34f5d502fbdea8396fd55c8f8478459b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Chapter 9 (8) Stock Valuation Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 9 (8) Stock Valuation Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Key Concepts and Skills o Understand how stock prices depend on future dividends and dividend growth o Be able to compute stock prices using the dividend growth model o Understand how growth opportunities affect stock values o Understand valuation comparables o Understand how stock markets work 9 -1
Key Concepts and Skills o Understand how stock prices depend on future dividends and dividend growth o Be able to compute stock prices using the dividend growth model o Understand how growth opportunities affect stock values o Understand valuation comparables o Understand how stock markets work 9 -1
 Chapter Outline 9. 1 9. 2 9. 3 9. 4 9. 5 9. 6 The Present Value of Common Stocks Estimates of Parameters in the Dividend Discount Model Growth Opportunities Comparables Valuing the Entire Firm The Stock Markets 9 -2
Chapter Outline 9. 1 9. 2 9. 3 9. 4 9. 5 9. 6 The Present Value of Common Stocks Estimates of Parameters in the Dividend Discount Model Growth Opportunities Comparables Valuing the Entire Firm The Stock Markets 9 -2
 9. 1 The PV of Common Stocks o o The value of any asset is the present value of its expected future cash flows. Stock ownership produces cash flows from: n n o Dividends Capital Gains Valuation of Different Types of Stocks n n n Zero Growth Constant Growth Differential Growth 9 -3
9. 1 The PV of Common Stocks o o The value of any asset is the present value of its expected future cash flows. Stock ownership produces cash flows from: n n o Dividends Capital Gains Valuation of Different Types of Stocks n n n Zero Growth Constant Growth Differential Growth 9 -3
 Case 1: Zero Growth o Assume that dividends will remain at the same level forever · Since future cash flows are constant, the value of a zero growth stock is the present value of a perpetuity: 9 -4
Case 1: Zero Growth o Assume that dividends will remain at the same level forever · Since future cash flows are constant, the value of a zero growth stock is the present value of a perpetuity: 9 -4
 Case 2: Constant Growth Assume that dividends will grow at a constant rate, g, forever, i. e. , . . . Since future cash flows grow at a constant rate forever, the value of a constant growth stock is the present value of a growing perpetuity: 9 -5
Case 2: Constant Growth Assume that dividends will grow at a constant rate, g, forever, i. e. , . . . Since future cash flows grow at a constant rate forever, the value of a constant growth stock is the present value of a growing perpetuity: 9 -5
 Constant Growth Example o Suppose Big D, Inc. , just paid a dividend of $. 50. It is expected to increase its dividend by 2% per year. If the market requires a return of 15% on assets of this risk level, how much should the stock be selling for? o P 0 =. 50(1+. 02) / (. 15 -. 02) = $3. 92 9 -6
Constant Growth Example o Suppose Big D, Inc. , just paid a dividend of $. 50. It is expected to increase its dividend by 2% per year. If the market requires a return of 15% on assets of this risk level, how much should the stock be selling for? o P 0 =. 50(1+. 02) / (. 15 -. 02) = $3. 92 9 -6
 Case 3: Differential Growth Assume that dividends will grow at different rates in the foreseeable future and then will grow at a constant rate thereafter. o To value a Differential Growth Stock, we need to: o Estimate future dividends in the foreseeable future. n Estimate the future stock price when the stock becomes a Constant Growth Stock (case 2). n Compute the total present value of the estimated future dividends and future stock price at the appropriate discount rate. n 9 -7
Case 3: Differential Growth Assume that dividends will grow at different rates in the foreseeable future and then will grow at a constant rate thereafter. o To value a Differential Growth Stock, we need to: o Estimate future dividends in the foreseeable future. n Estimate the future stock price when the stock becomes a Constant Growth Stock (case 2). n Compute the total present value of the estimated future dividends and future stock price at the appropriate discount rate. n 9 -7
 Case 3: Differential Growth · Assume that dividends will grow at rate g 1 for N years and grow at rate g 2 thereafter. . . . 9 -8
Case 3: Differential Growth · Assume that dividends will grow at rate g 1 for N years and grow at rate g 2 thereafter. . . . 9 -8
 Case 3: Differential Growth Dividends will grow at rate g 1 for N years and grow at rate g 2 thereafter … 0 1 2 … … N N+1 9 -9
Case 3: Differential Growth Dividends will grow at rate g 1 for N years and grow at rate g 2 thereafter … 0 1 2 … … N N+1 9 -9
 Case 3: Differential Growth We can value this as the sum of: § a T-year annuity growing at rate g 1 § plus the discounted value of a perpetuity growing at rate g 2 that starts in year T+1 9 -10
Case 3: Differential Growth We can value this as the sum of: § a T-year annuity growing at rate g 1 § plus the discounted value of a perpetuity growing at rate g 2 that starts in year T+1 9 -10
 Case 3: Differential Growth Consolidating gives: Or, we can “cash flow” it out. 9 -11
Case 3: Differential Growth Consolidating gives: Or, we can “cash flow” it out. 9 -11
 A Differential Growth Example A common stock just paid a dividend of $2. The dividend is expected to grow at 8% for 3 years, then it will grow at 4% in perpetuity. What is the stock worth? The discount rate is 12%. 9 -12
A Differential Growth Example A common stock just paid a dividend of $2. The dividend is expected to grow at 8% for 3 years, then it will grow at 4% in perpetuity. What is the stock worth? The discount rate is 12%. 9 -12
 With the Formula 9 -13
With the Formula 9 -13
 Equity Valuation o The present value of a stock (Pt) assuming zero growth in dividends can be written as: D = dividend paid at end of every year Pt = the stock’s price at the end of year t R = the interest rate used to discount future cash flows 9 -14
Equity Valuation o The present value of a stock (Pt) assuming zero growth in dividends can be written as: D = dividend paid at end of every year Pt = the stock’s price at the end of year t R = the interest rate used to discount future cash flows 9 -14
 Equity Valuation o The present value of a stock (Pt) assuming constant growth in dividends can be written as: D 0 = current value of dividends Dt = value of dividends at time t = 1, 2, …, ∞ g = the constant dividend growth rate 9 -15
Equity Valuation o The present value of a stock (Pt) assuming constant growth in dividends can be written as: D 0 = current value of dividends Dt = value of dividends at time t = 1, 2, …, ∞ g = the constant dividend growth rate 9 -15
 Equity Valuation o The return on a stock with zero dividend growth, if purchased at current price P 0, can be written as: o The return on a stock with constant dividend growth, if purchased at price P 0, can be written as: 9 -16
Equity Valuation o The return on a stock with zero dividend growth, if purchased at current price P 0, can be written as: o The return on a stock with constant dividend growth, if purchased at price P 0, can be written as: 9 -16
 9. 2 Estimates of Parameters o The value of a firm depends upon its growth rate, g, and its discount rate, R. n Where does g come from? g = Retention ratio × Return on retained earnings 9 -17
9. 2 Estimates of Parameters o The value of a firm depends upon its growth rate, g, and its discount rate, R. n Where does g come from? g = Retention ratio × Return on retained earnings 9 -17
 Where Does R Come From? o The discount rate can be broken into two parts. The dividend yield n The growth rate (in dividends) n o In practice, there is a great deal of estimation error involved in estimating R. 9 -18
Where Does R Come From? o The discount rate can be broken into two parts. The dividend yield n The growth rate (in dividends) n o In practice, there is a great deal of estimation error involved in estimating R. 9 -18
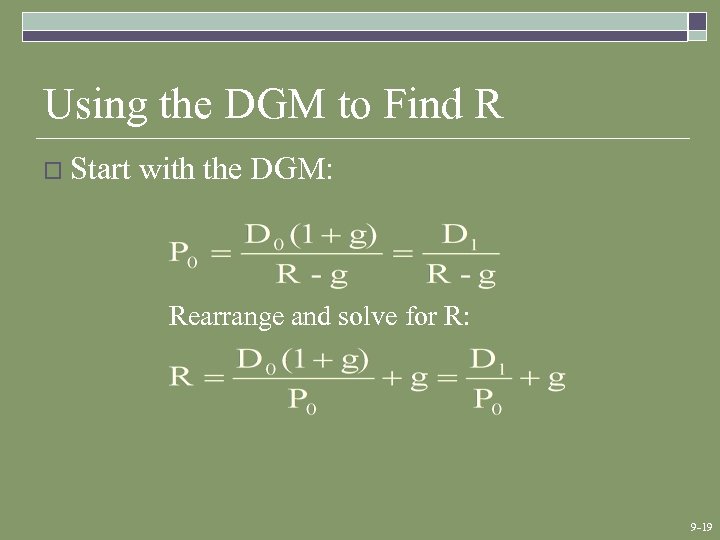 Using the DGM to Find R o Start with the DGM: Rearrange and solve for R: 9 -19
Using the DGM to Find R o Start with the DGM: Rearrange and solve for R: 9 -19
 9. 4 Comparables o o Comparables are used to value companies based primarily on multiples. Common multiples include: n n Price-to-Earnings Enterprise Value Ratios 9 -20
9. 4 Comparables o o Comparables are used to value companies based primarily on multiples. Common multiples include: n n Price-to-Earnings Enterprise Value Ratios 9 -20
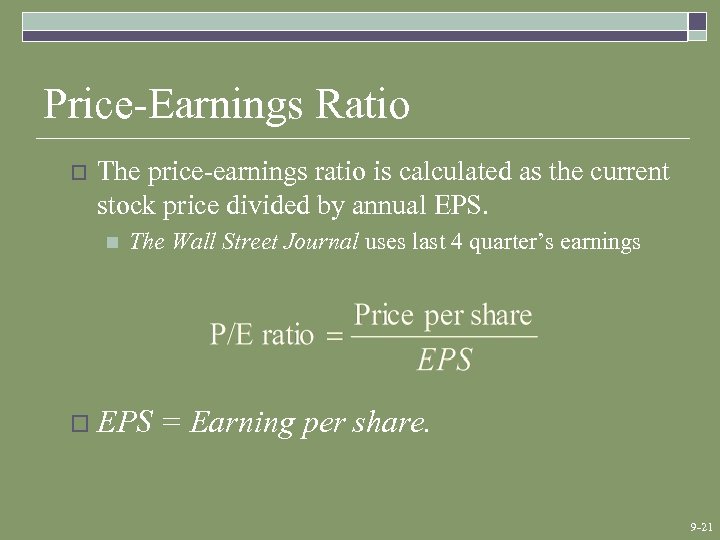 Price-Earnings Ratio o The price-earnings ratio is calculated as the current stock price divided by annual EPS. n The Wall Street Journal uses last 4 quarter’s earnings o EPS = Earning per share. 9 -21
Price-Earnings Ratio o The price-earnings ratio is calculated as the current stock price divided by annual EPS. n The Wall Street Journal uses last 4 quarter’s earnings o EPS = Earning per share. 9 -21
 Enterprise Value Ratios o o The PE ratio focuses on equity, but what if we want the value of the firm? Use Enterprise Value: n o Like PE, we compare the value to a measure of earnings. From a firm level, this is EBITDA, or earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. n o EV = market value of equity + market value of debt - cash EBITDA represents a measure of total firm cash flow The Enterprise Value Ratio = EV / EBITDA 9 -22
Enterprise Value Ratios o o The PE ratio focuses on equity, but what if we want the value of the firm? Use Enterprise Value: n o Like PE, we compare the value to a measure of earnings. From a firm level, this is EBITDA, or earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. n o EV = market value of equity + market value of debt - cash EBITDA represents a measure of total firm cash flow The Enterprise Value Ratio = EV / EBITDA 9 -22
 9. 5 The Stock Markets o Dealers vs. Brokers o New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) Largest stock market in the world n License Holders (formerly “Members”) n o Entitled to buy or sell on the exchange floor Operations n Floor activity n 9 -23
9. 5 The Stock Markets o Dealers vs. Brokers o New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) Largest stock market in the world n License Holders (formerly “Members”) n o Entitled to buy or sell on the exchange floor Operations n Floor activity n 9 -23
 NASDAQ o Not a physical exchange – computer-based quotation system o Multiple market makers o Electronic Communications Networks o Three levels of information Level 1 – median quotes, registered representatives n Level 2 – view quotes, brokers & dealers n Level 3 – view and update quotes, dealers only n o Large portion of technology stocks 9 -24
NASDAQ o Not a physical exchange – computer-based quotation system o Multiple market makers o Electronic Communications Networks o Three levels of information Level 1 – median quotes, registered representatives n Level 2 – view quotes, brokers & dealers n Level 3 – view and update quotes, dealers only n o Large portion of technology stocks 9 -24
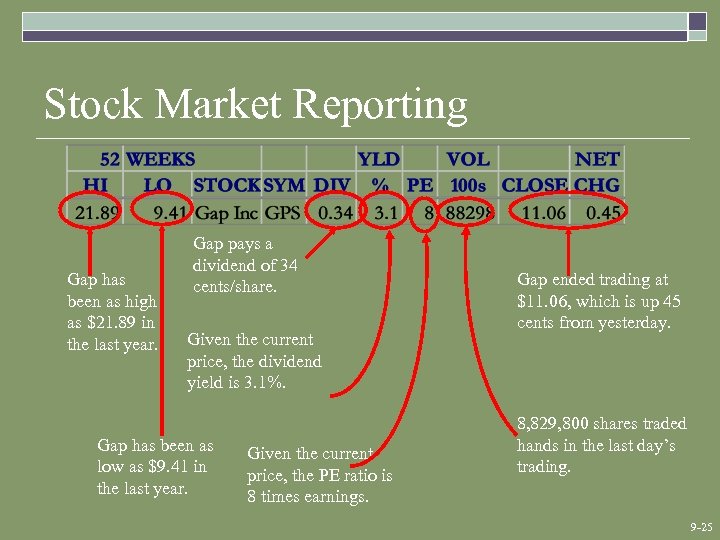 Stock Market Reporting Gap has been as high as $21. 89 in the last year. Gap pays a dividend of 34 cents/share. Given the current price, the dividend yield is 3. 1%. Gap has been as low as $9. 41 in the last year. Given the current price, the PE ratio is 8 times earnings. Gap ended trading at $11. 06, which is up 45 cents from yesterday. 8, 829, 800 shares traded hands in the last day’s trading. 9 -25
Stock Market Reporting Gap has been as high as $21. 89 in the last year. Gap pays a dividend of 34 cents/share. Given the current price, the dividend yield is 3. 1%. Gap has been as low as $9. 41 in the last year. Given the current price, the PE ratio is 8 times earnings. Gap ended trading at $11. 06, which is up 45 cents from yesterday. 8, 829, 800 shares traded hands in the last day’s trading. 9 -25
 Quick Quiz o What determines the price of a share of stock? o What determines g and R in the DGM? o Discuss the importance of valuation ratios. o What are some of the major characteristics of NYSE and Nasdaq? 9 -26
Quick Quiz o What determines the price of a share of stock? o What determines g and R in the DGM? o Discuss the importance of valuation ratios. o What are some of the major characteristics of NYSE and Nasdaq? 9 -26


