A (stolen) account is used as repository for attack tools. A scan is performed to identify potential victims. A script is used to compromise the victims.
 Phase 2: Install Attack Tools • An automated installation script is then run on the “owned” systems to download and install the attack tool(s) from the repository. • Optionally, a “root kit” is installed on the compromised systems.
Phase 2: Install Attack Tools • An automated installation script is then run on the “owned” systems to download and install the attack tool(s) from the repository. • Optionally, a “root kit” is installed on the compromised systems.
 Phase 3: Launch attack • Launch a coordinated DDo. S from different sites against a single victim. • Network pipes of attackers can be small, but aggregated bw is far larger than victim’s pipe. • Victim’s ISP may notice elevated traffic. • DDo. S attacks are harder to track than a Do. S.
Phase 3: Launch attack • Launch a coordinated DDo. S from different sites against a single victim. • Network pipes of attackers can be small, but aggregated bw is far larger than victim’s pipe. • Victim’s ISP may notice elevated traffic. • DDo. S attacks are harder to track than a Do. S.
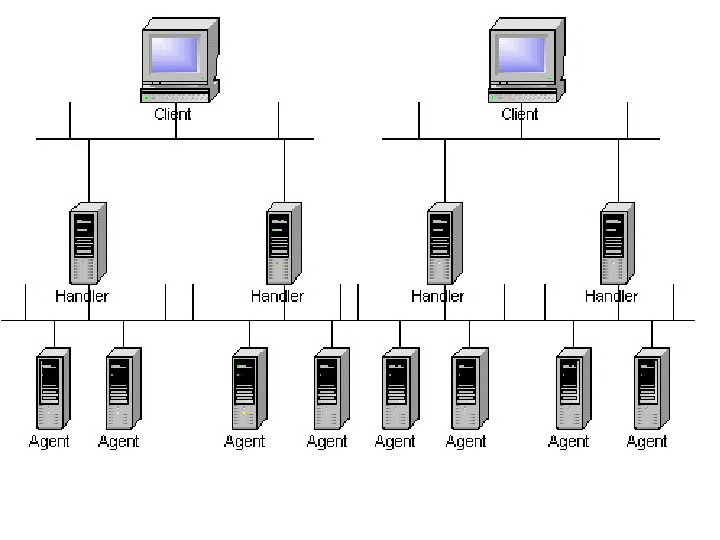
 Some Known DDo. S attack tools §Trin 00 §Tribal Flood Network (TFN) §Tribal Flood Network 2000 (TFN 2 K) §Stacheldraht
Some Known DDo. S attack tools §Trin 00 §Tribal Flood Network (TFN) §Tribal Flood Network 2000 (TFN 2 K) §Stacheldraht
 Stacheldraht § Combines features of trin 00 and TFN. § Adds encryption between the attacker and masters and automated update of agents. § Communication between attacker and masters take place on tcp port 16660. § Daemons receive commands from masters through ICMP echo replies §ICMP, UDP, SYN flood and SMURF attack.
Stacheldraht § Combines features of trin 00 and TFN. § Adds encryption between the attacker and masters and automated update of agents. § Communication between attacker and masters take place on tcp port 16660. § Daemons receive commands from masters through ICMP echo replies §ICMP, UDP, SYN flood and SMURF attack.
![#. /client 192. 168. 0. 1 [*] stacheldraht [*] (c) in 1999 by. . #. /client 192. 168. 0. 1 [*] stacheldraht [*] (c) in 1999 by. .](https://present5.com/presentation/116692b3637f9e71e1b56ea211a950cb/image-18.jpg) #. /client 192. 168. 0. 1 [*] stacheldraht [*] (c) in 1999 by. . . trying to connect. . . connection established. -------------------enter the passphrase : sicken -------------------entering interactive session. *************** welcome to stacheldraht *************** type. help if you are lame stacheldraht(status: a!1 d!0)>
#. /client 192. 168. 0. 1 [*] stacheldraht [*] (c) in 1999 by. . . trying to connect. . . connection established. -------------------enter the passphrase : sicken -------------------entering interactive session. *************** welcome to stacheldraht *************** type. help if you are lame stacheldraht(status: a!1 d!0)>
 stacheldraht(status: a!1 d!0)>. help available commands in this version are: -------------------------. mtimer. mudp. micmp. msyn. msort. mping. madd. mlist. msadd. msrem. distro. help. setusize. setisize. mdie. sprange. mstop. killall. showdead. showalive -------------------------stacheldraht(status: a!1 d!0)>
stacheldraht(status: a!1 d!0)>. help available commands in this version are: -------------------------. mtimer. mudp. micmp. msyn. msort. mping. madd. mlist. msadd. msrem. distro. help. setusize. setisize. mdie. sprange. mstop. killall. showdead. showalive -------------------------stacheldraht(status: a!1 d!0)>
 Some Commands -------. distro user server Instructs the agent to install and run a new copy of itself using the Berkeley "rcp" command, on the system "server", using the account "user" (e. g. , "rcp user@server: linux. bin ttymon"). madd ip 1[: ip 2[: ip. N]] Add IP addresses to list of attack victims. . mdie Sends die request to all agents.
Some Commands -------. distro user server Instructs the agent to install and run a new copy of itself using the Berkeley "rcp" command, on the system "server", using the account "user" (e. g. , "rcp user@server: linux. bin ttymon"). madd ip 1[: ip 2[: ip. N]] Add IP addresses to list of attack victims. . mdie Sends die request to all agents.
 COSSACK: Coordinated Suppression of Simultaneous Attacks Computer Networks Division ISI http: //www. isi. edu/cossack
COSSACK: Coordinated Suppression of Simultaneous Attacks Computer Networks Division ISI http: //www. isi. edu/cossack
 People § Co-PIs: Christos Papadopoulos, Bob Lindell (USC/ISI) § Affiliations: Ramesh Govindan (USC/ISI) § Staff: John Mehringer (ISI) § Students: Alefiya Hussain (USC) § DARPA synergies: § DWARD - Peter Reiher, Jelena Mirkovic (UCLA) § SAMAN - John Heidemann (USC/ISI)
People § Co-PIs: Christos Papadopoulos, Bob Lindell (USC/ISI) § Affiliations: Ramesh Govindan (USC/ISI) § Staff: John Mehringer (ISI) § Students: Alefiya Hussain (USC) § DARPA synergies: § DWARD - Peter Reiher, Jelena Mirkovic (UCLA) § SAMAN - John Heidemann (USC/ISI)
 Cossack Overview q. Distributed set of watchdogs at network perimeter q. Local IDS q. Group communication q. Topology information (when available) q. Fully distributed approach q. Peer-to-peer rather than master-slave q. Attack-driven dynamic grouping of watchdogs q. Attack correlation via coordination with other watchdogs q. Independent, selective deployment of countermeasures
Cossack Overview q. Distributed set of watchdogs at network perimeter q. Local IDS q. Group communication q. Topology information (when available) q. Fully distributed approach q. Peer-to-peer rather than master-slave q. Attack-driven dynamic grouping of watchdogs q. Attack correlation via coordination with other watchdogs q. Independent, selective deployment of countermeasures
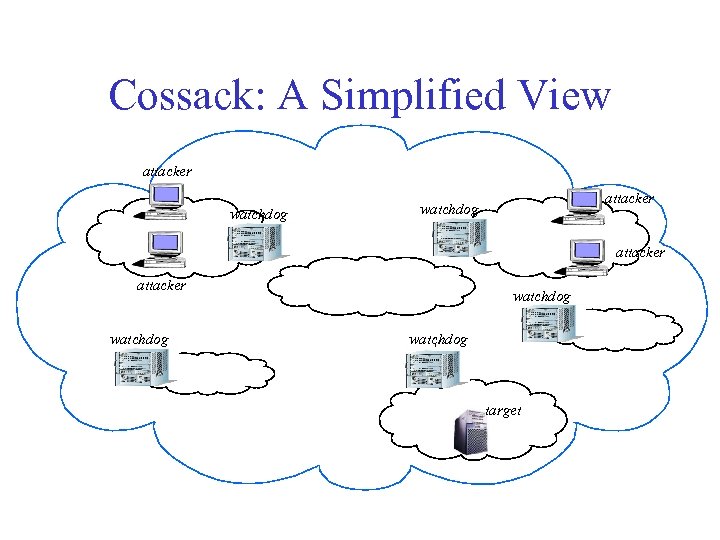 Cossack: A Simplified View attacker watchdog W W attacker watchdog W target
Cossack: A Simplified View attacker watchdog W W attacker watchdog W target
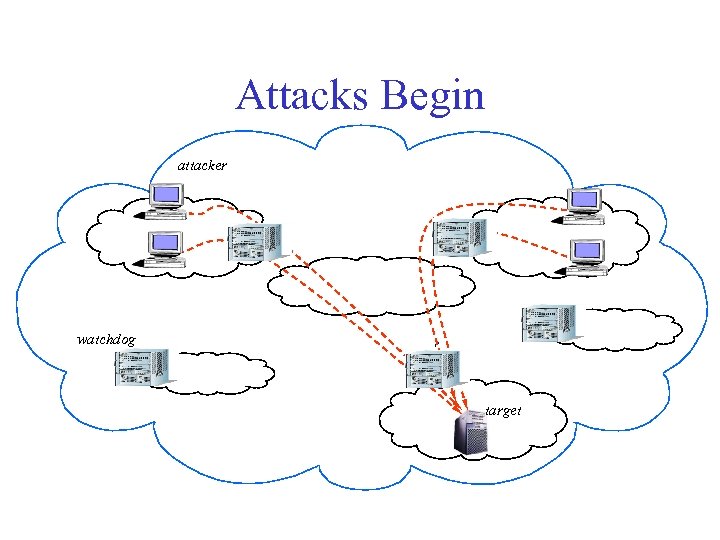 Attacks Begin attacker W W watchdog W target
Attacks Begin attacker W W watchdog W target
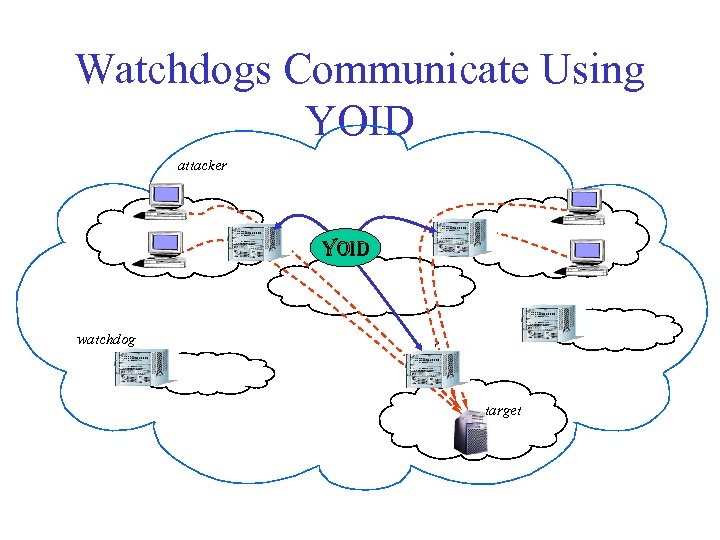 Watchdogs Communicate Using YOID attacker W W YOID watchdog W target
Watchdogs Communicate Using YOID attacker W W YOID watchdog W target
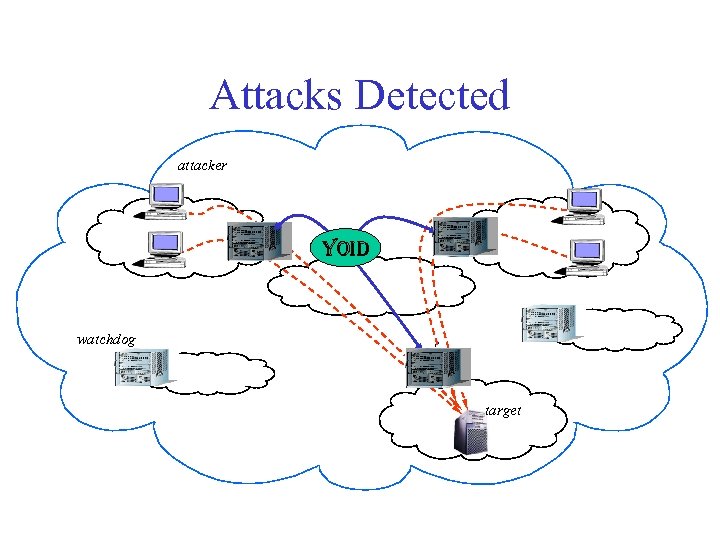 Attacks Detected attacker W W YOID watchdog W target
Attacks Detected attacker W W YOID watchdog W target
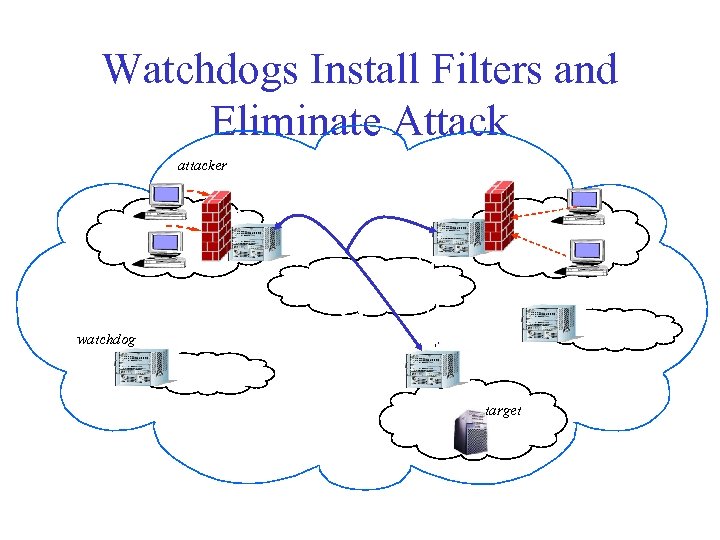 Watchdogs Install Filters and Eliminate Attack attacker W W watchdog W target
Watchdogs Install Filters and Eliminate Attack attacker W W watchdog W target
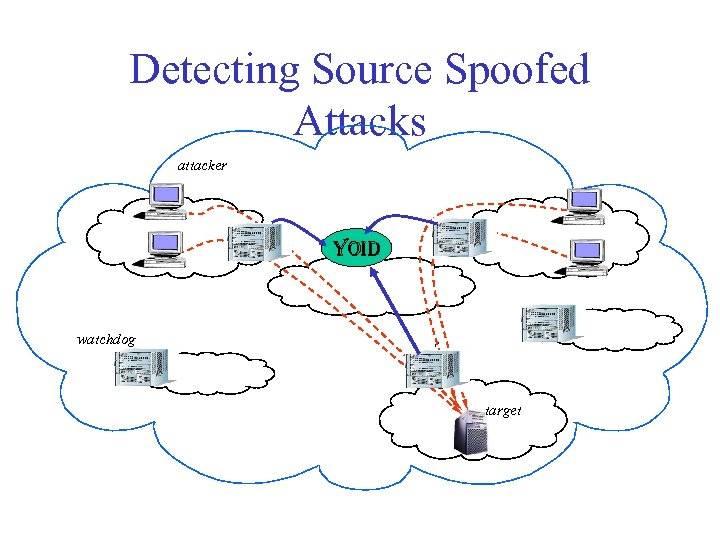 Detecting Source Spoofed Attacks attacker W W YOID watchdog W target
Detecting Source Spoofed Attacks attacker W W YOID watchdog W target
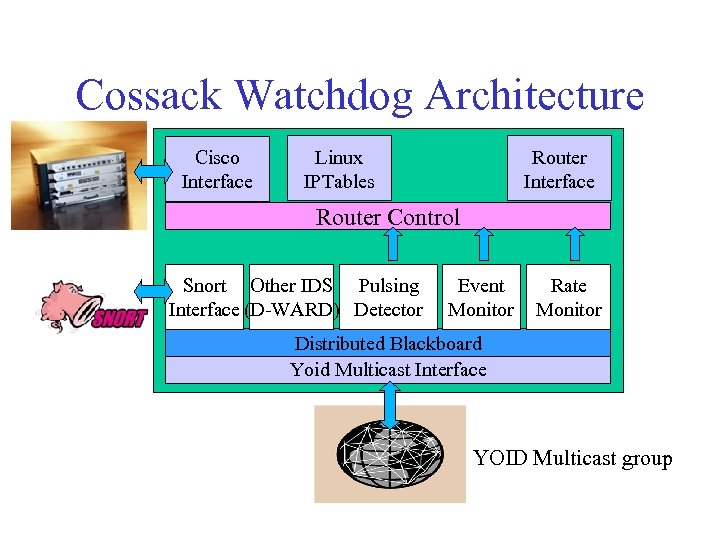 Cossack Watchdog Architecture Cisco Interface Linux IPTables Router Interface Router Control Snort Other IDS Pulsing Interface (D-WARD) Detector Event Monitor Rate Monitor Distributed Blackboard Yoid Multicast Interface YOID Multicast group
Cossack Watchdog Architecture Cisco Interface Linux IPTables Router Interface Router Control Snort Other IDS Pulsing Interface (D-WARD) Detector Event Monitor Rate Monitor Distributed Blackboard Yoid Multicast Interface YOID Multicast group
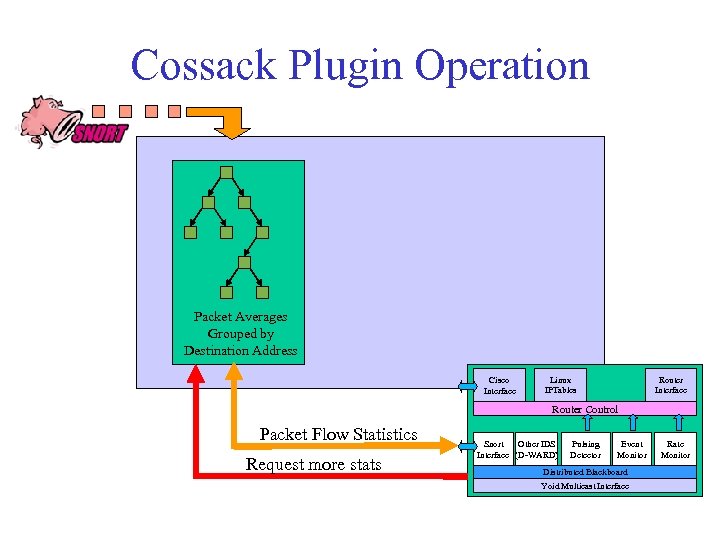 Cossack Plugin Operation Packet Averages Grouped by Destination Address Cisco Interface Linux IPTables Router Interface Router Control Packet Flow Statistics Request more stats Snort Other IDS Interface (D-WARD) Pulsing Detector Event Monitor Distributed Blackboard Yoid Multicast Interface Rate Monitor
Cossack Plugin Operation Packet Averages Grouped by Destination Address Cisco Interface Linux IPTables Router Interface Router Control Packet Flow Statistics Request more stats Snort Other IDS Interface (D-WARD) Pulsing Detector Event Monitor Distributed Blackboard Yoid Multicast Interface Rate Monitor
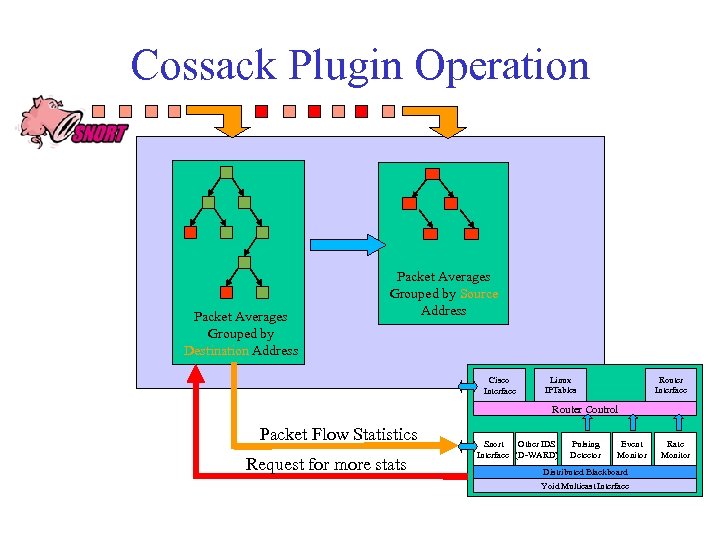 Cossack Plugin Operation Packet Averages Grouped by Destination Address Packet Averages Grouped by Source Address Cisco Interface Linux IPTables Router Interface Router Control Packet Flow Statistics Request for more stats Snort Other IDS Interface (D-WARD) Pulsing Detector Event Monitor Distributed Blackboard Yoid Multicast Interface Rate Monitor
Cossack Plugin Operation Packet Averages Grouped by Destination Address Packet Averages Grouped by Source Address Cisco Interface Linux IPTables Router Interface Router Control Packet Flow Statistics Request for more stats Snort Other IDS Interface (D-WARD) Pulsing Detector Event Monitor Distributed Blackboard Yoid Multicast Interface Rate Monitor
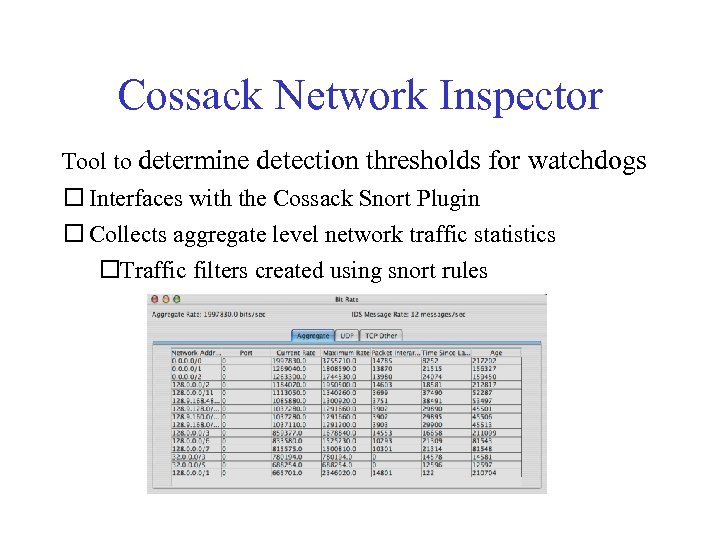 Cossack Network Inspector Tool to determine detection thresholds for watchdogs Interfaces with the Cossack Snort Plugin Collects aggregate level network traffic statistics Traffic filters created using snort rules
Cossack Network Inspector Tool to determine detection thresholds for watchdogs Interfaces with the Cossack Snort Plugin Collects aggregate level network traffic statistics Traffic filters created using snort rules
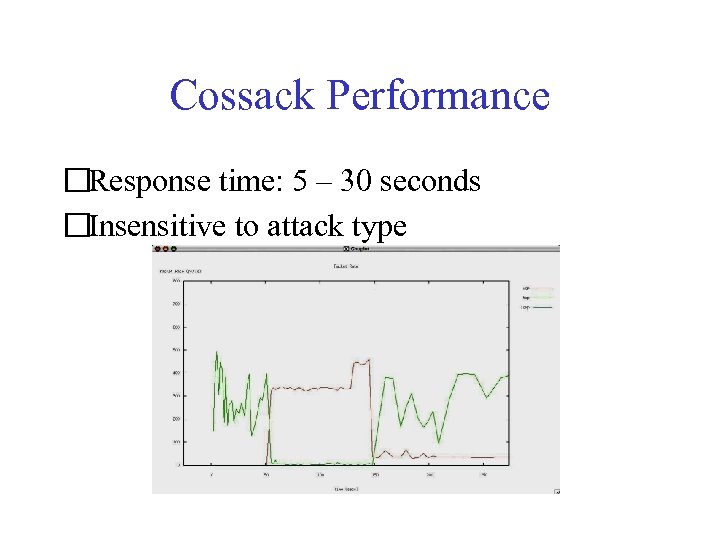 Cossack Performance Response time: 5 – 30 seconds Insensitive to attack type
Cossack Performance Response time: 5 – 30 seconds Insensitive to attack type
 Attack Capture and Analysis Goal: Capture some attacks, analyze and learn from them Packet-level capture facilities in several sites: Los Nettos USC CAIDA [Telcordia, Sprint] Spectral analysis
Attack Capture and Analysis Goal: Capture some attacks, analyze and learn from them Packet-level capture facilities in several sites: Los Nettos USC CAIDA [Telcordia, Sprint] Spectral analysis
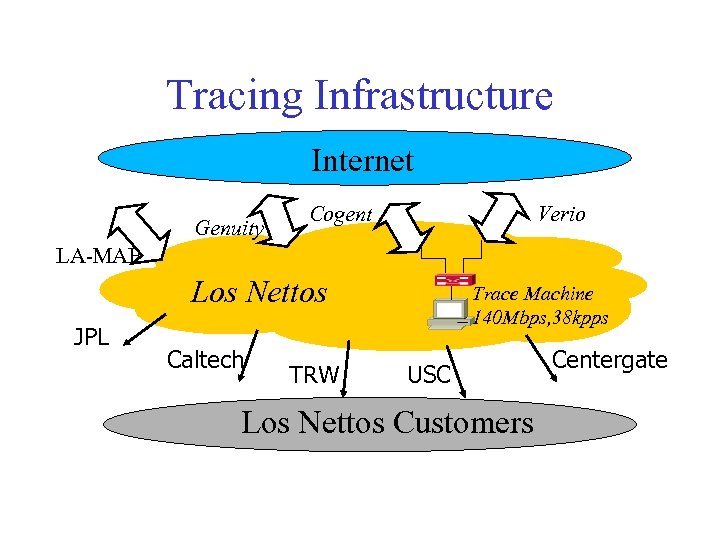 Tracing Infrastructure Internet Genuity Cogent Verio LA-MAE Los Nettos JPL Caltech TRW Trace Machine 140 Mbps, 38 kpps USC Los Nettos Customers Centergate
Tracing Infrastructure Internet Genuity Cogent Verio LA-MAE Los Nettos JPL Caltech TRW Trace Machine 140 Mbps, 38 kpps USC Los Nettos Customers Centergate
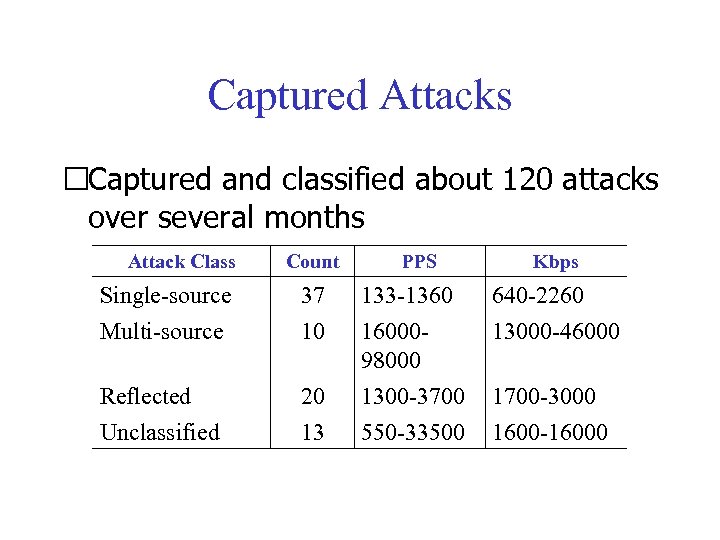 Captured Attacks Captured and classified about 120 attacks over several months Attack Class Count Single-source Multi-source 37 10 Reflected Unclassified 20 13 PPS 133 -1360 1600098000 1300 -3700 550 -33500 Kbps 640 -2260 13000 -46000 1700 -3000 1600 -16000
Captured Attacks Captured and classified about 120 attacks over several months Attack Class Count Single-source Multi-source 37 10 Reflected Unclassified 20 13 PPS 133 -1360 1600098000 1300 -3700 550 -33500 Kbps 640 -2260 13000 -46000 1700 -3000 1600 -16000
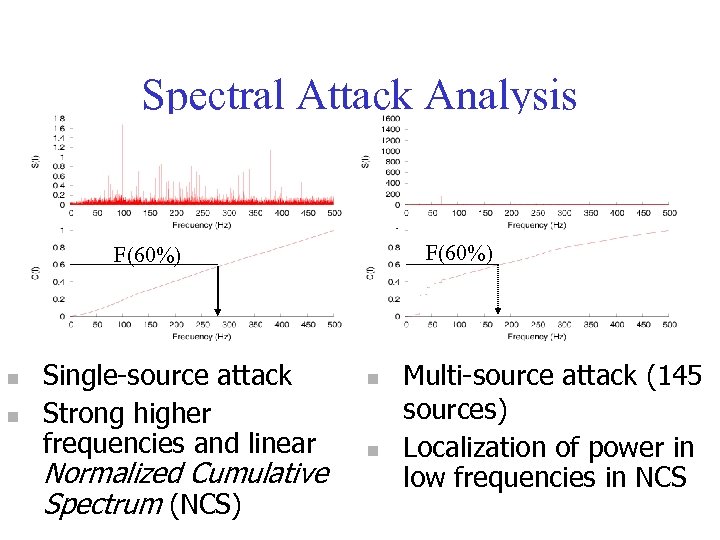 Spectral Attack Analysis F(60%) n n Single-source attack Strong higher frequencies and linear Normalized Cumulative Spectrum (NCS) n n Multi-source attack (145 sources) Localization of power in low frequencies in NCS
Spectral Attack Analysis F(60%) n n Single-source attack Strong higher frequencies and linear Normalized Cumulative Spectrum (NCS) n n Multi-source attack (145 sources) Localization of power in low frequencies in NCS
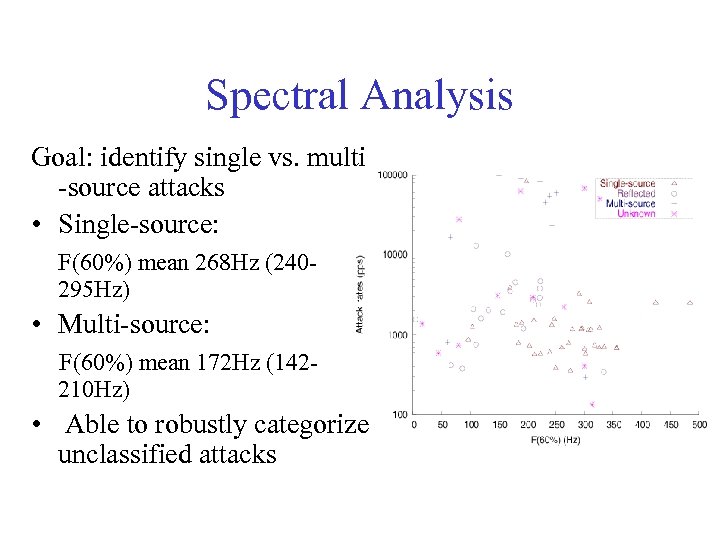 Spectral Analysis Goal: identify single vs. multi -source attacks • Single-source: F(60%) mean 268 Hz (240295 Hz) • Multi-source: F(60%) mean 172 Hz (142210 Hz) • Able to robustly categorize unclassified attacks
Spectral Analysis Goal: identify single vs. multi -source attacks • Single-source: F(60%) mean 268 Hz (240295 Hz) • Multi-source: F(60%) mean 172 Hz (142210 Hz) • Able to robustly categorize unclassified attacks
 Conclusions q. Cossack is a fully distributed approach against DDo. S attacks q. Software is operational and currently undergoing Red Team testing q. We continue to capture attacks, analyze and learn from them q. Spectral analysis work very promising http: //www. isi. edu/cossack
Conclusions q. Cossack is a fully distributed approach against DDo. S attacks q. Software is operational and currently undergoing Red Team testing q. We continue to capture attacks, analyze and learn from them q. Spectral analysis work very promising http: //www. isi. edu/cossack


