800f224b1a23e22e82ce8e34353d3903.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Chapter Five The Market for Foreign Exchange • Chapter Objectives: • This chapter serves to introduce the student to the institutional framework within which exchange rates are determined. • This chapter lays the foundation for much of the discussion throughout the remainder of the text, thus it deserves your careful attention. 1
Chapter Five The Market for Foreign Exchange • Chapter Objectives: • This chapter serves to introduce the student to the institutional framework within which exchange rates are determined. • This chapter lays the foundation for much of the discussion throughout the remainder of the text, thus it deserves your careful attention. 1
 Chapter Outline • Function and Structure of the FOREX Market • The Spot Market • The Forward Market 2 2
Chapter Outline • Function and Structure of the FOREX Market • The Spot Market • The Forward Market 2 2
 The Function and Structure of the FOREX Market • FOREX Market Participants • Correspondent Banking Relationships 3
The Function and Structure of the FOREX Market • FOREX Market Participants • Correspondent Banking Relationships 3
 FOREX Market • Forex market is the largest and most active financial market in the world. • On an average day in 2004, $1. 88 trillion in foreign currency was traded in a market that operates 24 hours a day (P 110) • The U. S. dollar is one side of roughly 90% of these currency transactions. • London is the world’s largest foreign exchange trading center. 10 -4 4
FOREX Market • Forex market is the largest and most active financial market in the world. • On an average day in 2004, $1. 88 trillion in foreign currency was traded in a market that operates 24 hours a day (P 110) • The U. S. dollar is one side of roughly 90% of these currency transactions. • London is the world’s largest foreign exchange trading center. 10 -4 4
 FOREX Market Participants • The FOREX market is a two-tiered market: – Interbank Market (Wholesale) • About 700 banks worldwide stand ready to make a market in Foreign exchange. • Nonbank dealers account for about 20% of the market. • There are FX brokers who match buy and sell orders but do not carry inventory and FX specialists. – Client Market (Retail) • Market participants include international banks, their customers, nonbank dealers, FOREX brokers, and central banks. 5
FOREX Market Participants • The FOREX market is a two-tiered market: – Interbank Market (Wholesale) • About 700 banks worldwide stand ready to make a market in Foreign exchange. • Nonbank dealers account for about 20% of the market. • There are FX brokers who match buy and sell orders but do not carry inventory and FX specialists. – Client Market (Retail) • Market participants include international banks, their customers, nonbank dealers, FOREX brokers, and central banks. 5
 Correspondent Banking Relationships • Large commercial banks maintain demand deposit • accounts with one another which facilitates the efficient functioning of the forex market. International commercial banks communicate with one another with: – SWIFT: The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications. – CHIPS: Clearing House Interbank Payments System – ECHO Exchange Clearing House Limited, the first global clearinghouse for settling interbank FOREX transactions. 6
Correspondent Banking Relationships • Large commercial banks maintain demand deposit • accounts with one another which facilitates the efficient functioning of the forex market. International commercial banks communicate with one another with: – SWIFT: The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications. – CHIPS: Clearing House Interbank Payments System – ECHO Exchange Clearing House Limited, the first global clearinghouse for settling interbank FOREX transactions. 6
 The Spot Market • Spot Rate Quotations • The Bid-Ask Spread • Spot FX trading • Cross Rates Quotations • Triangular Arbitrage • Spot Foreign Exchange Market Microstructure 7
The Spot Market • Spot Rate Quotations • The Bid-Ask Spread • Spot FX trading • Cross Rates Quotations • Triangular Arbitrage • Spot Foreign Exchange Market Microstructure 7
 Spot Rate Quotations • Direct quotation – the price of foreign currency in the domestic currency – e. g. “a dollar is worth about 6. 2 RMB” • Indirect Quotation – the price of domestic currency in the foreign currency – e. g. “you get 16. 1 dollar yen to 100 RMB”. 8
Spot Rate Quotations • Direct quotation – the price of foreign currency in the domestic currency – e. g. “a dollar is worth about 6. 2 RMB” • Indirect Quotation – the price of domestic currency in the foreign currency – e. g. “you get 16. 1 dollar yen to 100 RMB”. 8
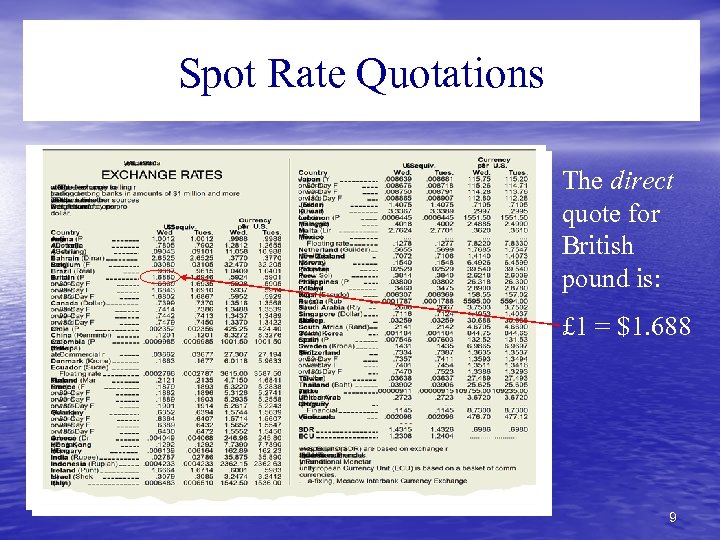 Spot Rate Quotations The direct quote for British pound is: £ 1 = $1. 688 9
Spot Rate Quotations The direct quote for British pound is: £ 1 = $1. 688 9
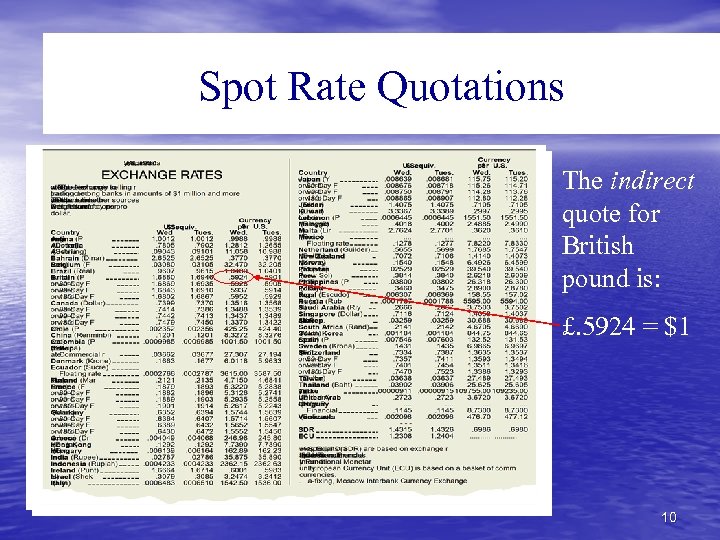 Spot Rate Quotations The indirect quote for British pound is: £. 5924 = $1 10
Spot Rate Quotations The indirect quote for British pound is: £. 5924 = $1 10
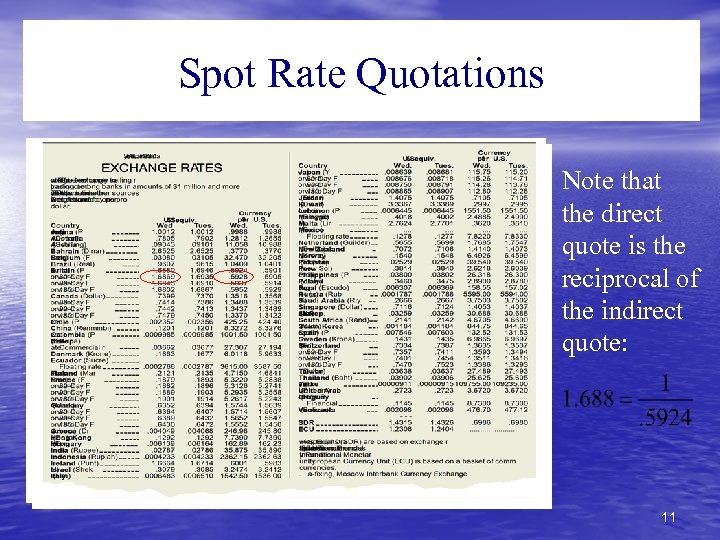 Spot Rate Quotations Note that the direct quote is the reciprocal of the indirect quote: 11
Spot Rate Quotations Note that the direct quote is the reciprocal of the indirect quote: 11
 Exchange Rates Depreciation • A decline in the value of one currency relative to another is called depreciation. Appreciation • The rise in the value of one currency relative to another is called an appreciation. Note: When one currency goes up in value relative to another, the other currency must go down. 10 -12 12
Exchange Rates Depreciation • A decline in the value of one currency relative to another is called depreciation. Appreciation • The rise in the value of one currency relative to another is called an appreciation. Note: When one currency goes up in value relative to another, the other currency must go down. 10 -12 12
 The Bid-Ask Spread • The bid price is the price a dealer is willing to • • pay you for something. The ask price is the amount the dealer wants you to pay for the thing. The bid-ask spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices. E. g. $/£=1. 9072/77 (small figure) Bid-Ask spreads in the spot FX market: – increase with FX exchange rate volatility and 13
The Bid-Ask Spread • The bid price is the price a dealer is willing to • • pay you for something. The ask price is the amount the dealer wants you to pay for the thing. The bid-ask spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices. E. g. $/£=1. 9072/77 (small figure) Bid-Ask spreads in the spot FX market: – increase with FX exchange rate volatility and 13
 Spot FX trading • Forex purchase and sale take place nearly immediately. • In the interbank market, the standard size trade is about U. S. $10 million. • A bank trading room is a noisy, active place. • The stakes are high. • The “long term” is about 10 minutes. 14
Spot FX trading • Forex purchase and sale take place nearly immediately. • In the interbank market, the standard size trade is about U. S. $10 million. • A bank trading room is a noisy, active place. • The stakes are high. • The “long term” is about 10 minutes. 14
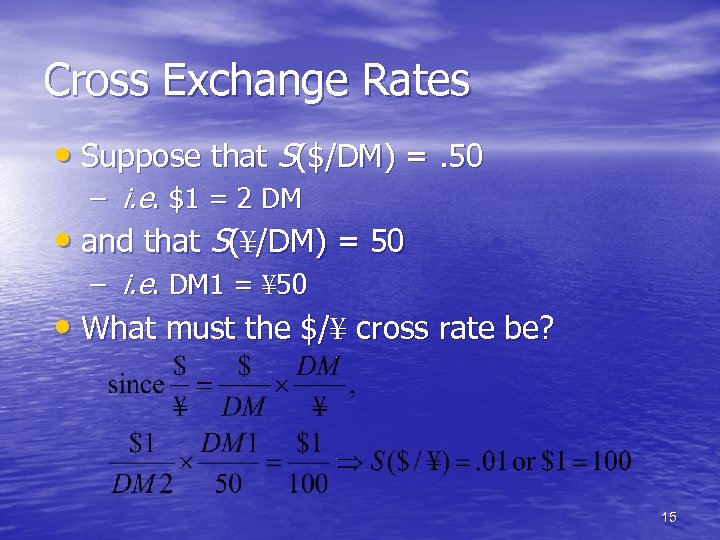 Cross Exchange Rates • Suppose that S($/DM) =. 50 – i. e. $1 = 2 DM • and that S(¥/DM) = 50 – i. e. DM 1 = ¥ 50 • What must the $/¥ cross rate be? 15
Cross Exchange Rates • Suppose that S($/DM) =. 50 – i. e. $1 = 2 DM • and that S(¥/DM) = 50 – i. e. DM 1 = ¥ 50 • What must the $/¥ cross rate be? 15
 Cross Exchange Rates • Most interbank trading goes through the dollar. • • A nondollar trade is referred to a currency against currency trade. A cross exchange rate is an exchange rate between a currency pair where neither currency is U. S. dollar. nondollar trade must satisfy the bid-ask spread determined from the cross-rate formula, or a triangular arbitrage opportunity exists. 16
Cross Exchange Rates • Most interbank trading goes through the dollar. • • A nondollar trade is referred to a currency against currency trade. A cross exchange rate is an exchange rate between a currency pair where neither currency is U. S. dollar. nondollar trade must satisfy the bid-ask spread determined from the cross-rate formula, or a triangular arbitrage opportunity exists. 16
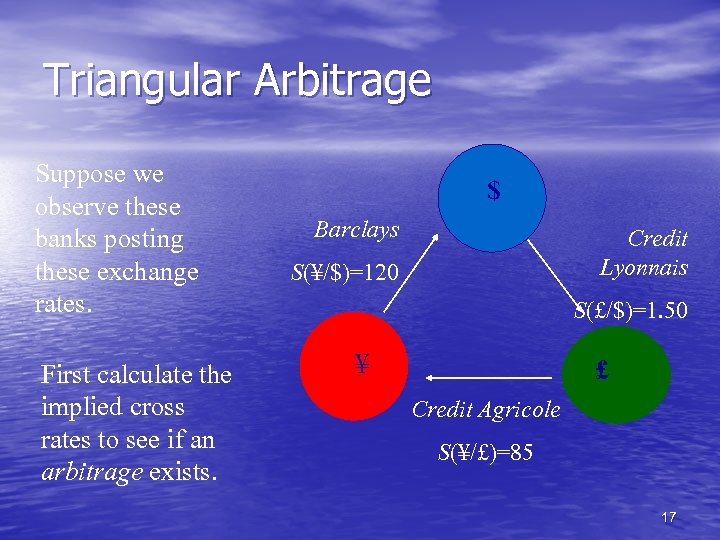 Triangular Arbitrage Suppose we observe these banks posting these exchange rates. First calculate the implied cross rates to see if an arbitrage exists. $ Barclays Credit Lyonnais S(¥/$)=120 S(£/$)=1. 50 ¥ £ Credit Agricole S(¥/£)=85 17
Triangular Arbitrage Suppose we observe these banks posting these exchange rates. First calculate the implied cross rates to see if an arbitrage exists. $ Barclays Credit Lyonnais S(¥/$)=120 S(£/$)=1. 50 ¥ £ Credit Agricole S(¥/£)=85 17
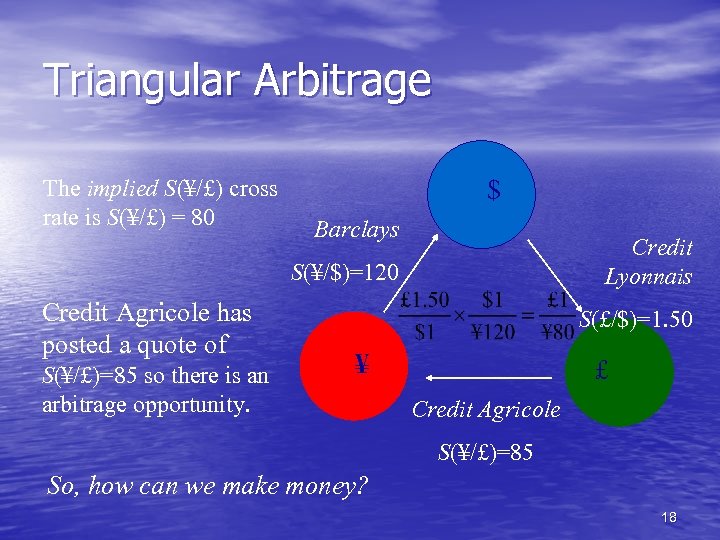 Triangular Arbitrage The implied S(¥/£) cross rate is S(¥/£) = 80 $ Barclays Credit Lyonnais S(¥/$)=120 Credit Agricole has posted a quote of S(¥/£)=85 so there is an arbitrage opportunity. S(£/$)=1. 50 ¥ £ Credit Agricole S(¥/£)=85 So, how can we make money? 18
Triangular Arbitrage The implied S(¥/£) cross rate is S(¥/£) = 80 $ Barclays Credit Lyonnais S(¥/$)=120 Credit Agricole has posted a quote of S(¥/£)=85 so there is an arbitrage opportunity. S(£/$)=1. 50 ¥ £ Credit Agricole S(¥/£)=85 So, how can we make money? 18
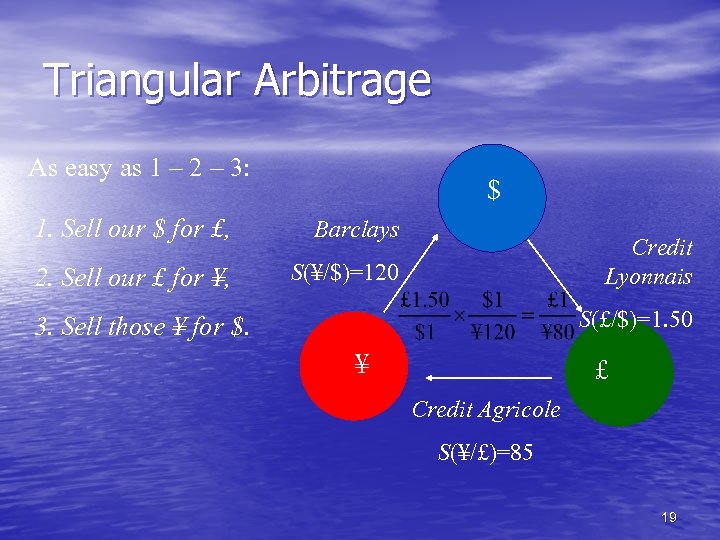 Triangular Arbitrage As easy as 1 – 2 – 3: $ 1. Sell our $ for £, Barclays 2. Sell our £ for ¥, S(¥/$)=120 Credit Lyonnais S(£/$)=1. 50 3. Sell those ¥ for $. ¥ £ Credit Agricole S(¥/£)=85 19
Triangular Arbitrage As easy as 1 – 2 – 3: $ 1. Sell our $ for £, Barclays 2. Sell our £ for ¥, S(¥/$)=120 Credit Lyonnais S(£/$)=1. 50 3. Sell those ¥ for $. ¥ £ Credit Agricole S(¥/£)=85 19
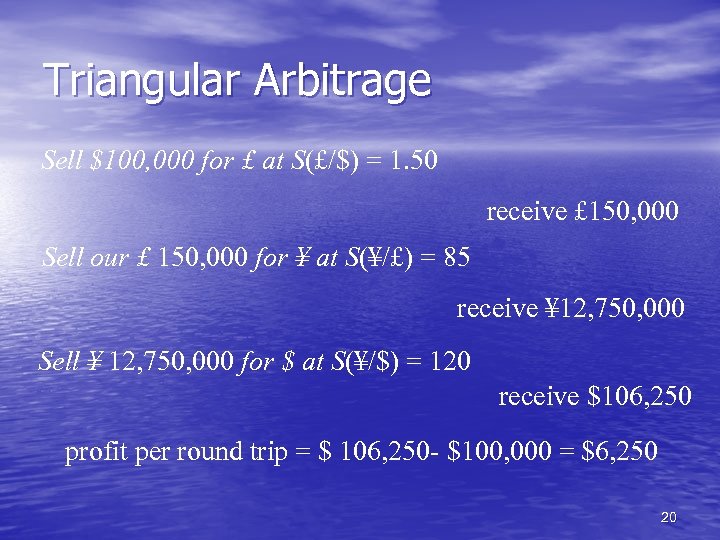 Triangular Arbitrage Sell $100, 000 for £ at S(£/$) = 1. 50 receive £ 150, 000 Sell our £ 150, 000 for ¥ at S(¥/£) = 85 receive ¥ 12, 750, 000 Sell ¥ 12, 750, 000 for $ at S(¥/$) = 120 receive $106, 250 profit per round trip = $ 106, 250 - $100, 000 = $6, 250 20
Triangular Arbitrage Sell $100, 000 for £ at S(£/$) = 1. 50 receive £ 150, 000 Sell our £ 150, 000 for ¥ at S(¥/£) = 85 receive ¥ 12, 750, 000 Sell ¥ 12, 750, 000 for $ at S(¥/$) = 120 receive $106, 250 profit per round trip = $ 106, 250 - $100, 000 = $6, 250 20
 The Forward Market • Forward Rate Quotations • Forward Premium/discount • Long and Short Forward Positions 21
The Forward Market • Forward Rate Quotations • Forward Premium/discount • Long and Short Forward Positions 21
 The Forward Market • A forward contract is an agreement to buy or sell an asset in the future at prices agreed upon today. • If you have ever had to order an out-ofstock textbook, then you have entered into a forward contract. 22
The Forward Market • A forward contract is an agreement to buy or sell an asset in the future at prices agreed upon today. • If you have ever had to order an out-ofstock textbook, then you have entered into a forward contract. 22
 Forward Rate Quotations • The forward market for FOREX involves agreements to buy and sell foreign currencies in the future at prices agreed upon today. • Bank quotes for 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 month maturities are readily available forward contracts. 23
Forward Rate Quotations • The forward market for FOREX involves agreements to buy and sell foreign currencies in the future at prices agreed upon today. • Bank quotes for 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 month maturities are readily available forward contracts. 23
 Forward Rate Quotationsoutright forward rate • Consider the example from above: for Japanese yen, the spot rate is ¥ 115. 75 = $1. 00 While the 180 -day forward rate is £ 112. 80 = $1. 00 • What’s up with that? – The market participants expect that the yen will be worth MORE in dollars in six months. 24
Forward Rate Quotationsoutright forward rate • Consider the example from above: for Japanese yen, the spot rate is ¥ 115. 75 = $1. 00 While the 180 -day forward rate is £ 112. 80 = $1. 00 • What’s up with that? – The market participants expect that the yen will be worth MORE in dollars in six months. 24
 Forward Premium/discount • The forward premium • The forward discount • At par 25
Forward Premium/discount • The forward premium • The forward discount • At par 25
 forward points Quotations-a shorthand method • S($/£)= 1. 9072 -1. 9077 – – – One-month 32 -30 Three-month 57 -54 Six-month 145 -138 – – – F 30($/£)=1. 9072 -0. 0032/1. 9077 -0. 0030=1. 1. 9040/1. 9047 F 60($/£)=1. 9015/23 F 180($/£)=1. 8927/39 • Outright forward bid-ask rate is: • The bid-ask spread increases in time to maturity. 26
forward points Quotations-a shorthand method • S($/£)= 1. 9072 -1. 9077 – – – One-month 32 -30 Three-month 57 -54 Six-month 145 -138 – – – F 30($/£)=1. 9072 -0. 0032/1. 9077 -0. 0030=1. 1. 9040/1. 9047 F 60($/£)=1. 9015/23 F 180($/£)=1. 8927/39 • Outright forward bid-ask rate is: • The bid-ask spread increases in time to maturity. 26
 Long and Short Forward Positions • If you have agreed to sell forex forward, you are short. • If you have agreed to buy forex forward, you are long. 27
Long and Short Forward Positions • If you have agreed to sell forex forward, you are short. • If you have agreed to buy forex forward, you are long. 27
 • FOREX market covers a broad range of topics. • We have discuss the spot and forward market for FOREX in this chapter • In chapter 7, we examine currency futures and option contracts; in chapter 14, currency swaps are discussed. 28
• FOREX market covers a broad range of topics. • We have discuss the spot and forward market for FOREX in this chapter • In chapter 7, we examine currency futures and option contracts; in chapter 14, currency swaps are discussed. 28


