2d826772bcfa1bbd11771b3fca00b21e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 87
 CHAPTER THREE THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM
CHAPTER THREE THE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM
 The Account. . . An individual accounting record of increases and decreases to any specific • Asset • Liability • Stockholders’ Equity • Revenue • Expense
The Account. . . An individual accounting record of increases and decreases to any specific • Asset • Liability • Stockholders’ Equity • Revenue • Expense
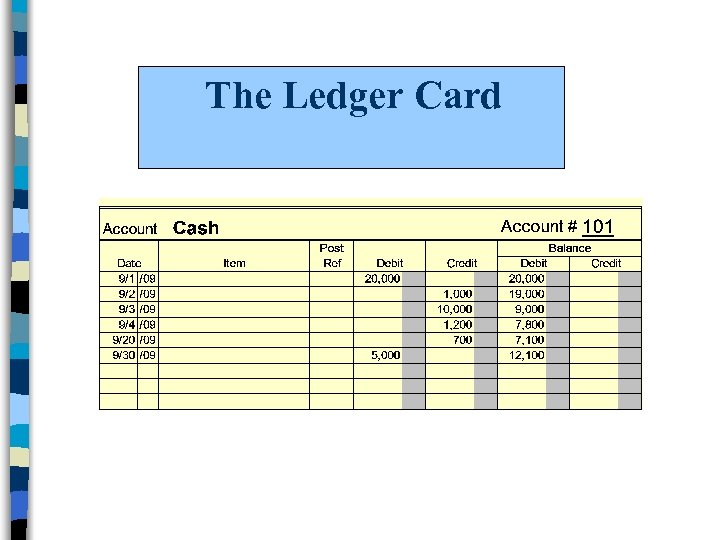 The Ledger Card
The Ledger Card
 Using Accounts l Accounts provide an efficient method to categorize transactions. l It is the location where we record activity and maintain a running balance for any particular item. l Each account is maintained on its own ledger card. l All of the ledger cards combined become the General Ledger.
Using Accounts l Accounts provide an efficient method to categorize transactions. l It is the location where we record activity and maintain a running balance for any particular item. l Each account is maintained on its own ledger card. l All of the ledger cards combined become the General Ledger.
 Accounts Where all activity and the resulting balances are kept for everything we want to keep track of.
Accounts Where all activity and the resulting balances are kept for everything we want to keep track of.
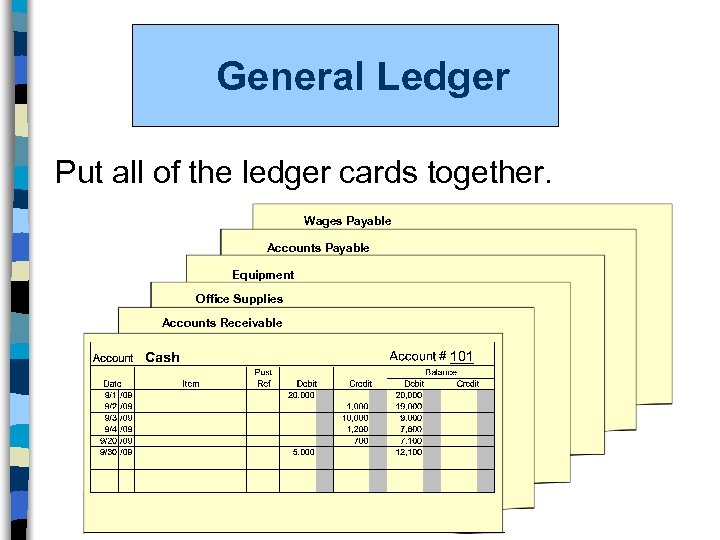 General Ledger Put all of the ledger cards together. Wages Payable Accounts Payable Equipment Office Supplies Accounts Receivable
General Ledger Put all of the ledger cards together. Wages Payable Accounts Payable Equipment Office Supplies Accounts Receivable
 Chart of Accounts. . . is a list of a company’s accounts. Jim’s Lemonade Chart of Accounts 101 105 110 150 201 210 305 320 401 410 501 505 510 - Cash Accts Receivable Office Supplies Equipment Accounts Payable Wages Payable Common Stock Retained Earnings Sales - Lemonade Sales – Catering Lemon Expense Insurance Expense Office Expense
Chart of Accounts. . . is a list of a company’s accounts. Jim’s Lemonade Chart of Accounts 101 105 110 150 201 210 305 320 401 410 501 505 510 - Cash Accts Receivable Office Supplies Equipment Accounts Payable Wages Payable Common Stock Retained Earnings Sales - Lemonade Sales – Catering Lemon Expense Insurance Expense Office Expense
 When a transaction occurs: Basic Steps in the Recording Process. 1. Analyze 2. Journalize 3. Post
When a transaction occurs: Basic Steps in the Recording Process. 1. Analyze 2. Journalize 3. Post
 Recording Process Step 1 Analyze each transaction and effect on accounts
Recording Process Step 1 Analyze each transaction and effect on accounts
 If you don’t understand what happened (the transaction) you cannot account for it! So. . . This is a pretty good place to start !!!
If you don’t understand what happened (the transaction) you cannot account for it! So. . . This is a pretty good place to start !!!
 Accounting Transactions. . . n are economic events that must be recorded in the financial statements because they affect assets n liabilities n and/or stockholders’ equity n
Accounting Transactions. . . n are economic events that must be recorded in the financial statements because they affect assets n liabilities n and/or stockholders’ equity n
 Transaction Analysis l The process of identifying the specific effects of economic events on the accounting equation. l Each transaction has a dual (double- sided) effect on the accounting equation.
Transaction Analysis l The process of identifying the specific effects of economic events on the accounting equation. l Each transaction has a dual (double- sided) effect on the accounting equation.
 Recording Process Step 2 Enter transaction information in a journal, a process called journalizing
Recording Process Step 2 Enter transaction information in a journal, a process called journalizing
 The Journal. . . is an accounting record where the transactions are recorded in chronological order.
The Journal. . . is an accounting record where the transactions are recorded in chronological order.
 Recording Process Step 3 Copy (post) the journal information to the appropriate accounts in the ledger
Recording Process Step 3 Copy (post) the journal information to the appropriate accounts in the ledger
 “T” Accounts SHAPED LIKE a “T” Debit Credit
“T” Accounts SHAPED LIKE a “T” Debit Credit
 “T” Accounts Debit means Left Credit means Right Debit Credit
“T” Accounts Debit means Left Credit means Right Debit Credit
 “T” Accounts Abbreviation for Debit Dr. Cr. Abbreviation for Credit
“T” Accounts Abbreviation for Debit Dr. Cr. Abbreviation for Credit
 “T” Accounts ACCOUNT NAME CASH Dr. Cr.
“T” Accounts ACCOUNT NAME CASH Dr. Cr.
 The Ledger Card Cash The T Account
The Ledger Card Cash The T Account
 Every Account has: è An Increase Side, and è A Decrease Side è But, Some Accounts Increase on the Debit Side è And, Some Accounts Increase on the Credit Side
Every Account has: è An Increase Side, and è A Decrease Side è But, Some Accounts Increase on the Debit Side è And, Some Accounts Increase on the Credit Side
 7 RULES OF DEBITS AND CREDITS
7 RULES OF DEBITS AND CREDITS
 RULE #1 ASSET ACCOUNTS Increase on Debit Side Dr. + Cr. Decrease on Credit Side
RULE #1 ASSET ACCOUNTS Increase on Debit Side Dr. + Cr. Decrease on Credit Side
 EXAMPLE: PURCHASED OFFICE SUPPLIES FOR $800 CASH
EXAMPLE: PURCHASED OFFICE SUPPLIES FOR $800 CASH
 STEP #1 Name the accounts affected: CASH OFFICE SUPPLIES
STEP #1 Name the accounts affected: CASH OFFICE SUPPLIES
 STEP #2 Determine Classification of Accounts AS SE ASSE T CASH T OFFICE SUPPLIES
STEP #2 Determine Classification of Accounts AS SE ASSE T CASH T OFFICE SUPPLIES
 STEP #3 Now that we know the classification, we can identify increase and decrease sides. CASH DR. + CR. OFFICE SUPPLIES DR. + CR.
STEP #3 Now that we know the classification, we can identify increase and decrease sides. CASH DR. + CR. OFFICE SUPPLIES DR. + CR.
 PURCHASED OFFICE SUPPLIES FOR $800 CASH Did Office Supplies Increase or Decrease in this transaction?
PURCHASED OFFICE SUPPLIES FOR $800 CASH Did Office Supplies Increase or Decrease in this transaction?
 INCREASED OFFICE SUPPLIES DR. + $800 CR.
INCREASED OFFICE SUPPLIES DR. + $800 CR.
 PURCHASED OFFICE SUPPLIES FOR $800 CASH What about Cash? Increase or Decrease in this transaction?
PURCHASED OFFICE SUPPLIES FOR $800 CASH What about Cash? Increase or Decrease in this transaction?
 DECREASED CASH DR. + CR. $800
DECREASED CASH DR. + CR. $800
 RULE #2 IN EVERY TRANSACTION DEBITS MUST EQUAL CREDITS
RULE #2 IN EVERY TRANSACTION DEBITS MUST EQUAL CREDITS
 DEBITS = CREDITS OFFICE SUPPLIES DR. CR. + $800 CASH DR. CR. + $800
DEBITS = CREDITS OFFICE SUPPLIES DR. CR. + $800 CASH DR. CR. + $800
 RULE #3 LIABILITY ACCOUNTS Decrease on Debit Side Dr. Cr. + Increase on Credit Side
RULE #3 LIABILITY ACCOUNTS Decrease on Debit Side Dr. Cr. + Increase on Credit Side
 EXAMPLE: PURCHASED EQUIPMENT ON ACCOUNT FOR $3, 000.
EXAMPLE: PURCHASED EQUIPMENT ON ACCOUNT FOR $3, 000.
 STEP #1 Name the accounts affected: ACCOUNTS PAYABLE EQUIPMENT
STEP #1 Name the accounts affected: ACCOUNTS PAYABLE EQUIPMENT
 STEP #2 Determine Classification of Accounts: A SS ET LIA B ILIT Y ACCOUNTS PAYABLE EQUIPMENT
STEP #2 Determine Classification of Accounts: A SS ET LIA B ILIT Y ACCOUNTS PAYABLE EQUIPMENT
 STEP #3 Now that we know the classification, we can identify increase and decrease sides. EQUIPMENT DR. + CR. ACCOUNTS PAYABLE DR. CR. +
STEP #3 Now that we know the classification, we can identify increase and decrease sides. EQUIPMENT DR. + CR. ACCOUNTS PAYABLE DR. CR. +
 PURCHASED EQUIPMENT ON ACCOUNT FOR $3, 000. Did Equipment Increase or Decrease in this transaction?
PURCHASED EQUIPMENT ON ACCOUNT FOR $3, 000. Did Equipment Increase or Decrease in this transaction?
 INCREASED EQUIPMENT DR. + $3000 CR.
INCREASED EQUIPMENT DR. + $3000 CR.
 PURCHASED EQUIPMENT ON ACCOUNT FOR $3, 000. Accounts Payable? Increase or Decrease in this transaction?
PURCHASED EQUIPMENT ON ACCOUNT FOR $3, 000. Accounts Payable? Increase or Decrease in this transaction?
 INCREASED ACCOUNTS PAYBLE DR. CR. + $3000
INCREASED ACCOUNTS PAYBLE DR. CR. + $3000
 DEBITS = CREDITS EQUIPMENT DR. CR. + $3000 ACCOUNTS PAYABLE DR. CR. + $3000
DEBITS = CREDITS EQUIPMENT DR. CR. + $3000 ACCOUNTS PAYABLE DR. CR. + $3000
 RULE #4 CAPITAL ACCOUNT Decrease on Debit Side Dr. Cr. + JUST LIKE LIABILITY ACCOUNTS Increase on Credit Side
RULE #4 CAPITAL ACCOUNT Decrease on Debit Side Dr. Cr. + JUST LIKE LIABILITY ACCOUNTS Increase on Credit Side
 EXAMPLE: MARY ADAMS, THE OWNER, INVESTED $25, 000 IN THE BUSINESS
EXAMPLE: MARY ADAMS, THE OWNER, INVESTED $25, 000 IN THE BUSINESS
 STEPS #1 & 2 Name and classify the accounts affected: OWNER’S EQUITY M. ADAMS, CAPITAL DR. CR. ASSET CASH DR. CR.
STEPS #1 & 2 Name and classify the accounts affected: OWNER’S EQUITY M. ADAMS, CAPITAL DR. CR. ASSET CASH DR. CR.
 STEP #3 Now that we know the classification, we can identify increase and decrease sides. M. ADAMS, CAPITAL DR. CR. + CASH DR. + CR.
STEP #3 Now that we know the classification, we can identify increase and decrease sides. M. ADAMS, CAPITAL DR. CR. + CASH DR. + CR.
 INCREASED OR DECREASED? INCREASED M. ADAMS, CAPITAL DR. CR. + $25, 000 CASH DR. + $25, 000 CR.
INCREASED OR DECREASED? INCREASED M. ADAMS, CAPITAL DR. CR. + $25, 000 CASH DR. + $25, 000 CR.
 DEBITS = CREDITS CASH DR. CR. + $25, 000 M. ADAMS, CAPITAL DR. CR. + $25, 000
DEBITS = CREDITS CASH DR. CR. + $25, 000 M. ADAMS, CAPITAL DR. CR. + $25, 000
 RULE #5 DIVIDEND / DRAWING ACCOUNT Increase on the Debit Side Dr. Cr. + JUST LIKE ASSET ACCOUNTS Decrease on the Credit Side
RULE #5 DIVIDEND / DRAWING ACCOUNT Increase on the Debit Side Dr. Cr. + JUST LIKE ASSET ACCOUNTS Decrease on the Credit Side
 EXAMPLE: MARY WITHDREW $1, 500 FOR PERSONAL EXPENSES
EXAMPLE: MARY WITHDREW $1, 500 FOR PERSONAL EXPENSES
 STEPS #1 & #2 Name and classify the accounts affected: OWNER’S EQUITY M. ADAMS, DRAWING DR. CR. ASSET CASH DR. CR.
STEPS #1 & #2 Name and classify the accounts affected: OWNER’S EQUITY M. ADAMS, DRAWING DR. CR. ASSET CASH DR. CR.
 INCREASED OR DECREASED? INCREASED DECREASED M. ADAMS, DRAWING CASH DR. + $1, 500 CR. DR. + CR. $1, 500
INCREASED OR DECREASED? INCREASED DECREASED M. ADAMS, DRAWING CASH DR. + $1, 500 CR. DR. + CR. $1, 500
 DEBITS = CREDITS M. ADAMS, DRAWING DR. CR. + $1, 500 CASH DR. CR. + $1, 500
DEBITS = CREDITS M. ADAMS, DRAWING DR. CR. + $1, 500 CASH DR. CR. + $1, 500
 RULE #6 REVENUE ACCOUNTS Decrease on Debit Side Dr. Cr. + JUST LIKE LIABILITY & CAPITAL ACCOUNTS Increase on Credit Side
RULE #6 REVENUE ACCOUNTS Decrease on Debit Side Dr. Cr. + JUST LIKE LIABILITY & CAPITAL ACCOUNTS Increase on Credit Side
 EXAMPLE: MARY PERFORMED SERVICES AND RECEIVED $4, 500 IN CASH
EXAMPLE: MARY PERFORMED SERVICES AND RECEIVED $4, 500 IN CASH
 STEPS #1 & #2 Name and classify the accounts affected: REVENUE CONSULTING FEES DR. CR. ASSET CASH DR. CR.
STEPS #1 & #2 Name and classify the accounts affected: REVENUE CONSULTING FEES DR. CR. ASSET CASH DR. CR.
 STEP #3 Now that we know the classification, we can identify increase and decrease sides. CONSULTING FEES DR. CR. + CASH DR. + CR.
STEP #3 Now that we know the classification, we can identify increase and decrease sides. CONSULTING FEES DR. CR. + CASH DR. + CR.
 INCREASED OR DECREASED? INCREASED CONSULTING FEES DR. CASH CR. DR. $4, 500 + + CR.
INCREASED OR DECREASED? INCREASED CONSULTING FEES DR. CASH CR. DR. $4, 500 + + CR.
 DEBITS = CREDITS CASH DR. CR. + $4, 500 CONSULTING FEES DR. CR. + $4, 500
DEBITS = CREDITS CASH DR. CR. + $4, 500 CONSULTING FEES DR. CR. + $4, 500
 EXAMPLE: MARY PERFORMED $6, 000 OF SERVICES ON ACCOUNT
EXAMPLE: MARY PERFORMED $6, 000 OF SERVICES ON ACCOUNT
 DEBITS = CREDITS ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE DR. CR. + $6, 000 ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE INSTEAD OF CASH CONSULT. FEES DR. CR. + $6, 000
DEBITS = CREDITS ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE DR. CR. + $6, 000 ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE INSTEAD OF CASH CONSULT. FEES DR. CR. + $6, 000
 RULE #7 EXPENSE ACCOUNTS Increase on the Debit Side Dr. Cr. + JUST LIKE ASSET ACCOUNTS Decrease on the Credit Side
RULE #7 EXPENSE ACCOUNTS Increase on the Debit Side Dr. Cr. + JUST LIKE ASSET ACCOUNTS Decrease on the Credit Side
 EXAMPLE MARY ADAMS PAID HER ASSISTANT $750 IN WAGES
EXAMPLE MARY ADAMS PAID HER ASSISTANT $750 IN WAGES
 STEPS #1 & #2 Name and classify the accounts affected: EXPENSE WAGES EXPENSE DR. CR. ASSET CASH DR. CR.
STEPS #1 & #2 Name and classify the accounts affected: EXPENSE WAGES EXPENSE DR. CR. ASSET CASH DR. CR.
 STEP #3 Now that we know the classification, we can identify increase and decrease sides. WAGES EXPENSE DR. + CR. CASH DR. + CR.
STEP #3 Now that we know the classification, we can identify increase and decrease sides. WAGES EXPENSE DR. + CR. CASH DR. + CR.
 INCREASED OR DECREASED? INCREASED DECREASED WAGES EXPENSE DR. + $750 CR. CASH DR. + CR. $750
INCREASED OR DECREASED? INCREASED DECREASED WAGES EXPENSE DR. + $750 CR. CASH DR. + CR. $750
 DEBITS = CREDITS WAGES EXPENSE DR. CR. + $750 CASH DR. CR. + $750
DEBITS = CREDITS WAGES EXPENSE DR. CR. + $750 CASH DR. CR. + $750
 Whichever side you increase is the NORMAL balance!
Whichever side you increase is the NORMAL balance!

 Expansion of Basic Equation Assets Liabilities Equity Retained Earnings Dr Cr + - - + - + Revenue Expenses Dividends Dr Cr - + + + - - Accounting Education Drives = Large Rich Enterprises Assets Expenses Dividends Liabilities Revenues Equity
Expansion of Basic Equation Assets Liabilities Equity Retained Earnings Dr Cr + - - + - + Revenue Expenses Dividends Dr Cr - + + + - - Accounting Education Drives = Large Rich Enterprises Assets Expenses Dividends Liabilities Revenues Equity
 Review What is the normal balance for the following accounts? Cash Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable Service Revenue Common Stock Salaries Expense Debit Credit Debit
Review What is the normal balance for the following accounts? Cash Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable Service Revenue Common Stock Salaries Expense Debit Credit Debit
 Review What is the normal balance for the following accounts? Dividends Building Taxes Payable Unearned Revenus Prepaid Insurance Rent Expense Debit Credit Debit
Review What is the normal balance for the following accounts? Dividends Building Taxes Payable Unearned Revenus Prepaid Insurance Rent Expense Debit Credit Debit
 GENERAL JOURNAL Date Account Titles and Explanations Oct. 1 Cash Common Stock Issued common stock for cash Debit Credit 10, 000 Cash 5, 000 Notes Payable Issued 3 -month, 12% note payable for cash Office Equipment Cash Purchased office equipment for cash 5, 000
GENERAL JOURNAL Date Account Titles and Explanations Oct. 1 Cash Common Stock Issued common stock for cash Debit Credit 10, 000 Cash 5, 000 Notes Payable Issued 3 -month, 12% note payable for cash Office Equipment Cash Purchased office equipment for cash 5, 000
 Posting Entries GENERAL JOURNAL Oct. 1 Cash Common Stock 10, 000 Issued common stock for cash Account CASH Date ref Debit Acct 1010 Balance Debit Credit Account COMMON STOCK Date ref Debit Credit Acct 3010 Balance Debit Credit
Posting Entries GENERAL JOURNAL Oct. 1 Cash Common Stock 10, 000 Issued common stock for cash Account CASH Date ref Debit Acct 1010 Balance Debit Credit Account COMMON STOCK Date ref Debit Credit Acct 3010 Balance Debit Credit
 Posting Entries GENERAL JOURNAL Oct. 1 Cash Common Stock 10, 000 Issued common stock for cash Account CASH Date Oct 1 ref gj 1 Debit Credit 10, 000 Acct 1010 Balance Debit Credit 10, 000 Account COMMON STOCK Date Oct 1 ref gj 1 Debit Acct 3010 Balance Credit Debit Credit 10, 000
Posting Entries GENERAL JOURNAL Oct. 1 Cash Common Stock 10, 000 Issued common stock for cash Account CASH Date Oct 1 ref gj 1 Debit Credit 10, 000 Acct 1010 Balance Debit Credit 10, 000 Account COMMON STOCK Date Oct 1 ref gj 1 Debit Acct 3010 Balance Credit Debit Credit 10, 000
 TRIAL BALANCE l List of all accounts with a balance l Including their balances l Total all debits and all credits l Prove debits equal credits l Used as an aid in preparing financial statements
TRIAL BALANCE l List of all accounts with a balance l Including their balances l Total all debits and all credits l Prove debits equal credits l Used as an aid in preparing financial statements
 Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Debit Balance Credit Balance HEADING should include: èName of the Company èTitle of Document “Trial Balance” èDate of the Trial Balance
Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Debit Balance Credit Balance HEADING should include: èName of the Company èTitle of Document “Trial Balance” èDate of the Trial Balance
 Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Delivery Equipment Debit Balance Credit Balance 370 00 650 00 80 00 200 00 3600 00 All Asset accounts listed first
Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Delivery Equipment Debit Balance Credit Balance 370 00 650 00 80 00 200 00 3600 00 All Asset accounts listed first
 Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Delivery Equipment Accounts Payable Liabilities are shown next Debit Balance Credit Balance 370 00 650 00 80 00 200 00 3600 00 1800 00
Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Delivery Equipment Accounts Payable Liabilities are shown next Debit Balance Credit Balance 370 00 650 00 80 00 200 00 3600 00 1800 00
 Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Delivery Equipment Accounts Payable Jessica Jane, Capital Jessica Jane, Drawing Debit Balance Credit Balance 370 00 650 00 80 00 200 00 3600 00 1800 00 2000 00 150 00 Now the Owner’s Equity Accounts
Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Delivery Equipment Accounts Payable Jessica Jane, Capital Jessica Jane, Drawing Debit Balance Credit Balance 370 00 650 00 80 00 200 00 3600 00 1800 00 2000 00 150 00 Now the Owner’s Equity Accounts
 Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Delivery Equipment Accounts Payable Jessica Jane, Capital Jessica Jane, Drawing Delivery Fees Then Debit Balance Credit Balance 370 00 650 00 80 00 200 00 3600 00 1800 00 2000 00 150 00 2150 00 the R e venue Accou n t
Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Delivery Equipment Accounts Payable Jessica Jane, Capital Jessica Jane, Drawing Delivery Fees Then Debit Balance Credit Balance 370 00 650 00 80 00 200 00 3600 00 1800 00 2000 00 150 00 2150 00 the R e venue Accou n t
 Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Delivery Equipment Accounts Payable Jessica Jane, Capital Jessica Jane, Drawing Delivery Fees Wages Expense Rent Expense Telephone Expense Debit Balance Credit Balance 370 00 650 00 80 00 200 00 3600 00 ses 1800 00 pen Ex 2000 00 he t ly, 150 00 nal Fi 2150 00 650 00 200 00 50 00
Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Cash Accounts Receivable Supplies Prepaid Insurance Delivery Equipment Accounts Payable Jessica Jane, Capital Jessica Jane, Drawing Delivery Fees Wages Expense Rent Expense Telephone Expense Debit Balance Credit Balance 370 00 650 00 80 00 200 00 3600 00 ses 1800 00 pen Ex 2000 00 he t ly, 150 00 nal Fi 2150 00 650 00 200 00 50 00
 Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Debit Balance Credit Balance Cash 370 00 Accounts Receivable 650 00 Supplies 80 00 Prepaid Insurance It Balances!!! 200 00 Delivery Equipment 3600 00 Debits = Credits Accounts Payable 1800 00 Jessica Jane, Capital 2000 00 Jessica Jane, Drawing 150 00 Delivery Fees 2150 00 Wages Expense 650 00 Rent Expense 200 00 Telephone Expense 50 00 5950 00
Jessica Jane’s Campus Delivery Trial Balance June 30, 20 -Account Title Debit Balance Credit Balance Cash 370 00 Accounts Receivable 650 00 Supplies 80 00 Prepaid Insurance It Balances!!! 200 00 Delivery Equipment 3600 00 Debits = Credits Accounts Payable 1800 00 Jessica Jane, Capital 2000 00 Jessica Jane, Drawing 150 00 Delivery Fees 2150 00 Wages Expense 650 00 Rent Expense 200 00 Telephone Expense 50 00 5950 00





