 Chapter 9 Energy in a Cell
Chapter 9 Energy in a Cell
 What would you do if you need to buy a soda but had a 100 dollar bill? • All living things need energy to survive. • They get energy from the things around them.
What would you do if you need to buy a soda but had a 100 dollar bill? • All living things need energy to survive. • They get energy from the things around them.
 • Several cell process require energy. • Cell division, movement, storage of protein are a few examples. • How about your muscles working, heart pumping and brain activity.
• Several cell process require energy. • Cell division, movement, storage of protein are a few examples. • How about your muscles working, heart pumping and brain activity.
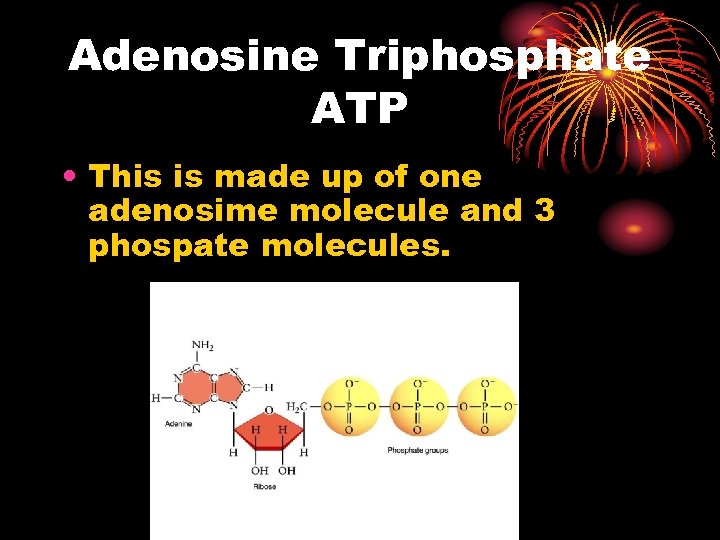 Adenosine Triphosphate ATP • This is made up of one adenosime molecule and 3 phospate molecules.
Adenosine Triphosphate ATP • This is made up of one adenosime molecule and 3 phospate molecules.
 • Phosphate molecules are charged – molecules of the same charge don’t like being around each other. • AMP(adensoine monophosphate) • Not much energy • ADP(adensoine triphosphate) • More energy needed When the bonds are broken, energy is released!
• Phosphate molecules are charged – molecules of the same charge don’t like being around each other. • AMP(adensoine monophosphate) • Not much energy • ADP(adensoine triphosphate) • More energy needed When the bonds are broken, energy is released!
 When the bond is broken between the 2 and third phosphate group is broken – energy is release and ATP becomes ADP
When the bond is broken between the 2 and third phosphate group is broken – energy is release and ATP becomes ADP
 Like the 100 dollar bill • When broken down, the cell can use the energy. • Proteins have a site where ATP can bind. This makes the energy usable for the cell aka – enzymes!!!! Remember, enzymes help chemical process in the body!
Like the 100 dollar bill • When broken down, the cell can use the energy. • Proteins have a site where ATP can bind. This makes the energy usable for the cell aka – enzymes!!!! Remember, enzymes help chemical process in the body!
 Cells use energy: • Maintaining homeostatsis • Move molecules and ions • Making new molecules
Cells use energy: • Maintaining homeostatsis • Move molecules and ions • Making new molecules
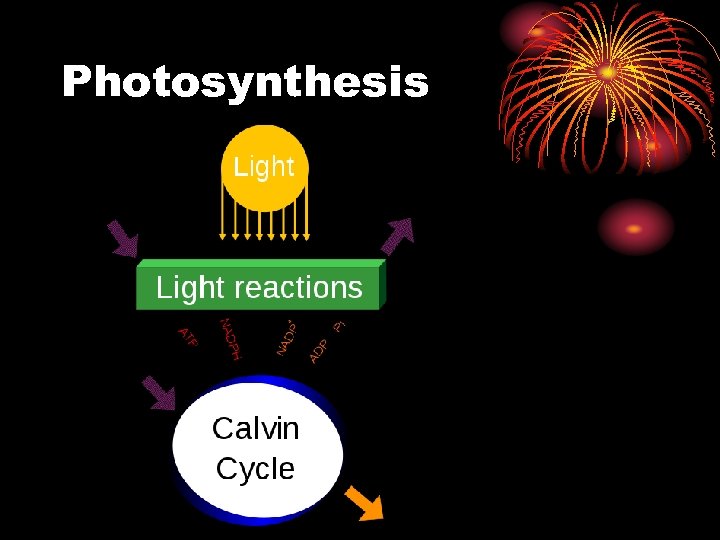 Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
 2 phases to photosynthesis • Light-dependent reaction – • Covert light energy into chem. energy • Light-independent reaction – • The ATP molecule produced in the light are used to fuel and produce simple sugars.
2 phases to photosynthesis • Light-dependent reaction – • Covert light energy into chem. energy • Light-independent reaction – • The ATP molecule produced in the light are used to fuel and produce simple sugars.
 Chloroplast and pigment • Light reactions take place in the thylakoid discs in the CP • Cholorophyll absorbs most wave lengths green – that is why plants are green! The color is the reflection
Chloroplast and pigment • Light reactions take place in the thylakoid discs in the CP • Cholorophyll absorbs most wave lengths green – that is why plants are green! The color is the reflection
 Light Dependant • 1 st phase of photo. Syth. • Chlorophyll molecules transfer the energy in the light to electrons. The energy is then passed on through an electron transport chain • Protiens “pass” the energized electrons along. Sometimes the energy spills out and forms ATP from ADP
Light Dependant • 1 st phase of photo. Syth. • Chlorophyll molecules transfer the energy in the light to electrons. The energy is then passed on through an electron transport chain • Protiens “pass” the energized electrons along. Sometimes the energy spills out and forms ATP from ADP
 After the e- have traveled down the chain they are reenergized are passed down a second chain. At the bottom of this chain NADP+ is used. This combines with 2 e- and a H ion to become NADPH. The energy is stored here NADPH – important to light independent reaction pg 227
After the e- have traveled down the chain they are reenergized are passed down a second chain. At the bottom of this chain NADP+ is used. This combines with 2 e- and a H ion to become NADPH. The energy is stored here NADPH – important to light independent reaction pg 227
 Light-Independent Reaction • 2 nd phase of photo synth • CALVIN CYCLE - uses carbon dioxide to form sugars • Takes place in the chloroplast • Read aloud Light-Independent Reactions • Page 229
Light-Independent Reaction • 2 nd phase of photo synth • CALVIN CYCLE - uses carbon dioxide to form sugars • Takes place in the chloroplast • Read aloud Light-Independent Reactions • Page 229