e9e8064dfacd5d8b0fc253714d9fa3a1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 CHAPTER 9 EXPRESSING GENETIC INFO. P. 233 -254 copyright cmassengale 1
CHAPTER 9 EXPRESSING GENETIC INFO. P. 233 -254 copyright cmassengale 1
 RNA copyright cmassengale 2
RNA copyright cmassengale 2
 Roles of RNA and DNA • DNA is the MASTER PLAN • RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan copyright cmassengale 3
Roles of RNA and DNA • DNA is the MASTER PLAN • RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan copyright cmassengale 3
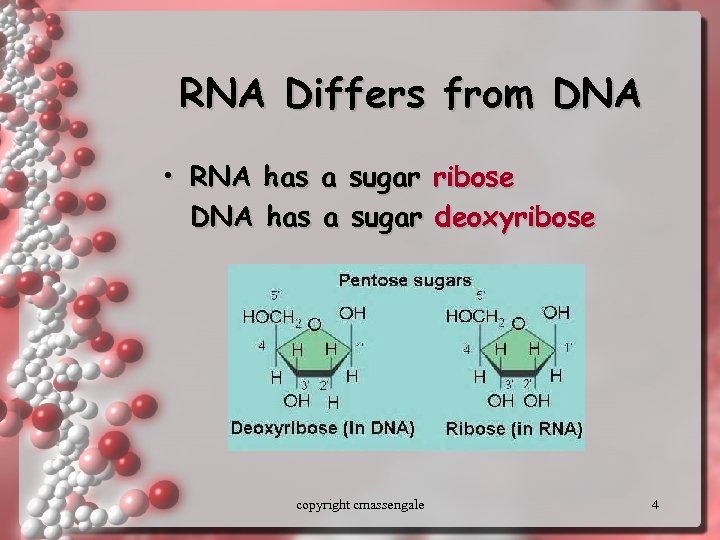 RNA Differs from DNA • RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose copyright cmassengale 4
RNA Differs from DNA • RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose copyright cmassengale 4
 Other Differences • • RNA contains the base uracil (U) DNA has thymine (T) RNA molecule is single-stranded DNA is doublestranded copyright cmassengale DNA 5
Other Differences • • RNA contains the base uracil (U) DNA has thymine (T) RNA molecule is single-stranded DNA is doublestranded copyright cmassengale DNA 5
 Remember the Complementary Bases On DNA: A-T C-G On RNA: A-U C-G copyright cmassengale 6
Remember the Complementary Bases On DNA: A-T C-G On RNA: A-U C-G copyright cmassengale 6
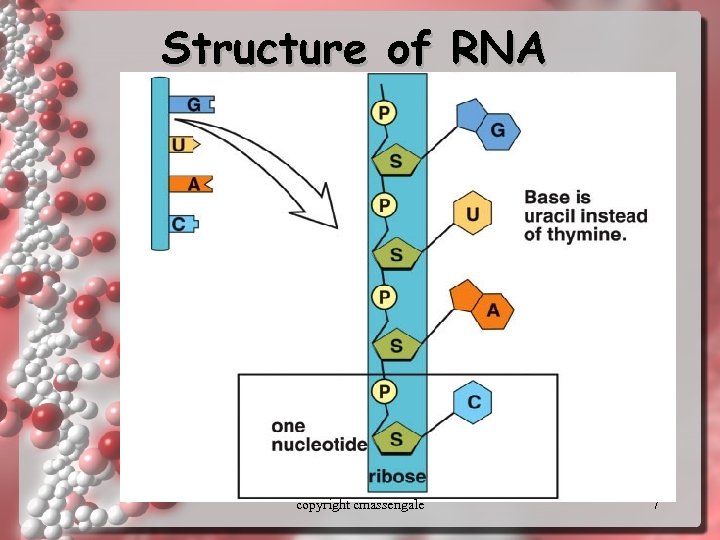 Structure of RNA copyright cmassengale 7
Structure of RNA copyright cmassengale 7
 . Three Types of RNA • Messenger RNA (m. RNA) copies DNA’s code & carries the genetic information to the ribosomes • Ribosomal RNA (r. RNA), along with protein, makes up the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (t. RNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesized copyright cmassengale 8
. Three Types of RNA • Messenger RNA (m. RNA) copies DNA’s code & carries the genetic information to the ribosomes • Ribosomal RNA (r. RNA), along with protein, makes up the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (t. RNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesized copyright cmassengale 8
 Messenger RNA • TEMPORARY COPY OF A GENE THAT ENCODES A PROTEIN (CARRIES THE GENETIC MESSAGE FROM DNA) • MADE THROUGH TRANSCRIPTION • PROVIDES THE PATTERN THAT DETERMINES THE ORDER OF AMINO ACIDS OF A PROTEIN STRAND copyright cmassengale 9
Messenger RNA • TEMPORARY COPY OF A GENE THAT ENCODES A PROTEIN (CARRIES THE GENETIC MESSAGE FROM DNA) • MADE THROUGH TRANSCRIPTION • PROVIDES THE PATTERN THAT DETERMINES THE ORDER OF AMINO ACIDS OF A PROTEIN STRAND copyright cmassengale 9
 Messenger RNA (m. RNA) • Carries the information for a specific protein • Sequence of 3 bases called codon • AUG – methionine or start codon • UAA, UAG, or UGA – stop codons copyright cmassengale 10
Messenger RNA (m. RNA) • Carries the information for a specific protein • Sequence of 3 bases called codon • AUG – methionine or start codon • UAA, UAG, or UGA – stop codons copyright cmassengale 10
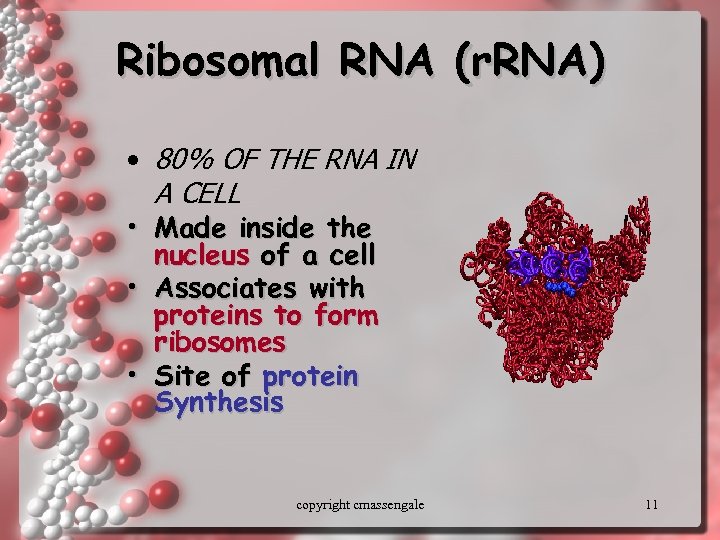 Ribosomal RNA (r. RNA) • 80% OF THE RNA IN A CELL • Made inside the nucleus of a cell • Associates with proteins to form ribosomes • Site of protein Synthesis copyright cmassengale 11
Ribosomal RNA (r. RNA) • 80% OF THE RNA IN A CELL • Made inside the nucleus of a cell • Associates with proteins to form ribosomes • Site of protein Synthesis copyright cmassengale 11
 Transfer RNA (t. RNA) • Clover-leaf shape • Single stranded molecule with attachment site at one end for an amino acid, LINKED TOGETHER DURING THE PROCESS OF TRANSLATION • Opposite end has three nucleotide bases called the copyright 12 anticodon cmassengale
Transfer RNA (t. RNA) • Clover-leaf shape • Single stranded molecule with attachment site at one end for an amino acid, LINKED TOGETHER DURING THE PROCESS OF TRANSLATION • Opposite end has three nucleotide bases called the copyright 12 anticodon cmassengale
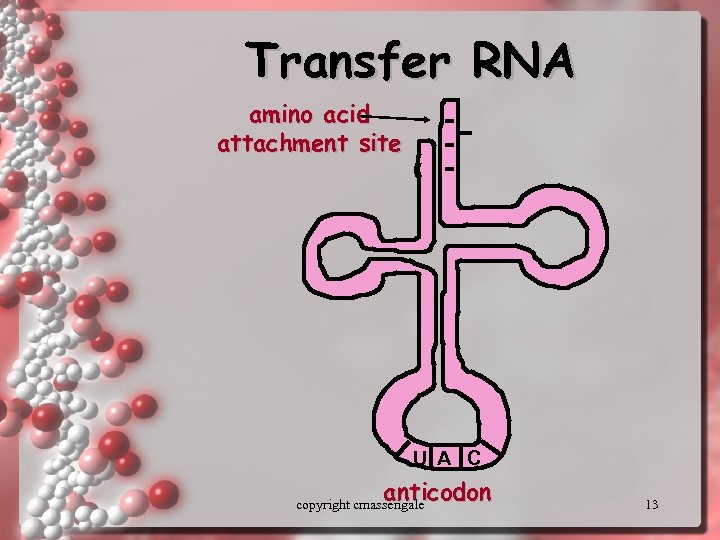 Transfer RNA amino acid attachment site U A C anticodon copyright cmassengale 13
Transfer RNA amino acid attachment site U A C anticodon copyright cmassengale 13
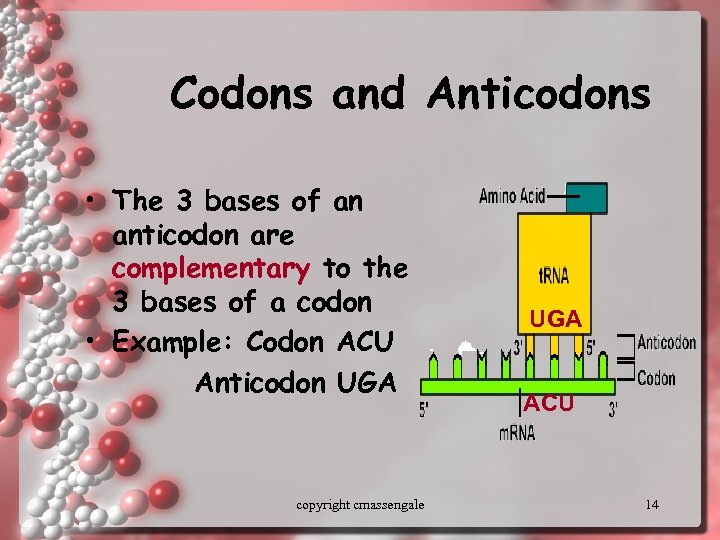 Codons and Anticodons • The 3 bases of an anticodon are complementary to the 3 bases of a codon • Example: Codon ACU Anticodon UGA copyright cmassengale UGA ACU 14
Codons and Anticodons • The 3 bases of an anticodon are complementary to the 3 bases of a codon • Example: Codon ACU Anticodon UGA copyright cmassengale UGA ACU 14
 The Genetic Code • A codon designates an amino acid • An amino acid may have more than one codon • There are 20 amino acids, but 64 possible codons • Some codons tell the ribosome to stop translating copyright cmassengale 15
The Genetic Code • A codon designates an amino acid • An amino acid may have more than one codon • There are 20 amino acids, but 64 possible codons • Some codons tell the ribosome to stop translating copyright cmassengale 15
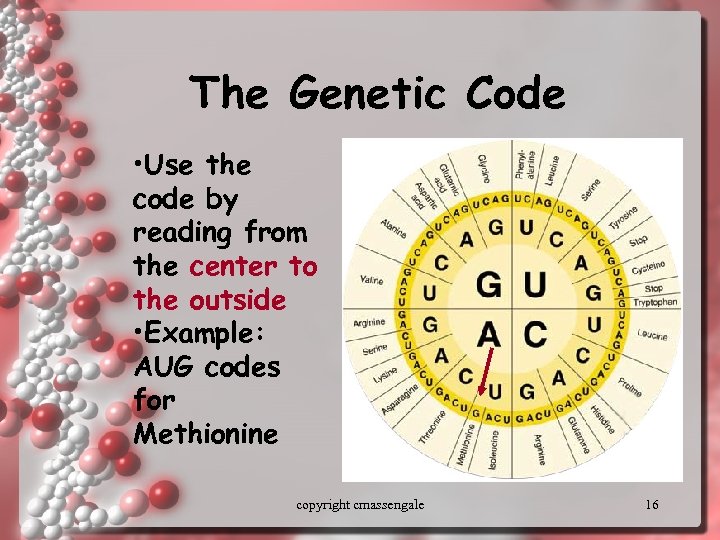 The Genetic Code • Use the code by reading from the center to the outside • Example: AUG codes for Methionine copyright cmassengale 16
The Genetic Code • Use the code by reading from the center to the outside • Example: AUG codes for Methionine copyright cmassengale 16
 Name the Amino Acids • • • GGG? UCA? CAU? GCA? AAA? copyright cmassengale 17
Name the Amino Acids • • • GGG? UCA? CAU? GCA? AAA? copyright cmassengale 17
 Transcription and Translation copyright cmassengale 18
Transcription and Translation copyright cmassengale 18
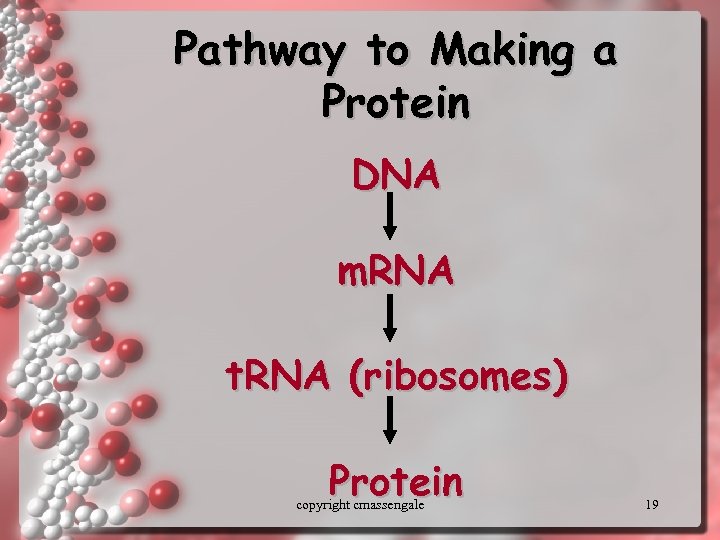 Pathway to Making a Protein DNA m. RNA t. RNA (ribosomes) Protein copyright cmassengale 19
Pathway to Making a Protein DNA m. RNA t. RNA (ribosomes) Protein copyright cmassengale 19
 Protein Synthesis § The production or synthesis of polypeptide chains (proteins) § Two phases: Transcription & Translation § m. RNA must be processed before it leaves the nucleus of eukaryotic cells copyright cmassengale 20
Protein Synthesis § The production or synthesis of polypeptide chains (proteins) § Two phases: Transcription & Translation § m. RNA must be processed before it leaves the nucleus of eukaryotic cells copyright cmassengale 20
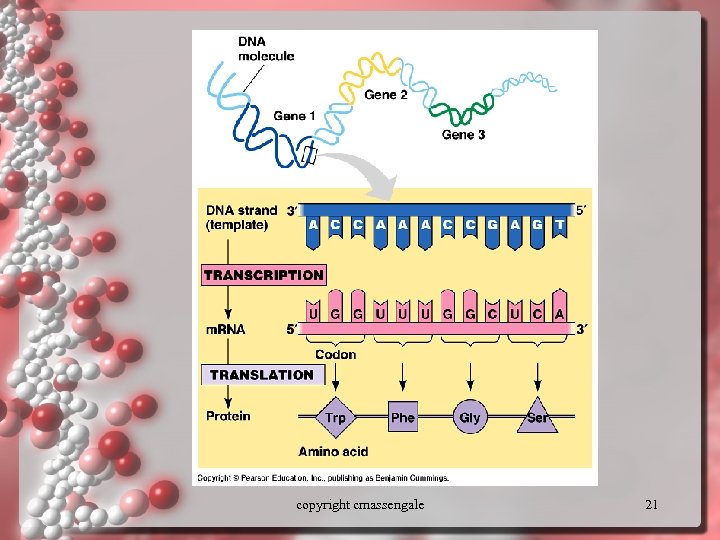 copyright cmassengale 21
copyright cmassengale 21
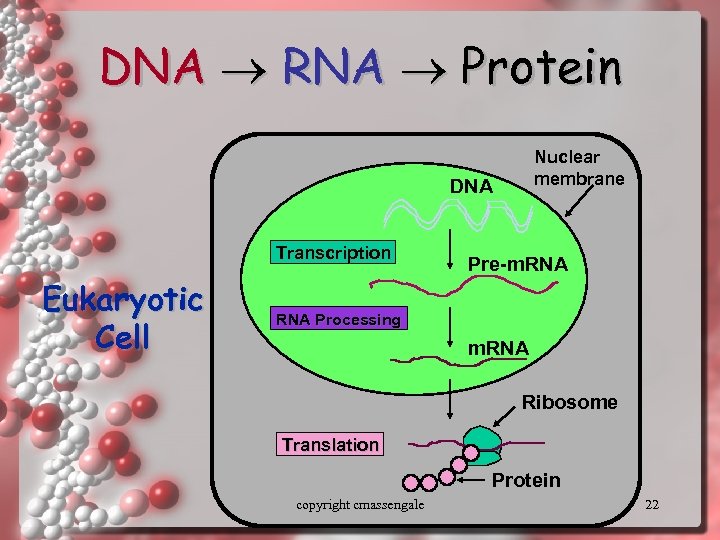 DNA RNA Protein Nuclear membrane DNA Transcription Eukaryotic Cell Pre-m. RNA Processing m. RNA Ribosome Translation Protein copyright cmassengale 22
DNA RNA Protein Nuclear membrane DNA Transcription Eukaryotic Cell Pre-m. RNA Processing m. RNA Ribosome Translation Protein copyright cmassengale 22
 Transcription • MAKING m. RNA FROM THE GENETIC CODE OF DNA copyright cmassengale 23
Transcription • MAKING m. RNA FROM THE GENETIC CODE OF DNA copyright cmassengale 23
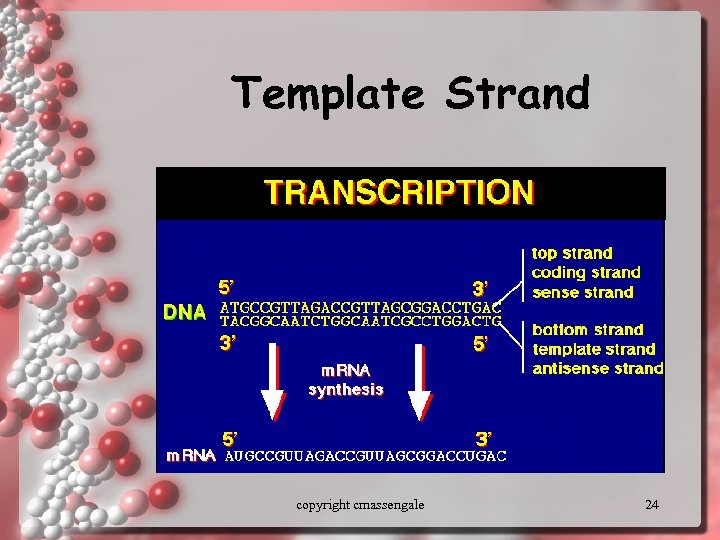 Template Strand copyright cmassengale 24
Template Strand copyright cmassengale 24
 Question: § What would be the complementary RNA strand for the following DNA sequence? DNA 5’-ATCGGCTAT -3’ copyright cmassengale 25
Question: § What would be the complementary RNA strand for the following DNA sequence? DNA 5’-ATCGGCTAT -3’ copyright cmassengale 25
 Answer: • DNA: 5’-ATCGGCTAT -3’ • RNA: 3’-UAGCCGAUA -5’ copyright cmassengale 26
Answer: • DNA: 5’-ATCGGCTAT -3’ • RNA: 3’-UAGCCGAUA -5’ copyright cmassengale 26
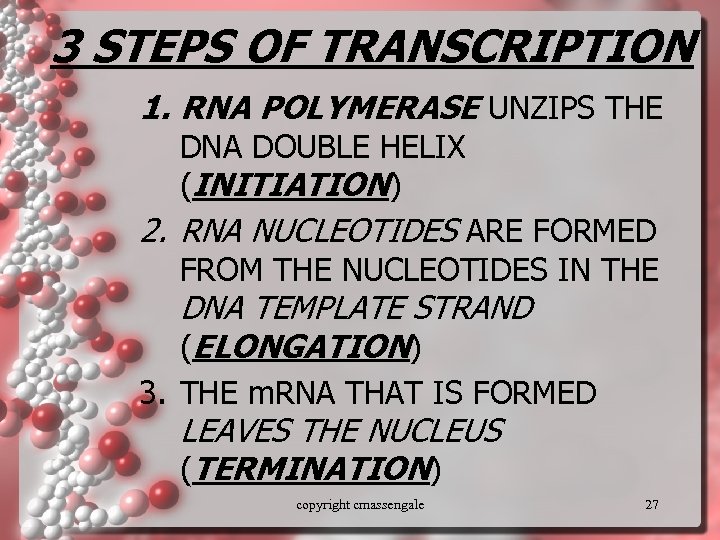 3 STEPS OF TRANSCRIPTION 1. RNA POLYMERASE UNZIPS THE DNA DOUBLE HELIX (INITIATION) 2. RNA NUCLEOTIDES ARE FORMED FROM THE NUCLEOTIDES IN THE DNA TEMPLATE STRAND (ELONGATION) 3. THE m. RNA THAT IS FORMED LEAVES THE NUCLEUS (TERMINATION) copyright cmassengale 27
3 STEPS OF TRANSCRIPTION 1. RNA POLYMERASE UNZIPS THE DNA DOUBLE HELIX (INITIATION) 2. RNA NUCLEOTIDES ARE FORMED FROM THE NUCLEOTIDES IN THE DNA TEMPLATE STRAND (ELONGATION) 3. THE m. RNA THAT IS FORMED LEAVES THE NUCLEUS (TERMINATION) copyright cmassengale 27
 m. RNA Processing • PIECES OF DNA CALLED INTRONS THAT DO NOT CODE FOR PROTEINS ARE REMOVED LEAVING THE CODING SEGMENTS CALLED EXONS copyright cmassengale 28
m. RNA Processing • PIECES OF DNA CALLED INTRONS THAT DO NOT CODE FOR PROTEINS ARE REMOVED LEAVING THE CODING SEGMENTS CALLED EXONS copyright cmassengale 28
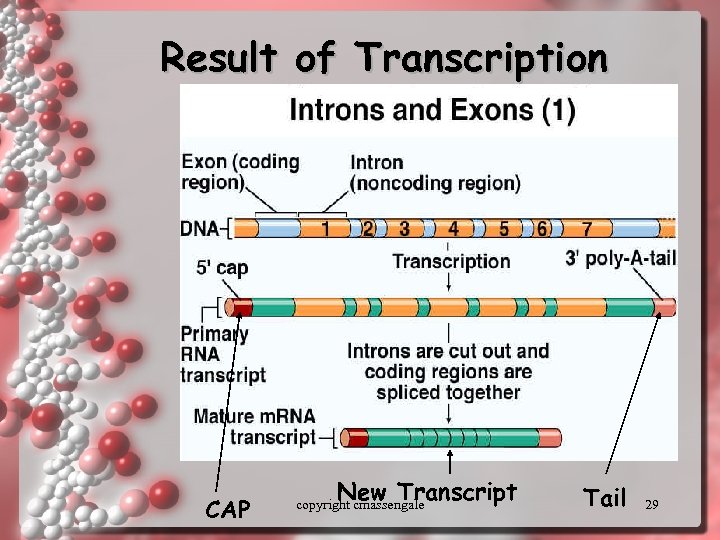 Result of Transcription CAP New Transcript copyright cmassengale Tail 29
Result of Transcription CAP New Transcript copyright cmassengale Tail 29
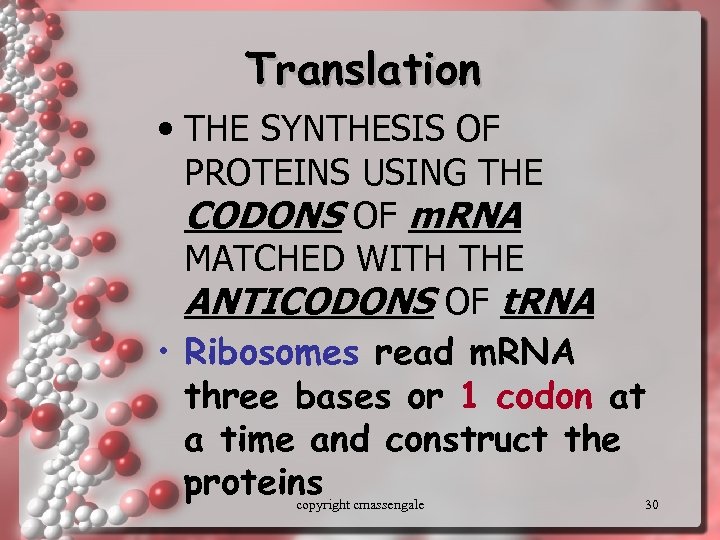 Translation • THE SYNTHESIS OF PROTEINS USING THE CODONS OF m. RNA MATCHED WITH THE ANTICODONS OF t. RNA • Ribosomes read m. RNA three bases or 1 codon at a time and construct the proteins copyright cmassengale 30
Translation • THE SYNTHESIS OF PROTEINS USING THE CODONS OF m. RNA MATCHED WITH THE ANTICODONS OF t. RNA • Ribosomes read m. RNA three bases or 1 codon at a time and construct the proteins copyright cmassengale 30
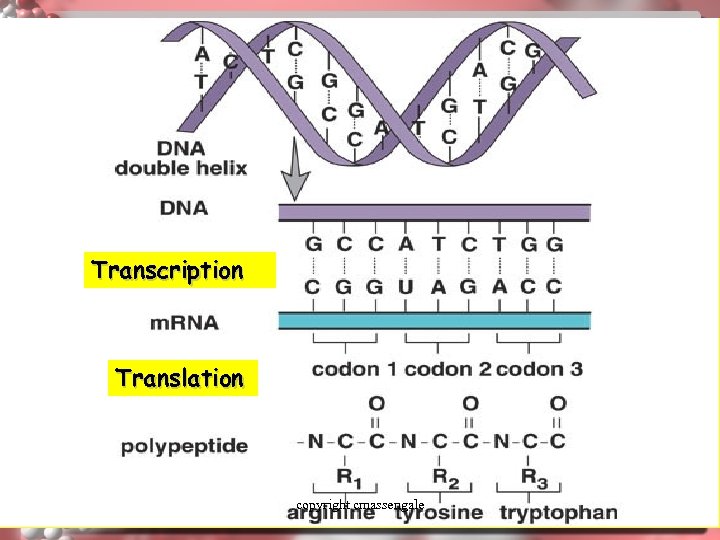 Transcription Translation copyright cmassengale 31
Transcription Translation copyright cmassengale 31
 CHARACTERISTICS • DETERMINES THE AMINO ACID SEQUENCE IN A PROTEIN • 64 DIFFERENT THREE-BASE CODONS “CODE” FOR 20 DIFFERENT AMINO ACIDS (CARRIED BY t. RNA) • THERE ALSO START (1) AND STOP (3) CODONS • OCCURS AT THE RIBOSOMES • REQUIRES ENZYMES AND ENERGY copyright cmassengale 32
CHARACTERISTICS • DETERMINES THE AMINO ACID SEQUENCE IN A PROTEIN • 64 DIFFERENT THREE-BASE CODONS “CODE” FOR 20 DIFFERENT AMINO ACIDS (CARRIED BY t. RNA) • THERE ALSO START (1) AND STOP (3) CODONS • OCCURS AT THE RIBOSOMES • REQUIRES ENZYMES AND ENERGY copyright cmassengale 32
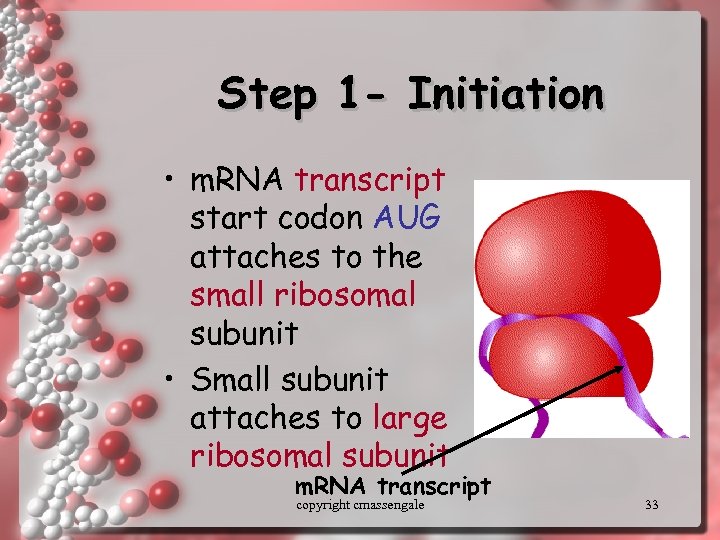 Step 1 - Initiation • m. RNA transcript start codon AUG attaches to the small ribosomal subunit • Small subunit attaches to large ribosomal subunit m. RNA transcript copyright cmassengale 33
Step 1 - Initiation • m. RNA transcript start codon AUG attaches to the small ribosomal subunit • Small subunit attaches to large ribosomal subunit m. RNA transcript copyright cmassengale 33
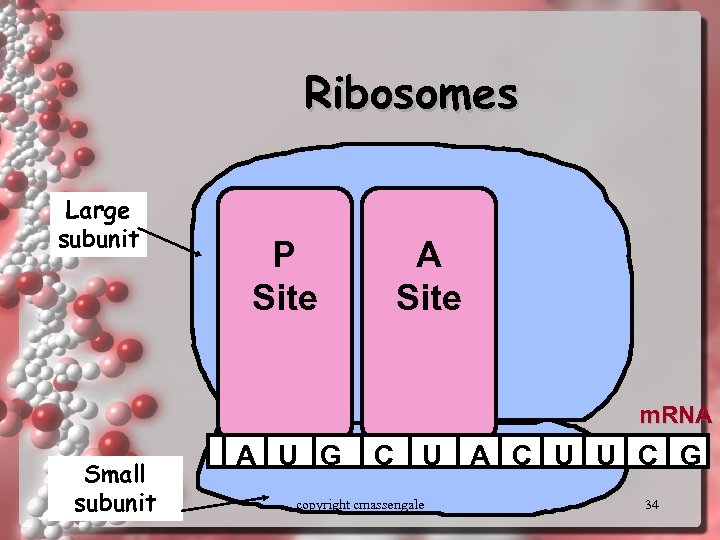 Ribosomes Large subunit P Site A Site m. RNA Small subunit A U G C U A C U U C G copyright cmassengale 34
Ribosomes Large subunit P Site A Site m. RNA Small subunit A U G C U A C U U C G copyright cmassengale 34
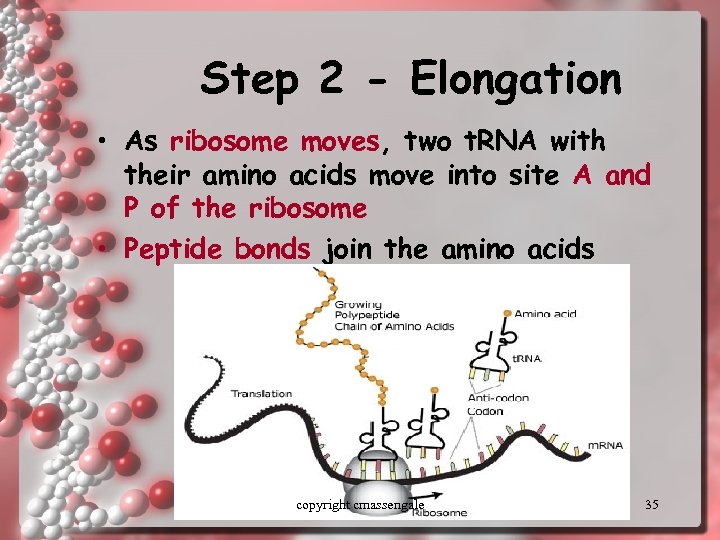 Step 2 - Elongation • As ribosome moves, two t. RNA with their amino acids move into site A and P of the ribosome • Peptide bonds join the amino acids copyright cmassengale 35
Step 2 - Elongation • As ribosome moves, two t. RNA with their amino acids move into site A and P of the ribosome • Peptide bonds join the amino acids copyright cmassengale 35
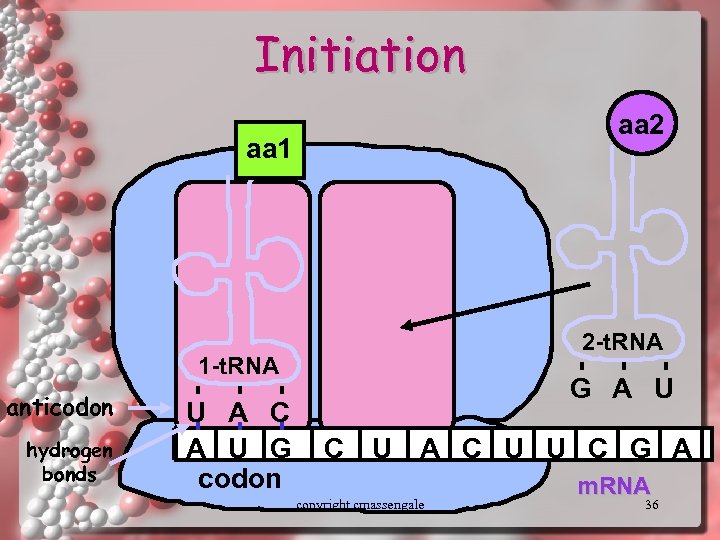 Initiation aa 2 aa 1 2 -t. RNA 1 -t. RNA anticodon hydrogen bonds U A C A U G codon G A U C U A C U U C G A copyright cmassengale m. RNA 36
Initiation aa 2 aa 1 2 -t. RNA 1 -t. RNA anticodon hydrogen bonds U A C A U G codon G A U C U A C U U C G A copyright cmassengale m. RNA 36
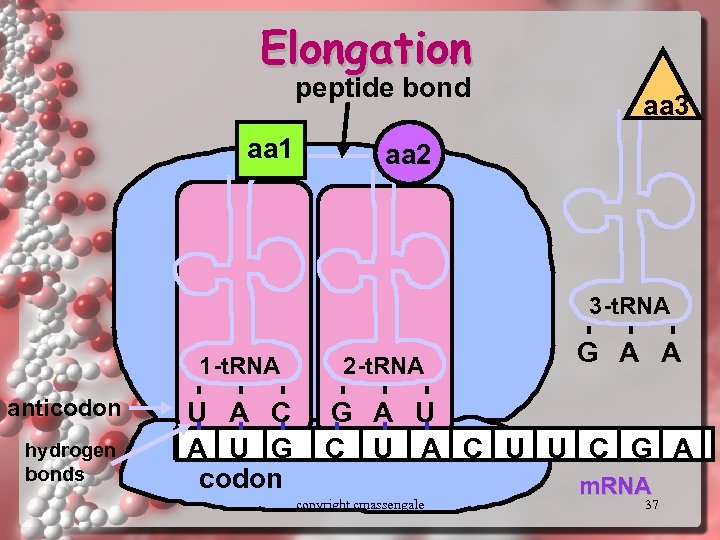 Elongation peptide bond aa 1 aa 3 aa 2 3 -t. RNA 1 -t. RNA anticodon hydrogen bonds U A C A U G codon 2 -t. RNA G A U C U A C U U C G A copyright cmassengale m. RNA 37
Elongation peptide bond aa 1 aa 3 aa 2 3 -t. RNA 1 -t. RNA anticodon hydrogen bonds U A C A U G codon 2 -t. RNA G A U C U A C U U C G A copyright cmassengale m. RNA 37
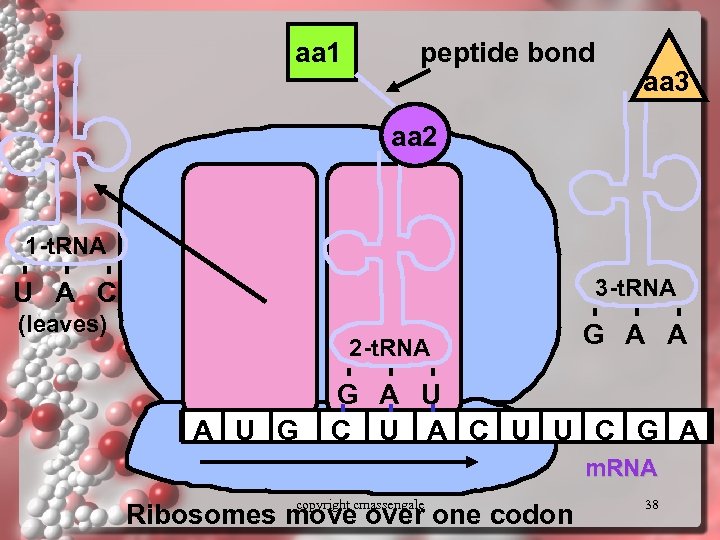 aa 1 peptide bond aa 3 aa 2 1 -t. RNA 3 -t. RNA U A C (leaves) 2 -t. RNA A U G G A A G A U C U A C U U C G A m. RNA copyright cmassengale Ribosomes move over one codon 38
aa 1 peptide bond aa 3 aa 2 1 -t. RNA 3 -t. RNA U A C (leaves) 2 -t. RNA A U G G A A G A U C U A C U U C G A m. RNA copyright cmassengale Ribosomes move over one codon 38
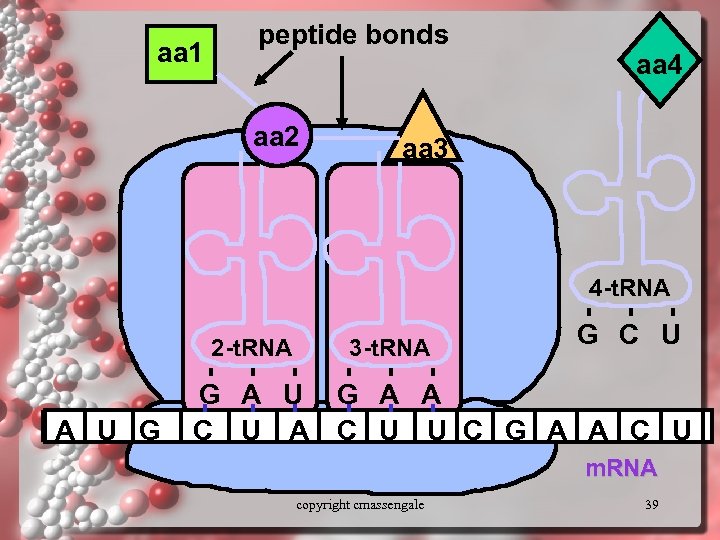 aa 1 peptide bonds aa 2 aa 4 aa 3 4 -t. RNA 2 -t. RNA A U G 3 -t. RNA G C U G A A C U U C G A A C U m. RNA copyright cmassengale 39
aa 1 peptide bonds aa 2 aa 4 aa 3 4 -t. RNA 2 -t. RNA A U G 3 -t. RNA G C U G A A C U U C G A A C U m. RNA copyright cmassengale 39
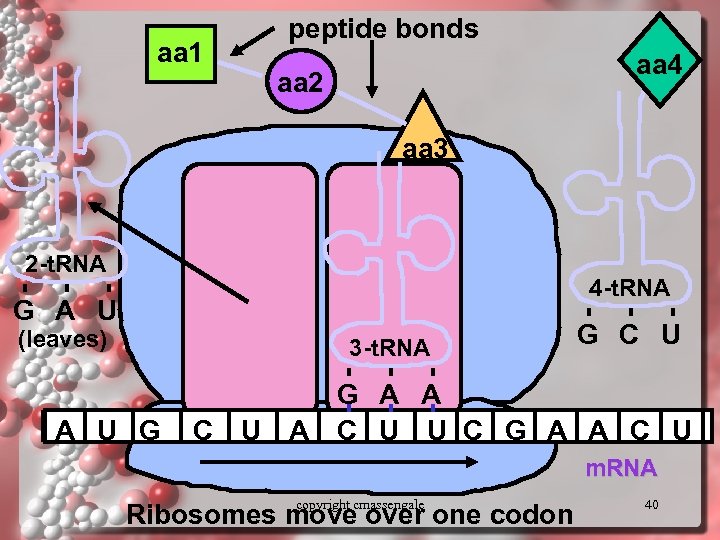 aa 1 peptide bonds aa 4 aa 2 aa 3 2 -t. RNA 4 -t. RNA G A U (leaves) 3 -t. RNA A U G G C U G A A C U U C G A A C U m. RNA copyright cmassengale Ribosomes move over one codon 40
aa 1 peptide bonds aa 4 aa 2 aa 3 2 -t. RNA 4 -t. RNA G A U (leaves) 3 -t. RNA A U G G C U G A A C U U C G A A C U m. RNA copyright cmassengale Ribosomes move over one codon 40
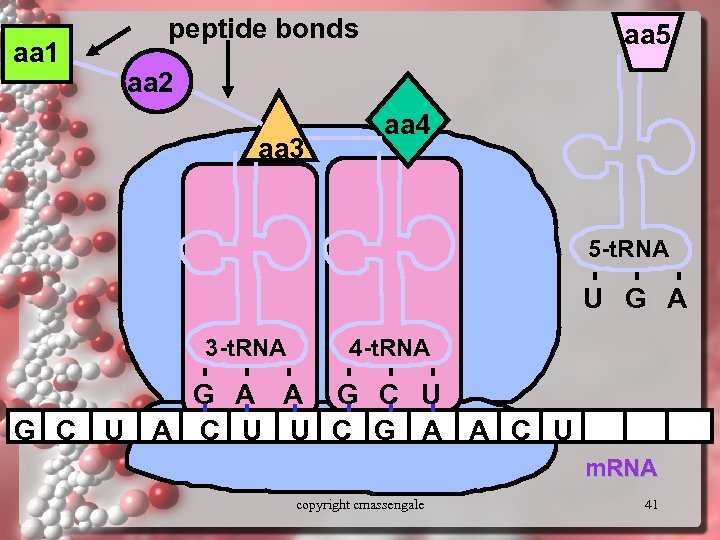 aa 1 peptide bonds aa 5 aa 2 aa 3 aa 4 5 -t. RNA U G A 3 -t. RNA 4 -t. RNA G A A G C U A C U U C G A A C U m. RNA copyright cmassengale 41
aa 1 peptide bonds aa 5 aa 2 aa 3 aa 4 5 -t. RNA U G A 3 -t. RNA 4 -t. RNA G A A G C U A C U U C G A A C U m. RNA copyright cmassengale 41
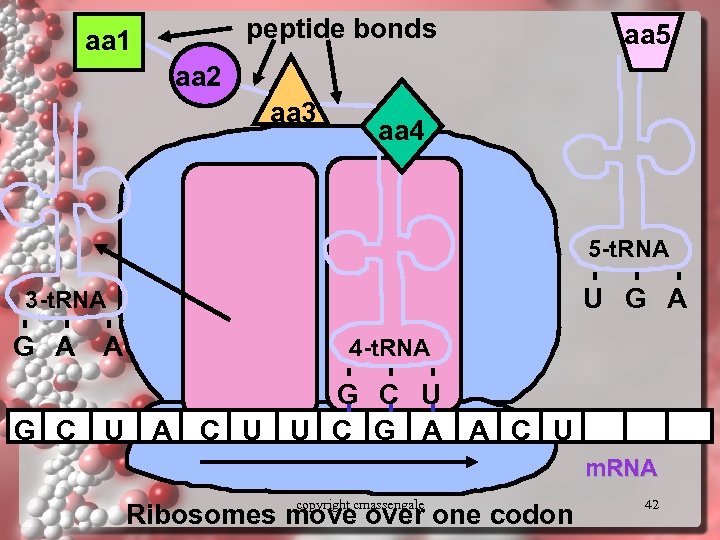 peptide bonds aa 1 aa 5 aa 2 aa 3 aa 4 5 -t. RNA U G A 3 -t. RNA G A A 4 -t. RNA G C U A C U U C G A A C U m. RNA copyright cmassengale Ribosomes move over one codon 42
peptide bonds aa 1 aa 5 aa 2 aa 3 aa 4 5 -t. RNA U G A 3 -t. RNA G A A 4 -t. RNA G C U A C U U C G A A C U m. RNA copyright cmassengale Ribosomes move over one codon 42
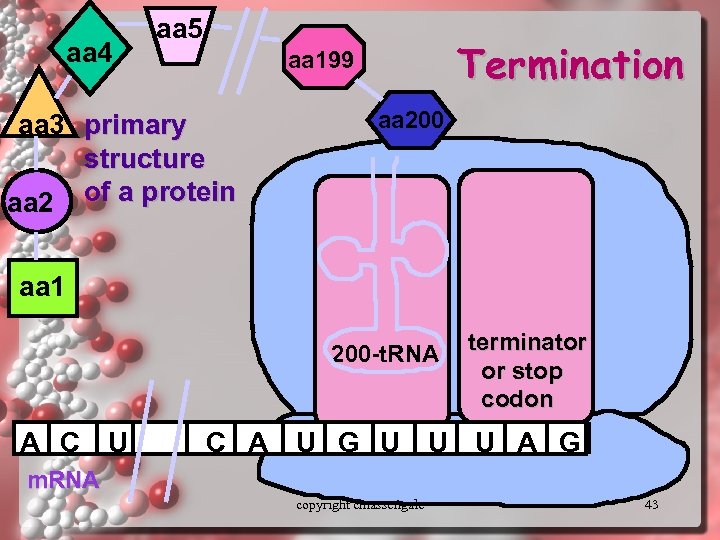 aa 4 aa 5 Termination aa 199 aa 3 primary structure aa 2 of a protein aa 200 aa 1 200 -t. RNA A C U terminator or stop codon C A U G U U U A G m. RNA copyright cmassengale 43
aa 4 aa 5 Termination aa 199 aa 3 primary structure aa 2 of a protein aa 200 aa 1 200 -t. RNA A C U terminator or stop codon C A U G U U U A G m. RNA copyright cmassengale 43
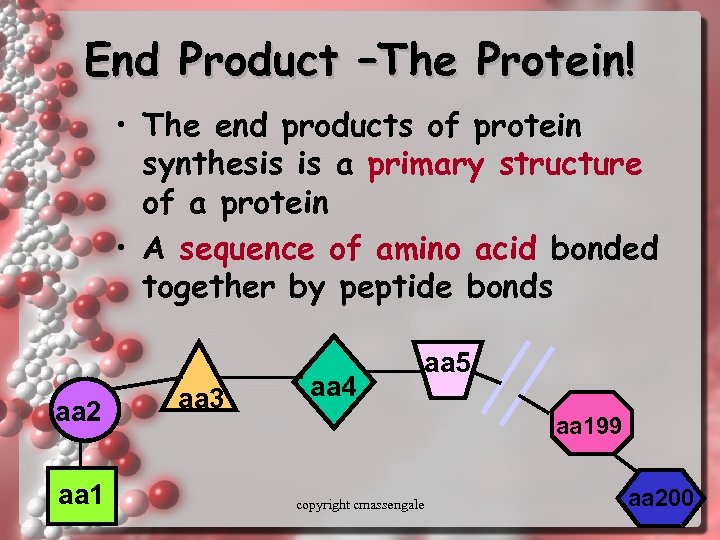 End Product –The Protein! • The end products of protein synthesis is a primary structure of a protein • A sequence of amino acid bonded together by peptide bonds aa 2 aa 1 aa 3 aa 4 aa 5 aa 199 copyright cmassengale aa 200 44
End Product –The Protein! • The end products of protein synthesis is a primary structure of a protein • A sequence of amino acid bonded together by peptide bonds aa 2 aa 1 aa 3 aa 4 aa 5 aa 199 copyright cmassengale aa 200 44
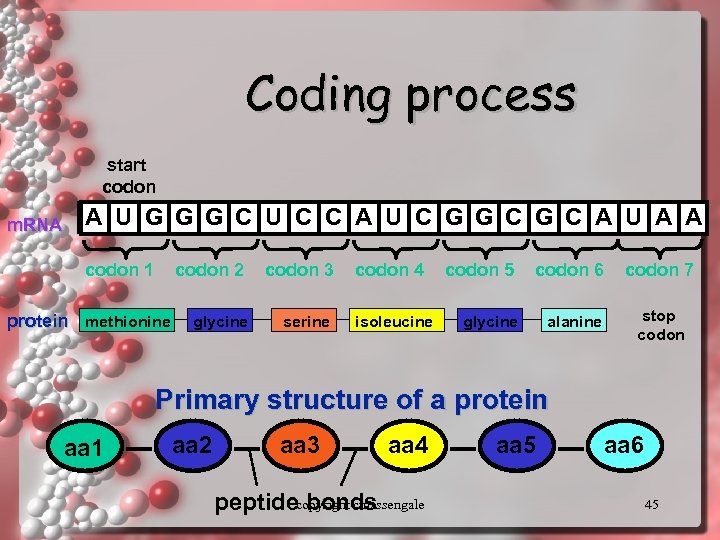 Coding process start codon m. RNA A U G G G C U C C A U C G G C A U A A codon 1 codon 2 protein methionine codon 3 glycine serine codon 4 isoleucine codon 5 codon 6 glycine alanine codon 7 stop codon Primary structure of a protein aa 1 aa 2 aa 3 aa 4 peptidecopyright cmassengale bonds aa 5 aa 6 45
Coding process start codon m. RNA A U G G G C U C C A U C G G C A U A A codon 1 codon 2 protein methionine codon 3 glycine serine codon 4 isoleucine codon 5 codon 6 glycine alanine codon 7 stop codon Primary structure of a protein aa 1 aa 2 aa 3 aa 4 peptidecopyright cmassengale bonds aa 5 aa 6 45


