754f5e7e8c4121a9421b90c36e451317.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

CHAPTER SEVEN SEGMENTING AND TARGETING MARKETS Prepared by Jack Gifford Miami University (Ohio) © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 1

WHAT IS A MARKET? X A market is (1) people or organizations with (2) needs or wants and with (3) the ability and (4) the willingness to buy. A group of people that lacks any one of these characteristics is not a market. QUALIFIERS INDIVIDUALS NEEDS PRODUCTS ABILITY WILLINGNESS ORGANIZATIONS WANTS © 2000 SERVICES South-Western College Publishing AUTHORITY 2

TYPES OF MARKETS? X CONSUMER: Intend to consume or benefit, but not to make a profit X ORGANIZATIONAL: Resale Direct use in production Use in daily operations © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 3

THE IMPORTANCE OF MARKET SEGMENTATION X Market segmentation plays a key role in the marketing strategy of almost all successful organizations. X Because market segments differ in size and potential, segmentation helps decision makers more accurately define marketing objectives and better allocate resources. © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 4

MARKET SEGMENTATION X There are very few products which can be sold to all people or organizations. Therefore, marketers must segment potential customers into subsets, or target markets that can be effectively and efficiently reached. X A viable target market must be… © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 5

VIABLE TARGET MARKETS X IDENTIFIABLE X MEASURABLE X ACCESSIBLE X SUBSTANTIAL X RESPONSIVE © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 6

MARKET SEGMENTATION X Almost any variable may be used as a segmentation variable as long as the marketer remembers… Not all buyers are alike Meaningful sub groups must have similar purchasing motives Every time a marketer adds another segmentation dimension, the market gets smaller © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 7

MAYBE I WON’T SEGMENT MY MARKET AT ALL X MASS MARKETING + Economies of scale + Appropriate if all consumers have the same needs and wants + Simplicity ------------------- Ideal method IF all consumers have identical purchasing motives. Reality = RARELY HAPPENS © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 8
DEVELOPING A TARGET MARKET STRATEGY X Analyze consumer demand X Segment the market into like clusters X Select one or more segments to target with a specific marketing mix X Position the product or service so that it is perceived by each target market segment as satisfying their needs better than the opposition. © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 9
COMMON CONSUMER MARKET SEGMENTATON BASES X Geographic segmentation X Demographic segmentation X Family Life-Style segmentation X Psychographic segmentation X Behavioral segmentation Occasions Benefits sought User rates Loyalty X Personal characteristics X Multi-dimensional cross-classification segmentation matrices © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 10

GEOGRAPHIC AND DEMOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION X GEOGRAPHIC X DEMOGRAPHICS USA / JAPAN / AUSTRALIA SMALL TOWNS TOURIST DESTINATIONS RURAL LIVING CLIMATE POPULATION DENSITY © 2000 MARITAL STATUS INCOME EDUCATION OCCUPATION ETHNIC GENDER AGE RELIGION South-Western College Publishing 11

FAMILY LIFE STYLE SEGMENTATION X FAMILY LIFE STYLE SINGLE YOUNG MARRIED W/O CHILDREN YOUNG MARRIED WITH CHILDREN MIDDLE AGED MARRIED W/O DEPENDENT CHILDREN OLDER MARRIED OLDER UNMARRIED © 2000 South-Western College Publishing DIVORCED WITH CHILDREN DIVORCED WITHOUT CHILDREN YOUNG MIDDLE AGED OLD 12
PSYCHOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION X PERSONALITY VALS 2 X MOTIVES • RESOURCES X LIFESTYLES • SELF-ORIENTATION X VALUES X ATTITUDES X BELIEFS X PERCEPTIONS OF RISK X REFERENCE GROUPS X NEEDS © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 13
BEHAVIORAL SEGMENTATION X BENEFIT • Nutrition, taste, calories, value to price, alcohol content, longevity, etc. SEGMENTATION X USAGE • Light, medium or heavy user; purchase pattern, how product is used, family or economy size vs singles, etc. SEGMENTATION X LOYALTY • Level of brand, company, family of brands, store loyalty; situation specific brand loyalty SEGMENTATION © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 14

THE 80/20 PRINCIPLE X 20% OF YOUR CUSTOMERS ACCOUNT FOR 80% OF YOUR PROFITABLE SALES. © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 15
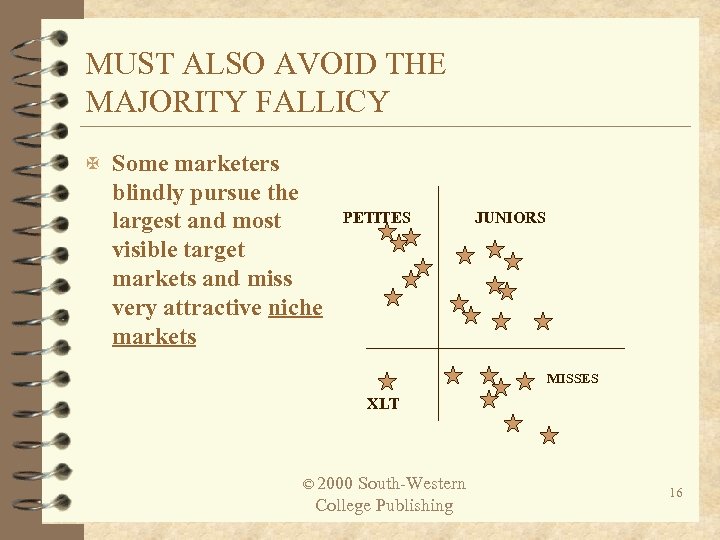
MUST ALSO AVOID THE MAJORITY FALLICY X Some marketers blindly pursue the largest and most visible target markets and miss very attractive niche markets PETITES JUNIORS MISSES XLT © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 16
BASIS FOR SEGMENTING BUSINESS MARKETS X PRODUCERS Marketers further divide one or more of these segments into microsegmentation or macrosegmentation variables X RESELLERS X INSTITUTIONS X GOVERNMENT © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 17
MACROSEGMENTATION VARIABLES X Geographic location X Customer type X Customer size For example, Home Depot (retailer) targets two principal segments: X Product use Professionals © 2000 South-Western College Publishing DIY Consumers 18
MICROSEGMENTATION EXAMPLES X Key purchasing criteria • Technical support • Product quality X Purchasing strategies • Satisficers • Optimizers X Importance of purchase • Routine & small • Major expenditure X Personal characteristics © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 19
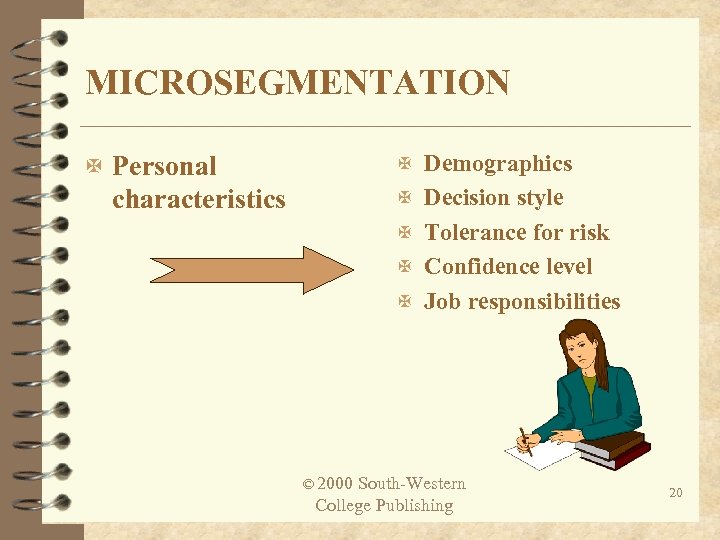
MICROSEGMENTATION X Demographics X Personal characteristics X Decision style X Tolerance for risk X Confidence level X Job responsibilities © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 20

STEPS IN SEGMENTING A MARKET 1 Select a market or product category for study 2 Choose a basis or bases for segmenting the market 3 Select the specific segmentation variables for use (descriptors) 4 Profile and evaluate segment(s) A B C D E F Size Expected growth Purchase frequency Current brand usage Brand loyalty Long-term sales and profit potential © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 21

STEPS IN SEGMENTING A MARKET 5 Select the target market(s) 6 Design, implement and maintain appropriate marketing mixes (product, price, promotion, distribution) Steps five and six are actually marketing activities that follow market segmentation, but are natural outcomes of the segmentation process. © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 22
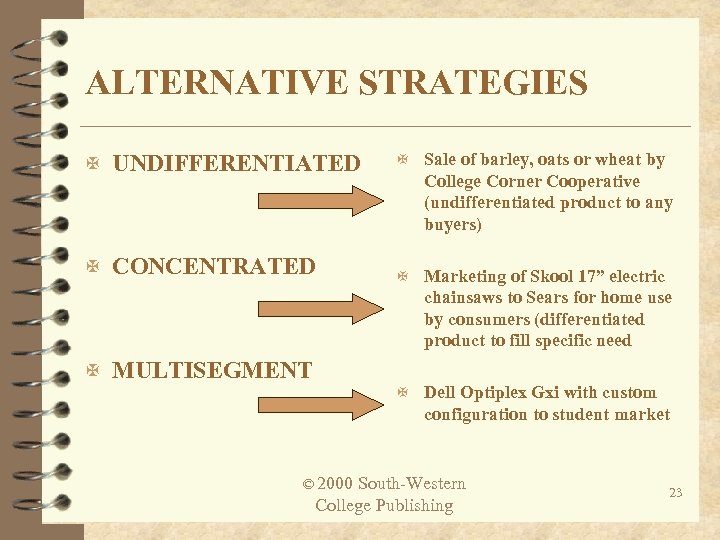
ALTERNATIVE STRATEGIES X UNDIFFERENTIATED X Sale of barley, oats or wheat by X CONCENTRATED X Marketing of Skool 17” electric College Corner Cooperative (undifferentiated product to any buyers) chainsaws to Sears for home use by consumers (differentiated product to fill specific need X MULTISEGMENT X Dell Optiplex Gxi with custom configuration to student market © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 23
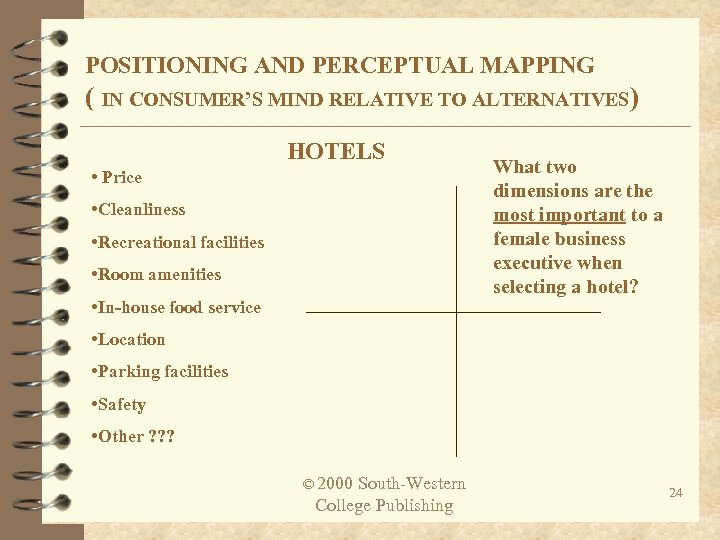
POSITIONING AND PERCEPTUAL MAPPING ( IN CONSUMER’S MIND RELATIVE TO ALTERNATIVES) HOTELS • Price • Cleanliness • Recreational facilities • Room amenities • In-house food service What two dimensions are the most important to a female business executive when selecting a hotel? • Location • Parking facilities • Safety • Other ? ? ? © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 24

PERCEPTUAL MAP: HOTELS 1 Days Inn/Ameri. Host 2 Embassy Suites 3 Holiday Inn 4 Holiday Express 5 Howard Johnson 6 Hyatt Using your two dimensions, where would you place on this perceptual map each of these hotels? © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 25

REPOSITIONING X Sometimes a firm finds itself in a quadrant of the perceptual map that has become saturated with competing customers. In this case the company may choose to REPOSITION itself in a less competitive quadrant to draw customers who value other product or service attributes © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 26

GLOBAL SEGMENTATION © 2000 South-Western College Publishing 27
754f5e7e8c4121a9421b90c36e451317.ppt