35816608f2c382b621b28789080762fb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Chapter 9 Part 2 Decision Support Systems Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2008, The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved
Chapter 9 Part 2 Decision Support Systems Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2008, The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved
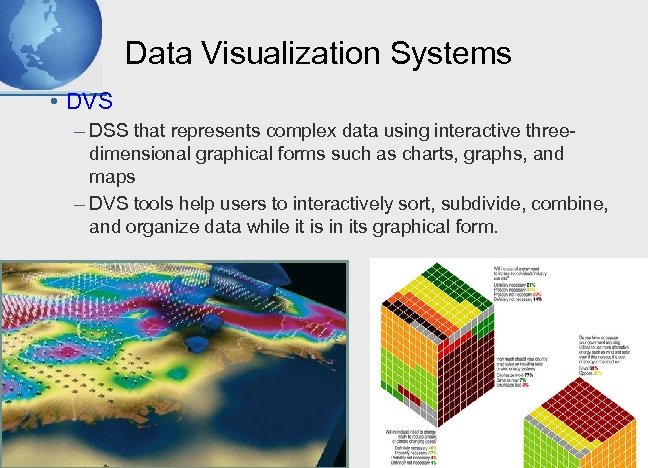 Data Visualization Systems • DVS – DSS that represents complex data using interactive threedimensional graphical forms such as charts, graphs, and maps – DVS tools help users to interactively sort, subdivide, combine, and organize data while it is in its graphical form. 9 - 2
Data Visualization Systems • DVS – DSS that represents complex data using interactive threedimensional graphical forms such as charts, graphs, and maps – DVS tools help users to interactively sort, subdivide, combine, and organize data while it is in its graphical form. 9 - 2
 Data Mining • to provide decision support to managers and business professionals through knowledge discovery • Analyzes vast store of historical business data, from many databases and data warehouse • Tries to discover patterns, trends, and correlations hidden in the data that can help a company improve its business performance • E. g. Blockbuster Entertainment mines its video rental history database to recommend rentals to individual customers. American Express can suggest products to its cardholders based on analysis of their monthly expenditures. • Market basket analysis - the combinations of items consumers group together in one purchase. Tales of diapers. 9 - 3
Data Mining • to provide decision support to managers and business professionals through knowledge discovery • Analyzes vast store of historical business data, from many databases and data warehouse • Tries to discover patterns, trends, and correlations hidden in the data that can help a company improve its business performance • E. g. Blockbuster Entertainment mines its video rental history database to recommend rentals to individual customers. American Express can suggest products to its cardholders based on analysis of their monthly expenditures. • Market basket analysis - the combinations of items consumers group together in one purchase. Tales of diapers. 9 - 3
 Enterprise Interface Portals • EIP – Web-based interface – Integration of MIS, DSS, EIS, and other technologies – Gives all intranet users and selected extranet users access – To a variety of internal and external business applications and services • Typically tailored to the user giving them a personalized digital dashboard 9 - 4
Enterprise Interface Portals • EIP – Web-based interface – Integration of MIS, DSS, EIS, and other technologies – Gives all intranet users and selected extranet users access – To a variety of internal and external business applications and services • Typically tailored to the user giving them a personalized digital dashboard 9 - 4
 Enterprise Information Portal Components 9 - 5
Enterprise Information Portal Components 9 - 5
 Knowledge Management Systems • The use of information technology to help gather, organize, and share business knowledge within an organization ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺗﻜﻨﻮﻟﻮﺟﻴﺎ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﻟﻠﻤﺴﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﻓﻲ ﺟﻤﻊ ﻭﺗﻨﻈﻴﻢ ﻭﺗﺒﺎﺩﻝ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﺠﺎﺭﻳﺔ ﺩﺍﺧﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ – Documents storing both facts and procedures – Examples • Databases, manuals, diagrams, books, bulletin, emails etc. • Enterprise Knowledge Portals – EIPs that are the entry to corporate intranets that serve as knowledge management systems – See KAU portal 9 - 6
Knowledge Management Systems • The use of information technology to help gather, organize, and share business knowledge within an organization ﺍﺳﺘﺨﺪﺍﻡ ﺗﻜﻨﻮﻟﻮﺟﻴﺎ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﻟﻠﻤﺴﺎﻋﺪﺓ ﻓﻲ ﺟﻤﻊ ﻭﺗﻨﻈﻴﻢ ﻭﺗﺒﺎﺩﻝ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻠﻮﻣﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﺠﺎﺭﻳﺔ ﺩﺍﺧﻞ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﻈﻤﺔ – Documents storing both facts and procedures – Examples • Databases, manuals, diagrams, books, bulletin, emails etc. • Enterprise Knowledge Portals – EIPs that are the entry to corporate intranets that serve as knowledge management systems – See KAU portal 9 - 6
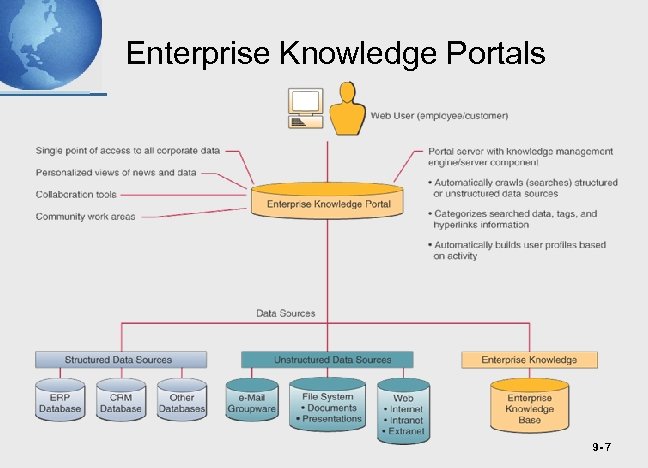 Enterprise Knowledge Portals 9 - 7
Enterprise Knowledge Portals 9 - 7
 Artificial Intelligence (AI) • Simulation of human intelligence • Goal is to develop computers that can simulate the ability to think, as well as see, hear, walk, talk, and feel 9 - 8
Artificial Intelligence (AI) • Simulation of human intelligence • Goal is to develop computers that can simulate the ability to think, as well as see, hear, walk, talk, and feel 9 - 8
 Domains of Artificial Intelligence Cognitive Science ﺍﻟﻌﻠﻮﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﻴﺔ • Based in biology, neurology, psychology, etc. • Focuses on researching how the human brain works and how humans think and learn • Expert system, fuzzy logics, neural network Robotics • Based in AI, engineering and physiology • Robot machines with computer intelligence and computer controlled, humanlike physical capabilities Natural language • Based in linguistics, psychology, computer science, etc. • Includes natural language and speech recognition, virtual reality 9 - 9
Domains of Artificial Intelligence Cognitive Science ﺍﻟﻌﻠﻮﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻓﻴﺔ • Based in biology, neurology, psychology, etc. • Focuses on researching how the human brain works and how humans think and learn • Expert system, fuzzy logics, neural network Robotics • Based in AI, engineering and physiology • Robot machines with computer intelligence and computer controlled, humanlike physical capabilities Natural language • Based in linguistics, psychology, computer science, etc. • Includes natural language and speech recognition, virtual reality 9 - 9
 Expert Systems • ES • A knowledge-based information system (KBIS) that uses its knowledge about a specific, complex application to act as an expert consultant to end users • ES use inference engines that match facts and rules, sequence questions for the user, draw a conclusion, and present the user a recommendation 9 - 10
Expert Systems • ES • A knowledge-based information system (KBIS) that uses its knowledge about a specific, complex application to act as an expert consultant to end users • ES use inference engines that match facts and rules, sequence questions for the user, draw a conclusion, and present the user a recommendation 9 - 10
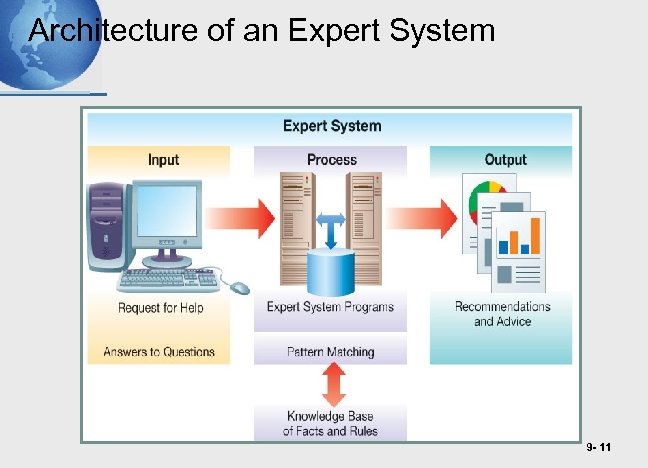 Architecture of an Expert System 9 - 11
Architecture of an Expert System 9 - 11
 ES: Rule-Based • Rule-Based – knowledge represented in rules and statements of fact – Rules: statements that typically take the form of a premise and a conclusion – Such as, If (condition) then (conclusion) • Rule based – loan processing • If personal income is $50, 000. 00 and more – Then approve loan 9 - 12
ES: Rule-Based • Rule-Based – knowledge represented in rules and statements of fact – Rules: statements that typically take the form of a premise and a conclusion – Such as, If (condition) then (conclusion) • Rule based – loan processing • If personal income is $50, 000. 00 and more – Then approve loan 9 - 12
 ES: Fuzzy Logic • Method of reasoning that resembles human reasoning • Allows for approximate values and inferences and incomplete or ambiguous data instead of relying only on crisp (fact) data • Uses terms such as “very high” rather than precise measures • Fuzzy logic rules – loan processing • Risk should be acceptable • If debt is very high – Then risk is positively increased • If income is increasing – Then risk is somewhat decreased • If cash reserves are low to very low – Then risk is very increased 9 - 13
ES: Fuzzy Logic • Method of reasoning that resembles human reasoning • Allows for approximate values and inferences and incomplete or ambiguous data instead of relying only on crisp (fact) data • Uses terms such as “very high” rather than precise measures • Fuzzy logic rules – loan processing • Risk should be acceptable • If debt is very high – Then risk is positively increased • If income is increasing – Then risk is somewhat decreased • If cash reserves are low to very low – Then risk is very increased 9 - 13
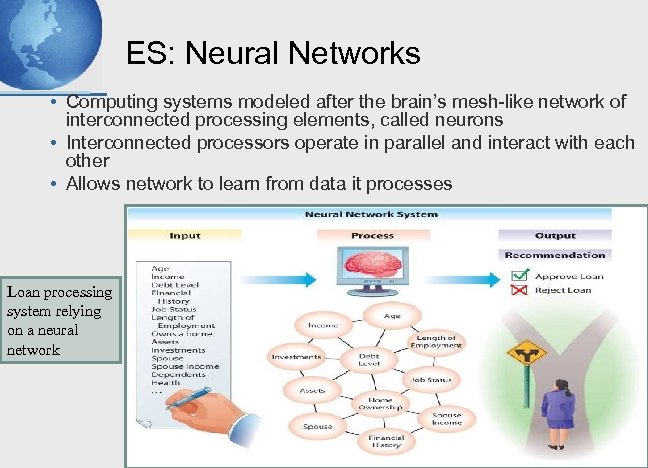 ES: Neural Networks • Computing systems modeled after the brain’s mesh-like network of interconnected processing elements, called neurons • Interconnected processors operate in parallel and interact with each other • Allows network to learn from data it processes Loan processing system relying on a neural network 9 - 14
ES: Neural Networks • Computing systems modeled after the brain’s mesh-like network of interconnected processing elements, called neurons • Interconnected processors operate in parallel and interact with each other • Allows network to learn from data it processes Loan processing system relying on a neural network 9 - 14
 Virtual Reality (VR) • Virtual reality – Using multisensory human-computer interfaces that enable human users to experience computer-simulated objects, spaces and “worlds” as if they actually exist • Computer-simulated reality • Relies on multisensory input/output devices such as – a tracking headset with video goggles and stereo earphones, – a data glove or jumpsuit with fiber-optic sensors that track your body movements, and – a walker that monitors the movement of your feet 9 - 15
Virtual Reality (VR) • Virtual reality – Using multisensory human-computer interfaces that enable human users to experience computer-simulated objects, spaces and “worlds” as if they actually exist • Computer-simulated reality • Relies on multisensory input/output devices such as – a tracking headset with video goggles and stereo earphones, – a data glove or jumpsuit with fiber-optic sensors that track your body movements, and – a walker that monitors the movement of your feet 9 - 15
 Intelligent Agents • A software surrogate for an end user or a process that fulfills a stated need or activity • Uses its built-in and learned knowledge base • To make decisions and accomplish tasks in a way that fulfills the intentions of a user • Also called software robots or bots 9 - 16
Intelligent Agents • A software surrogate for an end user or a process that fulfills a stated need or activity • Uses its built-in and learned knowledge base • To make decisions and accomplish tasks in a way that fulfills the intentions of a user • Also called software robots or bots 9 - 16
 User Interface Agents • Interface Tutors – observe user computer operations, correct user mistakes, and provide hints and advice on efficient software use • Presentation – show information in a variety of forms and media based on user preferences • Network Navigation – discover paths to information and provide ways to view information based on user preferences • Role-Playing – play what-if games and other roles to help users understand information and make better decisions e. g. secondlife 9 - 17
User Interface Agents • Interface Tutors – observe user computer operations, correct user mistakes, and provide hints and advice on efficient software use • Presentation – show information in a variety of forms and media based on user preferences • Network Navigation – discover paths to information and provide ways to view information based on user preferences • Role-Playing – play what-if games and other roles to help users understand information and make better decisions e. g. secondlife 9 - 17
 9 - 18
9 - 18
 Information Management Agents • Used rapidly in the Internet and Web • Search Agents – help users find files and databases, search for desired information, and suggest and find new types of information products, media, and resources – General Search engine e. g. google, yahoo – Specific search engine e. g. google scholar, job search agents • Information Brokers – provide commercial services to discover and develop information resources that fit the business or personal needs of a user – E. g. ask. com, why? – http: //www. virtualfreesites. com/search. agents. htm • Information Filters – receive, find, filter, discard, save, forward, and notify users about products received or desired – E. g amazon. com 9 - 19
Information Management Agents • Used rapidly in the Internet and Web • Search Agents – help users find files and databases, search for desired information, and suggest and find new types of information products, media, and resources – General Search engine e. g. google, yahoo – Specific search engine e. g. google scholar, job search agents • Information Brokers – provide commercial services to discover and develop information resources that fit the business or personal needs of a user – E. g. ask. com, why? – http: //www. virtualfreesites. com/search. agents. htm • Information Filters – receive, find, filter, discard, save, forward, and notify users about products received or desired – E. g amazon. com 9 - 19
 Case 1: Oracle Corporation and Others: Dashboards for Executives and Business Professionals: The Power and the Challenge • The dashboard has become the CEO’s killer app. • Dashboards provide key business information to executives, managers, and business professionals. • At GE executives use dashboard to follow the production of everything from light bulbs to dishwashers, making sure production lines are running smoothly. • Dashboards have some challenges. These tools can raise pressure on employees, create divisions in the office, and lead workers to hoard information. • Dashboards can hurt the morale of employees. 9 - 20
Case 1: Oracle Corporation and Others: Dashboards for Executives and Business Professionals: The Power and the Challenge • The dashboard has become the CEO’s killer app. • Dashboards provide key business information to executives, managers, and business professionals. • At GE executives use dashboard to follow the production of everything from light bulbs to dishwashers, making sure production lines are running smoothly. • Dashboards have some challenges. These tools can raise pressure on employees, create divisions in the office, and lead workers to hoard information. • Dashboards can hurt the morale of employees. 9 - 20
 Case Study Questions 1. What is the attraction of dashboards to CEOs and other executives? What real business value do they provide to executives? 2. The case emphasizes that managers of small businesses and many business professionals now rely on dashboards. What business benefits do dashboards provide to this business audience? 3. What are several reasons for criticism of the use of dashboards by executives? Do you agree with any of this criticism? Why or why not? 9 - 21
Case Study Questions 1. What is the attraction of dashboards to CEOs and other executives? What real business value do they provide to executives? 2. The case emphasizes that managers of small businesses and many business professionals now rely on dashboards. What business benefits do dashboards provide to this business audience? 3. What are several reasons for criticism of the use of dashboards by executives? Do you agree with any of this criticism? Why or why not? 9 - 21
 Real World Internet Activity 1. Use the Internet to research makers of dashboards for large and small business. For example, try Net. Suite, Hyperion Solutions, and Salesforce. com for relatively inexpensive versions and Microsoft, Oracle, and SAP for more costly corporate dashboards. Evaluate the dashboard examples and demos you experience. Pick your favorites and explain your reasons for doing so to the class. 9 - 22
Real World Internet Activity 1. Use the Internet to research makers of dashboards for large and small business. For example, try Net. Suite, Hyperion Solutions, and Salesforce. com for relatively inexpensive versions and Microsoft, Oracle, and SAP for more costly corporate dashboards. Evaluate the dashboard examples and demos you experience. Pick your favorites and explain your reasons for doing so to the class. 9 - 22
 Real World Group Activity 2. How would you like to work for an executive whose dashboard provides the level of information about company and employee performance described in this case? Would you want that level of information when you enter the executive ranks? – Discuss this issue, and formulate suggestions on any changes or safeguards you would propose for the business use of dashboards. 9 - 23
Real World Group Activity 2. How would you like to work for an executive whose dashboard provides the level of information about company and employee performance described in this case? Would you want that level of information when you enter the executive ranks? – Discuss this issue, and formulate suggestions on any changes or safeguards you would propose for the business use of dashboards. 9 - 23
 Case 2: Harrah’s Entertainment, Lending. Tree, Deep. Green Financial, and Cisco Systems: • The promise of AI of automating decision making has been very slow to materialize. • The new generation AI applications are easier to create and manage, do not require anyone to identify the problems or to initiate the analysis, decision-making capabilities are embedded into the normal flow of work, and are triggered without human intervention. • They sense online data or conditions, apply codified knowledge or logic and make decisions with minimal human intervention. • But they rely on experts and managers to create and maintain rules and monitor the results. • Also, managers in charge of automated decision systems must develop processes for managing exceptions. 9 - 24
Case 2: Harrah’s Entertainment, Lending. Tree, Deep. Green Financial, and Cisco Systems: • The promise of AI of automating decision making has been very slow to materialize. • The new generation AI applications are easier to create and manage, do not require anyone to identify the problems or to initiate the analysis, decision-making capabilities are embedded into the normal flow of work, and are triggered without human intervention. • They sense online data or conditions, apply codified knowledge or logic and make decisions with minimal human intervention. • But they rely on experts and managers to create and maintain rules and monitor the results. • Also, managers in charge of automated decision systems must develop processes for managing exceptions. 9 - 24
 Case Study Questions 1. Why did some previous attempts to use artificial intelligence technologies fail? What key differences of the new AI-based applications versus the old cause the authors to declare that automated decision making is finally coming of age? 2. What types of decisions are best suited for automated decision making? Provide several examples of successful applications from the companies in this case to illustrate your answer. 9 - 25
Case Study Questions 1. Why did some previous attempts to use artificial intelligence technologies fail? What key differences of the new AI-based applications versus the old cause the authors to declare that automated decision making is finally coming of age? 2. What types of decisions are best suited for automated decision making? Provide several examples of successful applications from the companies in this case to illustrate your answer. 9 - 25
 Case Study Questions 3. What role do humans play in automated decision making applications? What are some of the challenges faced by managers where automated decision-making systems are being used? What solutions are needed to meet such challenges? 9 - 26
Case Study Questions 3. What role do humans play in automated decision making applications? What are some of the challenges faced by managers where automated decision-making systems are being used? What solutions are needed to meet such challenges? 9 - 26
 Real World Internet Activity 1. Use the Internet to find examples of companies that are using automated decision making or other business applications of artificial intelligence. You might begin by looking for such information on the companies mentioned in this case and their main competitors, and then widen your search to encompass other companies. What business benefits or challenges do you discover? 9 - 27
Real World Internet Activity 1. Use the Internet to find examples of companies that are using automated decision making or other business applications of artificial intelligence. You might begin by looking for such information on the companies mentioned in this case and their main competitors, and then widen your search to encompass other companies. What business benefits or challenges do you discover? 9 - 27
 Real World Group Activity 2. Artificial intelligence applications in business such as automated decision making pose potential business risks, as evidenced by the Cisco Systems experience, and have the potential for other risks to business and human security and safety, for example. – Discuss such risks and propose controls and safeguards to lessen the possibility of such occurrences. 9 - 28
Real World Group Activity 2. Artificial intelligence applications in business such as automated decision making pose potential business risks, as evidenced by the Cisco Systems experience, and have the potential for other risks to business and human security and safety, for example. – Discuss such risks and propose controls and safeguards to lessen the possibility of such occurrences. 9 - 28
 Case 3: IBM, Linden Labs, and Others: The Business Case for Virtual Worlds in a 3 D Internet • Second Life is a 3 -D virtual world entirely built and owned by its Residents. • Since opening to the public in 2003, it has grown explosively and today it is inhabited by more than eight million residents from around the globe. • It is catching the attention of many companies because of it’s ability to use as a platform for a whole new Net with huge opportunities to sell products and services. • It is also possible to exchange Second Life’s currency, called Linden dollars, for the real currency for a fee. • Residents could thus build, own, or sell their digital creations. • Second Life has become a real economy. 9 - 29
Case 3: IBM, Linden Labs, and Others: The Business Case for Virtual Worlds in a 3 D Internet • Second Life is a 3 -D virtual world entirely built and owned by its Residents. • Since opening to the public in 2003, it has grown explosively and today it is inhabited by more than eight million residents from around the globe. • It is catching the attention of many companies because of it’s ability to use as a platform for a whole new Net with huge opportunities to sell products and services. • It is also possible to exchange Second Life’s currency, called Linden dollars, for the real currency for a fee. • Residents could thus build, own, or sell their digital creations. • Second Life has become a real economy. 9 - 29
 Case Study Questions 1. What are the most important business benefits and limitations of 3 D virtual worlds like Second Life to real-world companies such as those mentioned in this case? 2. Why do you think IBM is taking a leadership role in promoting and using 3 D metaverses like Second Life? What business benefits might it expect to gain from its involvement in developing a 3 D Internet? Explain your reasoning. 9 - 30
Case Study Questions 1. What are the most important business benefits and limitations of 3 D virtual worlds like Second Life to real-world companies such as those mentioned in this case? 2. Why do you think IBM is taking a leadership role in promoting and using 3 D metaverses like Second Life? What business benefits might it expect to gain from its involvement in developing a 3 D Internet? Explain your reasoning. 9 - 30
 Case Study Questions 3. Are 3 D virtual worlds like Second Life “solutions in search of a problem” at this stage of their development, in that do not satisfy any vital business need? Why or why not? 9 - 31
Case Study Questions 3. Are 3 D virtual worlds like Second Life “solutions in search of a problem” at this stage of their development, in that do not satisfy any vital business need? Why or why not? 9 - 31
 Real World Internet Activity 1. Search the Internet to determine how Second Life, Linden Labs, IBM, and other companies mentioned in this case are doing in terms of the growth and business success of their development or use of 3 D virtual worlds. Have new competitors successfully entered the 3 D Internet market? If so, how do they differ in the products and services they offer? 9 - 32
Real World Internet Activity 1. Search the Internet to determine how Second Life, Linden Labs, IBM, and other companies mentioned in this case are doing in terms of the growth and business success of their development or use of 3 D virtual worlds. Have new competitors successfully entered the 3 D Internet market? If so, how do they differ in the products and services they offer? 9 - 32
 Real World Group Activity 2. Visit the Second Life Web site and evaluate the experience in terms of level of difficulty, response times, operation of basic functions, realism, and so forth. Are 3 D virtual worlds like Second Life ready for widespread use as an important form of social networking? How could they improve what they offer to make it more appealing and successful? Debate these issues. 9 - 33
Real World Group Activity 2. Visit the Second Life Web site and evaluate the experience in terms of level of difficulty, response times, operation of basic functions, realism, and so forth. Are 3 D virtual worlds like Second Life ready for widespread use as an important form of social networking? How could they improve what they offer to make it more appealing and successful? Debate these issues. 9 - 33


