ff57c11929d5e8c64463d618d84434b3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 CHAPTER TWO UNDERSTANDING RISK AND RETURN © 2001 South-Western College Publishing
CHAPTER TWO UNDERSTANDING RISK AND RETURN © 2001 South-Western College Publishing
 Outline u Return Holding Period Return Yield and Appreciation The Time Value of Money Compounding Compound Annual Return 2
Outline u Return Holding Period Return Yield and Appreciation The Time Value of Money Compounding Compound Annual Return 2
 Outline u Risk vs. Uncertainty Dispersion and the Chance of Loss The Problem with Losses Risk and the Time Horizon Risk Aversion Partitioning Risk u More on the Relationship between Risk and Return The Direct Relationship Risk, Return, and Dominance 3
Outline u Risk vs. Uncertainty Dispersion and the Chance of Loss The Problem with Losses Risk and the Time Horizon Risk Aversion Partitioning Risk u More on the Relationship between Risk and Return The Direct Relationship Risk, Return, and Dominance 3
 Return The simplest measure of return is the holding period return. Holding period = return Ending _ Beginning value + Income Beginning value 4
Return The simplest measure of return is the holding period return. Holding period = return Ending _ Beginning value + Income Beginning value 4
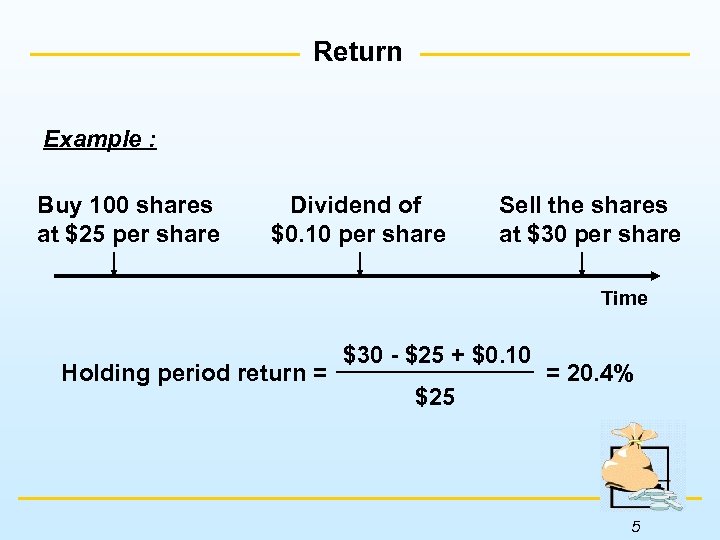 Return Example : Buy 100 shares at $25 per share Dividend of $0. 10 per share Sell the shares at $30 per share Time Holding period return = $30 - $25 + $0. 10 $25 = 20. 4% 5
Return Example : Buy 100 shares at $25 per share Dividend of $0. 10 per share Sell the shares at $30 per share Time Holding period return = $30 - $25 + $0. 10 $25 = 20. 4% 5
 Return Holding period return. . . is independent of the passage of time. when comparing investments, the periods should all be of the same length. is based on price, not total value. adjustments need to be made for corporate actions, such as stock splits, which affect the price but not the total value. 6
Return Holding period return. . . is independent of the passage of time. when comparing investments, the periods should all be of the same length. is based on price, not total value. adjustments need to be made for corporate actions, such as stock splits, which affect the price but not the total value. 6
 Return Current yield is annual income divided by current price. Dividend yield is used for stocks whose incomes exclusively from dividends. Example : For a stock selling for $40 and expected to pay $1 in dividends over the next year, current yield = $1 / $40 = 2. 5%. 7
Return Current yield is annual income divided by current price. Dividend yield is used for stocks whose incomes exclusively from dividends. Example : For a stock selling for $40 and expected to pay $1 in dividends over the next year, current yield = $1 / $40 = 2. 5%. 7
 Return Appreciation is the increase in value of an investment independent of its yield. It excludes accrued interest, as well as increases in value which are due to additional deposits. Example : When a stock bought at $95 rises to $97. 50, it has appreciated by $2. 50, or $2. 50 / $95 = 2. 6%. 8
Return Appreciation is the increase in value of an investment independent of its yield. It excludes accrued interest, as well as increases in value which are due to additional deposits. Example : When a stock bought at $95 rises to $97. 50, it has appreciated by $2. 50, or $2. 50 / $95 = 2. 6%. 8
 Return The time value of money is the notion that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow. the current price of any financial asset should be the present value of its expected future cash flows. Present. Value × ( 1 + r )n = Future. Value where r = interest rate period and n = number of periods 9
Return The time value of money is the notion that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow. the current price of any financial asset should be the present value of its expected future cash flows. Present. Value × ( 1 + r )n = Future. Value where r = interest rate period and n = number of periods 9
 Return Example : What is the most that an investor would pay for a zero coupon bond which matures in 4 years' time, and has a redemption value of $1, 000? The interest rate is 9. 19%. Present. Value × ( 1 + 0. 0919 )4 = $1, 000 Present. Value = $703. 50 10
Return Example : What is the most that an investor would pay for a zero coupon bond which matures in 4 years' time, and has a redemption value of $1, 000? The interest rate is 9. 19%. Present. Value × ( 1 + 0. 0919 )4 = $1, 000 Present. Value = $703. 50 10
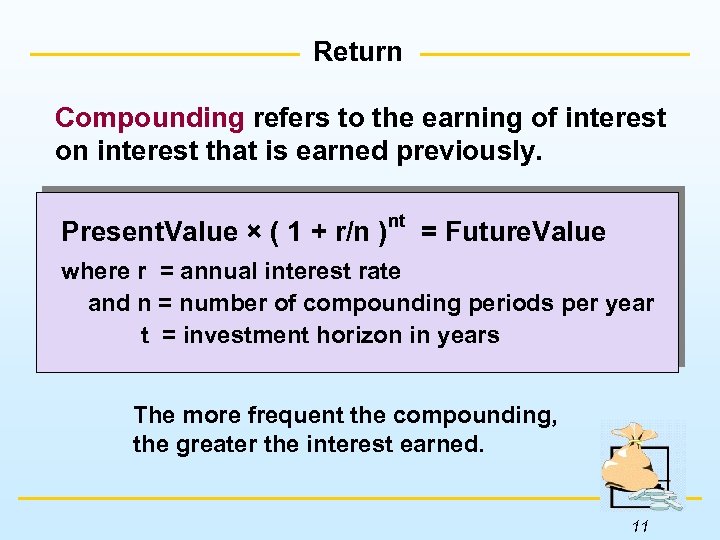 Return Compounding refers to the earning of interest on interest that is earned previously. Present. Value × ( 1 + r/n ) nt = Future. Value where r = annual interest rate and n = number of compounding periods per year t = investment horizon in years The more frequent the compounding, the greater the interest earned. 11
Return Compounding refers to the earning of interest on interest that is earned previously. Present. Value × ( 1 + r/n ) nt = Future. Value where r = annual interest rate and n = number of compounding periods per year t = investment horizon in years The more frequent the compounding, the greater the interest earned. 11
 Return Compound annual return is the annual interest rate that makes the time value of money relationship hold. It is also known as the effective annual rate. Example : A nondividend-paying stock bought 4. 5 years ago at $40 and sold today at $78 has a compound annual return of R, where $40(1+R)4. 5=$78. 12
Return Compound annual return is the annual interest rate that makes the time value of money relationship hold. It is also known as the effective annual rate. Example : A nondividend-paying stock bought 4. 5 years ago at $40 and sold today at $78 has a compound annual return of R, where $40(1+R)4. 5=$78. 12
 Risk vs. Uncertainty A truly risky situation must involve a chance of loss. 13
Risk vs. Uncertainty A truly risky situation must involve a chance of loss. 13
 Risk Dispersion and the Chance of Loss u There are 2 aspects to risk - the average outcome and the scattering of the possible outcomes about this average. u A common measure of statistical dispersion is variance. The standard deviation is the square root of the variance. 14
Risk Dispersion and the Chance of Loss u There are 2 aspects to risk - the average outcome and the scattering of the possible outcomes about this average. u A common measure of statistical dispersion is variance. The standard deviation is the square root of the variance. 14
 Risk The Problem with Losses u Big Losses - a large one-period loss can overwhelm a series of gains. u Small Losses - can be a problem too if they occur too often. 15
Risk The Problem with Losses u Big Losses - a large one-period loss can overwhelm a series of gains. u Small Losses - can be a problem too if they occur too often. 15
 Risk and the Time Horizon u There is an important distinction between the probability of losing money and the amount of money that may be lost. u In general, the longer a common stock investment is held, the lower the likelihood that money will be lost, but the greater the amount that may be lost. 16
Risk and the Time Horizon u There is an important distinction between the probability of losing money and the amount of money that may be lost. u In general, the longer a common stock investment is held, the lower the likelihood that money will be lost, but the greater the amount that may be lost. 16
 Risk Aversion and Rational People u A safe (certain) dollar is worth more than a risky dollar. u Risk averse persons will take risks, when they expect to be rewarded for taking the risks. u People have different degrees of risk aversion; some are more willing to take a chance than are others. 17
Risk Aversion and Rational People u A safe (certain) dollar is worth more than a risky dollar. u Risk averse persons will take risks, when they expect to be rewarded for taking the risks. u People have different degrees of risk aversion; some are more willing to take a chance than are others. 17
 Risk and Time u Probability theory deals with how much and how likely, but says nothing about when. u Forecast variance increases indefinitely as the length of the forecast period approaches infinity. u To be consistent, returns must be measured over consistent time intervals. 18
Risk and Time u Probability theory deals with how much and how likely, but says nothing about when. u Forecast variance increases indefinitely as the length of the forecast period approaches infinity. u To be consistent, returns must be measured over consistent time intervals. 18
 Risk Partitioning Risk u Undiversifiable risk - risk that must be borne by virtue of being in the market. Also known as systematic risk or market risk. Measured by beta. u Diversifiable risk - also known as unsystematic risk. 19
Risk Partitioning Risk u Undiversifiable risk - risk that must be borne by virtue of being in the market. Also known as systematic risk or market risk. Measured by beta. u Diversifiable risk - also known as unsystematic risk. 19
 Risk Partitioning Risk u Business risk - the variability in a firm's sales, or its ability to sell its product. u Financial risk - associated with the financial structure of the firm. u Purchasing power risk - the possibility that the rate of return on an investment will be insufficient to offset the rise in the cost of living. 20
Risk Partitioning Risk u Business risk - the variability in a firm's sales, or its ability to sell its product. u Financial risk - associated with the financial structure of the firm. u Purchasing power risk - the possibility that the rate of return on an investment will be insufficient to offset the rise in the cost of living. 20
 Risk Partitioning Risk u Interest rate risk - the chance of a loss in portfolio value due to an adverse change in interest rate. u Foreign exchange risk - the possibility of loss due to adverse changes in the relative values of world currencies. 21
Risk Partitioning Risk u Interest rate risk - the chance of a loss in portfolio value due to an adverse change in interest rate. u Foreign exchange risk - the possibility of loss due to adverse changes in the relative values of world currencies. 21
 Risk Partitioning Risk u Political risk - the possibility that a government will interfere with a firm's preferred manner of conducting business. u Social risk - the potentially adverse impact changing public attitudes can have on a firm's ability to sell its product. 22
Risk Partitioning Risk u Political risk - the possibility that a government will interfere with a firm's preferred manner of conducting business. u Social risk - the potentially adverse impact changing public attitudes can have on a firm's ability to sell its product. 22
 More on The Relationship between Risk and Return Riskier securities have higher expected returns. Expected Return Risk-free Return Risk 23
More on The Relationship between Risk and Return Riskier securities have higher expected returns. Expected Return Risk-free Return Risk 23
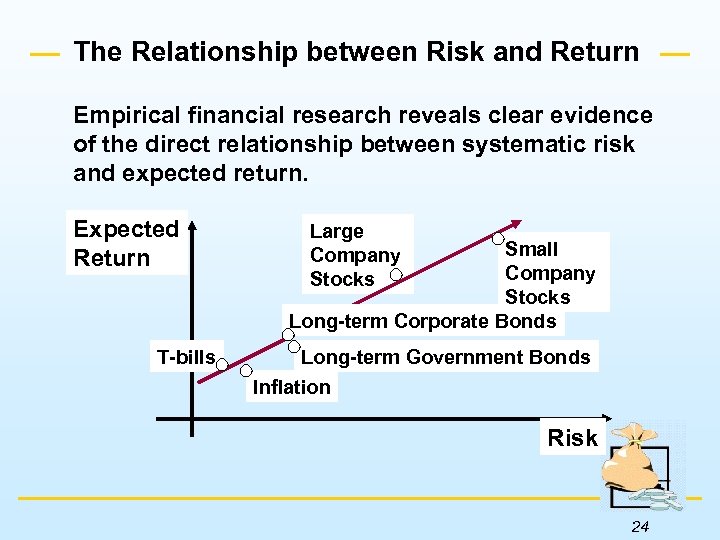 The Relationship between Risk and Return Empirical financial research reveals clear evidence of the direct relationship between systematic risk and expected return. Expected Return T-bills Large Company Stocks Small Company Stocks Long-term Corporate Bonds Long-term Government Bonds Inflation Risk 24
The Relationship between Risk and Return Empirical financial research reveals clear evidence of the direct relationship between systematic risk and expected return. Expected Return T-bills Large Company Stocks Small Company Stocks Long-term Corporate Bonds Long-term Government Bonds Inflation Risk 24
 The Relationship between Risk and Return u An investment alternative shows dominance over another if it offers the same expected return for less risk, or if the security has a higher expected return than another security of comparable risk. u Equivalent assets should sell for the same price. This is known as the law of one price. 25
The Relationship between Risk and Return u An investment alternative shows dominance over another if it offers the same expected return for less risk, or if the security has a higher expected return than another security of comparable risk. u Equivalent assets should sell for the same price. This is known as the law of one price. 25
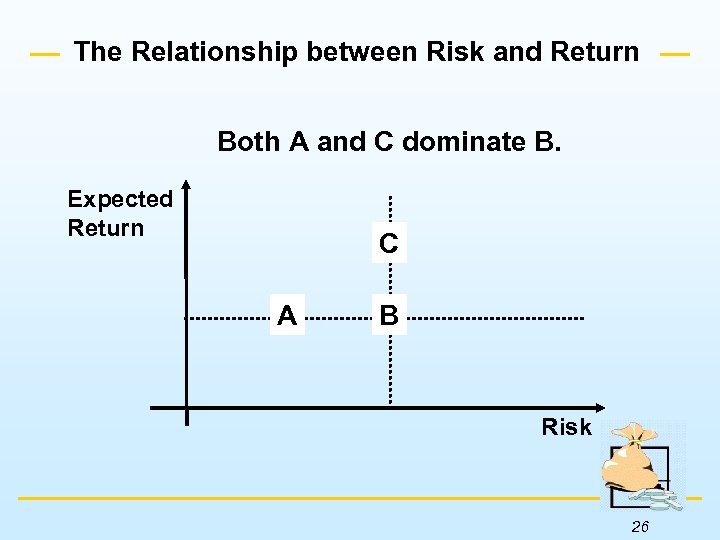 The Relationship between Risk and Return Both A and C dominate B. Expected Return C A B Risk 26
The Relationship between Risk and Return Both A and C dominate B. Expected Return C A B Risk 26
 Review u A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow. u A safe dollar is worth more than a risky dollar. u People have different degrees of risk aversion; some are more willing to take a chance than are others. u A tradeoff exists between risk and return. 27
Review u A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow. u A safe dollar is worth more than a risky dollar. u People have different degrees of risk aversion; some are more willing to take a chance than are others. u A tradeoff exists between risk and return. 27


