7ef5eff1a8a19d185fbd68937aea6f0c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Chapter Overview n n TCP/IP Services TCP/IP Utilities 1
Chapter Overview n n TCP/IP Services TCP/IP Utilities 1
 Automated TCP/IP Configuration Solutions n n n Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 2
Automated TCP/IP Configuration Solutions n n n Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 2
 RARP n n Uses the same message format as Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Designed for diskless workstations Supplies an Internet Protocol (IP) address only No longer used 3
RARP n n Uses the same message format as Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Designed for diskless workstations Supplies an Internet Protocol (IP) address only No longer used 3
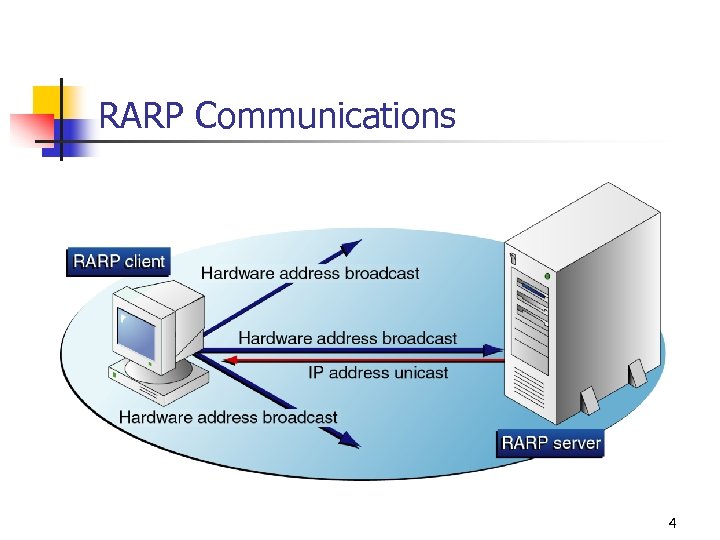 RARP Communications 4
RARP Communications 4
 BOOTP n n n Supplies an IP address and other Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) parameters Can supply an executable boot file using Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) Requires you to manually configure parameters for each client Cannot allocate IP addresses automatically Cannot prevent IP address duplication 5
BOOTP n n n Supplies an IP address and other Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) parameters Can supply an executable boot file using Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) Requires you to manually configure parameters for each client Cannot allocate IP addresses automatically Cannot prevent IP address duplication 5
 DHCP n n n Addresses the shortcomings of RARP and BOOTP Dynamically allocates IP addresses from a pool Reclaims unused addresses Prevents IP address duplication Supplies all TCP/IP parameters 6
DHCP n n n Addresses the shortcomings of RARP and BOOTP Dynamically allocates IP addresses from a pool Reclaims unused addresses Prevents IP address duplication Supplies all TCP/IP parameters 6
 DHCP Components n n n Client Server Protocol 7
DHCP Components n n n Client Server Protocol 7
 DHCP Address Allocation Types n n n Manual allocation Automatic allocation Dynamic allocation 8
DHCP Address Allocation Types n n n Manual allocation Automatic allocation Dynamic allocation 8
 Manual Allocation n n The administrator assigns a permanent IP address to the client. Manual allocation is used for computers that require permanent IP address assignments. 9
Manual Allocation n n The administrator assigns a permanent IP address to the client. Manual allocation is used for computers that require permanent IP address assignments. 9
 Automatic Allocation n The DHCP server assigns the client a permanent IP address chosen from a pool. Automatic allocation is used on networks where computers are rarely moved to other subnets. This minimizes DHCP traffic. 10
Automatic Allocation n The DHCP server assigns the client a permanent IP address chosen from a pool. Automatic allocation is used on networks where computers are rarely moved to other subnets. This minimizes DHCP traffic. 10
 Dynamic Allocation n n The DHCP server leases to the client an IP address chosen from a pool. The client must periodically renew the lease address. Unrenewed lease addresses are returned to the pool. Dynamic allocation allows you to add, remove, and relocate computers. 11
Dynamic Allocation n n The DHCP server leases to the client an IP address chosen from a pool. The client must periodically renew the lease address. Unrenewed lease addresses are returned to the pool. Dynamic allocation allows you to add, remove, and relocate computers. 11
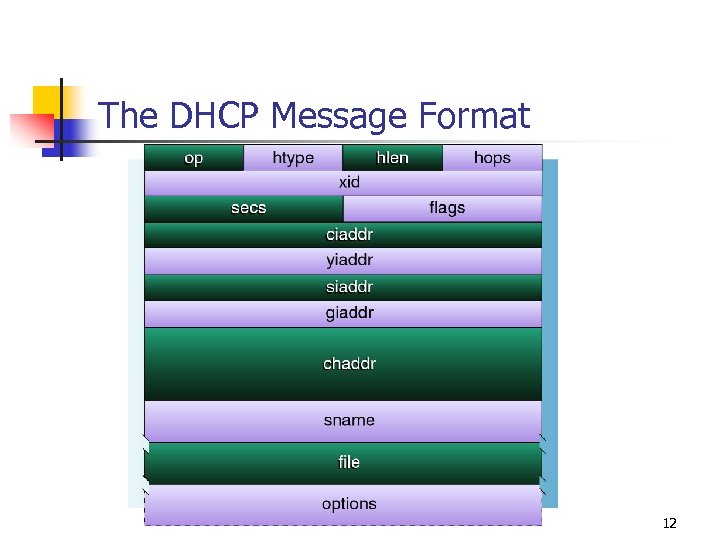 The DHCP Message Format 12
The DHCP Message Format 12
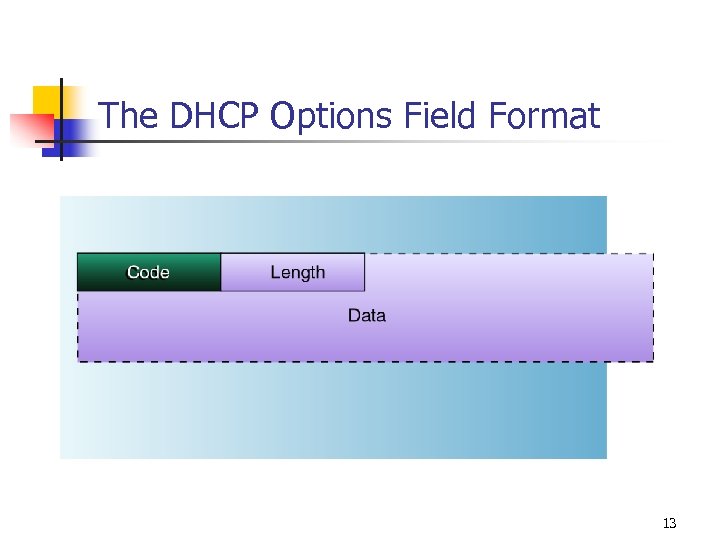 The DHCP Options Field Format 13
The DHCP Options Field Format 13
 DHCP Message Types n n n n 1—DHCPDISCOVER 2—DHCPOFFER 3—DHCPREQUEST 4—DHCPDECLINE 5—DHCPACK 6—DHCPNAK 7—DHCPRELEASE 8—DHCPINFORM 14
DHCP Message Types n n n n 1—DHCPDISCOVER 2—DHCPOFFER 3—DHCPREQUEST 4—DHCPDECLINE 5—DHCPACK 6—DHCPNAK 7—DHCPRELEASE 8—DHCPINFORM 14
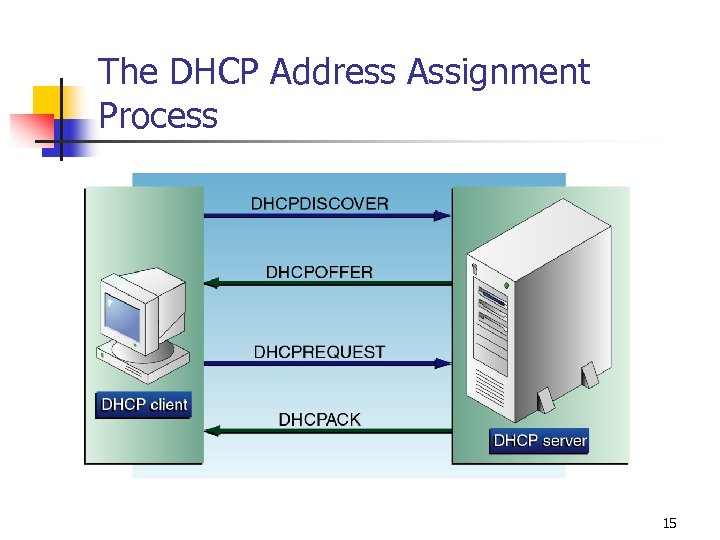 The DHCP Address Assignment Process 15
The DHCP Address Assignment Process 15
 The IP Address Leasing Process n The address assignment process is the same for all of the allocation methods. n n Clients using manual or automatic allocation receive no further communication after the address assignment. Clients using dynamic allocation lease IP addresses for a time interval specified by the server. The client must renew the lease on a regular basis to continue using it. DHCP address leases are typically measured in days. n n If addresses are in short supply, a shorter lease interval is warranted. If computers are rarely moved to other subnets, longer lease intervals reduce the DHCP traffic. 16
The IP Address Leasing Process n The address assignment process is the same for all of the allocation methods. n n Clients using manual or automatic allocation receive no further communication after the address assignment. Clients using dynamic allocation lease IP addresses for a time interval specified by the server. The client must renew the lease on a regular basis to continue using it. DHCP address leases are typically measured in days. n n If addresses are in short supply, a shorter lease interval is warranted. If computers are rarely moved to other subnets, longer lease intervals reduce the DHCP traffic. 16
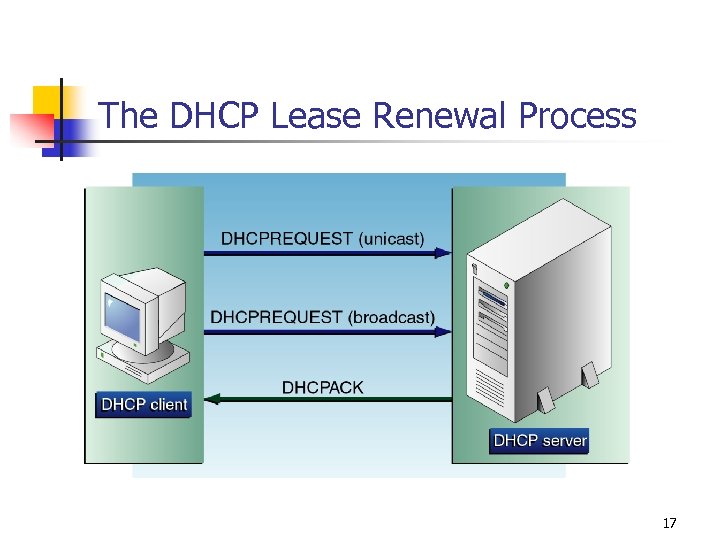 The DHCP Lease Renewal Process 17
The DHCP Lease Renewal Process 17
 The HOSTS File n n n A HOSTS file is a lookup table containing a list of host names and their equivalent IP addresses. Each computer has its own HOSTS file. As the Internet grew, the HOSTS file became impractical, and the Domain Name System (DNS) eventually replaced it. 18
The HOSTS File n n n A HOSTS file is a lookup table containing a list of host names and their equivalent IP addresses. Each computer has its own HOSTS file. As the Internet grew, the HOSTS file became impractical, and the Domain Name System (DNS) eventually replaced it. 18
 DNS Characteristics n n Defined in Request for Comments (RFC) 1034 and RFC 1035 DNS defines n n A hierarchical namespace for computer networks A service for resolving names into IP addresses 19
DNS Characteristics n n Defined in Request for Comments (RFC) 1034 and RFC 1035 DNS defines n n A hierarchical namespace for computer networks A service for resolving names into IP addresses 19
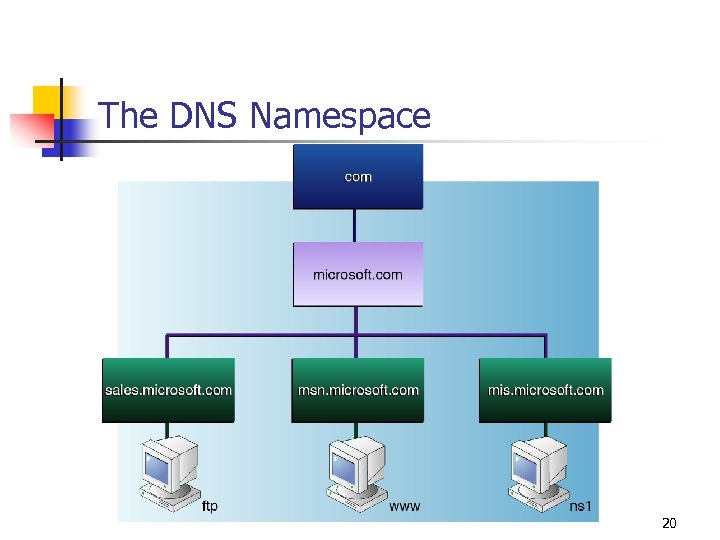 The DNS Namespace 20
The DNS Namespace 20
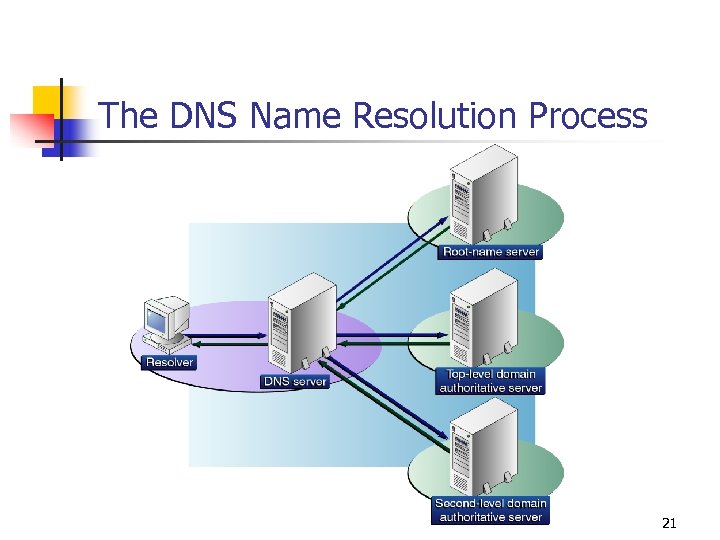 The DNS Name Resolution Process 21
The DNS Name Resolution Process 21
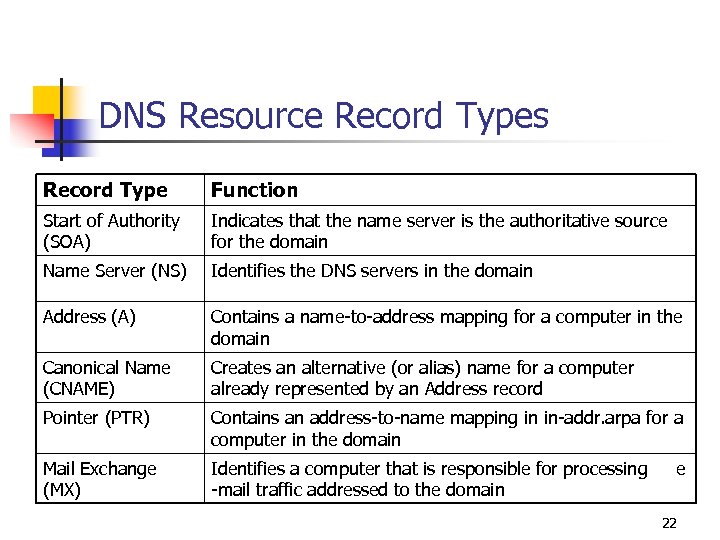 DNS Resource Record Types Record Type Function Start of Authority (SOA) Indicates that the name server is the authoritative source for the domain Name Server (NS) Identifies the DNS servers in the domain Address (A) Contains a name-to-address mapping for a computer in the domain Canonical Name (CNAME) Creates an alternative (or alias) name for a computer already represented by an Address record Pointer (PTR) Contains an address-to-name mapping in in-addr. arpa for a computer in the domain Mail Exchange (MX) Identifies a computer that is responsible for processing -mail traffic addressed to the domain e 22
DNS Resource Record Types Record Type Function Start of Authority (SOA) Indicates that the name server is the authoritative source for the domain Name Server (NS) Identifies the DNS servers in the domain Address (A) Contains a name-to-address mapping for a computer in the domain Canonical Name (CNAME) Creates an alternative (or alias) name for a computer already represented by an Address record Pointer (PTR) Contains an address-to-name mapping in in-addr. arpa for a computer in the domain Mail Exchange (MX) Identifies a computer that is responsible for processing -mail traffic addressed to the domain e 22
 WINS Characteristics n n Is the acronym for Windows Internet Name Service Is a Network Basic Input/Output System (Net. BIOS) name server Resolves Net. BIOS names into IP addresses Used only by Microsoft Windows computers 23
WINS Characteristics n n Is the acronym for Windows Internet Name Service Is a Network Basic Input/Output System (Net. BIOS) name server Resolves Net. BIOS names into IP addresses Used only by Microsoft Windows computers 23
 Ping Characteristics n n n Supplied with virtually every TCP/IP implementation Tests connectivity to another TCP/IP system Syntax: ping target 24
Ping Characteristics n n n Supplied with virtually every TCP/IP implementation Tests connectivity to another TCP/IP system Syntax: ping target 24
![Ping Output (Typical) Pinging cz 1 [192. 168. 2. 10] with 32 bytes of Ping Output (Typical) Pinging cz 1 [192. 168. 2. 10] with 32 bytes of](https://present5.com/presentation/7ef5eff1a8a19d185fbd68937aea6f0c/image-25.jpg) Ping Output (Typical) Pinging cz 1 [192. 168. 2. 10] with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192. 168. 2. 10: bytes=32 time<10 ms TTL=128 Ping statistics for 192. 168. 2. 10: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 0 ms, Maximum = 0 ms, Average = 0 ms 25
Ping Output (Typical) Pinging cz 1 [192. 168. 2. 10] with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 192. 168. 2. 10: bytes=32 time<10 ms TTL=128 Ping statistics for 192. 168. 2. 10: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 0 ms, Maximum = 0 ms, Average = 0 ms 25
 Traceroute Characteristics n n n Variant of the Ping program Displays a list of the routers on the path that packets take to a destination Uses Echo Request and Echo Reply messages, as Ping does Modifies the Time To Live value in each successive Echo Request message Can be used to troubleshoot network communications problems by specifying the location of the difficulty 26
Traceroute Characteristics n n n Variant of the Ping program Displays a list of the routers on the path that packets take to a destination Uses Echo Request and Echo Reply messages, as Ping does Modifies the Time To Live value in each successive Echo Request message Can be used to troubleshoot network communications problems by specifying the location of the difficulty 26
 IPCONFIG. EXE and WINIPCFG. EXE Characteristics n IPCONFIG. EXE and WINIPCFG. EXE are Windows utilities that display TCP/IP configuration parameters. n n n Use IPCONFIG. EXE on Microsoft Windows 2000 and Microsoft Windows NT. Use WINIPCFG. EXE on Microsoft Windows 95, Microsoft Windows 98, and Microsoft Windows Me. Both utilities can release and renew DHCP IP addresses. 27
IPCONFIG. EXE and WINIPCFG. EXE Characteristics n IPCONFIG. EXE and WINIPCFG. EXE are Windows utilities that display TCP/IP configuration parameters. n n n Use IPCONFIG. EXE on Microsoft Windows 2000 and Microsoft Windows NT. Use WINIPCFG. EXE on Microsoft Windows 95, Microsoft Windows 98, and Microsoft Windows Me. Both utilities can release and renew DHCP IP addresses. 27
 ARP. EXE Characteristics n n n ARP. EXE enables you to view and modify the contents of the ARP cache. Adding addresses to the ARP cache speeds up the connection process. Addresses added manually to the ARP cache are not purged. 28
ARP. EXE Characteristics n n n ARP. EXE enables you to view and modify the contents of the ARP cache. Adding addresses to the ARP cache speeds up the connection process. Addresses added manually to the ARP cache are not purged. 28
![Using ARP. EXE Syntax: ARP [-a {ipaddress}] [-n ipaddress] [-s ipaddress hwaddress {interface}] [ Using ARP. EXE Syntax: ARP [-a {ipaddress}] [-n ipaddress] [-s ipaddress hwaddress {interface}] [](https://present5.com/presentation/7ef5eff1a8a19d185fbd68937aea6f0c/image-29.jpg) Using ARP. EXE Syntax: ARP [-a {ipaddress}] [-n ipaddress] [-s ipaddress hwaddress {interface}] [ -d ipaddress {interface}] Parameter Function -a {ipaddress} Displays the contents of a specific ARP cache entry -n ipaddress Displays the contents of the ARP cache for a network interface -s ipaddress hwaddress {interface} Adds a new entry to the ARP cache -d ipaddress {interface} Deletes an entry in the ARP cache 29
Using ARP. EXE Syntax: ARP [-a {ipaddress}] [-n ipaddress] [-s ipaddress hwaddress {interface}] [ -d ipaddress {interface}] Parameter Function -a {ipaddress} Displays the contents of a specific ARP cache entry -n ipaddress Displays the contents of the ARP cache for a network interface -s ipaddress hwaddress {interface} Adds a new entry to the ARP cache -d ipaddress {interface} Deletes an entry in the ARP cache 29
![Using NETSTAT. EXE Syntax: NETSTAT [interval] [-a] [-p protocol] [-n] [-e] [-r] [-s] Parameter Using NETSTAT. EXE Syntax: NETSTAT [interval] [-a] [-p protocol] [-n] [-e] [-r] [-s] Parameter](https://present5.com/presentation/7ef5eff1a8a19d185fbd68937aea6f0c/image-30.jpg) Using NETSTAT. EXE Syntax: NETSTAT [interval] [-a] [-p protocol] [-n] [-e] [-r] [-s] Parameter Function interval Refreshes the display every interval seconds -a Displays the current network connections and the ports that are currently listening for incoming network connections -p protocol Displays the currently active connections for the protocol specified by the protocol variable -n Causes the program to identify computers using IP addresses instead of names -e Displays incoming and outgoing traffic statistics for the network interface -r Displays the routing table plus the current active connections -s Displays detailed network traffic statistics for the IP, Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), TCP, and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) protocols 30
Using NETSTAT. EXE Syntax: NETSTAT [interval] [-a] [-p protocol] [-n] [-e] [-r] [-s] Parameter Function interval Refreshes the display every interval seconds -a Displays the current network connections and the ports that are currently listening for incoming network connections -p protocol Displays the currently active connections for the protocol specified by the protocol variable -n Causes the program to identify computers using IP addresses instead of names -e Displays incoming and outgoing traffic statistics for the network interface -r Displays the routing table plus the current active connections -s Displays detailed network traffic statistics for the IP, Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), TCP, and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) protocols 30
![Using NBTSTAT. EXE Syntax: NBTSTAT [-a name] [-A ipaddress] [-c] [-n] [-r] [-R] [-s] Using NBTSTAT. EXE Syntax: NBTSTAT [-a name] [-A ipaddress] [-c] [-n] [-r] [-R] [-s]](https://present5.com/presentation/7ef5eff1a8a19d185fbd68937aea6f0c/image-31.jpg) Using NBTSTAT. EXE Syntax: NBTSTAT [-a name] [-A ipaddress] [-c] [-n] [-r] [-R] [-s] [-S] [-RR] Parameter Function -a name Displays the Net. BIOS names registered on the computer identified by the name variable -A ipaddress Displays the Net. BIOS names registered on the computer identified by the ipaddress variable -c Displays the contents of the local computer's Net. BIOS name cache -n Displays the Net. BIOS names registered on the local computer -r Displays the number of Net. BIOS names registered and resolved by the local computer, using both broadcasts and WINS 31
Using NBTSTAT. EXE Syntax: NBTSTAT [-a name] [-A ipaddress] [-c] [-n] [-r] [-R] [-s] [-S] [-RR] Parameter Function -a name Displays the Net. BIOS names registered on the computer identified by the name variable -A ipaddress Displays the Net. BIOS names registered on the computer identified by the ipaddress variable -c Displays the contents of the local computer's Net. BIOS name cache -n Displays the Net. BIOS names registered on the local computer -r Displays the number of Net. BIOS names registered and resolved by the local computer, using both broadcasts and WINS 31
![Using NBTSTAT. EXE (Cont. ) Syntax: NBTSTAT [-a name] [-A ipaddress] [-c] [ -n] Using NBTSTAT. EXE (Cont. ) Syntax: NBTSTAT [-a name] [-A ipaddress] [-c] [ -n]](https://present5.com/presentation/7ef5eff1a8a19d185fbd68937aea6f0c/image-32.jpg) Using NBTSTAT. EXE (Cont. ) Syntax: NBTSTAT [-a name] [-A ipaddress] [-c] [ -n] [-r] [-R] [-s] [-S] [-RR] Parameter Function -R Purges the local computer's Net. BIOS name cache of all entries and reloads the LMHOSTS file -s Displays a list of the computer's currently active Net. BIOS settings (identifying remote computers by name), their current status, and the amount of data transmitted to and received from each system -S Displays a list of the computer's currently active Net. BIOS settings (identifying remote computers by IP address), their current status, and the amount of data transmitted to and received from each system -RR Sends name release requests to WINS, then starts refresh 32
Using NBTSTAT. EXE (Cont. ) Syntax: NBTSTAT [-a name] [-A ipaddress] [-c] [ -n] [-r] [-R] [-s] [-S] [-RR] Parameter Function -R Purges the local computer's Net. BIOS name cache of all entries and reloads the LMHOSTS file -s Displays a list of the computer's currently active Net. BIOS settings (identifying remote computers by name), their current status, and the amount of data transmitted to and received from each system -S Displays a list of the computer's currently active Net. BIOS settings (identifying remote computers by IP address), their current status, and the amount of data transmitted to and received from each system -RR Sends name release requests to WINS, then starts refresh 32
 Nslookup Syntax: NSLOOKUP DNSname DNSserver Parameter Function DNSname Specifies the DNS name that you want to resolve DNSserver Specifies the DNS name or IP address of the DNS server that you want to query for the name specified in the DNSname variable 33
Nslookup Syntax: NSLOOKUP DNSname DNSserver Parameter Function DNSname Specifies the DNS name that you want to resolve DNSserver Specifies the DNS name or IP address of the DNS server that you want to query for the name specified in the DNSname variable 33
 Telnet n n n Telnet provides remote control capabilities. Telnet clients can execute commands on a server and view the results. Telnet was designed for UNIX systems. All Windows versions include a Telnet client. Windows 2000 and later versions have a Telnet server. 34
Telnet n n n Telnet provides remote control capabilities. Telnet clients can execute commands on a server and view the results. Telnet was designed for UNIX systems. All Windows versions include a Telnet client. Windows 2000 and later versions have a Telnet server. 34
 FTP n n n You can use the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) to transfer files between computers, create and remove directories, rename and delete files, and manage access permissions. FTP was designed for UNIX computers. FTP is the mainstay of Internet communications. All UNIX computers have FTP client and server capabilities. All Windows computers have a command-line FTP client. Windows 2000 and Windows NT servers have an FTP server built into Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS). 35
FTP n n n You can use the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) to transfer files between computers, create and remove directories, rename and delete files, and manage access permissions. FTP was designed for UNIX computers. FTP is the mainstay of Internet communications. All UNIX computers have FTP client and server capabilities. All Windows computers have a command-line FTP client. Windows 2000 and Windows NT servers have an FTP server built into Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS). 35
 Chapter Summary n TCP/IP services n n DHCP assigns IP addresses by using automatic, manual, or dynamic allocation. DNS resolves host and domain names into IP addresses. WINS resolves Net. BIOS names into IP addresses. TCP/IP utilities n n n Ping tests whether one computer running TCP/IP can communicate with another computer on the network. Traceroute displays the path that packets take through a network to reach their destinations. IPCONFIG. EXE and WINIPCFG. EXE display information about the computer’s TCP/IP configuration, and they release and renew DHCP IP address assignments. 36
Chapter Summary n TCP/IP services n n DHCP assigns IP addresses by using automatic, manual, or dynamic allocation. DNS resolves host and domain names into IP addresses. WINS resolves Net. BIOS names into IP addresses. TCP/IP utilities n n n Ping tests whether one computer running TCP/IP can communicate with another computer on the network. Traceroute displays the path that packets take through a network to reach their destinations. IPCONFIG. EXE and WINIPCFG. EXE display information about the computer’s TCP/IP configuration, and they release and renew DHCP IP address assignments. 36
 Chapter Summary (Cont. ) n TCP/IP utilities (Cont. ) n n n ARP. EXE enables you to view and modify the contents of the ARP cache maintained by a TCP/IP system. Netstat displays information about a computer’s TCP/IP connections and the traffic passing over them. NBTSTAT. EXE displays information about Net. BIOS connections and their traffic. Nslookup enables you to transmit DNS requests to specific servers. Telnet provides remote control access to another computer on the network. FTP lets you manage files and transfer them to and from a remote computer. 37
Chapter Summary (Cont. ) n TCP/IP utilities (Cont. ) n n n ARP. EXE enables you to view and modify the contents of the ARP cache maintained by a TCP/IP system. Netstat displays information about a computer’s TCP/IP connections and the traffic passing over them. NBTSTAT. EXE displays information about Net. BIOS connections and their traffic. Nslookup enables you to transmit DNS requests to specific servers. Telnet provides remote control access to another computer on the network. FTP lets you manage files and transfer them to and from a remote computer. 37


