f61e07de3dfda11bc6acc93754dd6bf3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Chapter Seventeen FOREIGN POLICY AND NATIONAL SECURITY Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning
Chapter Seventeen FOREIGN POLICY AND NATIONAL SECURITY Copyright © 2014 Cengage Learning
 Learning Outcomes 2 1. Define foreign policy, diplomacy and national security policy, and explain how these policies shape the position of the United States in the world. 2. Explain the role of the president in setting foreign policy and national security policy, and compare those powers to the powers of the Congress. Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Learning Outcomes 2 1. Define foreign policy, diplomacy and national security policy, and explain how these policies shape the position of the United States in the world. 2. Explain the role of the president in setting foreign policy and national security policy, and compare those powers to the powers of the Congress. Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 Learning Outcomes 3 3. Trace the evolution of United States foreign policy from isolationism to global leadership. 4. Explain the origins of the war on terror and how it has influenced domestic policy and relations with other nations. 5. Discuss the security and diplomatic challenges facing the United States today. Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Learning Outcomes 3 3. Trace the evolution of United States foreign policy from isolationism to global leadership. 4. Explain the origins of the war on terror and how it has influenced domestic policy and relations with other nations. 5. Discuss the security and diplomatic challenges facing the United States today. Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 Facing the World: Foreign and Defense Policy 4 § Foreign policy includes techniques and strategies used to achieve external goals and the goals themselves. § Techniques include: § § Diplomacy Economic aid Technical assistance Military intervention Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Facing the World: Foreign and Defense Policy 4 § Foreign policy includes techniques and strategies used to achieve external goals and the goals themselves. § Techniques include: § § Diplomacy Economic aid Technical assistance Military intervention Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 Facing the World: Foreign and Defense Policy 5 § National security policy § Protects U. S. independence and political integrity § Defense against actual or potential threat, either foreign or domestic § Influenced by Department of Defense, Department of State, NSC and other agencies § Defense policy § Subset of national security policy § Directs scale and size of armed forces Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Facing the World: Foreign and Defense Policy 5 § National security policy § Protects U. S. independence and political integrity § Defense against actual or potential threat, either foreign or domestic § Influenced by Department of Defense, Department of State, NSC and other agencies § Defense policy § Subset of national security policy § Directs scale and size of armed forces Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 Facing the World: Foreign and Defense Policy 6 § Diplomacy § Conducts nation’s external relationships § Settles disputes peacefully § Negotiating techniques used to carry out foreign policy § Only successful if participants willing Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Facing the World: Foreign and Defense Policy 6 § Diplomacy § Conducts nation’s external relationships § Settles disputes peacefully § Negotiating techniques used to carry out foreign policy § Only successful if participants willing Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 Who Makes Foreign Policy? 7 § Constitutional powers of the president § War powers § § President is commander in chief Approval of covert operations/surveillance Treaties and executive agreements Other powers § § Appointment Recognize foreign governments Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Who Makes Foreign Policy? 7 § Constitutional powers of the president § War powers § § President is commander in chief Approval of covert operations/surveillance Treaties and executive agreements Other powers § § Appointment Recognize foreign governments Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 White House Situation Room 8 Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
White House Situation Room 8 Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 Who Makes Foreign Policy? 9 § Informal techniques of presidential leadership § Tradition, precedent, personality Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Who Makes Foreign Policy? 9 § Informal techniques of presidential leadership § Tradition, precedent, personality Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 Who Makes Foreign Policy? 10 § Other sources of foreign policymaking § Department of State § National Security Council § Intelligence community § § § Covert actions Criticisms, especially after 9/11 Department of Defense Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Who Makes Foreign Policy? 10 § Other sources of foreign policymaking § Department of State § National Security Council § Intelligence community § § § Covert actions Criticisms, especially after 9/11 Department of Defense Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 The Pentagon 11 Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
The Pentagon 11 Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 Who Makes Foreign Policy? 12 § Congress balances the presidency § War Powers Resolution (1973) § § Passed over President Nixon’s veto Limits president’s military actions without approval Limits on presidential military requests Political considerations Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Who Makes Foreign Policy? 12 § Congress balances the presidency § War Powers Resolution (1973) § § Passed over President Nixon’s veto Limits president’s military actions without approval Limits on presidential military requests Political considerations Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 Domestic Sources of Foreign Policy 13 § Elite and mass opinion § Elite organizations § Attentive public § Interest group politics § Military-industrial complex § Congressional support in states that benefit Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Domestic Sources of Foreign Policy 13 § Elite and mass opinion § Elite organizations § Attentive public § Interest group politics § Military-industrial complex § Congressional support in states that benefit Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
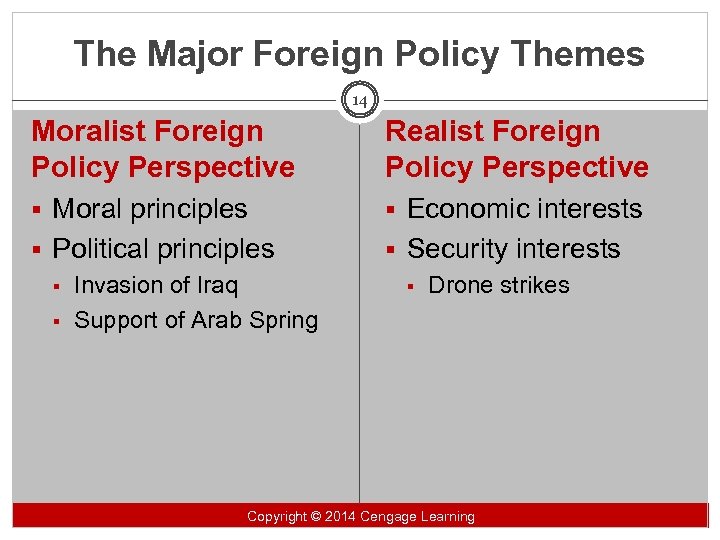 The Major Foreign Policy Themes 14 Moralist Foreign Policy Perspective Realist Foreign Policy Perspective § Moral principles § Economic interests § Political principles § Invasion of Iraq § Support of Arab Spring § Security interests § Drone strikes Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
The Major Foreign Policy Themes 14 Moralist Foreign Policy Perspective Realist Foreign Policy Perspective § Moral principles § Economic interests § Political principles § Invasion of Iraq § Support of Arab Spring § Security interests § Drone strikes Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 The Major Foreign Policy Themes 15 § Formative Years: Avoiding Entanglements § Little international power in early years § Monroe Doctrine and isolationism § Spanish-American War and World War I § 1920 s “back to normalcy” Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
The Major Foreign Policy Themes 15 § Formative Years: Avoiding Entanglements § Little international power in early years § Monroe Doctrine and isolationism § Spanish-American War and World War I § 1920 s “back to normalcy” Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 The Major Foreign Policy Themes 16 § Era of Internationalism § World War II § The Cold War § Containment policy § § Truman Doctrine NATO Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
The Major Foreign Policy Themes 16 § Era of Internationalism § World War II § The Cold War § Containment policy § § Truman Doctrine NATO Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 The Major Foreign Policy Themes 17 § Superpower Relations § Cuba missile crisis § Period of détente § § § SALT I Reagan-Bush years Dissolution of the Soviet Union Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
The Major Foreign Policy Themes 17 § Superpower Relations § Cuba missile crisis § Period of détente § § § SALT I Reagan-Bush years Dissolution of the Soviet Union Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 The Major Foreign Policy Themes 18 § The War on Terrorism § New kind of war after 9/11 attacks § U. S. presence in Afghanistan and Iraq § Preemptive war strategy (Bush doctrine) Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
The Major Foreign Policy Themes 18 § The War on Terrorism § New kind of war after 9/11 attacks § U. S. presence in Afghanistan and Iraq § Preemptive war strategy (Bush doctrine) Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 The Major Foreign Policy Themes 19 § Iraq and Afghanistan wars § First Gulf War § Iraq War § Occupied Iraq § The situation worsens § The Bush surge Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
The Major Foreign Policy Themes 19 § Iraq and Afghanistan wars § First Gulf War § Iraq War § Occupied Iraq § The situation worsens § The Bush surge Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
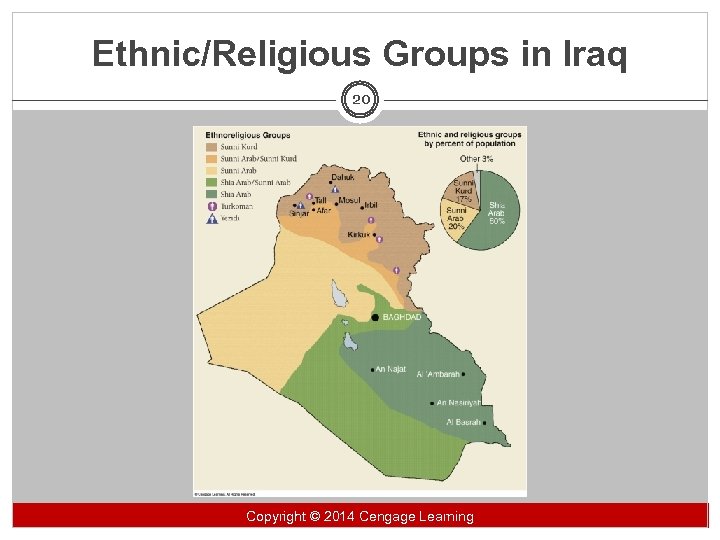 Ethnic/Religious Groups in Iraq 20 Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Ethnic/Religious Groups in Iraq 20 Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 Global Policy Challenges 21 § The emerging world order § Threat of terrorism § Terrorism and regional strife § Terrorist attacks against foreign civilians § London bombings Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Global Policy Challenges 21 § The emerging world order § Threat of terrorism § Terrorism and regional strife § Terrorist attacks against foreign civilians § London bombings Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 Global Policy Challenges 22 § Nuclear weapons § United States and the Soviet Union § Nuclear proliferation § § Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (Senate rejects) Working with allies to prevent nuclear Iran Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Global Policy Challenges 22 § Nuclear weapons § United States and the Soviet Union § Nuclear proliferation § § Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (Senate rejects) Working with allies to prevent nuclear Iran Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 The United States and Regional Conflicts 23 § Often over trade, weapons acquisition or political differences § The Middle East § § § Israel and the Palestinians The Arab Spring Iranian ambitions Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
The United States and Regional Conflicts 23 § Often over trade, weapons acquisition or political differences § The Middle East § § § Israel and the Palestinians The Arab Spring Iranian ambitions Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
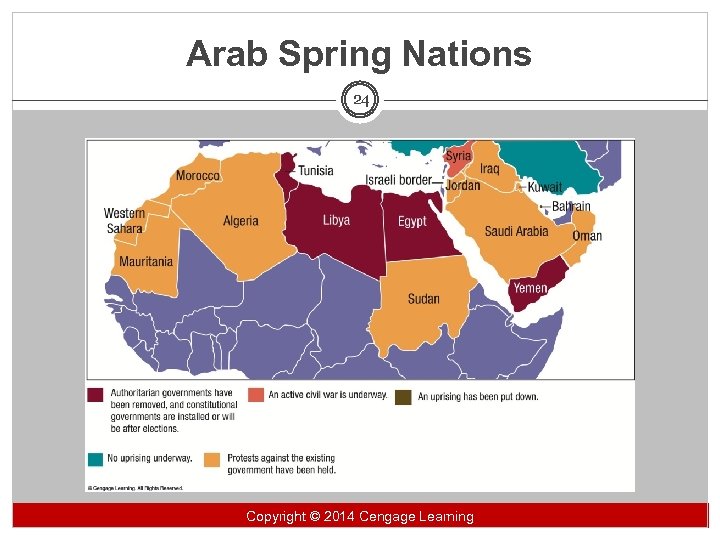 Arab Spring Nations 24 Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
Arab Spring Nations 24 Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
 The United States and Regional Conflicts 25 § Central and South America § Mostly protective attitude toward “neighbors” § Continuous tensions with Cuba § Venezuela and President Chavez § War and HIV/AIDS in Africa § U. S. trying to help with health issues § No direct intervention in conflicts and unstable regimes Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning
The United States and Regional Conflicts 25 § Central and South America § Mostly protective attitude toward “neighbors” § Continuous tensions with Cuba § Venezuela and President Chavez § War and HIV/AIDS in Africa § U. S. trying to help with health issues § No direct intervention in conflicts and unstable regimes Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning Copyright ©© 2014 Cengage Learning


