ea85e5c22ed82350a0434080c12ff680.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

CHAPTER ELEVEN BEHAVIORAL FINANCE Practical Investment Management Robert A. Strong
Outline w Introduction w Established Behaviors ú ú ú ú Representativeness Heuristic Loss Aversion Fear of Regret Myopic Loss Aversion Herding Anchoring Illusion of Control Prospect Theory South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 2
Outline w Established Behaviors … continued ú ú ú ú ú Mental Accounting Asset Segregation Hindsight Bias Overconfidence Framing Availability Heuristic Illusion of Truth Biased Expectations Reference Dependence South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 3
Outline w Mistaken Statistics ú ú ú The Special Nature of Round Numbers Extrapolation Percentages vs. Numbers Sample Size Apparent Order Regression to the Mean South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 4
Introduction w There are three sub fields to modern financial research. Theoretical finance is the study of logical relationships among assets. Empirical finance deals with the study of data in order to infer relationships. Behavioral finance integrates psychology into the investment process. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 5
Introduction “Financial economists have been aware for a long time that in laboratory settings, humans often make systematic mistakes and choices that cannot be explained by traditional models of choice under uncertainty. ” – Paul Pfleiderer South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 6

Introduction Behavioral finance research focuses on how investors make decisions to buy and sell securities, and how they choose between alternatives. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 7

Established Behaviors Representativeness Heuristic w The representativeness heuristic takes one characteristic of a company and extends it to other aspects of the firm. w In particular, many investors believe a wellrun company represents a good investment. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 8

Representativeness Heuristic Insert Table 11 -1 here. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 9
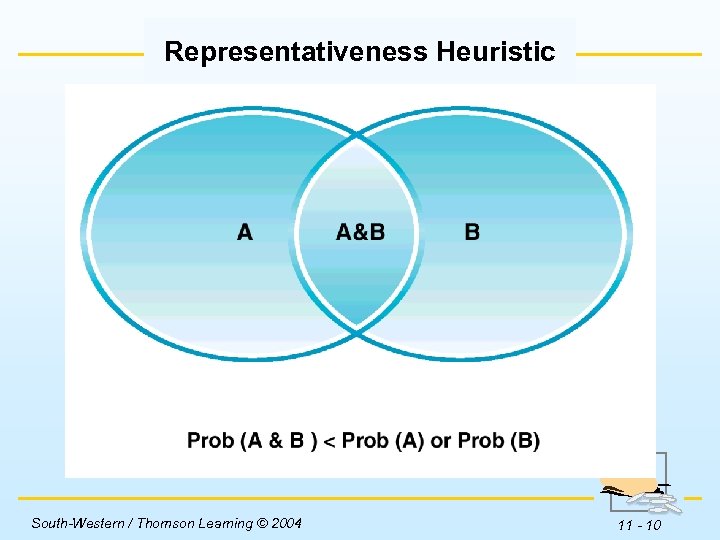
Representativeness Heuristic Insert Figure 11 -1 here. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 10
Established Behaviors Loss Aversion w Investors do not like losses and often engage in mental gymnastics to reduce their psychological impact. w Their tendency to sell a winning stock rather than a losing stock is called the disposition effect in some of the behavioral finance literature. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 11

Established Behaviors Fear of Regret w Investors do not like to make mistakes. w Rather than being unable to decide among attractive alternatives, their focus is on the negative: What if they pick the wrong stock? South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 12

Established Behaviors Myopic Loss Aversion w Investors have a tendency to assign too much importance to routine daily fluctuations in the market. w Abandoning a long-term investment program because of normal market behavior is sub optimal behavior. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 13

Established Behaviors Herding w Herding refers to the lemming-like behavior of investors and analysts looking around, seeing what each other is doing, and heading in that direction. w There may not have been safety in numbers, but there probably was some comfort in them. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 14

Established Behaviors Anchoring w Our decisions can be influenced by extraneous information contained in the problem statement. w For example, investors tend to remember the price they paid for a stock, and this information influences their subsequent decisions about what to do with it. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 15
Established Behaviors Illusion of Control w We like to pretend that we can influence the resulting score by varying the force with which we throw a dice. w Similarly, investors like to look at charts, although charts are theoretically not helpful in predicting the future prospects for a stock. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 16

Established Behaviors Prospect Theory w Risk averse investors get increasing utility from higher levels of wealth, but at a decreasing rate. w Research shows that while risk aversion may accurately describe investor behavior with gains, investors often show risk seeking behavior when they face a loss. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 17
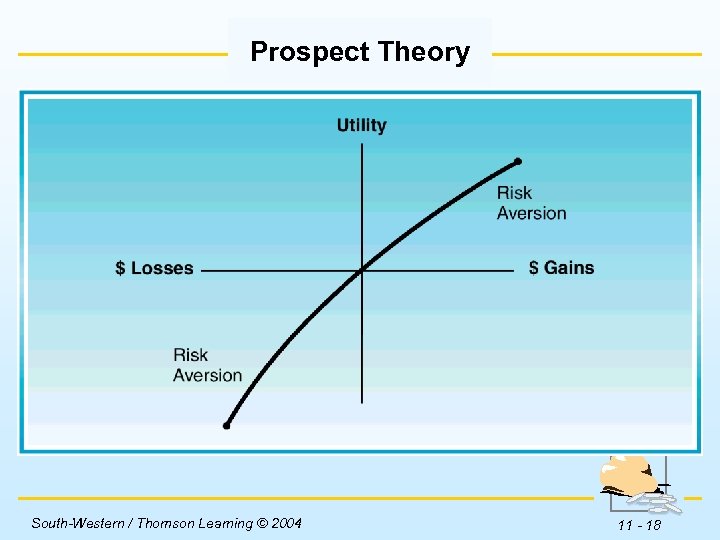
Prospect Theory Insert Figure 11 -2 here. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 18
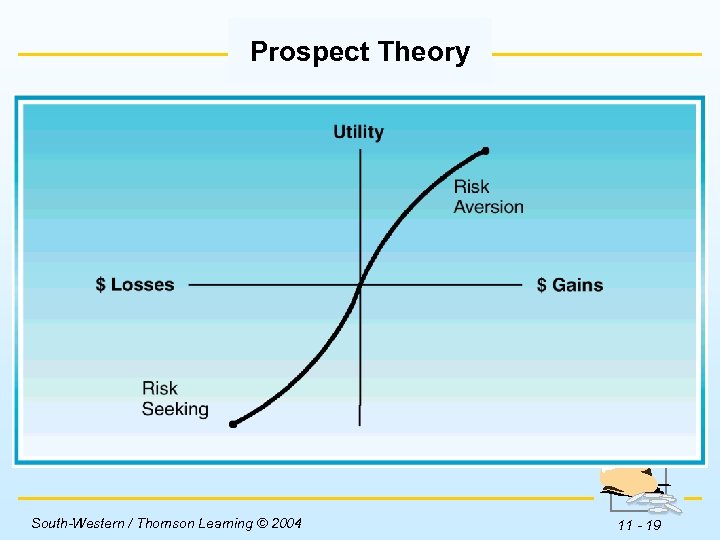
Prospect Theory Insert Figure 11 -3 here. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 19
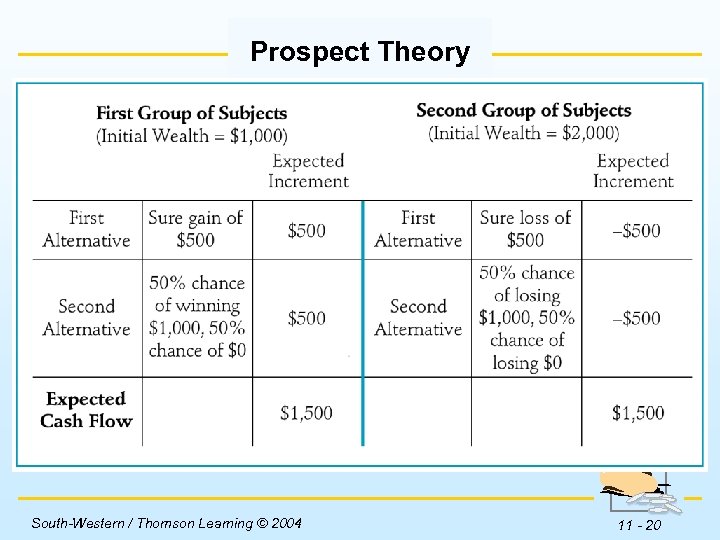
Prospect Theory Insert Table 11 -2 here. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 20

Established Behaviors Mental Accounting w Mental accounting refers to our tendency to “put things in boxes” and track them individually. w For example, investors tend to differentiate between dividend and capital dollars, and between realized and unrealized gains. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 21

Established Behaviors Asset Segregation w Asset segregation refers to our tendency to look at investment decisions individually rather than as part of a group. w The portfolio may be up handsomely for the reporting period, but the investor will still be concerned about the individual holdings that did not perform well. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 22
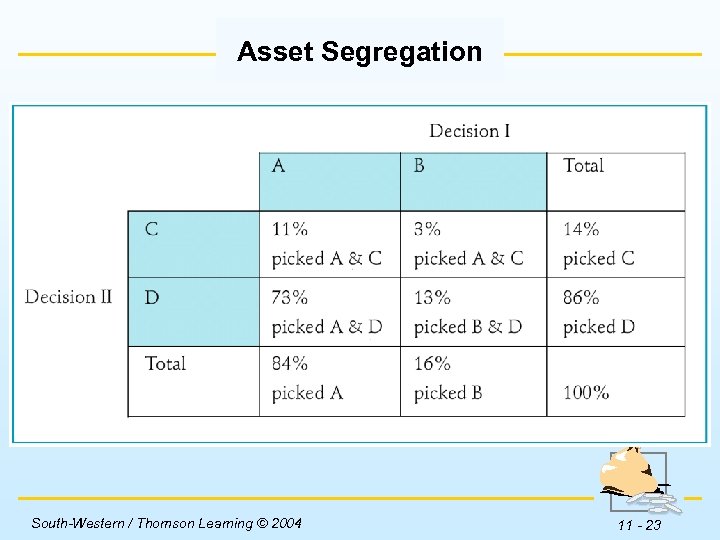
Asset Segregation Insert Table 11 -3 here. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 23

Established Behaviors Hindsight Bias w Hindsight bias refers to our tendency to remember positive outcomes and repress negative outcomes. w Investors remember when their pet trading strategy turned up roses, but do not dwell on the numerous times the strategy failed. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 24

Established Behaviors Overconfidence w Overconfidence refers to our tendency to believe that certain things are more likely than they really are. w For example, most investors think they are above-average stock pickers. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 25

Established Behaviors Framing w The concept of framing involves attempts to overlay a situation with an implied sense of gain or loss. w It is easier to pay $3, 400 for something that you expected to cost $3, 300 than it is to pay $100 for something you expected to be free. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 26
Established Behaviors Availability Heuristic w The availability heuristic is the contention that things that are easier to remember are thought to be more common. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 27
Established Behaviors Illusion of Truth w People tend to believe things that are easier to understand more readily than things that are more complicated. w Most investors prefer a low PE ratio, since they prefer to buy low-priced stocks with high earnings. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 28

Established Behaviors Biased Expectations w Our prior experience causes us to anticipate certain relationships or characteristics that may not apply outside our frame of reference. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 29

Established Behaviors Reference Dependence w Suppose you demand $75, 000 in salary for the next year. Your boss offers you $60, 000 and if things go to arbitration, $50, 000. w People currently earning $60, 000 tend to accept the offer, while people currently earning $75, 000 tend to take the gamble and go to arbitration. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 30

Mistaken Statistics w There are some other tendencies that may have a behavioral influence on asset values. w These involve “innumeracy” or a misunderstanding of the likeliness of an event or series of events. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 31

Mistaken Statistics The Special Nature of Round Numbers w Given a giant lottery wheel with numbers from one to one thousand, many of us would find a random outcome like 287 to be more reasonable than the “unusual” outcome of 1, 000. w Similarly, investors tend to make disproportionate use of round numbers when placing stop or limit orders. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 32
Mistaken Statistics Extrapolation w We have a tendency to assume that the past will repeat itself and to give too much weight to recent experience. w A belief that recent occurrences influence the next outcome in a sequence of independent events is known as the gambler’s fallacy. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 33

Mistaken Statistics Percentages vs. Numbers w Suppose the incidence of a particular disease rose from 10 in a million to 13 in a million. w We would likely find that to many people, 3 more cases is not a cause for concern, although a 30% increase is. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 34

Mistaken Statistics Sample Size w There are many instances where people draw incorrect inferences from statistical data. w The probability of a given person winning the lottery twice is very remote. However, the probability of someone winning twice is actually reasonably good. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 35
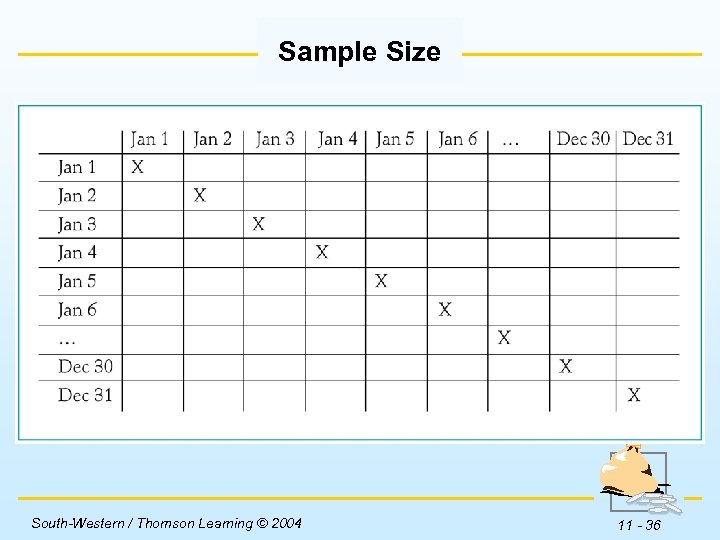
Sample Size Insert Table 11 -4 here. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 36
Mistaken Statistics Apparent Order w A single occurrence of an unlikely event becomes much more likely as the sample size increases. w However, many people will find a run of six consecutive numbers in a daily state lottery extremely unlikely. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 37
Mistaken Statistics Regression to the Mean w The regression to the mean concept states that given a series of random, independent data observations, an unusual occurrence tends to be followed by a more ordinary event. w Hence, chasing last year’s winning mutual fund is likely to be a losing strategy, although many investors do precisely this. South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 38

Review w Introduction w Established Behaviors ú ú ú ú Representativeness Heuristic Loss Aversion Fear of Regret Myopic Loss Aversion Herding Anchoring Illusion of Control Prospect Theory South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 39

Review w Established Behaviors … continued ú ú ú ú ú Mental Accounting Asset Segregation Hindsight Bias Overconfidence Framing Availability Heuristic Illusion of Truth Biased Expectations Reference Dependence South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 40
Review w Mistaken Statistics ú ú ú The Special Nature of Round Numbers Extrapolation Percentages vs. Numbers Sample Size Apparent Order Regression to the Mean South-Western / Thomson Learning © 2004 11 - 41
ea85e5c22ed82350a0434080c12ff680.ppt