2507ea767080d6192f9e2c7faf5a676f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 68
 Chapter Eleven Psychological Disorders
Chapter Eleven Psychological Disorders
 Did You Know That… • Behavior considered abnormal in one culture may be deemed perfectly normal in another? • Psychological disorders affect nearly everyone in one way or another? • Some people have such fear of leaving the house that they literally are unable to go out to buy a quart of milk? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -2
Did You Know That… • Behavior considered abnormal in one culture may be deemed perfectly normal in another? • Psychological disorders affect nearly everyone in one way or another? • Some people have such fear of leaving the house that they literally are unable to go out to buy a quart of milk? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -2
 Did You Know That… (Cont’d) • Some people have lost all feeling in an arm or leg but remain unconcerned about their ailments? • Some health professionals use bright light to treat depression – and it works? • Some people with schizophrenia sit motionless for hours as though they were statues? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -3
Did You Know That… (Cont’d) • Some people have lost all feeling in an arm or leg but remain unconcerned about their ailments? • Some health professionals use bright light to treat depression – and it works? • Some people with schizophrenia sit motionless for hours as though they were statues? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -3
 Did You Know That… (Cont’d) • People who receive the label of psychopath are not psychotic? • Despite popular beliefs to the contrary, people who threaten suicide are quite likely serious about taking their lives? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -4
Did You Know That… (Cont’d) • People who receive the label of psychopath are not psychotic? • Despite popular beliefs to the contrary, people who threaten suicide are quite likely serious about taking their lives? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -4
 Module 11. 1 What Is Abnormal Behavior?
Module 11. 1 What Is Abnormal Behavior?
 Module 11. 1 Preview Questions • What criteria are used to determine whether behavior is abnormal? • What are the major models of abnormal behavior? • What are psychological disorders? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -6
Module 11. 1 Preview Questions • What criteria are used to determine whether behavior is abnormal? • What are the major models of abnormal behavior? • What are psychological disorders? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -6
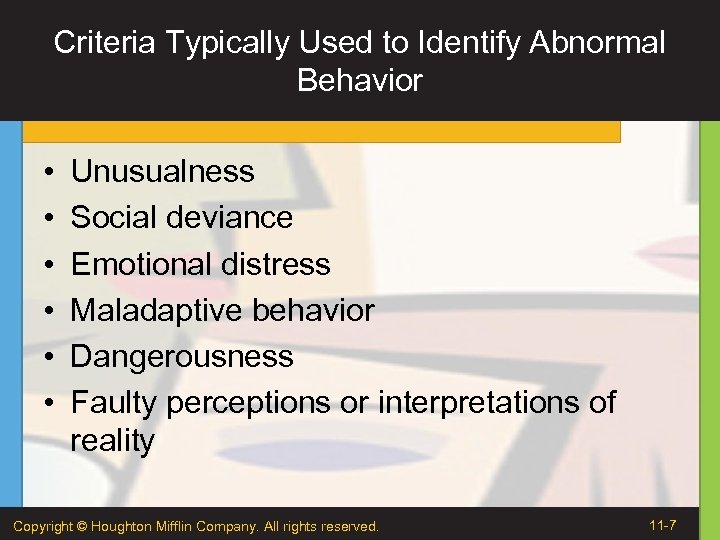 Criteria Typically Used to Identify Abnormal Behavior • • • Unusualness Social deviance Emotional distress Maladaptive behavior Dangerousness Faulty perceptions or interpretations of reality Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -7
Criteria Typically Used to Identify Abnormal Behavior • • • Unusualness Social deviance Emotional distress Maladaptive behavior Dangerousness Faulty perceptions or interpretations of reality Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -7
 Cultural Bases of Abnormal Behavior • Cultural context important when making judgments about abnormal behavior • Abnormal behavior patterns may be expressed differently in different cultures. • Judgments of what is abnormal behavior can change over time. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -8
Cultural Bases of Abnormal Behavior • Cultural context important when making judgments about abnormal behavior • Abnormal behavior patterns may be expressed differently in different cultures. • Judgments of what is abnormal behavior can change over time. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -8
 Early Beliefs About Abnormal Behavior • Abnormal behaviors caused by supernatural forces • Doctrine of demonic possession • Treatment was exorcism Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -9
Early Beliefs About Abnormal Behavior • Abnormal behaviors caused by supernatural forces • Doctrine of demonic possession • Treatment was exorcism Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -9
 Medical Model of Abnormal Behavior • Result of the rapid advances in medical science during 18 th and 19 th centuries • Abnormal behavior patterns represent mental illnesses that have a biological basis. • Can be classified by their particular characteristics or symptoms Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -10
Medical Model of Abnormal Behavior • Result of the rapid advances in medical science during 18 th and 19 th centuries • Abnormal behavior patterns represent mental illnesses that have a biological basis. • Can be classified by their particular characteristics or symptoms Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -10
 Psychological Models of Abnormal Behavior • Psychodynamic Model: Abnormal behaviors arise from unconscious conflicts. • Psychological symptoms are the outward expressions of inner turmoil. • Behavioral Model: Abnormal behaviors are learned. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -11
Psychological Models of Abnormal Behavior • Psychodynamic Model: Abnormal behaviors arise from unconscious conflicts. • Psychological symptoms are the outward expressions of inner turmoil. • Behavioral Model: Abnormal behaviors are learned. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -11
 Psychological Models of Abnormal Behavior (Cont’d) • Humanistic Model: Abnormal behaviors result from roadblocks on the path toward self-actualization. • Cognitive Model: Irrational or distorted thinking leads to emotional problems and maladaptive behaviors. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -12
Psychological Models of Abnormal Behavior (Cont’d) • Humanistic Model: Abnormal behaviors result from roadblocks on the path toward self-actualization. • Cognitive Model: Irrational or distorted thinking leads to emotional problems and maladaptive behaviors. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -12
 Sociocultural Model of Abnormal Behavior • Views causes of abnormal behavior within a broader social and cultural context • Abnormal behavior may have more to do with social ills or failures of society. • Focus also on the effects of labeling people as mentally ill Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -13
Sociocultural Model of Abnormal Behavior • Views causes of abnormal behavior within a broader social and cultural context • Abnormal behavior may have more to do with social ills or failures of society. • Focus also on the effects of labeling people as mentally ill Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -13
 Biopsychosocial Model of Abnormal Behavior • Abnormal behavior results from the complex interactions of biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors. • Example: Diathesis-Stress Model • Diathesis: What is the person’s vulnerability or predisposition to developing a disorder? • Stress: What level of stress is the person experiencing? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -14
Biopsychosocial Model of Abnormal Behavior • Abnormal behavior results from the complex interactions of biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors. • Example: Diathesis-Stress Model • Diathesis: What is the person’s vulnerability or predisposition to developing a disorder? • Stress: What level of stress is the person experiencing? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -14
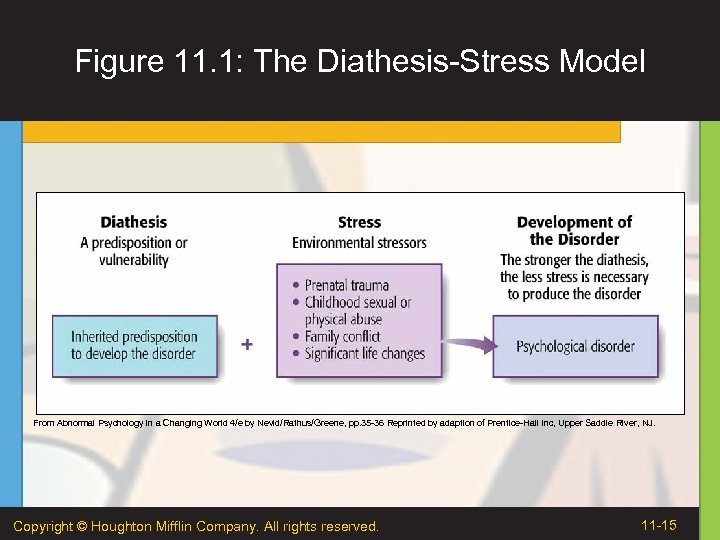 Figure 11. 1: The Diathesis-Stress Model From Abnormal Psychology in a Changing World 4/e by Nevid/Rathus/Greene, pp. 35 -36 Reprinted by adaption of Prentice-Hall Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -15
Figure 11. 1: The Diathesis-Stress Model From Abnormal Psychology in a Changing World 4/e by Nevid/Rathus/Greene, pp. 35 -36 Reprinted by adaption of Prentice-Hall Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -15
 Psychological Disorders • Distinctive patterns of abnormal behavior • Also known as “mental disorders” or “mental illnesses” • Involve disturbances of mood, behavior, thought processes, or perceptions that result in significant personal distress or impaired functioning Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -16
Psychological Disorders • Distinctive patterns of abnormal behavior • Also known as “mental disorders” or “mental illnesses” • Involve disturbances of mood, behavior, thought processes, or perceptions that result in significant personal distress or impaired functioning Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -16
 Classification of Psychological Disorders • Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) now in a 4 th, text revised edition (DSM-IV-TR). • Multiaxial system • • • Axis I: Clinical disorders Axis II: Personality disorders Axis III: General medical conditions Axis IV: Psychosocial and environmental problems Axis V: Global assessment of functioning Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -17
Classification of Psychological Disorders • Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) now in a 4 th, text revised edition (DSM-IV-TR). • Multiaxial system • • • Axis I: Clinical disorders Axis II: Personality disorders Axis III: General medical conditions Axis IV: Psychosocial and environmental problems Axis V: Global assessment of functioning Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -17
 Module 11. 2 Anxiety Disorders
Module 11. 2 Anxiety Disorders
 Module 13. 2 Preview Questions • What are anxiety disorders? • What causal factors are implicated in anxiety disorders? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -19
Module 13. 2 Preview Questions • What are anxiety disorders? • What causal factors are implicated in anxiety disorders? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -19
 What is an Anxiety Disorder? • Anxiety can be an adaptive response. • But can become abnormal when excessive or when interferes with ability to function • “Fear” is used to describe anxiety experienced in specific situations. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -20
What is an Anxiety Disorder? • Anxiety can be an adaptive response. • But can become abnormal when excessive or when interferes with ability to function • “Fear” is used to describe anxiety experienced in specific situations. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -20
 Phobias • An irrational or excessive fear of some object or situation • Three types of phobic disorders: • Social Phobia • Specific Phobia • Agoraphobia Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -21
Phobias • An irrational or excessive fear of some object or situation • Three types of phobic disorders: • Social Phobia • Specific Phobia • Agoraphobia Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -21
 Panic Disorder • Person experiences sudden episodes of sheer terror called panic attacks. • Panic attacks are characterized by intense physical symptoms. • Over time, panic attacks can become associated with specific situations. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -22
Panic Disorder • Person experiences sudden episodes of sheer terror called panic attacks. • Panic attacks are characterized by intense physical symptoms. • Over time, panic attacks can become associated with specific situations. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -22
 Generalized Anxiety Disorder • Persistent anxiety not tied to any particular object or situation • Anxiety has a “free-floating” quality • Key feature is excessive worry • Other characteristics include shakiness, inability to relax, fidgeting, and feelings of dread and foreboding. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -23
Generalized Anxiety Disorder • Persistent anxiety not tied to any particular object or situation • Anxiety has a “free-floating” quality • Key feature is excessive worry • Other characteristics include shakiness, inability to relax, fidgeting, and feelings of dread and foreboding. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -23
 Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder • Person experiences persistent obsessions and/or compulsions • Obsessions: Nagging, intrusive thoughts person feels unable to control • Compulsions: Repetitive behaviors or rituals the person feels compelled to perform repeatedly Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -24
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder • Person experiences persistent obsessions and/or compulsions • Obsessions: Nagging, intrusive thoughts person feels unable to control • Compulsions: Repetitive behaviors or rituals the person feels compelled to perform repeatedly Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -24
 Causes of Anxiety Disorders • Biological factors: • Heredity • Disturbances in brain biochemistry or circuits • Psychological factors: • Classical conditioning • Operant conditioning • Cognitive factors Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -25
Causes of Anxiety Disorders • Biological factors: • Heredity • Disturbances in brain biochemistry or circuits • Psychological factors: • Classical conditioning • Operant conditioning • Cognitive factors Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -25
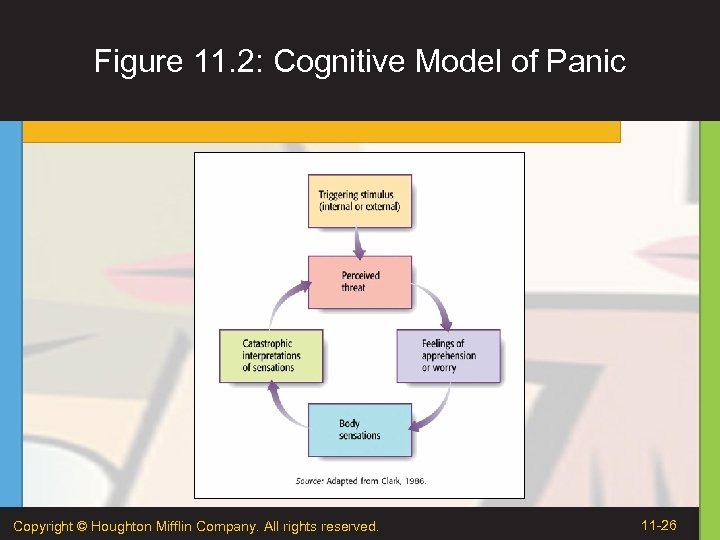 Figure 11. 2: Cognitive Model of Panic Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -26
Figure 11. 2: Cognitive Model of Panic Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -26
 Module 11. 3 Dissociative and Somatoform Disorders
Module 11. 3 Dissociative and Somatoform Disorders
 Module 11. 3 Preview Questions • What are dissociative disorders and somatoform disorders? • What causal factors are implicated in dissociative and somatoform disorders? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -28
Module 11. 3 Preview Questions • What are dissociative disorders and somatoform disorders? • What causal factors are implicated in dissociative and somatoform disorders? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -28
 Dissociative Disorders • Involve problems with memory or changes in consciousness or self-identity • Inability to maintain a cohesive sense of self or unity of consciousness • Results in unusual or bizarre behavior Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -29
Dissociative Disorders • Involve problems with memory or changes in consciousness or self-identity • Inability to maintain a cohesive sense of self or unity of consciousness • Results in unusual or bizarre behavior Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -29
 Dissociative Identity Disorder • Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID): Two or more distinct personalities exist within same individual • Commonly called “multiple” or “split personality” • Women tend to have 15+ identities; men tend to have 8+ identities. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -30
Dissociative Identity Disorder • Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID): Two or more distinct personalities exist within same individual • Commonly called “multiple” or “split personality” • Women tend to have 15+ identities; men tend to have 8+ identities. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -30
 Dissociative Amnesia • Loss of memory about self or life experiences • No physical cause for amnesia • Memory lost usually involves a stressful or traumatic event. • Generalized amnesia is much less common. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -31
Dissociative Amnesia • Loss of memory about self or life experiences • No physical cause for amnesia • Memory lost usually involves a stressful or traumatic event. • Generalized amnesia is much less common. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -31
 Causes of Dissociative Disorders • Role of traumatic experiences: • Childhood sexual abuse • Psychological pain or conflict • Is DID a genuine disorder? • A form of attention-seeking role playing? • Inadvertently cued by therapists? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -32
Causes of Dissociative Disorders • Role of traumatic experiences: • Childhood sexual abuse • Psychological pain or conflict • Is DID a genuine disorder? • A form of attention-seeking role playing? • Inadvertently cued by therapists? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -32
 Somatoform Disorders • Person has physical ailments or complaints that cannot be explained medically • Or may have belief that gravely ill despite reassurances to the contrary Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -33
Somatoform Disorders • Person has physical ailments or complaints that cannot be explained medically • Or may have belief that gravely ill despite reassurances to the contrary Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -33
 Conversion Disorder • Loss of functioning, feeling, or movement in specific body part • But no physical cause for the symptoms. • Lack of concern with symptoms • La belle indifférence • May be a way of avoiding anxiety associated with painful or stressful conflicts or situations • Many cases turn out to be unrecognized medical conditions. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -34
Conversion Disorder • Loss of functioning, feeling, or movement in specific body part • But no physical cause for the symptoms. • Lack of concern with symptoms • La belle indifférence • May be a way of avoiding anxiety associated with painful or stressful conflicts or situations • Many cases turn out to be unrecognized medical conditions. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -34
 Hypochondriasis • Preoccupied with idea of health problems • Attribute physical complaints or symptoms to a serious underlying disease • Rejects reassurances that concerns are groundless • May not realize how their anxiety may be causing the symptoms being experienced Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -35
Hypochondriasis • Preoccupied with idea of health problems • Attribute physical complaints or symptoms to a serious underlying disease • Rejects reassurances that concerns are groundless • May not realize how their anxiety may be causing the symptoms being experienced Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -35
 Causes of Somatoform Disorders • Freud: Hysterical symptom an indication of unconscious conflicts • Learning Theories: Symptoms help person avoid painful or anxiety-evoking situations • Reinforcement for “sick role” • Cognitive Theories: Cognitive biases lead to misinterpreting bodily symptoms. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -36
Causes of Somatoform Disorders • Freud: Hysterical symptom an indication of unconscious conflicts • Learning Theories: Symptoms help person avoid painful or anxiety-evoking situations • Reinforcement for “sick role” • Cognitive Theories: Cognitive biases lead to misinterpreting bodily symptoms. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -36
 Module 11. 4 Mood Disorders
Module 11. 4 Mood Disorders
 Module 13. 4 Preview Questions • What are mood disorders? • What causal factors are implicated in mood disorders? • Who is at risk for suicide? • Why do people commit suicide? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -38
Module 13. 4 Preview Questions • What are mood disorders? • What causal factors are implicated in mood disorders? • Who is at risk for suicide? • Why do people commit suicide? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -38
 Mood Disorders • Severe or persistent disturbances of mood that limit one’s ability to function • Will focus on two major forms of mood disorder: • Major Depressive Disorder • Bipolar Disorder Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -39
Mood Disorders • Severe or persistent disturbances of mood that limit one’s ability to function • Will focus on two major forms of mood disorder: • Major Depressive Disorder • Bipolar Disorder Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -39
 Major Depressive Disorder • Symptoms: • • • Depressed mood for at least two weeks Sadness Worthlessness Changes in sleep, appetite Lethargy Loss of interest, concentration Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -40
Major Depressive Disorder • Symptoms: • • • Depressed mood for at least two weeks Sadness Worthlessness Changes in sleep, appetite Lethargy Loss of interest, concentration Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -40
 Prevalence of Major Depression • About 16% of adult U. S. population develop major depression at some point. • Women twice as likely as men to develop disorder • Possibly due to hormonal or other biological differences one possible explanation • But also may be due to differences in levels of stress experienced • Gender differences in how one copes with depression Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -41
Prevalence of Major Depression • About 16% of adult U. S. population develop major depression at some point. • Women twice as likely as men to develop disorder • Possibly due to hormonal or other biological differences one possible explanation • But also may be due to differences in levels of stress experienced • Gender differences in how one copes with depression Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -41
 Bipolar Disorder • Person shifts between manic episodes and periods of depression with intervening periods of normal mood • Formerly called manic-depression • About 1% of adult U. S. population suffers from a bipolar disorder. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -42
Bipolar Disorder • Person shifts between manic episodes and periods of depression with intervening periods of normal mood • Formerly called manic-depression • About 1% of adult U. S. population suffers from a bipolar disorder. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -42
 Psychological Models of Depression • Classic Psychodynamic Theory: Depression involves anger turned inward against self. • Behavioral Model: Depression results from changes in reinforcement levels. • Cognitive Model: How people interpret events contributes to emotional disorders. • Aaron Beck: One is prone depression if adopt a negatively biased or distorted way of thinking. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -43
Psychological Models of Depression • Classic Psychodynamic Theory: Depression involves anger turned inward against self. • Behavioral Model: Depression results from changes in reinforcement levels. • Cognitive Model: How people interpret events contributes to emotional disorders. • Aaron Beck: One is prone depression if adopt a negatively biased or distorted way of thinking. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -43
 Cognitive Distortions Linked to Depression (see Table 11. 2 for more detail) • • • All-or-nothing thinking Misplaced blame Misfortune telling Negative focusing Dismissing the positive • Jumping to conclusions • Catastrophizing • Emotion-based reasoning • Shouldisms • Name calling • Mistaken responsibility Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -44
Cognitive Distortions Linked to Depression (see Table 11. 2 for more detail) • • • All-or-nothing thinking Misplaced blame Misfortune telling Negative focusing Dismissing the positive • Jumping to conclusions • Catastrophizing • Emotion-based reasoning • Shouldisms • Name calling • Mistaken responsibility Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -44
 Learned Helplessness Model • Depression results from belief that one is helpless to control reinforcements. • Reformulated Model: How are negative events explained? • Depressive Attributional Style involves making internal, global, and stable attributions for disappointments and failures. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -45
Learned Helplessness Model • Depression results from belief that one is helpless to control reinforcements. • Reformulated Model: How are negative events explained? • Depressive Attributional Style involves making internal, global, and stable attributions for disappointments and failures. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -45
 Causes of Mood Disorders: Biological Factors • Chemical imbalances in brain involving the levels or activity of neurotransmitters • Hereditary influences Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -46
Causes of Mood Disorders: Biological Factors • Chemical imbalances in brain involving the levels or activity of neurotransmitters • Hereditary influences Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -46
 Suicide • Nearly one-half million Americans make serious suicide attempts each year. • About 30, 000 Americans and 1 million people worldwide commit suicide each year. • Third leading cause of death among 15 -24 year olds. • About 10% of college students seriously thought of committing suicide during preceding year. • Nearly 1 in 20 adult Americans reported making a prior suicidal attempt. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -47
Suicide • Nearly one-half million Americans make serious suicide attempts each year. • About 30, 000 Americans and 1 million people worldwide commit suicide each year. • Third leading cause of death among 15 -24 year olds. • About 10% of college students seriously thought of committing suicide during preceding year. • Nearly 1 in 20 adult Americans reported making a prior suicidal attempt. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -47
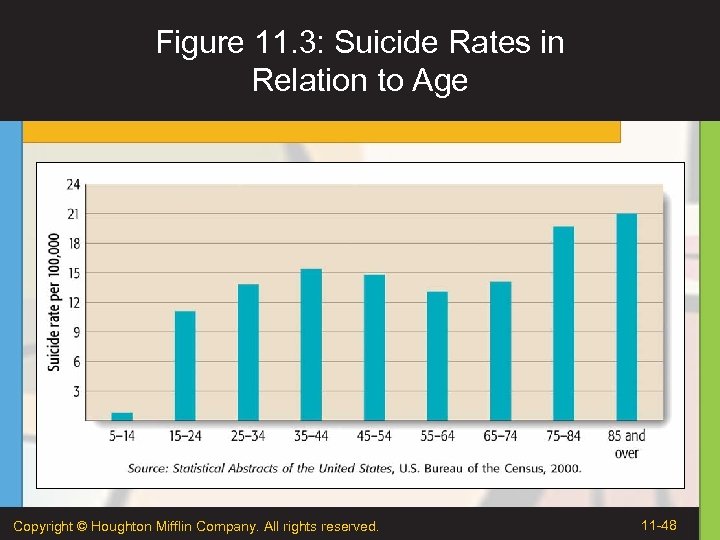 Figure 11. 3: Suicide Rates in Relation to Age Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -48
Figure 11. 3: Suicide Rates in Relation to Age Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -48
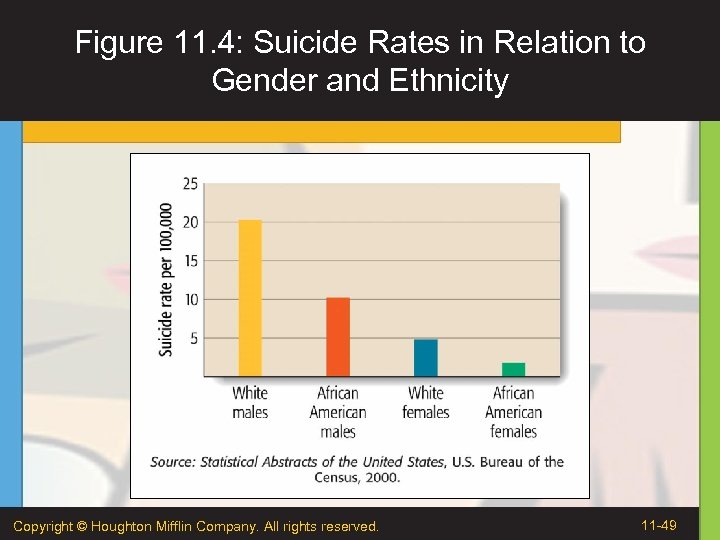 Figure 11. 4: Suicide Rates in Relation to Gender and Ethnicity Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -49
Figure 11. 4: Suicide Rates in Relation to Gender and Ethnicity Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -49
 Factors in Suicide • Closely linked to mood disorders • Role of biochemical factors? • Lack of serotonin may lead to a disinhibition effect • • Drugs and alcohol Lack of coping responses Exit events or losses of supportive persons Teens and copycat suicides Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -50
Factors in Suicide • Closely linked to mood disorders • Role of biochemical factors? • Lack of serotonin may lead to a disinhibition effect • • Drugs and alcohol Lack of coping responses Exit events or losses of supportive persons Teens and copycat suicides Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -50
 Myths About Suicide (see Table 11. 3 for more detail) • People who threaten suicide are only seeking attention. • A person must be insane to attempt suicide. • Talking about suicide with a depressed person may prompt the person to attempt it. • People who attempt suicide and fail aren’t serious about killing themselves. • If someone threatens suicide, it is best to ignore it so as not to encourage repeated threats. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -51
Myths About Suicide (see Table 11. 3 for more detail) • People who threaten suicide are only seeking attention. • A person must be insane to attempt suicide. • Talking about suicide with a depressed person may prompt the person to attempt it. • People who attempt suicide and fail aren’t serious about killing themselves. • If someone threatens suicide, it is best to ignore it so as not to encourage repeated threats. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -51
 Module 11. 5 Schizophrenia
Module 11. 5 Schizophrenia
 Module 11. 5 Preview Questions • What is schizophrenia? • What are three specific types of schizophrenia? • What causal factors are implicated in schizophrenia? • What is the diathesis-stress model of schizophrenia? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -53
Module 11. 5 Preview Questions • What is schizophrenia? • What are three specific types of schizophrenia? • What causal factors are implicated in schizophrenia? • What is the diathesis-stress model of schizophrenia? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -53
 Schizophrenia • Most closely corresponds to popular notion of insanity or madness • Affects about one adult in a hundred • Characterized by bizarre, irrational behavior • Somewhat more common in men than in women • Follows a lifelong course • Typically develops in late adolescence or early adulthood Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -54
Schizophrenia • Most closely corresponds to popular notion of insanity or madness • Affects about one adult in a hundred • Characterized by bizarre, irrational behavior • Somewhat more common in men than in women • Follows a lifelong course • Typically develops in late adolescence or early adulthood Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -54
 Symptoms of Schizophrenia • A psychotic disorder: • Confuses fantasy with reality • Experiences hallucinations and delusions • May exhibit bizarre behavior, incoherent speech, and illogical thinking • Positive vs. negative symptoms • Behavioral excesses vs. behavioral deficits Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -55
Symptoms of Schizophrenia • A psychotic disorder: • Confuses fantasy with reality • Experiences hallucinations and delusions • May exhibit bizarre behavior, incoherent speech, and illogical thinking • Positive vs. negative symptoms • Behavioral excesses vs. behavioral deficits Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -55
 Types of Schizophrenia • Disorganized • Catatonic • Paranoid Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -56
Types of Schizophrenia • Disorganized • Catatonic • Paranoid Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -56
 Causes of Schizophrenia • • Genetic factors Biochemical imbalances Brain abnormalities Psychosocial influences • Stressful life experiences • Diathesis-stress model revisited Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -57
Causes of Schizophrenia • • Genetic factors Biochemical imbalances Brain abnormalities Psychosocial influences • Stressful life experiences • Diathesis-stress model revisited Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -57
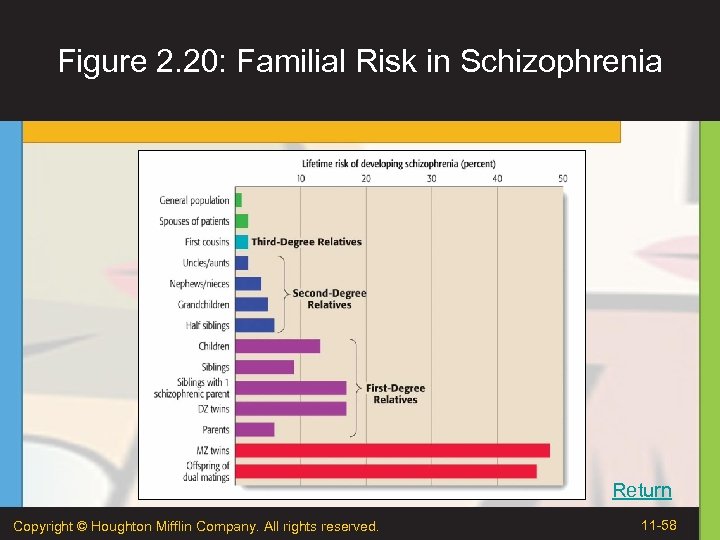 Figure 2. 20: Familial Risk in Schizophrenia Return Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -58
Figure 2. 20: Familial Risk in Schizophrenia Return Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -58
 Module 11. 6 Personality Disorders
Module 11. 6 Personality Disorders
 Module 11. 6 Preview Questions • What are personality disorders? • What characteristics are associated with antisocial personality disorder? • What causal factors are implicated in antisocial personality disorder? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -60
Module 11. 6 Preview Questions • What are personality disorders? • What characteristics are associated with antisocial personality disorder? • What causal factors are implicated in antisocial personality disorder? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -60
 Personality Disorders • A cluster of psychological disorders characterized by excessively rigid patterns of behavior • Behavioral patterns become self-defeating. • Person has deeply ingrained maladaptive personality traits Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -61
Personality Disorders • A cluster of psychological disorders characterized by excessively rigid patterns of behavior • Behavioral patterns become self-defeating. • Person has deeply ingrained maladaptive personality traits Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -61
 Types of Personality Disorders • • • Paranoid Schizotypal Antisocial Borderline • • • Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Histrionic Narcissistic Avoidant Dependent Obsessivecompulsive 11 -62
Types of Personality Disorders • • • Paranoid Schizotypal Antisocial Borderline • • • Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Histrionic Narcissistic Avoidant Dependent Obsessivecompulsive 11 -62
 Symptoms of Antisocial Personality Disorder • • • Disregard for rules Lack of concern for others Act on selfish impulse Irresponsible Take advantage of others for own need or personal gain. • Lack remorse for mistreatment of others • May be highly intelligent and charming Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -63
Symptoms of Antisocial Personality Disorder • • • Disregard for rules Lack of concern for others Act on selfish impulse Irresponsible Take advantage of others for own need or personal gain. • Lack remorse for mistreatment of others • May be highly intelligent and charming Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -63
 Causes of Antisocial Personality Disorder • Brain abnormalities • Genetic contributions • Exaggerated cravings for stimulation • Environmental factors • Family history Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -64
Causes of Antisocial Personality Disorder • Brain abnormalities • Genetic contributions • Exaggerated cravings for stimulation • Environmental factors • Family history Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -64
 Application: Module 11. 7 Suicide Prevention
Application: Module 11. 7 Suicide Prevention
 Module 11. 7 Preview Question • What steps can you take to help someone who is threatening suicide? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -66
Module 11. 7 Preview Question • What steps can you take to help someone who is threatening suicide? Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -66
 Facing the Threat of Suicide • Recognize the seriousness of the situation. • Take implied threats seriously. • Express understanding. • Focus on alternatives. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -67
Facing the Threat of Suicide • Recognize the seriousness of the situation. • Take implied threats seriously. • Express understanding. • Focus on alternatives. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -67
 Facing the Threat of Suicide (Cont’d) • Assess the immediate danger. • Enlist the person’s agreement to seek help. • Accompany the person to seek help. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -68
Facing the Threat of Suicide (Cont’d) • Assess the immediate danger. • Enlist the person’s agreement to seek help. • Accompany the person to seek help. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11 -68


