06219af24e7e1909883127855fac4357.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

CHAPTER Day 16 BUS 222

Agenda • Questions? • Quiz 4 Today (45 min. ) – Chaps 10, 11 & 12 – 15 M/C and 1 extra credit – Open Book, Open Notes 45 mins • Assignment 5 Due • Assignment posted – Due April 10 – Marketing Assignment 6. pdf • Begin Discussion on Pricing Concepts for Establishing Value (30 min. )

CHAPTER PRICING CONCEPTS FOR ESTABLISHING VALUE Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin 13 Copyright © 2012 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.

Pricing Concepts for Establishing Value LEARNING OBJECTIVES LO 1 List the four pricing orientations. LO 2 Explain the relationship between price and quantity sold. LO 3 Explain price elasticity. LO 4 Describe how to calculate a product’s break-even point. LO 5 Indicate the four types of price competitive levels.

Which is the best Wine? $40 $70 $22

Price and Value What’s the most you will pay for a nice hotel? ©Uden Graham/Redlink/Corbis
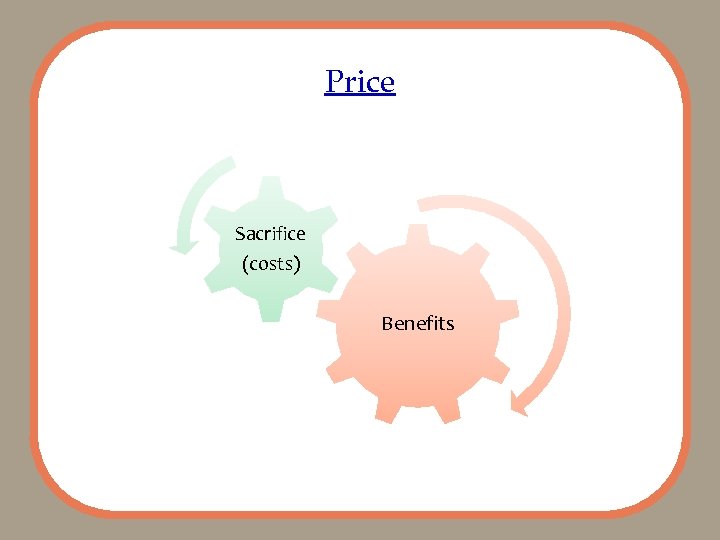
Price Sacrifice (costs) Benefits

Bottled vs. Tap Water
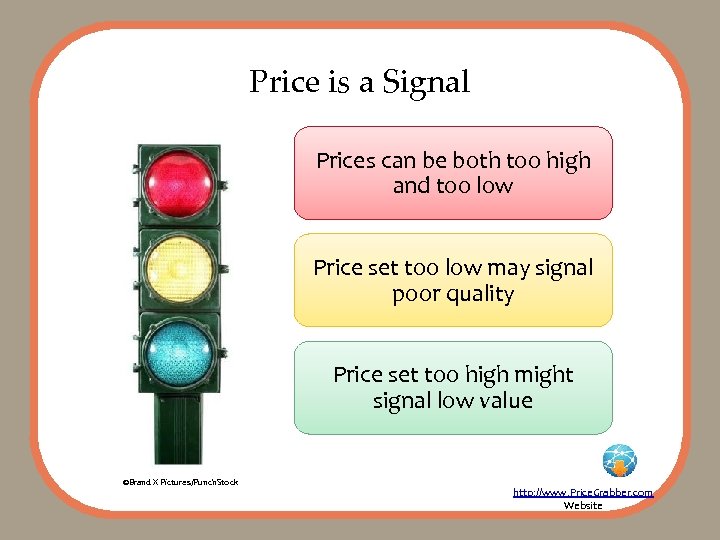
Price is a Signal Prices can be both too high and too low Price set too low may signal poor quality Price set too high might signal low value ©Brand X Pictures/Punch. Stock http: //www. Price. Grabber. com Website

The Role of Price in the Marketing Mix Chad Baker/Ryan Mc. Vay/Getty Images Price is usually ranked as one of the most important factors in purchase decisions Price is the only marketing mix element that generates revenue
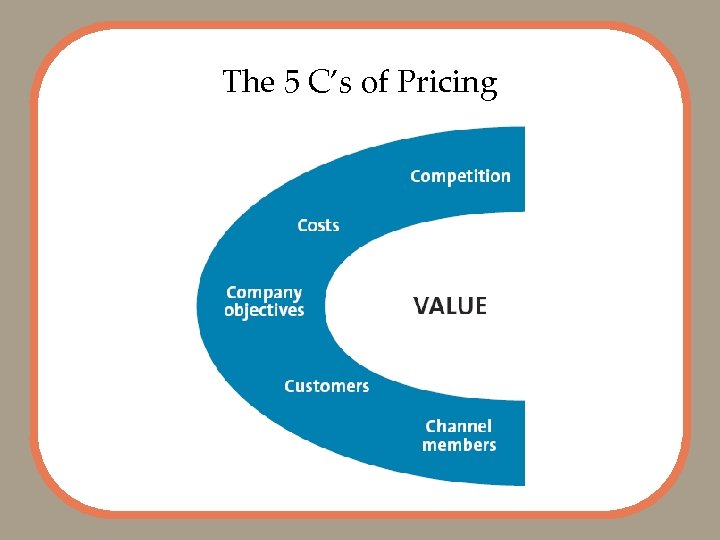
The 5 C’s of Pricing

1 st C: Company Objectives
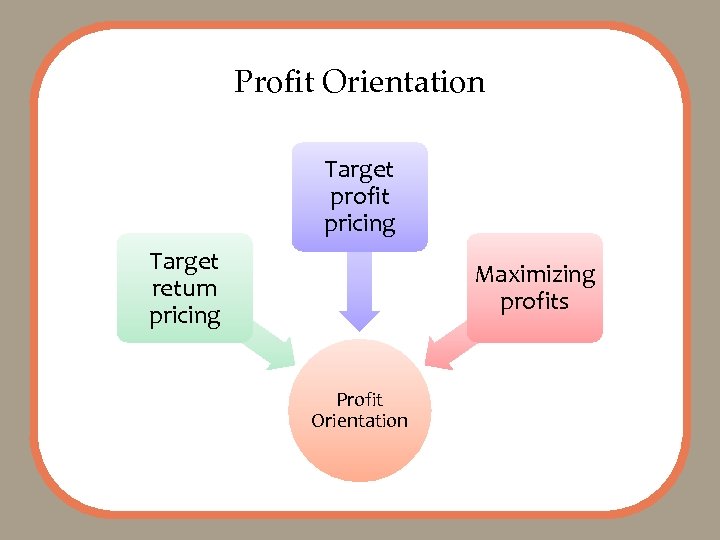
Profit Orientation Target profit pricing Target return pricing Maximizing profits Profit Orientation
Sales Orientation Focus on increasing sales Does not always imply setting low prices More concerned with overall market share

Competitor Orientation Roz Woodward/Getty Images • Competitive parity • Status quo pricing • Value is not part of this pricing strategy

Customer Orientation = C Borland/Photo. Link/Getty Images Don Farrall/Getty Images Focus on customer expectations by matching prices to customer expectations

What are they trying to accomplish with this ad? http: //www. zipcar. com/
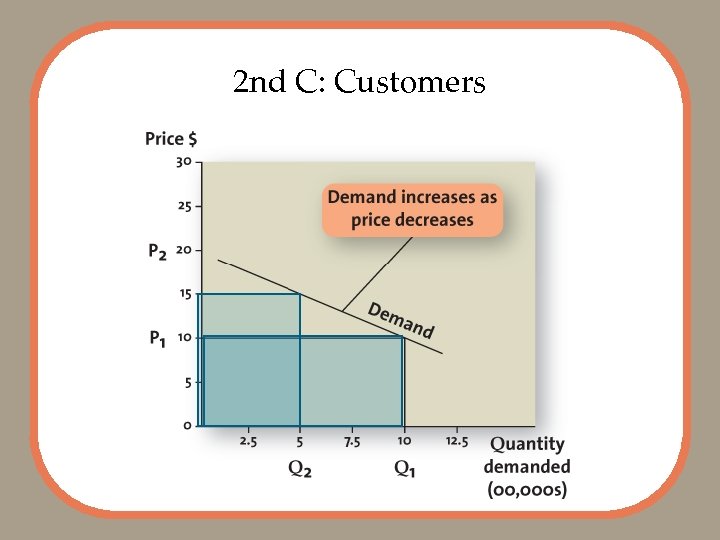
2 nd C: Customers

Demand Curves and Pricing Knowing demand curve enables to see relationship between price and demand Photo by Simon Frederick/Getty Images

Can you name the price? $89. 95 $199. 95 $399. 95 $799. 95 $1795. 95 $3795. 95 http: //woodlandcreekfurniture. com/product/bungalow-dresser-with-five-drawers-or-six-drawers/
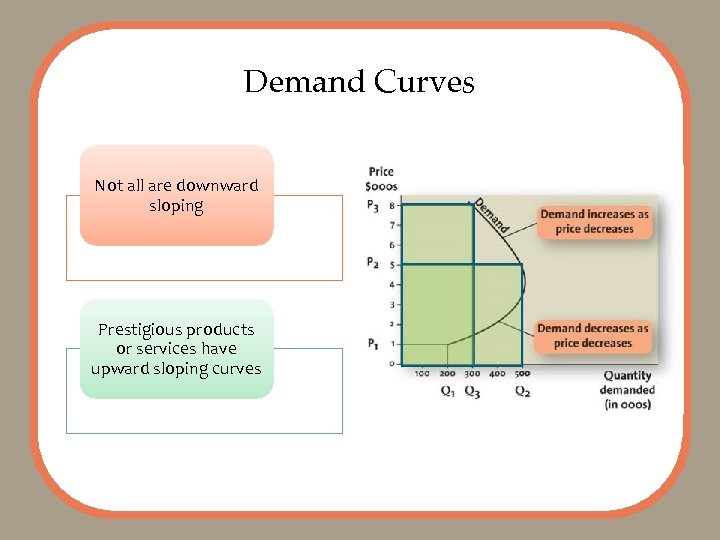
Demand Curves Not all are downward sloping Prestigious products or services have upward sloping curves
Price Elasticity of Demand Elastic (price sensitive) Inelastic (price insensitive) Consumers are less sensitive to price increases for necessities ©Photo. Link/Getty Images

Price Elasticity of Demand ©Dennis Mac. Donald/Photo. Edit, Inc. ©Bill Aron/Photo. Edit, Inc.

Price Elasticity of Demand Example • When price of Porterhouse Steak is $10/lb I may buy one 32 oz steak every month • When the price drops to $8/lb I will buy four 32 oz steaks every month • % change of demand is (8 -2)/8 = 75% • % change in price is ($8 – $10)/$8 = -25% • Price elasticity of demand is 75%/-25% = -3
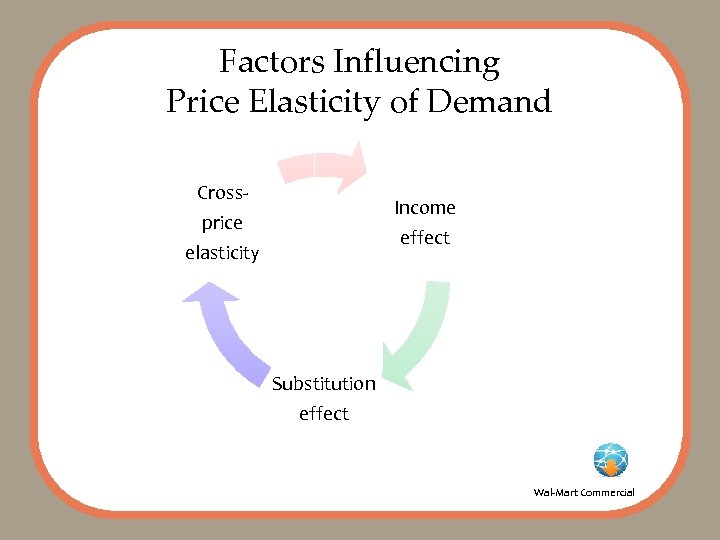
Factors Influencing Price Elasticity of Demand Cross- Income price effect elasticity Substitution effect Wal-Mart Commercial

Substitution Effect • Meet Pete, college student on a budget: • Old Spice Sport Deodorant user • At the store he notices that Old Spice is more expensive • Pete decides to give another brand a try and save money Banana. Stock/Jupiter. Images

Cross-Price Elasticity Getty Images/Digital Vision • Meet Kendra, selfsupporting college student: • Buys a new printer on sale for a great price • Learns it requires special ink cartridges that cost more than the printer
3 rd C: Costs • Variable Costs – Vary with production volume • Fixed Costs – Unaffected by production volume • Total Cost – Sum of variable and fixed costs Michael Rosenfeld/Stone/Getty Images
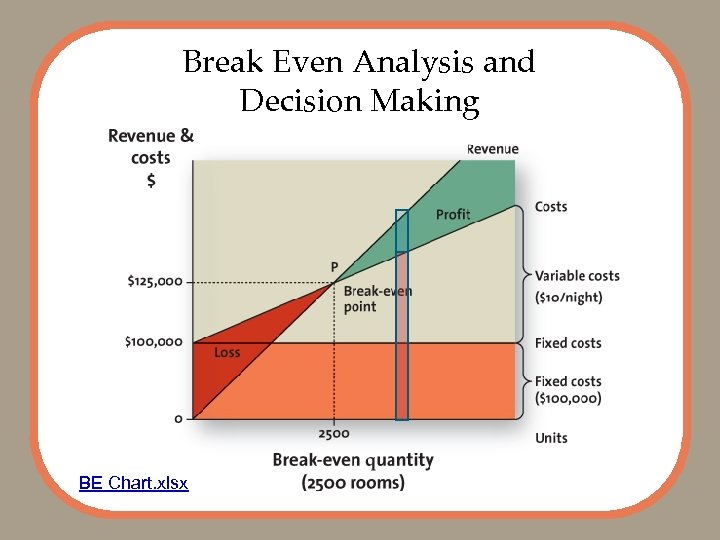
Break Even Analysis and Decision Making BE Chart. xlsx
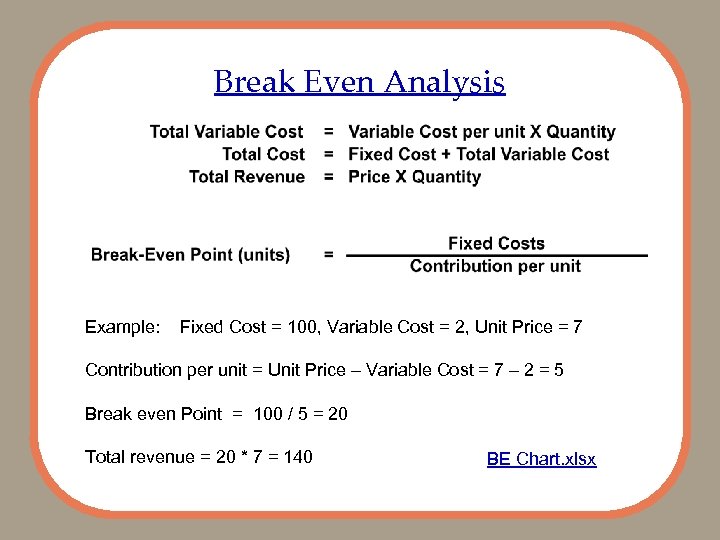
Break Even Analysis Example: Fixed Cost = 100, Variable Cost = 2, Unit Price = 7 Contribution per unit = Unit Price – Variable Cost = 7 – 2 = 5 Break even Point = 100 / 5 = 20 Total revenue = 20 * 7 = 140 BE Chart. xlsx

4 th C: Competition Subway Commercial

Wal-Mart vs. Target

5 th C: Channel Members • Manufacturers, wholesalers and retailers can have different perspectives on pricing strategies • Manufactures must protect against gray market transactions

Check Yourself 1. 2. 3. 4. What are the five Cs of pricing? Identify the four types of company objectives. What is the difference between elastic versus inelastic demand? How does one calculate the breakeven point in units?

Macro Influences on Pricing • The Internet • Increased price sensitivity • Growth of online auctions Ryan Mc. Vay/Getty Images
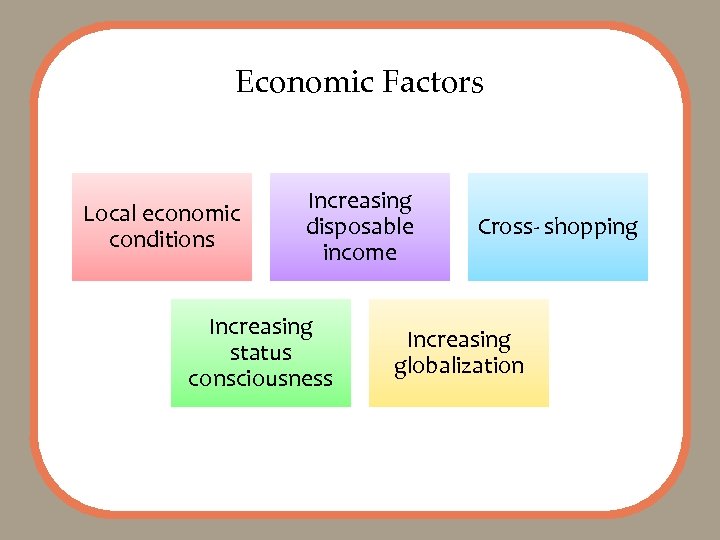
Economic Factors Local economic conditions Increasing disposable income Increasing status consciousness Cross- shopping Increasing globalization

Check Yourself 1. How have the Internet and economic factors affected the way people react to prices?
06219af24e7e1909883127855fac4357.ppt