171c278ec0dd38fcc56d4cf745c0c8a6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Chapter Three IT Risks and Controls 1
Chapter Three IT Risks and Controls 1
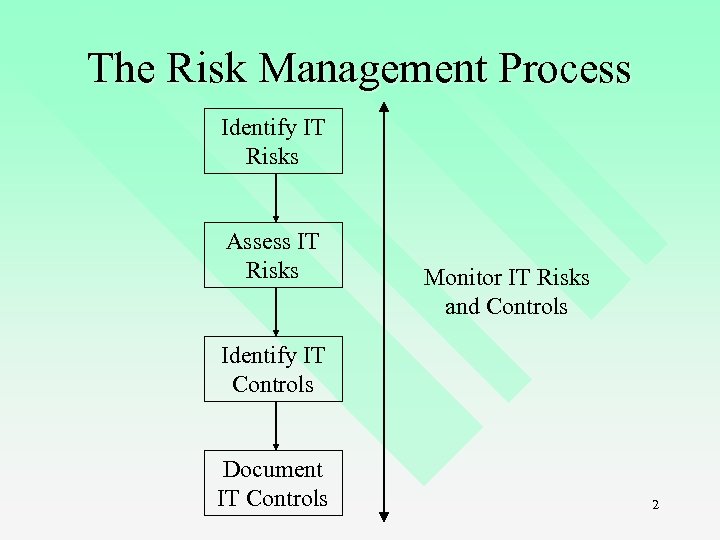 The Risk Management Process Identify IT Risks Assess IT Risks Monitor IT Risks and Controls Identify IT Controls Document IT Controls 2
The Risk Management Process Identify IT Risks Assess IT Risks Monitor IT Risks and Controls Identify IT Controls Document IT Controls 2
 Types of IT Risks Business risk n Audit risk = IR * CR * DR n – inherent risk (IR) – control risk (CR) – detection risk (DR) Security risk n Continuity risk n 3
Types of IT Risks Business risk n Audit risk = IR * CR * DR n – inherent risk (IR) – control risk (CR) – detection risk (DR) Security risk n Continuity risk n 3
 Assessing IT Risk n Threats and vulnerabilities Risk (residual risk) = + Expected value of risk (Asset Value * Risk Likelihood) – Percentage of risk mitigated by the current controls + Uncertainty of knowledge about the vulnerability n Risk indicators and risk measurement – Risks relative to IT processes 4
Assessing IT Risk n Threats and vulnerabilities Risk (residual risk) = + Expected value of risk (Asset Value * Risk Likelihood) – Percentage of risk mitigated by the current controls + Uncertainty of knowledge about the vulnerability n Risk indicators and risk measurement – Risks relative to IT processes 4
 Valuation of Asset n Assets: People, Data, Hardware, Software, Facilities, (Procedures) n Valuation Methods – Criticallity to the organization’s success – Revenue generated – Profitability – Cost to replace – Cost to protect – Embarrassment/Liability 5
Valuation of Asset n Assets: People, Data, Hardware, Software, Facilities, (Procedures) n Valuation Methods – Criticallity to the organization’s success – Revenue generated – Profitability – Cost to replace – Cost to protect – Embarrassment/Liability 5
 Internal Control (IC) n COSO – 5 components of IC – – – n Control environment Risk assessment Control activities Information and communication Monitoring International IC Standards – Cadbury – Co. Co – Other country standards 6
Internal Control (IC) n COSO – 5 components of IC – – – n Control environment Risk assessment Control activities Information and communication Monitoring International IC Standards – Cadbury – Co. Co – Other country standards 6
 Quality Control Standards ISO 9000 series – certifies that organizations comply with documented quality standards n Six Sigma – an approach to process and quality improvement n 7
Quality Control Standards ISO 9000 series – certifies that organizations comply with documented quality standards n Six Sigma – an approach to process and quality improvement n 7
 Statements on Auditing Standards Issued by AICPA’s Accounting Standards Board n SAS 78 Consideration of IC in a Financial Statement Audit: An Amendment to SAS No. 55 n SAS 94 The Effect of IT on the Auditor’s Consideration of IC in a Financial Staetment Audit n New standards related to risk assessment n 8
Statements on Auditing Standards Issued by AICPA’s Accounting Standards Board n SAS 78 Consideration of IC in a Financial Statement Audit: An Amendment to SAS No. 55 n SAS 94 The Effect of IT on the Auditor’s Consideration of IC in a Financial Staetment Audit n New standards related to risk assessment n 8
 ISACA’s Cobi. T n n Integrates IC with information and IT Three dimensions: information criteria, IT processes, and IT resources Requirements (information criteria) of quality, fiduciary, and security Organizes IT internal control into domains and processes – Domains: planning and organization, acquisition and implementation, delivery and support, and monitoring – Processes detail steps in each domain 9
ISACA’s Cobi. T n n Integrates IC with information and IT Three dimensions: information criteria, IT processes, and IT resources Requirements (information criteria) of quality, fiduciary, and security Organizes IT internal control into domains and processes – Domains: planning and organization, acquisition and implementation, delivery and support, and monitoring – Processes detail steps in each domain 9
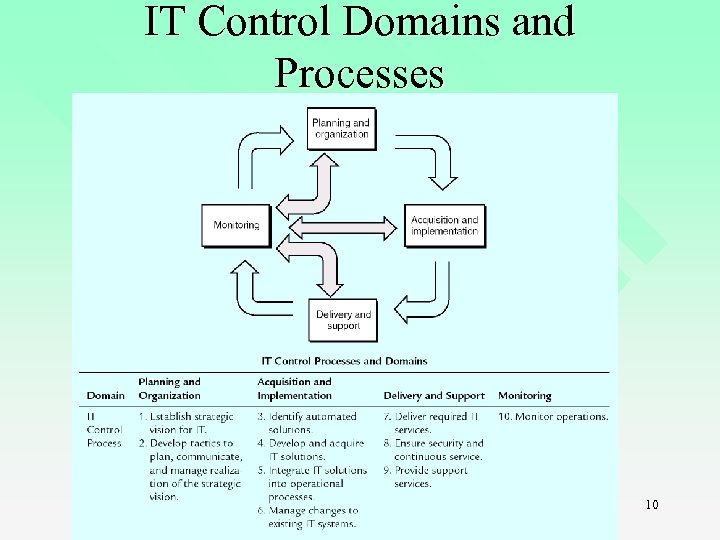 IT Control Domains and Processes 10
IT Control Domains and Processes 10
 IT Controls n COSO identifies two groups of IT controls: – Application controls – apply to specific applications and programs, and ensure data validity, completeness and accuracy – General controls – apply to all systems and address IT governance and infrastructure, security of operating systems and databases, and application and program acquisition and development A 574 Internal Controls For Business 11
IT Controls n COSO identifies two groups of IT controls: – Application controls – apply to specific applications and programs, and ensure data validity, completeness and accuracy – General controls – apply to all systems and address IT governance and infrastructure, security of operating systems and databases, and application and program acquisition and development A 574 Internal Controls For Business 11
 Segregation of Duties n. Transaction authorization is separate from transaction processing. n. Asset custody is separate from record-keeping responsibilities. n. The tasks needed to process the transactions are subdivided so that fraud requires collusion. A 574 Internal Controls For Business 12
Segregation of Duties n. Transaction authorization is separate from transaction processing. n. Asset custody is separate from record-keeping responsibilities. n. The tasks needed to process the transactions are subdivided so that fraud requires collusion. A 574 Internal Controls For Business 12
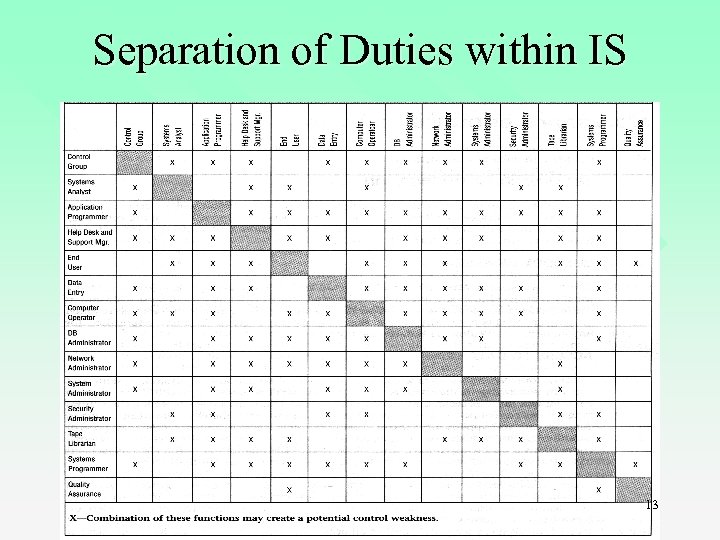 Separation of Duties within IS 13
Separation of Duties within IS 13
 Classification of Controls n. Preventive Controls: Issue is prevented from occurring – cash receipts are immediately deposited to avoid loss n. Detective Controls: Issue is discovered – unauthorized disbursement is discovered during reconciliation n. Corrective Controls: issue is corrected – erroneous data is entered in the system and reported on an error and summary report; a clerk re-enters the data 14
Classification of Controls n. Preventive Controls: Issue is prevented from occurring – cash receipts are immediately deposited to avoid loss n. Detective Controls: Issue is discovered – unauthorized disbursement is discovered during reconciliation n. Corrective Controls: issue is corrected – erroneous data is entered in the system and reported on an error and summary report; a clerk re-enters the data 14
 Application Control Goals For business event inputs, ensure – Input validity – Input completeness – Input accuracy n For master data, ensure – Update completeness – Update accuracy n 15
Application Control Goals For business event inputs, ensure – Input validity – Input completeness – Input accuracy n For master data, ensure – Update completeness – Update accuracy n 15
 Application Control Goals n Input validity – Input data approved and represent actual economic events and objects n Input completeness – Requires that all valid events or objects be captured and entered into the system n Input Accuracy – Requires that events be correctly captured and entered into the system 16
Application Control Goals n Input validity – Input data approved and represent actual economic events and objects n Input completeness – Requires that all valid events or objects be captured and entered into the system n Input Accuracy – Requires that events be correctly captured and entered into the system 16
 Systems Reliability Assurance Sys. Trust n Web. Trust n New AICPA Trust Principles n 17
Systems Reliability Assurance Sys. Trust n Web. Trust n New AICPA Trust Principles n 17
 Documenting IT Controls Internal control narratives n Flowcharts – internal control flowchart n IC questionnaires n 18
Documenting IT Controls Internal control narratives n Flowcharts – internal control flowchart n IC questionnaires n 18
 Risk Control Strategies n Avoidance – Policy, Training and Education, or Technology n Transference – shifting the risk to other assets, processes, or organizations (insurance, outsourcing, etc. ) n Mitigation – reducing the impact through planning and preparation n Acceptance – doing nothing if the cost of protection does not justify the expense of the control 19
Risk Control Strategies n Avoidance – Policy, Training and Education, or Technology n Transference – shifting the risk to other assets, processes, or organizations (insurance, outsourcing, etc. ) n Mitigation – reducing the impact through planning and preparation n Acceptance – doing nothing if the cost of protection does not justify the expense of the control 19
 Monitoring IT Risks and Controls Cobi. T control objectives associated with monitoring and evaluation n Need for independent assurance and audit of IT controls n 20
Monitoring IT Risks and Controls Cobi. T control objectives associated with monitoring and evaluation n Need for independent assurance and audit of IT controls n 20
 21
21


