9f028b9ea94aa2de723ee6bc4061b27d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 73
Chapter 8 - Web Application System Design w Modeling Web Application using UML w Application Server w Web Application Design Object Oriented Analysis and Design 1
Modeling Web Application using UML Object Oriented Analysis and Design 2

8. 1 - Modeling Web Application using UML w Modeling Web Pages w Modeling EJB Object Oriented Analysis and Design 3
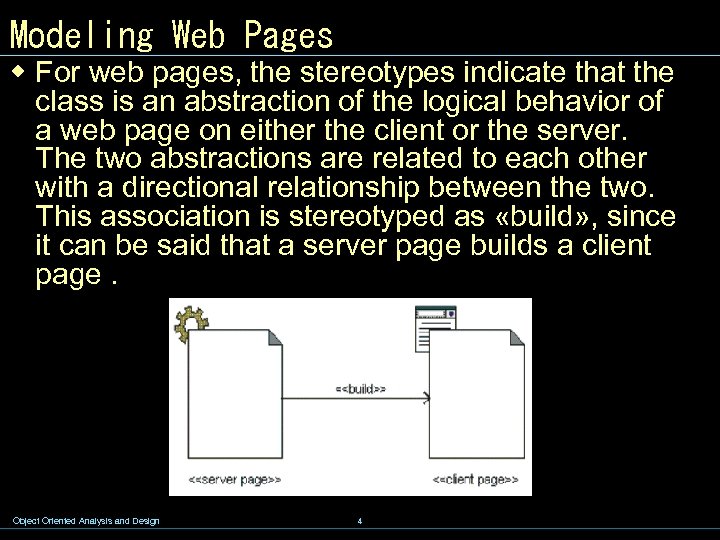
Modeling Web Pages w For web pages, the stereotypes indicate that the class is an abstraction of the logical behavior of a web page on either the client or the server. The two abstractions are related to each other with a directional relationship between the two. This association is stereotyped as «build» , since it can be said that a server page builds a client page. Object Oriented Analysis and Design 4
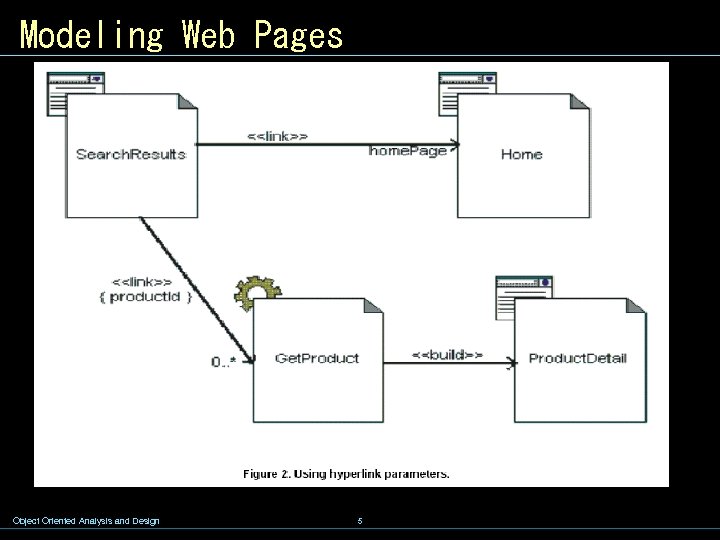
Modeling Web Pages Object Oriented Analysis and Design 5

Modeling Web Pages Object Oriented Analysis and Design 6
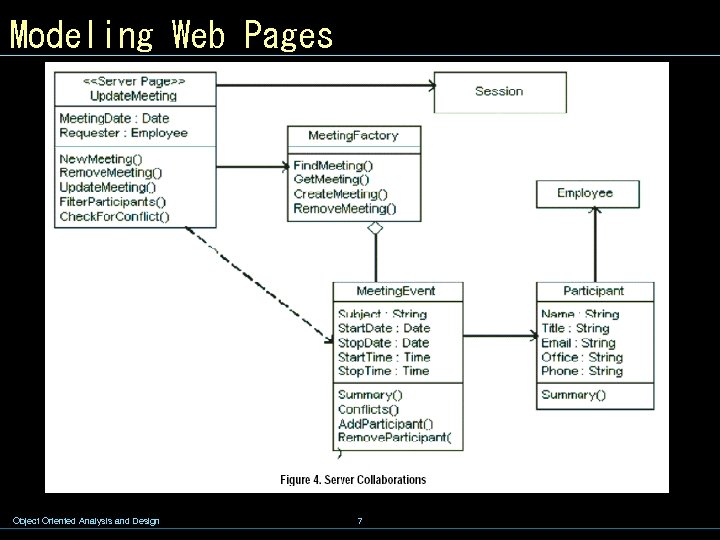
Modeling Web Pages Object Oriented Analysis and Design 7
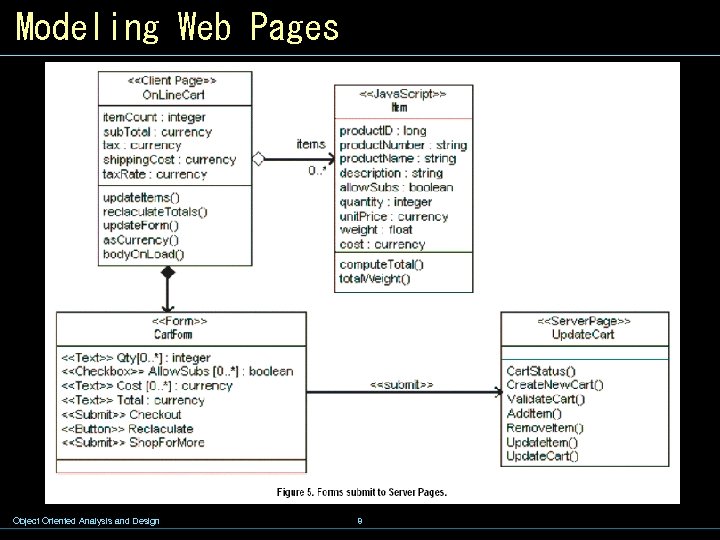
Modeling Web Pages Object Oriented Analysis and Design 8
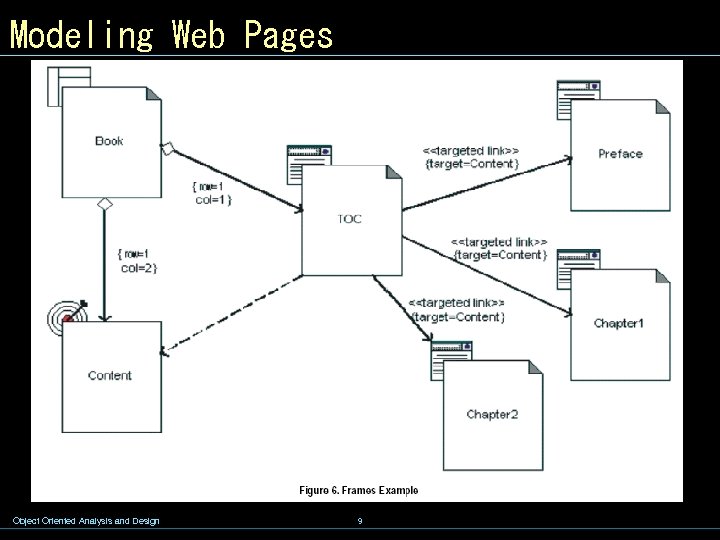
Modeling Web Pages Object Oriented Analysis and Design 9
Modeling EJB w Modeling EJB as a subsystem w Two approach: § Standard UML-Java Mapping § Sun JSR-000026 UML/EJB Mapping Object Oriented Analysis and Design 10
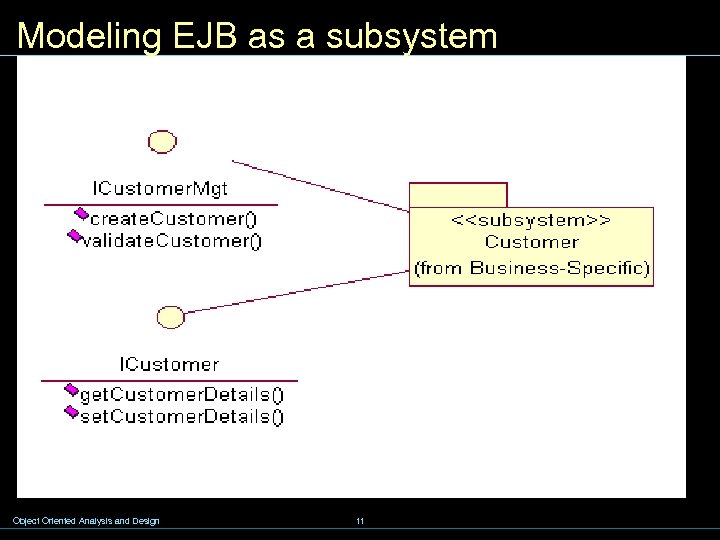
Modeling EJB as a subsystem Object Oriented Analysis and Design 11
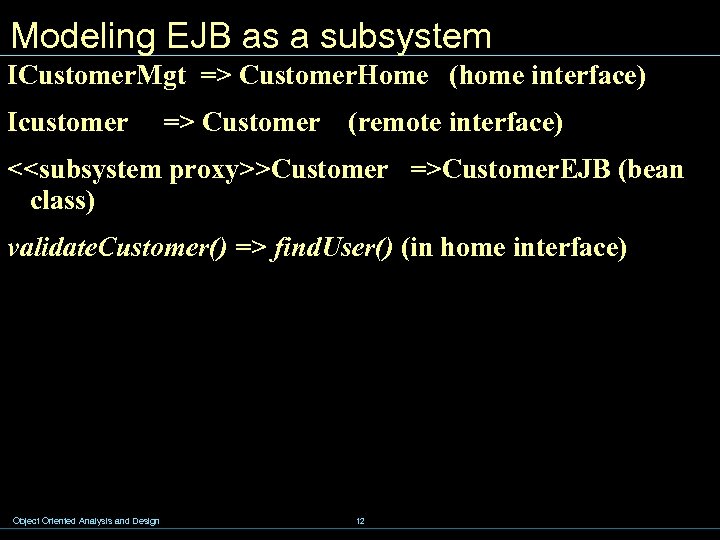
Modeling EJB as a subsystem ICustomer. Mgt => Customer. Home (home interface) Icustomer => Customer (remote interface) <<subsystem proxy>>Customer =>Customer. EJB (bean class) validate. Customer() => find. User() (in home interface) Object Oriented Analysis and Design 12
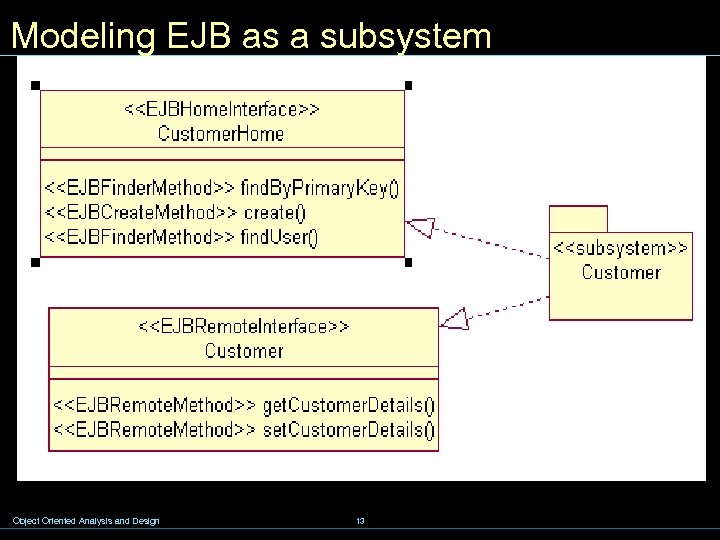
Modeling EJB as a subsystem Object Oriented Analysis and Design 13
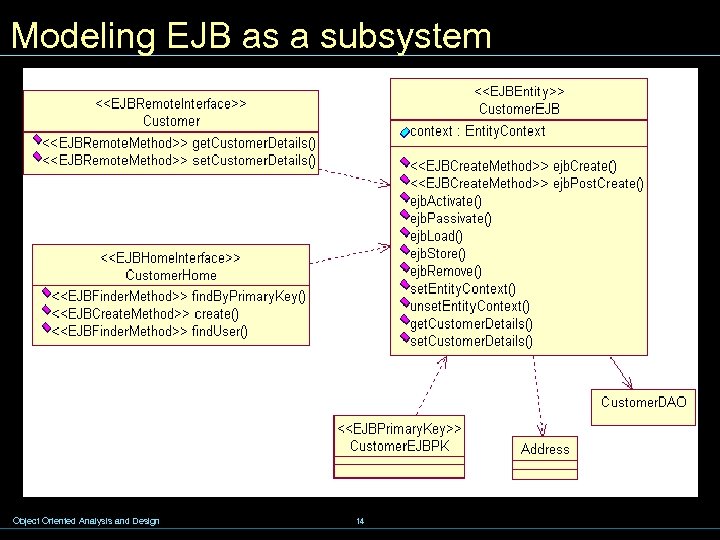
Modeling EJB as a subsystem Object Oriented Analysis and Design 14
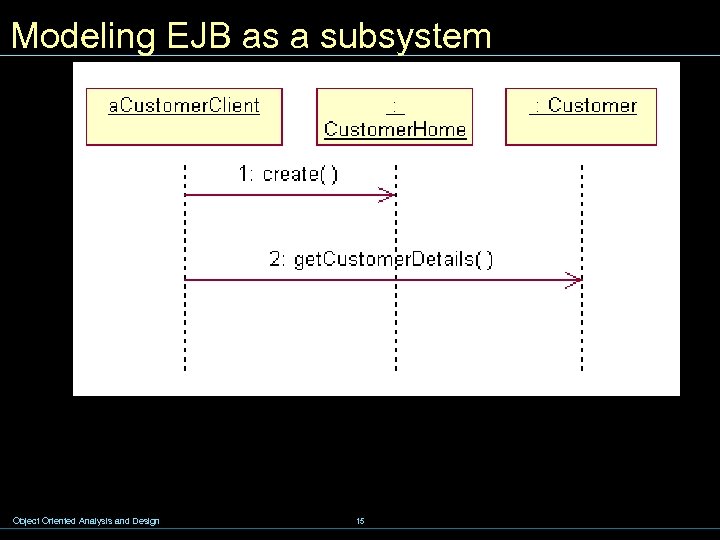
Modeling EJB as a subsystem Object Oriented Analysis and Design 15
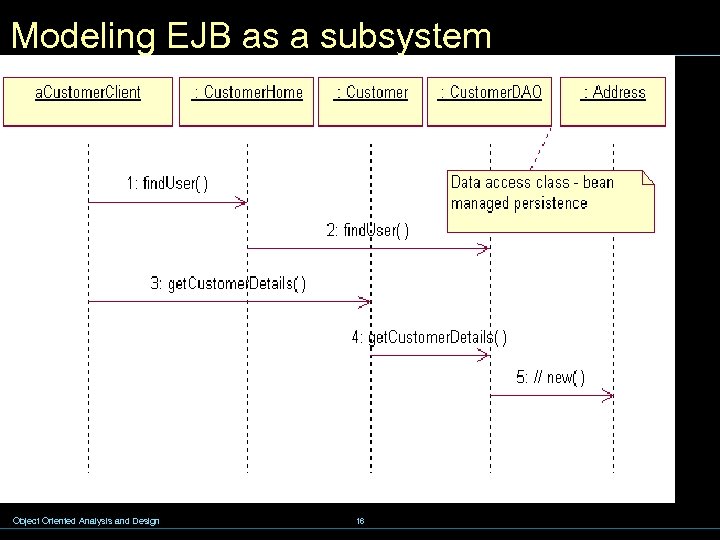
Modeling EJB as a subsystem Object Oriented Analysis and Design 16
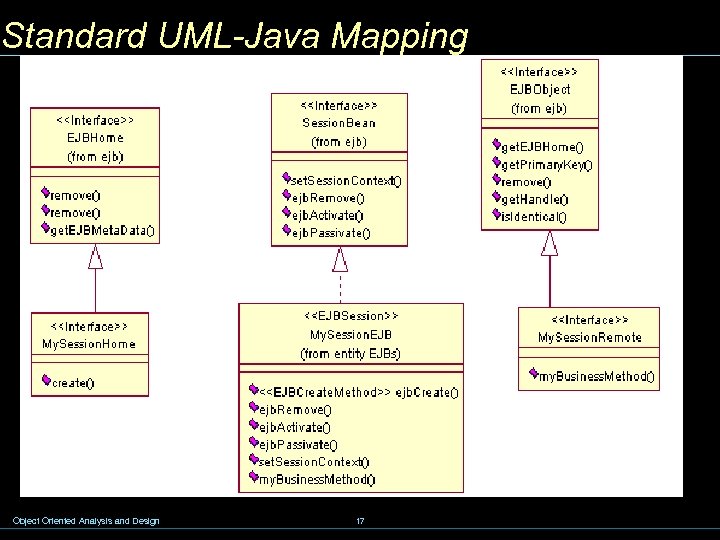
Standard UML-Java Mapping Object Oriented Analysis and Design 17
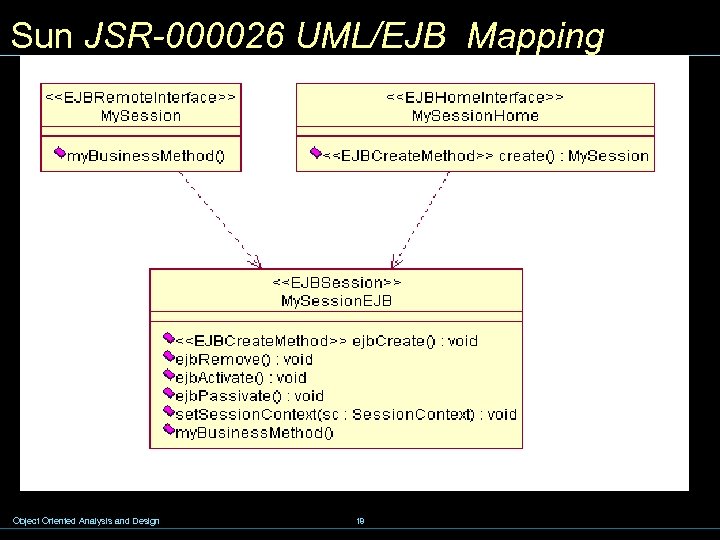
Sun JSR-000026 UML/EJB Mapping Object Oriented Analysis and Design 18
Application Server Object Oriented Analysis and Design 19

8. 2 - Application Server w Application Servers w J 2 EE Application Servers w Web Server and Application Server Object Oriented Analysis and Design 20
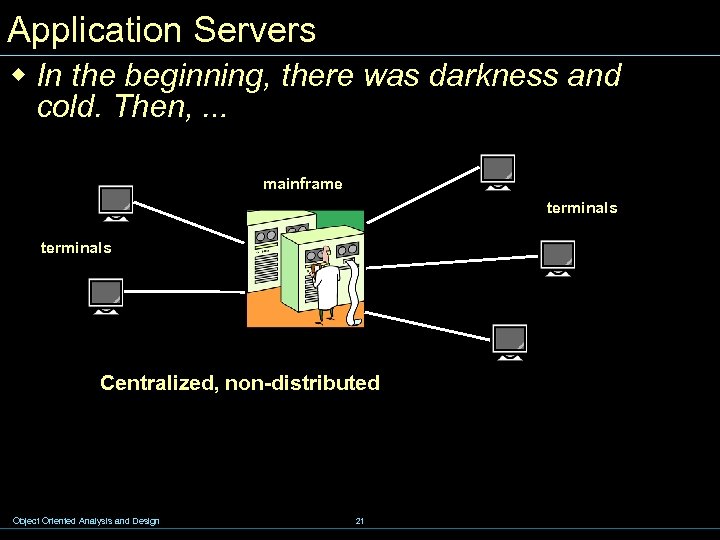
Application Servers w In the beginning, there was darkness and cold. Then, … mainframe terminals Centralized, non-distributed Object Oriented Analysis and Design 21
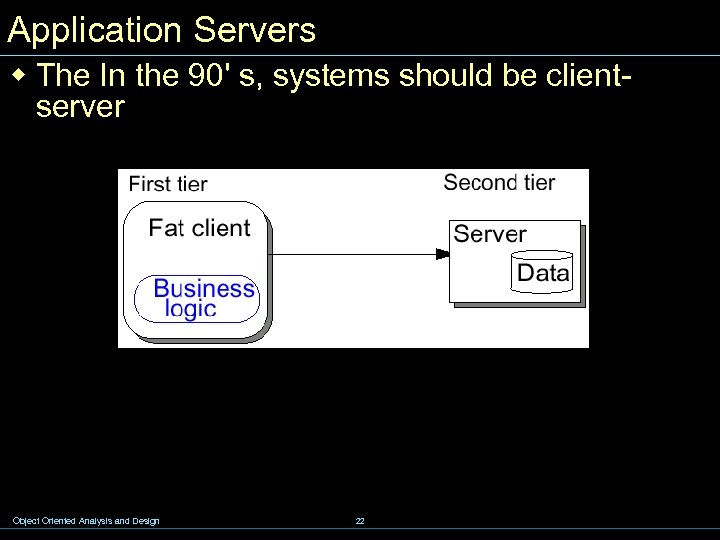
Application Servers w The In the 90' s, systems should be clientserver Object Oriented Analysis and Design 22
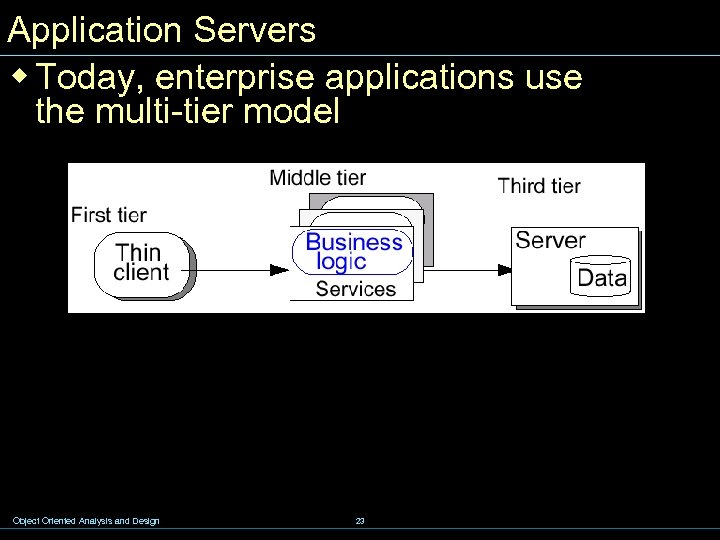
Application Servers w Today, enterprise applications use the multi-tier model Object Oriented Analysis and Design 23

Application Servers w " The Multi- tier applications" have several independent components w An application server provides the infrastructure and services to run such applications Object Oriented Analysis and Design 24

Application Servers w Application server products can be separated into 3 categories: § J 2 EE-based solutions § Non-J 2 EE solutions (PHP, Cold. Fusion, Perl, etc. ) § And the Microsoft solution (ASP/COM and now. NET with ASP. NET, VB. NET, C#, etc. ) Object Oriented Analysis and Design 25

J 2 EE Application Servers w Major J 2 EE products: § BEA Web. Logic § IBM Web. Sphere § Sun i. Planet Application Server § Oracle 9 i. AS § HP/Bluestone Total-e-Server § Borland App. Server § Jboss (free open source) Object Oriented Analysis and Design 26
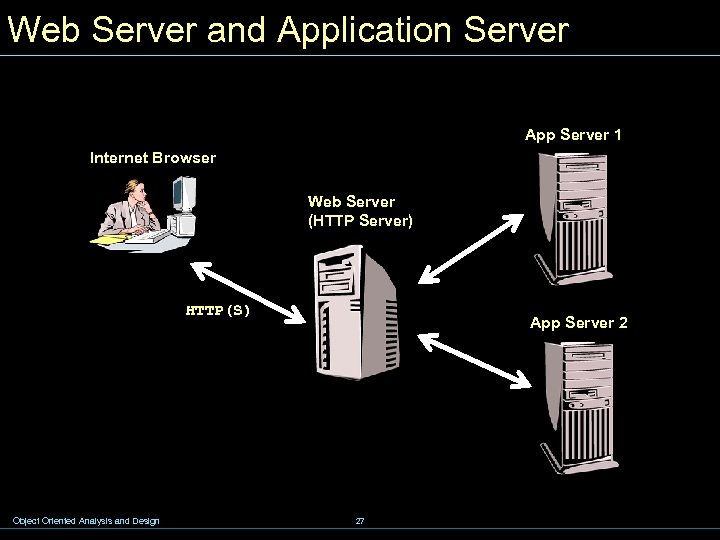
Web Server and Application Server App Server 1 Internet Browser Web Server (HTTP Server) HTTP(S) Object Oriented Analysis and Design App Server 2 27
Web Application Design Object Oriented Analysis and Design 28

8. 3 - Web Application Design w Application Layer w Business Layer w J 2 EE Multi-tier Model w J 2 EE Application Scenarios w Main Technologies w Examples w Case Study –Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 29
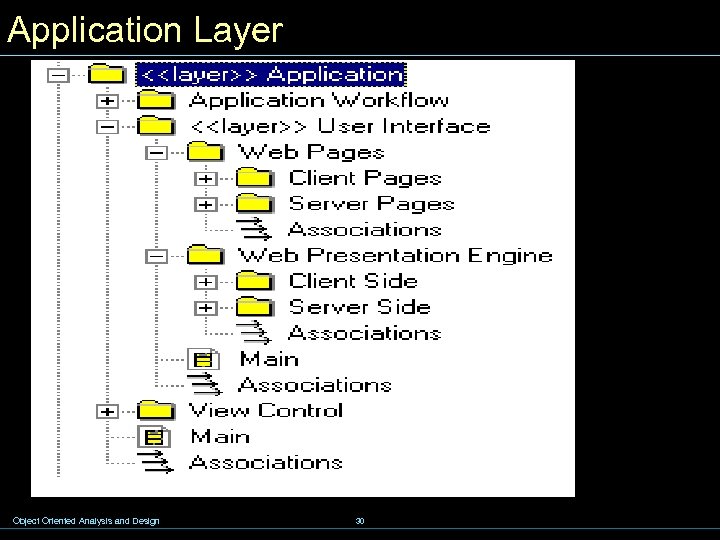
Application Layer Object Oriented Analysis and Design 30
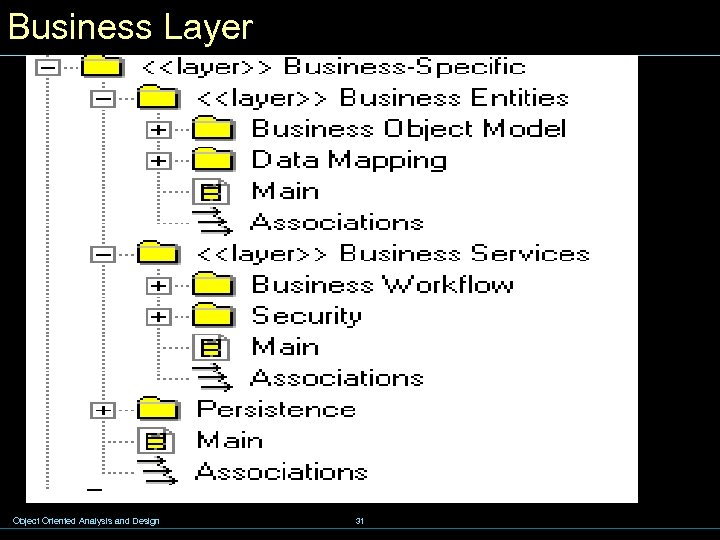
Business Layer Object Oriented Analysis and Design 31
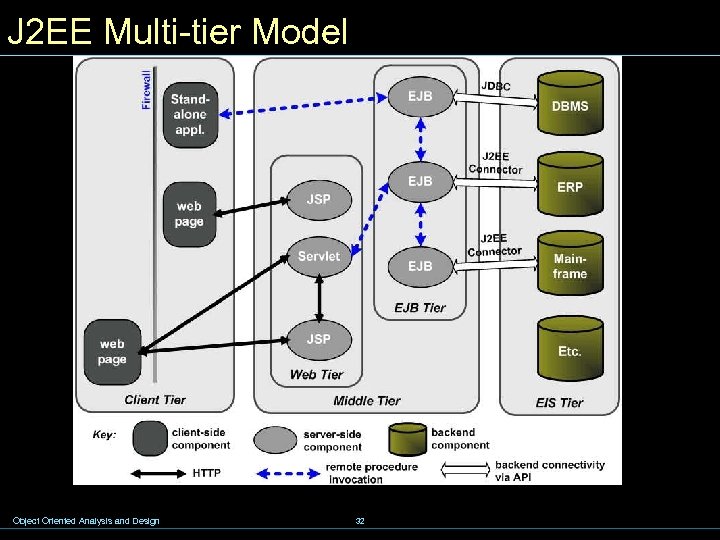
J 2 EE Multi-tier Model Object Oriented Analysis and Design 32
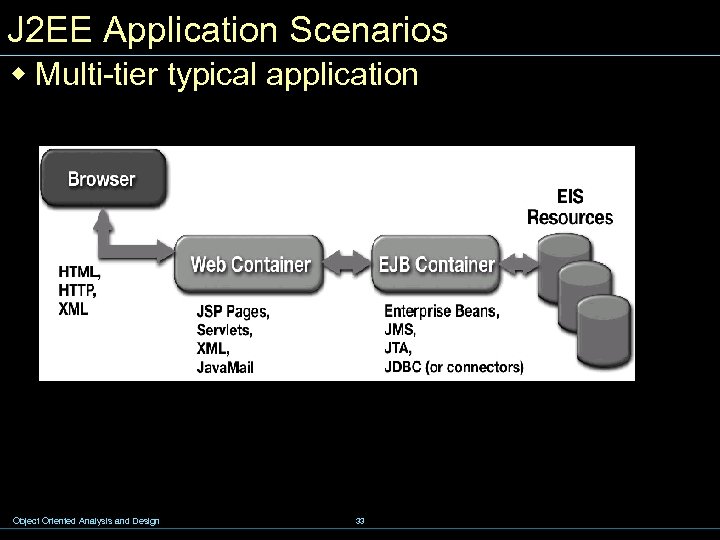
J 2 EE Application Scenarios w Multi-tier typical application Object Oriented Analysis and Design 33
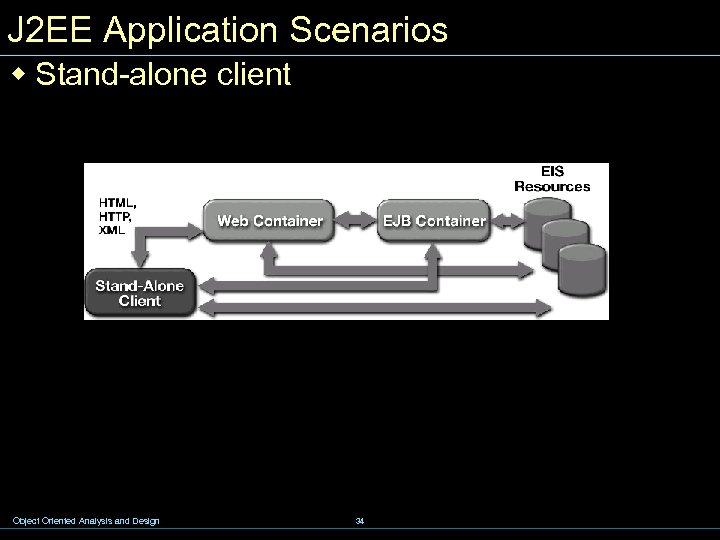
J 2 EE Application Scenarios w Stand-alone client Object Oriented Analysis and Design 34
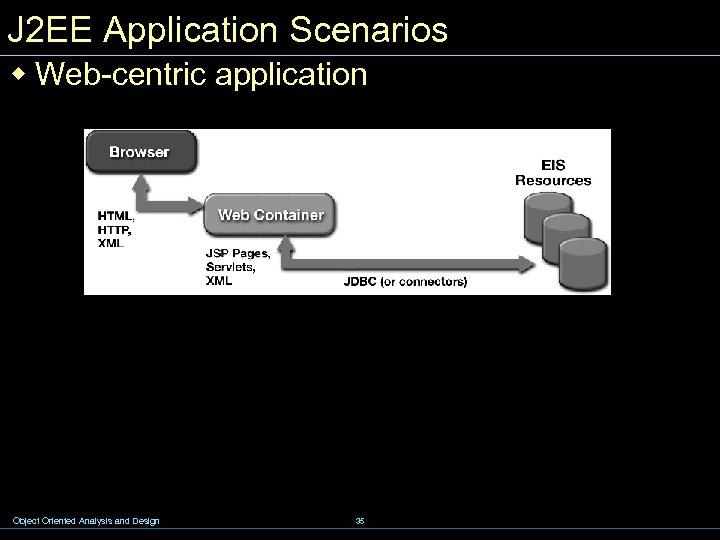
J 2 EE Application Scenarios w Web-centric application Object Oriented Analysis and Design 35
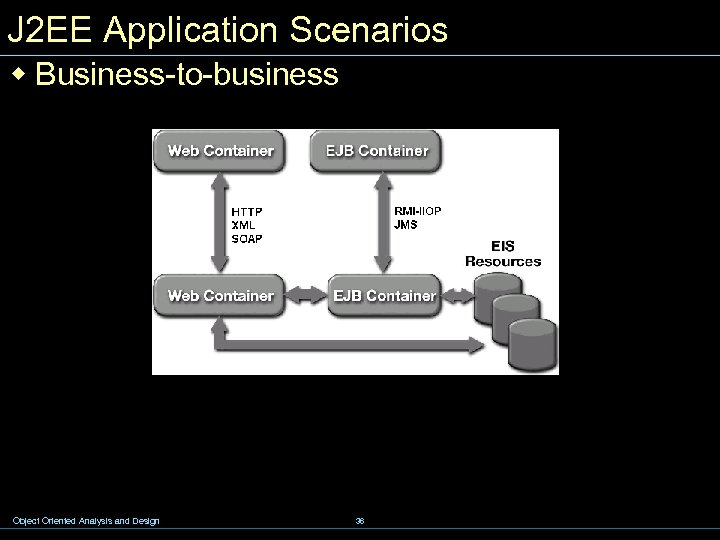
J 2 EE Application Scenarios w Business-to-business Object Oriented Analysis and Design 36
Main technologies w Java. Server Pages (JSP) w Servlet w Enterprise Java. Beans (EJB) FJSPs, servlets and EJBs are application components Object Oriented Analysis and Design 37

JSP w Used for web pages with dynamic content w Processes HTTP requests (non-blocking call-andreturn) w Accepts HTML tags, special JSP tags, and scriptlets of Java code w Separates static content from presentation logic w Can be created by web designer using HTML tools Object Oriented Analysis and Design 38

Servlet w Used for web pages with dynamic content w Processes HTTP requests (non-blocking call-and -return) w Written in Java; uses print statements to render HTML w Loaded into memory once and then called many times w Provides APIs for session management Object Oriented Analysis and Design 39
EJB w EJBs are distributed components used to implement business logic (no UI) w Developer concentrates on business logic w Availability, scalability, security, interoperability and integrability handled by the J 2 EE server w Client of EJBs can be JSPs, servlets, other EJBs and external aplications w Clients see interfaces Object Oriented Analysis and Design 40
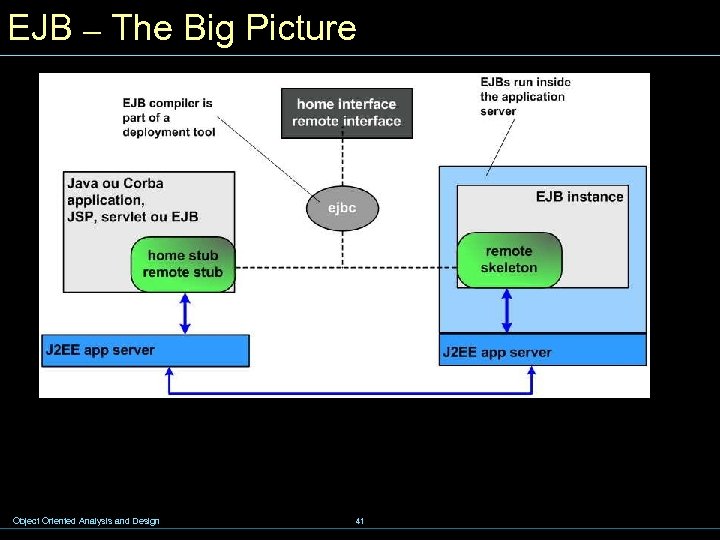
EJB – The Big Picture Object Oriented Analysis and Design 41
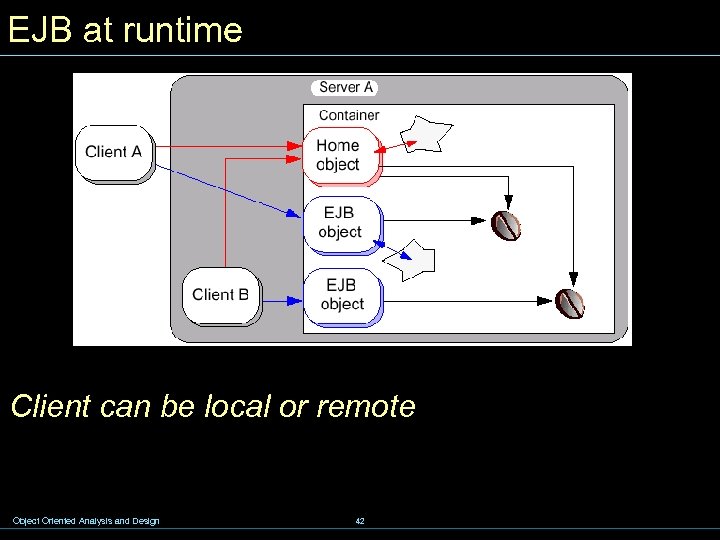
EJB at runtime Client can be local or remote Object Oriented Analysis and Design 42
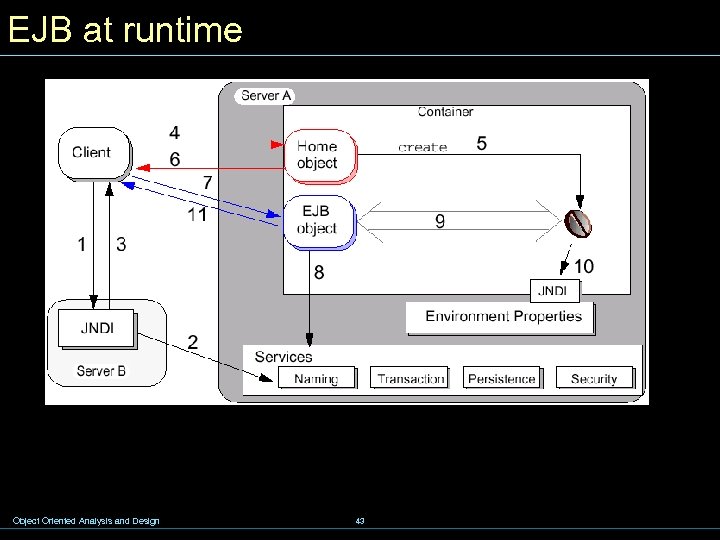
EJB at runtime Object Oriented Analysis and Design 43
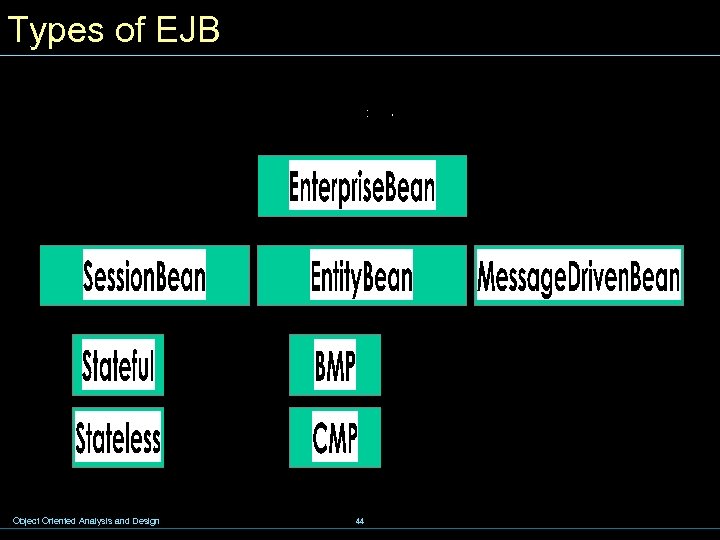
Types of EJB Object Oriented Analysis and Design 44

Session Bean w Stateful session bean: § Retains conversational state (data) on behalf of an individual client § If state changed during this invocation, the same state will be available upon the following invocation § Example: shopping cart Object Oriented Analysis and Design 45

Session Bean w Stateless session bean: § Contains no user-specific data § Business process that provides a generic service § Container can pool stateless beans § Example: shopping catalog Object Oriented Analysis and Design 46

Entity Bean w Represents business data stored in a database ? persistent object w Underlying data is normally one row of a table w A primary key uniquely identifies each bean instance w Allows shared access from multiple clients w The Can live past the duration of client' s session w Example: shopping order Object Oriented Analysis and Design 47

Entity Bean w Bean-managed persistence (BMP): bean developer writes JDBC code to access the database; allows better control for the developer w Container-managed persistence (CMP): container generates all JDBC code to access the database; developer has less code to write, but also less control Object Oriented Analysis and Design 48

Message-Driven Bean w Message consumer for a JMS queue or topic w Benefits from EJB container services that are not available to standard JMS consumers w Has no home or remote interface w Example: Order processing – stock info Object Oriented Analysis and Design 49

Examples w JSP example w Servlet example w EJB example Object Oriented Analysis and Design 50
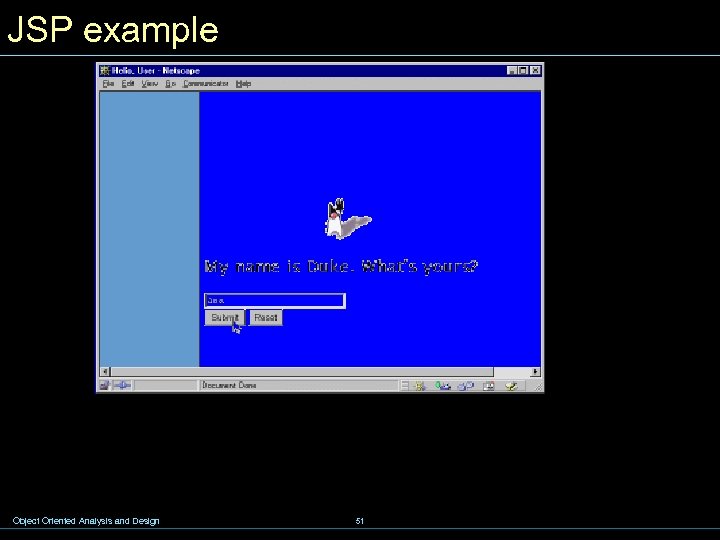
JSP example Object Oriented Analysis and Design 51

JSP example <%@ page import="hello. Greeting" %> <jsp: use. Bean id="mybean" scope="page" class="hello. Greeting"/> <jsp: set. Property name="mybean" property="*" /> <html> <head><title>Hello, User</title></head> <body bgcolor="#ffffff" background="background. gif"> <%@ include file="dukebanner. html" %> <table border="0" width="700"> <tr> <td width="150"> </td> <td width="550"> <h 1>My name is Duke. What's yours? </h 1> </td> </tr> Object Oriented Analysis and Design 52
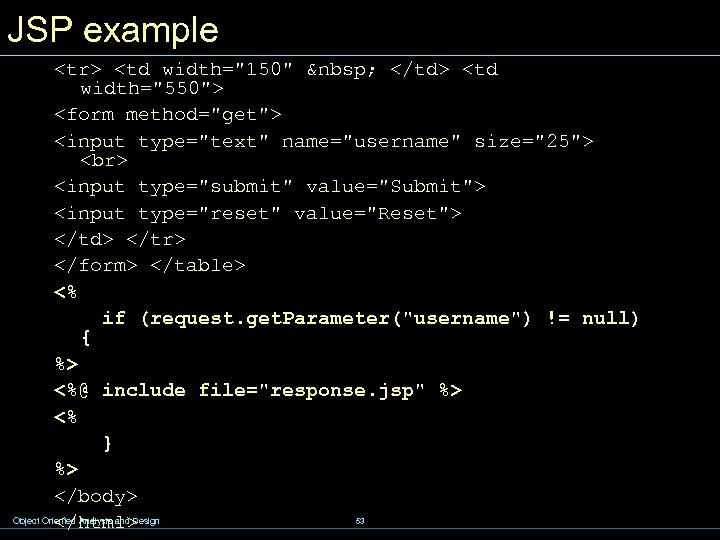
JSP example <tr> <td width="150" </td> <td width="550"> <form method="get"> <input type="text" name="username" size="25"> <input type="submit" value="Submit"> <input type="reset" value="Reset"> </td> </tr> </form> </table> <% if (request. get. Parameter("username") != null) { %> <%@ include file="response. jsp" %> <% } %> </body> Object Oriented Analysis and Design </html> 53

Servlet example public class Hello. World. Servlet extends Http. Servlet { public void service(Http. Servlet. Request req, Http. Servlet. Response res) throws IOException { res. set. Content. Type("text/html"); Print. Writer out = res. get. Writer(); out. println("<html><head><title>Hello World Servlet</title></head>"); out. println("<body><h 1>Hello World!</h 1></body></html>"); } } Object Oriented Analysis and Design 54

EJB Example // Shopping Cart example // Home interface public interface Cart. Home extends EJBHome { Cart create(String person) throws Remote. Exception, Create. Exception; Cart create(String person, String id) throws Remote. Exception, Create. Exception; } Object Oriented Analysis and Design 55

EJB Example // Remote interface public interface Cart extends EJBObject { public void add. Book(String title) throws Remote. Exception; public void remove. Book(String title) throws Book. Exception, Remote. Exception; public Vector get. Contents() throws Remote. Exception; } Object Oriented Analysis and Design 56
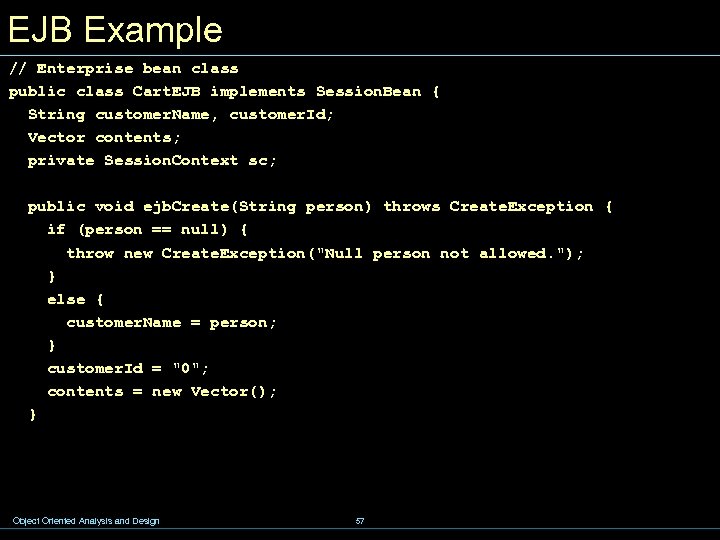
EJB Example // Enterprise bean class public class Cart. EJB implements Session. Bean { String customer. Name, customer. Id; Vector contents; private Session. Context sc; public void ejb. Create(String person) throws Create. Exception { if (person == null) { throw new Create. Exception("Null person not allowed. "); } else { customer. Name = person; } customer. Id = "0"; contents = new Vector(); } Object Oriented Analysis and Design 57

EJB Example public void ejb. Create(String person, String id) throws Create. Exception { if (person == null) { throw new Create. Exception("Null person not allowed. "); } else { customer. Name = person; } Id. Verifier id. Checker = new Id. Verifier(); if (id. Checker. validate(id)) { customer. Id = id; } else { throw new Create. Exception("Invalid id: " + id); } contents = new Vector(); } Object Oriented Analysis and Design 58
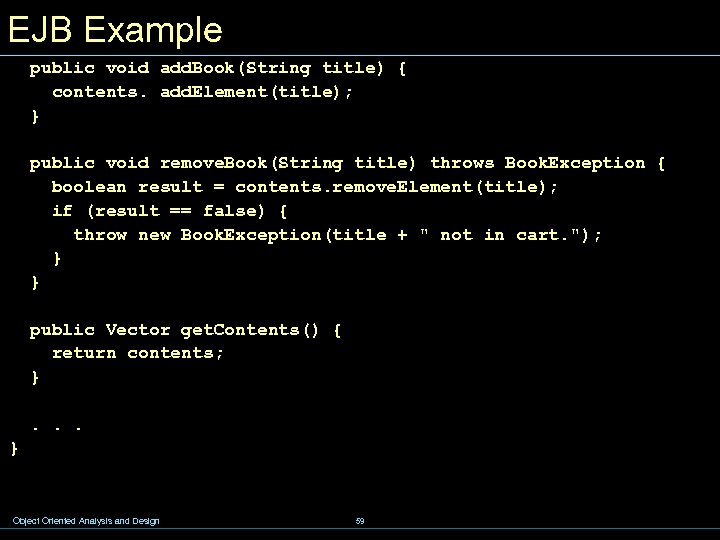
EJB Example public void add. Book(String title) { contents. add. Element(title); } public void remove. Book(String title) throws Book. Exception { boolean result = contents. remove. Element(title); if (result == false) { throw new Book. Exception(title + " not in cart. "); } } public Vector get. Contents() { return contents; }. . . } Object Oriented Analysis and Design 59

EJB Example // EJB client (stand-alone application) public class Cart. Client { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Cart. Home home = (Cart. Home)initial. lookup("My. Cart"); Cart shopping. Cart = home. create("Duke De. Earl", "123"); shopping. Cart. add. Book("The Martian Chronicles"); shopping. Cart. add. Book("2001 A Space Odyssey"); shopping. Cart. remove(); } catch (Book. Exception ex) { System. err. println("Caught a Book. Exception: " + ex. get. Message()); } catch (Exception ex) { System. err. println("Caught an unexpected exception!"); } } } Object Oriented Analysis and Design 60
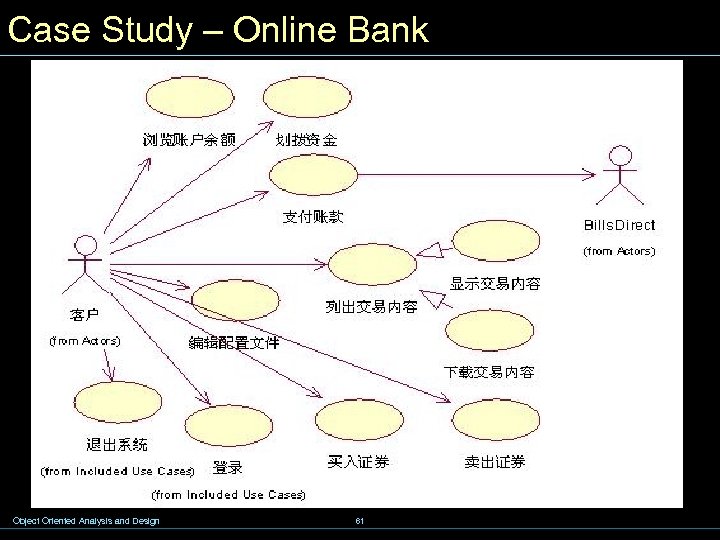
Case Study – Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 61
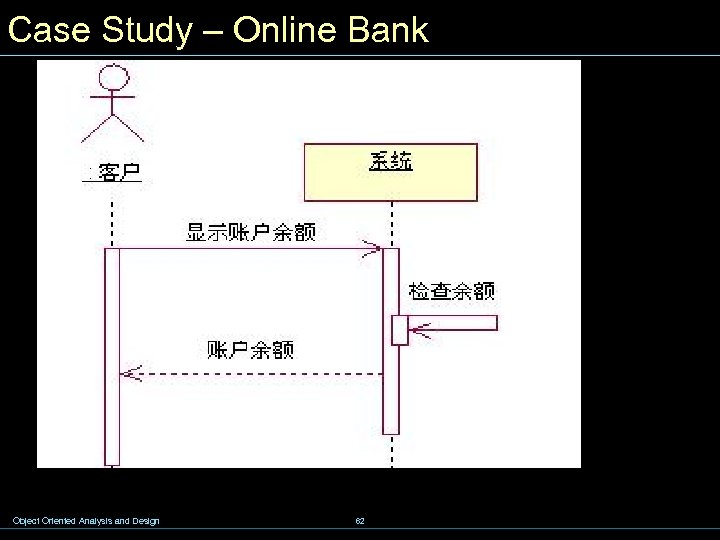
Case Study – Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 62
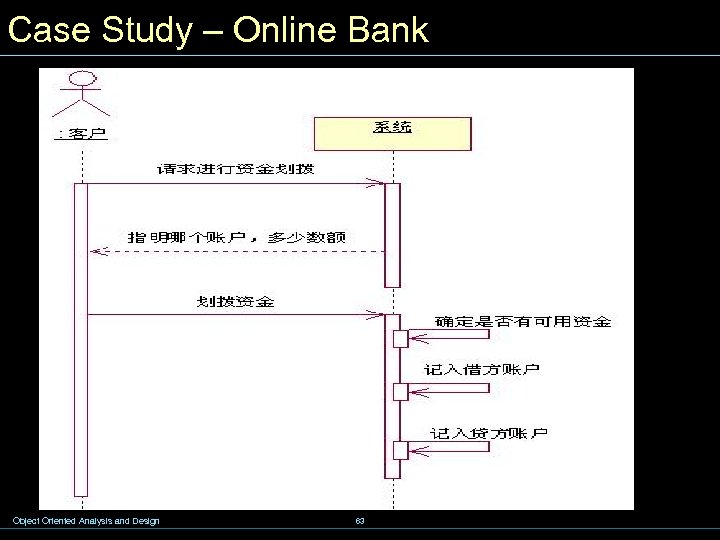
Case Study – Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 63
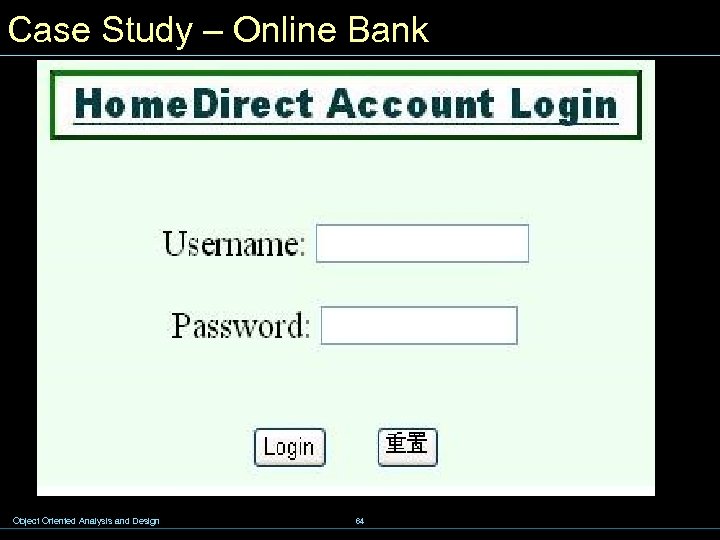
Case Study – Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 64

Case Study – Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 65
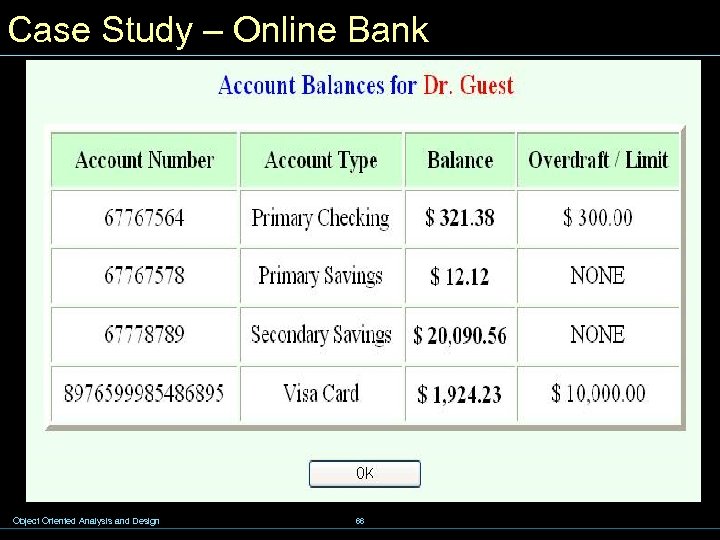
Case Study – Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 66
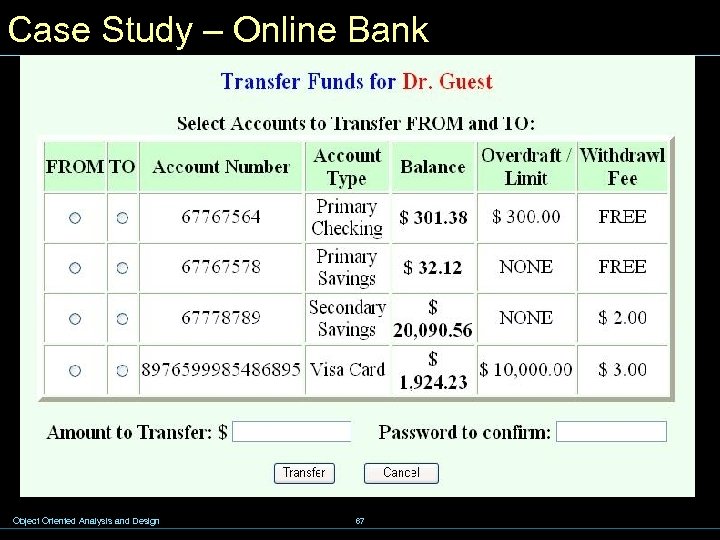
Case Study – Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 67
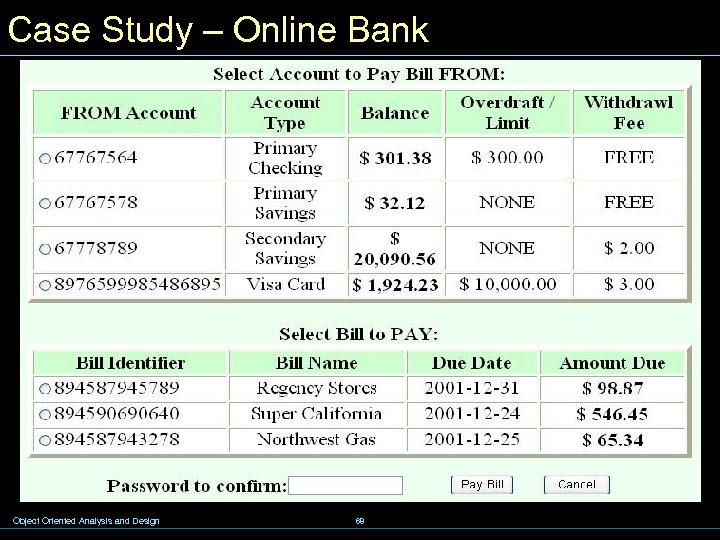
Case Study – Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 68
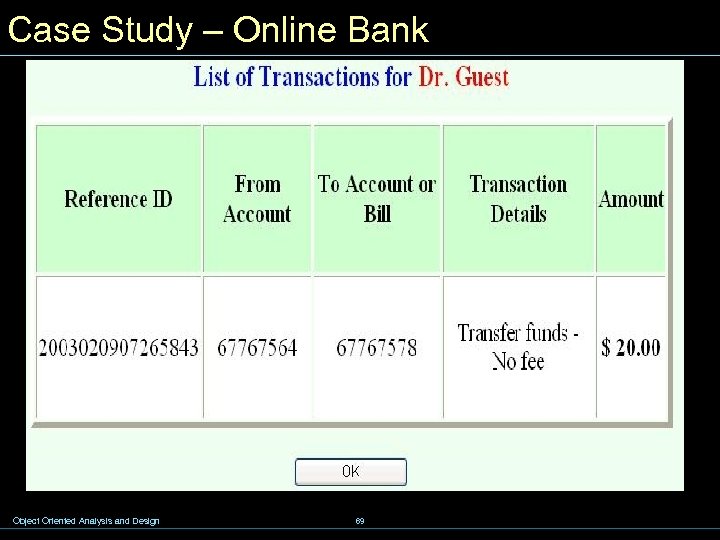
Case Study – Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 69
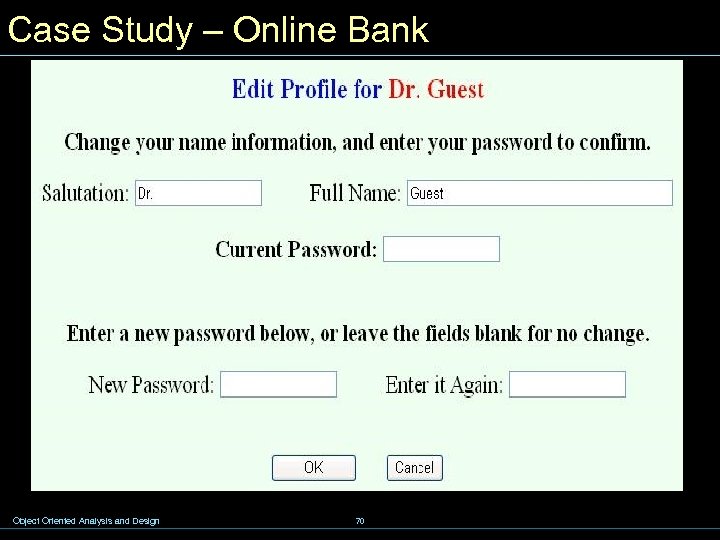
Case Study – Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 70
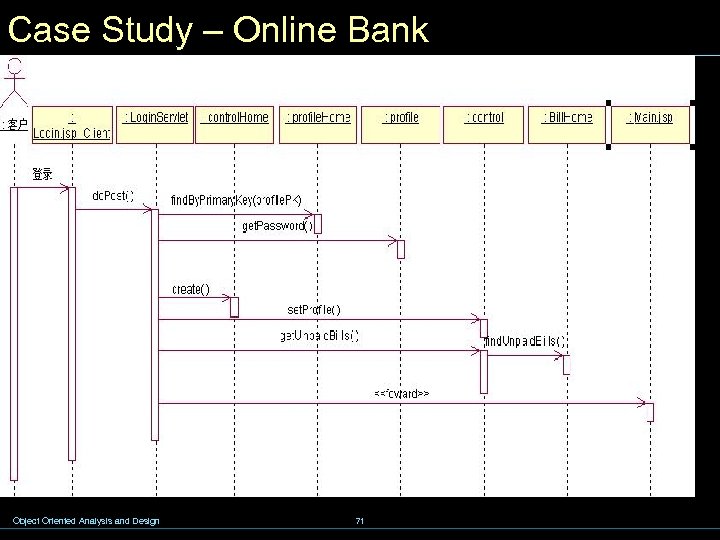
Case Study – Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 71
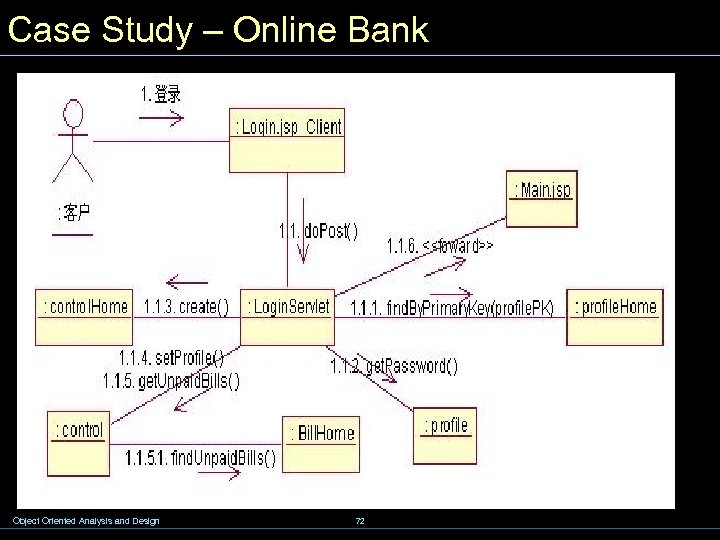
Case Study – Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 72
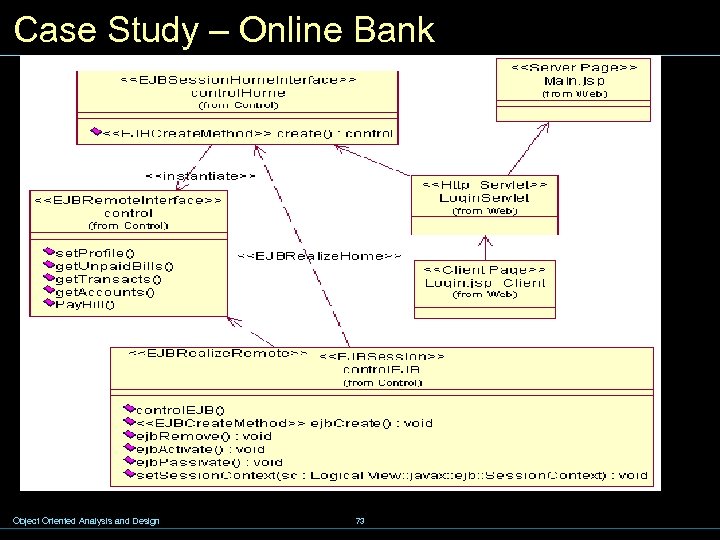
Case Study – Online Bank Object Oriented Analysis and Design 73
9f028b9ea94aa2de723ee6bc4061b27d.ppt