2665db09a3837962d8657405784a307b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Chapters 10 -12 Investments
Chapters 10 -12 Investments
 How Are Saving and Investing Related? • Savings is money set aside for the future. • Investing is a strategy to earn more on your money than the rate of inflation. • Different rates of return 10 -1 Reasons for Saving and Investing Slide 2
How Are Saving and Investing Related? • Savings is money set aside for the future. • Investing is a strategy to earn more on your money than the rate of inflation. • Different rates of return 10 -1 Reasons for Saving and Investing Slide 2
 How Are Saving and Investing Related? • High versus low risk • Rate of return • Liquidity – Emergency funds • Financial security Slide 3
How Are Saving and Investing Related? • High versus low risk • Rate of return • Liquidity – Emergency funds • Financial security Slide 3
 How Is Risk Related to Return? • The higher the risk, the greater your possible return. • Risk-free investments are guaranteed by the government—U. S. savings bonds, Treasury bills. • Return on Investment (ROI) is the amount that savings or investments grow expressed as a percentage. 10 -2 Principles of Saving and Investing Slide 4
How Is Risk Related to Return? • The higher the risk, the greater your possible return. • Risk-free investments are guaranteed by the government—U. S. savings bonds, Treasury bills. • Return on Investment (ROI) is the amount that savings or investments grow expressed as a percentage. 10 -2 Principles of Saving and Investing Slide 4
 What Types of Risk Do Investors Face? Investment risk is the potential for change in the value of an investment. • Inflation risk • Industry risk • Political risk • Stock risk 10 -2 Principles of Saving and Investing Slide 5
What Types of Risk Do Investors Face? Investment risk is the potential for change in the value of an investment. • Inflation risk • Industry risk • Political risk • Stock risk 10 -2 Principles of Saving and Investing Slide 5
 How Do Saving and Investing Meet Personal Goals? • Short-Term Goals o Emergency fund o Vacation planning Less than 2 years • Medium-Term Goals o Buying a car o Paying for college o Planning a wedding • Long-Term Goals o Providing for a family o Buying a house 10 -1 Reasons for Saving and Investing 2 -5 years More than 5 years Slide 6
How Do Saving and Investing Meet Personal Goals? • Short-Term Goals o Emergency fund o Vacation planning Less than 2 years • Medium-Term Goals o Buying a car o Paying for college o Planning a wedding • Long-Term Goals o Providing for a family o Buying a house 10 -1 Reasons for Saving and Investing 2 -5 years More than 5 years Slide 6
 How Does Investing Prepare You for Retirement and Beyond? • Retirement is the period of time when you are not working but are able to meet expenses. • Sources of income include: o Retirement plans o Social security o Savings o Investments 10 -1 Reasons for Saving and Investing Slide 7
How Does Investing Prepare You for Retirement and Beyond? • Retirement is the period of time when you are not working but are able to meet expenses. • Sources of income include: o Retirement plans o Social security o Savings o Investments 10 -1 Reasons for Saving and Investing Slide 7
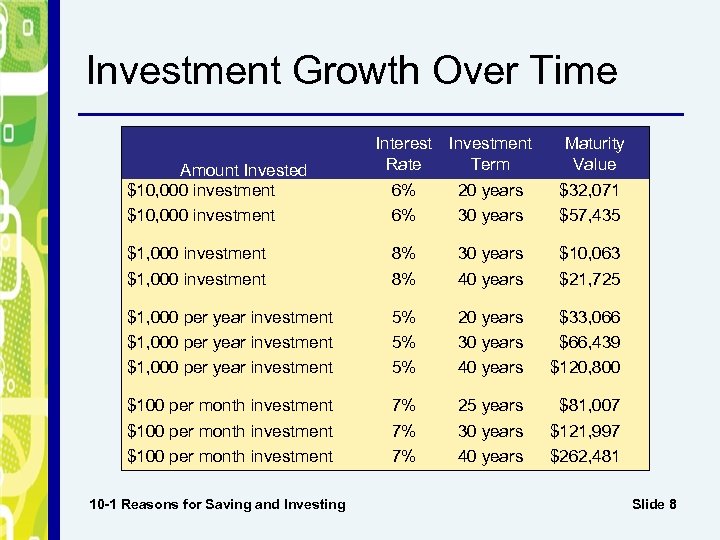 Investment Growth Over Time Amount Invested $10, 000 investment Interest Investment Rate Term Maturity Value 6% 6% 20 years 30 years $32, 071 $57, 435 $1, 000 investment 8% 8% 30 years 40 years $10, 063 $21, 725 $1, 000 per year investment 5% 5% 5% 20 years 30 years 40 years $33, 066 $66, 439 $120, 800 $100 per month investment 7% 7% 7% 25 years 30 years 40 years $81, 007 $121, 997 $262, 481 10 -1 Reasons for Saving and Investing Slide 8
Investment Growth Over Time Amount Invested $10, 000 investment Interest Investment Rate Term Maturity Value 6% 6% 20 years 30 years $32, 071 $57, 435 $1, 000 investment 8% 8% 30 years 40 years $10, 063 $21, 725 $1, 000 per year investment 5% 5% 5% 20 years 30 years 40 years $33, 066 $66, 439 $120, 800 $100 per month investment 7% 7% 7% 25 years 30 years 40 years $81, 007 $121, 997 $262, 481 10 -1 Reasons for Saving and Investing Slide 8
 Textbook page 321 #’s: 1 -16 (skip 2 and 3) Slide 9
Textbook page 321 #’s: 1 -16 (skip 2 and 3) Slide 9
 What Are Systematic Saving and Investing Strategies? • Systematic saving involves regularly setting aside cash to achieve goals. • Systematic investing is a planned approach to making investments on a regular basis. 10 -3 Strategies for Saving and Investing Slide 10
What Are Systematic Saving and Investing Strategies? • Systematic saving involves regularly setting aside cash to achieve goals. • Systematic investing is a planned approach to making investments on a regular basis. 10 -3 Strategies for Saving and Investing Slide 10
 What Are Systematic Saving and Investing Strategies? • Market timing involves buying and selling stocks based on what the market is expected to do. • Investment tracking involves making investment choices by following stock prices over time. • Dollar-cost averaging investing the same amount of money regularly regardless of the market conditions 10 -3 Strategies for Saving and Investing Slide 11
What Are Systematic Saving and Investing Strategies? • Market timing involves buying and selling stocks based on what the market is expected to do. • Investment tracking involves making investment choices by following stock prices over time. • Dollar-cost averaging investing the same amount of money regularly regardless of the market conditions 10 -3 Strategies for Saving and Investing Slide 11
 How Can You Reduce Investment Risk? 10 -3 Strategies for Saving and Investing Slide 12
How Can You Reduce Investment Risk? 10 -3 Strategies for Saving and Investing Slide 12
 How Can You Maximize Investment Return? • A bull market exists when stock prices are steadily increasing. • Usually followed by profit-taking. • Common for the past 20 years. 10 -3 Strategies for Saving and Investing Slide 13
How Can You Maximize Investment Return? • A bull market exists when stock prices are steadily increasing. • Usually followed by profit-taking. • Common for the past 20 years. 10 -3 Strategies for Saving and Investing Slide 13
 How Can You Maximize Investment Return? • A bear market exists when prices are steadily decreasing. • Good time to buy stocks that are considered sound investments. (prices are lower) 10 -3 Strategies for Saving and Investing Slide 14
How Can You Maximize Investment Return? • A bear market exists when prices are steadily decreasing. • Good time to buy stocks that are considered sound investments. (prices are lower) 10 -3 Strategies for Saving and Investing Slide 14
 Tracking a Stock’s Price • Common investment strategy • Choose a large corporation you are interested in • Find its stock symbol – Example: Walmart is WMT • Find the close price for yesterday – Record the date and price • Track every class period in this unit Slide 15
Tracking a Stock’s Price • Common investment strategy • Choose a large corporation you are interested in • Find its stock symbol – Example: Walmart is WMT • Find the close price for yesterday – Record the date and price • Track every class period in this unit Slide 15
 Low Risk Choices Slide 16
Low Risk Choices Slide 16
 What Are Low-Risk Savings Options? • Liquid savings include cash or investments that can be changed into cash quickly. • Savings and checking accounts are liquid. • Illiquid investments cannot be converted to cash quickly or without a penalty. 11 -1 Low-Risk Choices Slide 17
What Are Low-Risk Savings Options? • Liquid savings include cash or investments that can be changed into cash quickly. • Savings and checking accounts are liquid. • Illiquid investments cannot be converted to cash quickly or without a penalty. 11 -1 Low-Risk Choices Slide 17
 What Are Low-Risk Savings Options? • Savings accounts • Money market accounts • Certificates of deposit o Money set aside for specific length of time at a fixed interest rate o Withdrawal penalties o Special Features 11 -1 Low-Risk Choices Slide 18
What Are Low-Risk Savings Options? • Savings accounts • Money market accounts • Certificates of deposit o Money set aside for specific length of time at a fixed interest rate o Withdrawal penalties o Special Features 11 -1 Low-Risk Choices Slide 18
 What Are Low-Risk Savings Options? • Life insurance savings plans o Borrow against the policy’s cash value o Not insured o Not liquid • Brokerage accounts o An account at an investment company o Clearing account: money is used to buy and sell investments o Not insured o Liquid 11 -1 Low-Risk Choices Slide 19
What Are Low-Risk Savings Options? • Life insurance savings plans o Borrow against the policy’s cash value o Not insured o Not liquid • Brokerage accounts o An account at an investment company o Clearing account: money is used to buy and sell investments o Not insured o Liquid 11 -1 Low-Risk Choices Slide 19
 What Are Low-Risk Investing Options? Bonds • • • A bond is a loan that a buyer makes to a bond issuer. Government and corporations issue bonds. The face value is the amount the bondholder will be repaid on the maturity date. The maturity date is the date the borrowed money must be repaid. Coupon rate – fixed rate of interest that is paid semiannually for the life of the bond 11 -1 Low-Risk Choices Slide 20
What Are Low-Risk Investing Options? Bonds • • • A bond is a loan that a buyer makes to a bond issuer. Government and corporations issue bonds. The face value is the amount the bondholder will be repaid on the maturity date. The maturity date is the date the borrowed money must be repaid. Coupon rate – fixed rate of interest that is paid semiannually for the life of the bond 11 -1 Low-Risk Choices Slide 20
 What Are Low-Risk Investing Options? • Corporate Bonds – – – Callable Convertible Zero Coupon Investment-grade Speculative-grade (junk bonds) • Government Bonds – Series EE Bonds, I Series Bonds, Treasury Bills, Treasury Notes, Treasury Bonds, Municipal Bonds 11 -1 Low-Risk Choices Slide 21
What Are Low-Risk Investing Options? • Corporate Bonds – – – Callable Convertible Zero Coupon Investment-grade Speculative-grade (junk bonds) • Government Bonds – Series EE Bonds, I Series Bonds, Treasury Bills, Treasury Notes, Treasury Bonds, Municipal Bonds 11 -1 Low-Risk Choices Slide 21
 What Are Low-Risk Investing Options? Annuities • • • An annuity is a contract purchased from an insurance company that guarantees a series of regular monthly payments for a set time Not insured Generally used as a source of retirement income 11 -1 Low-Risk Choices Slide 22
What Are Low-Risk Investing Options? Annuities • • • An annuity is a contract purchased from an insurance company that guarantees a series of regular monthly payments for a set time Not insured Generally used as a source of retirement income 11 -1 Low-Risk Choices Slide 22
 Medium Risk Choices Slide 23
Medium Risk Choices Slide 23
 What Are Good Financial Market Investments? • A mutual fund is a professionally managed group of investments. • It is bought using a pool of money from many investors. • Indirect investing – buying shares of a fund, not a specific company • Asset allocation involves choosing a combination of funds. 11 -2 Medium-Risk Choices Slide 24
What Are Good Financial Market Investments? • A mutual fund is a professionally managed group of investments. • It is bought using a pool of money from many investors. • Indirect investing – buying shares of a fund, not a specific company • Asset allocation involves choosing a combination of funds. 11 -2 Medium-Risk Choices Slide 24
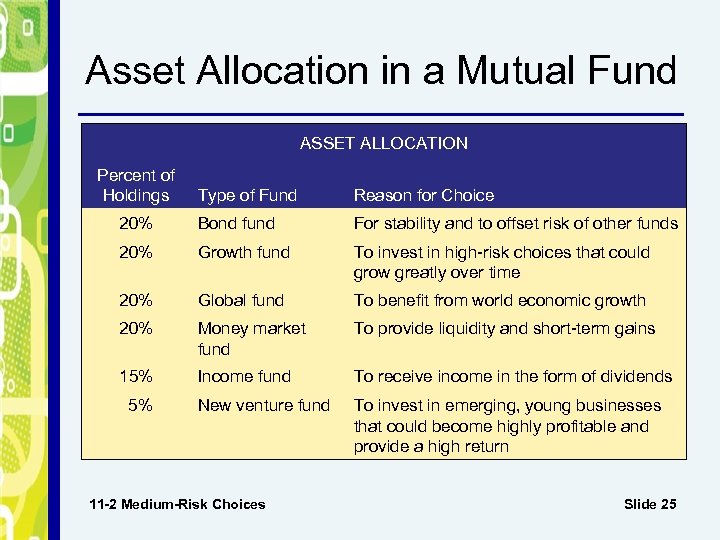 Asset Allocation in a Mutual Fund ASSET ALLOCATION Percent of Holdings Type of Fund Reason for Choice 20% Bond fund For stability and to offset risk of other funds 20% Growth fund To invest in high-risk choices that could grow greatly over time 20% Global fund To benefit from world economic growth 20% Money market fund To provide liquidity and short-term gains 15% Income fund To receive income in the form of dividends New venture fund To invest in emerging, young businesses that could become highly profitable and provide a high return 5% 11 -2 Medium-Risk Choices Slide 25
Asset Allocation in a Mutual Fund ASSET ALLOCATION Percent of Holdings Type of Fund Reason for Choice 20% Bond fund For stability and to offset risk of other funds 20% Growth fund To invest in high-risk choices that could grow greatly over time 20% Global fund To benefit from world economic growth 20% Money market fund To provide liquidity and short-term gains 15% Income fund To receive income in the form of dividends New venture fund To invest in emerging, young businesses that could become highly profitable and provide a high return 5% 11 -2 Medium-Risk Choices Slide 25
 What Are Individual Retirement Account Options? • An IRA allows you to deposit money into an account during your working years and withdraw it upon retirement. • Traditional IRA’s allow you to contribute pre-tax money and you do not have to pay taxes until you withdraw the money • With a Roth IRA, contributions are taxed but earnings are not 11 -2 Medium-Risk Choices Slide 26
What Are Individual Retirement Account Options? • An IRA allows you to deposit money into an account during your working years and withdraw it upon retirement. • Traditional IRA’s allow you to contribute pre-tax money and you do not have to pay taxes until you withdraw the money • With a Roth IRA, contributions are taxed but earnings are not 11 -2 Medium-Risk Choices Slide 26
 What Retirement Plans Are Available through Employers? • Defined-contribution plans o 401(k) plans: tax-deferred plans for profit-seeking businesses o 403(b) plans: tax-deferred plans for government and nonprofit organizations • Defined-benefit plans o Pension plan • Retirement accounts may be portable, meaning you can take the account with you when you leave a job. (Rollover) 11 -2 Medium-Risk Choices Slide 27
What Retirement Plans Are Available through Employers? • Defined-contribution plans o 401(k) plans: tax-deferred plans for profit-seeking businesses o 403(b) plans: tax-deferred plans for government and nonprofit organizations • Defined-benefit plans o Pension plan • Retirement accounts may be portable, meaning you can take the account with you when you leave a job. (Rollover) 11 -2 Medium-Risk Choices Slide 27
 High Risk Choices Slide 28
High Risk Choices Slide 28
 How Can You Invest Directly in Financial Markets? • Direct investing is buying stocks and other investments directly from companies and holding them. • If you buy the stock of only one company, the risk is high because your money is invested in only one place. 11 -3 High-Risk Choices Slide 29
How Can You Invest Directly in Financial Markets? • Direct investing is buying stocks and other investments directly from companies and holding them. • If you buy the stock of only one company, the risk is high because your money is invested in only one place. 11 -3 High-Risk Choices Slide 29
 How Can You Invest Directly in Financial Markets? • Buying stocks o You become a stockholder and own shares in a company. o Common Stock: pays variable dividends and gives owners voting rights o Preferred Stock: fixed dividends but no voting rights 11 -3 High-Risk Choices Slide 30
How Can You Invest Directly in Financial Markets? • Buying stocks o You become a stockholder and own shares in a company. o Common Stock: pays variable dividends and gives owners voting rights o Preferred Stock: fixed dividends but no voting rights 11 -3 High-Risk Choices Slide 30
 How Can You Invest Directly in Financial Markets? • Futures contracts and commodities o You agree to buy or sell a commodity at a set price and date in the future. o Commodities are items that have the same value across the market with little or no difference in quality (examples: soybeans, silver, cattle) • Investment clubs o You pool your money with other people and invest together. (example: time shares) 11 -3 High-Risk Choices Slide 31
How Can You Invest Directly in Financial Markets? • Futures contracts and commodities o You agree to buy or sell a commodity at a set price and date in the future. o Commodities are items that have the same value across the market with little or no difference in quality (examples: soybeans, silver, cattle) • Investment clubs o You pool your money with other people and invest together. (example: time shares) 11 -3 High-Risk Choices Slide 31
 What Professional Advice Is Available? • A stockbroker buys and sells securities on behalf of others. o Full-service brokers o Discount brokers o Online brokers • A financial planner helps people make investment decisions to meet goals. • Banks and credit unions sell securities that they endorse. 12 -1 Researching Investments and Markets Slide 32
What Professional Advice Is Available? • A stockbroker buys and sells securities on behalf of others. o Full-service brokers o Discount brokers o Online brokers • A financial planner helps people make investment decisions to meet goals. • Banks and credit unions sell securities that they endorse. 12 -1 Researching Investments and Markets Slide 32
 What Professional Advice Is Available? Full Service or Discount Brokers? • Discount brokers: o Charge a smaller fee o May charge extra for information • Full service brokers: o Give sound investment advice for a higher fee • When making a choice, consider: services, fees, location of nearest brokerage office, minimum deposits, etc. 12 -1 Researching Investments and Markets Slide 33
What Professional Advice Is Available? Full Service or Discount Brokers? • Discount brokers: o Charge a smaller fee o May charge extra for information • Full service brokers: o Give sound investment advice for a higher fee • When making a choice, consider: services, fees, location of nearest brokerage office, minimum deposits, etc. 12 -1 Researching Investments and Markets Slide 33
 How Are Financial Markets Designed? • Securities exchanges are places for brokers to buy and sell securities for their clients. • Direct investing involves buying securities directly from a corporation. • Reinvesting involves getting stock dividends instead of cash dividends. 12 -1 Researching Investments and Markets Slide 34
How Are Financial Markets Designed? • Securities exchanges are places for brokers to buy and sell securities for their clients. • Direct investing involves buying securities directly from a corporation. • Reinvesting involves getting stock dividends instead of cash dividends. 12 -1 Researching Investments and Markets Slide 34
 How Are Stocks Bought and Sold? 1. Set up an account. • Choose your venue (fullservice broker, discount broker, bank, etc. ) • Provide identification. • Access your account online. • Make minimum or regular monthly deposit. 12 -2 Buying and Selling Securities Slide 35
How Are Stocks Bought and Sold? 1. Set up an account. • Choose your venue (fullservice broker, discount broker, bank, etc. ) • Provide identification. • Access your account online. • Make minimum or regular monthly deposit. 12 -2 Buying and Selling Securities Slide 35
 How Are Stocks Bought and Sold? 2. Place transactions. • A market order is a request to buy or sell a stock at the current market price. • A limit order is a request to buy or sell a stock at a specific price. • A stop order is a request to sell a stock when it reaches a certain price. • A discretionary order allows the broker to buy or sell a stock to get the best price. 12 -2 Buying and Selling Securities Slide 36
How Are Stocks Bought and Sold? 2. Place transactions. • A market order is a request to buy or sell a stock at the current market price. • A limit order is a request to buy or sell a stock at a specific price. • A stop order is a request to sell a stock when it reaches a certain price. • A discretionary order allows the broker to buy or sell a stock to get the best price. 12 -2 Buying and Selling Securities Slide 36
 Buying Patterns • Buy and hold is a plan to purchase and keep stock for the long term. • Stock turning is making regular and systematic changes in stock ownership based on trends in the economy. • Watch-and-wait investing involves making a comparative analysis of securities periodically. 12 -2 Buying and Selling Securities Slide 37
Buying Patterns • Buy and hold is a plan to purchase and keep stock for the long term. • Stock turning is making regular and systematic changes in stock ownership based on trends in the economy. • Watch-and-wait investing involves making a comparative analysis of securities periodically. 12 -2 Buying and Selling Securities Slide 37
 What Are Financial Reform Laws? • Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) sets standards for public companies and accounting firms for the reporting of finances. o Created in response to financial scandals at large companies. o Requires improved financial reporting, audits, and accounting services. 12 -3 Regulatory Agencies and Laws Slide 38
What Are Financial Reform Laws? • Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) sets standards for public companies and accounting firms for the reporting of finances. o Created in response to financial scandals at large companies. o Requires improved financial reporting, audits, and accounting services. 12 -3 Regulatory Agencies and Laws Slide 38


