f788b55266d05661f8afeab860787909.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 Chapter 8 Warehousing Decisions
Chapter 8 Warehousing Decisions
 The Nature and Importance of Warehousing n Warehousing provides time and place utility (primarily time) for raw materials, industrial goods, and finished products, allowing firms to use customer service as a dynamic valueadding competitive tool. Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 2
The Nature and Importance of Warehousing n Warehousing provides time and place utility (primarily time) for raw materials, industrial goods, and finished products, allowing firms to use customer service as a dynamic valueadding competitive tool. Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 2
 The Role of the Warehouse in the Logistics System: A Basic Conceptual Rationale n n Functions of The warehouse is warehousing include: where the supply n Transportation chain holds or stores consolidation goods. n Product mixing n Cross-docking n Service n Protection against contingencies n Smoothing Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 3
The Role of the Warehouse in the Logistics System: A Basic Conceptual Rationale n n Functions of The warehouse is warehousing include: where the supply n Transportation chain holds or stores consolidation goods. n Product mixing n Cross-docking n Service n Protection against contingencies n Smoothing Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 3
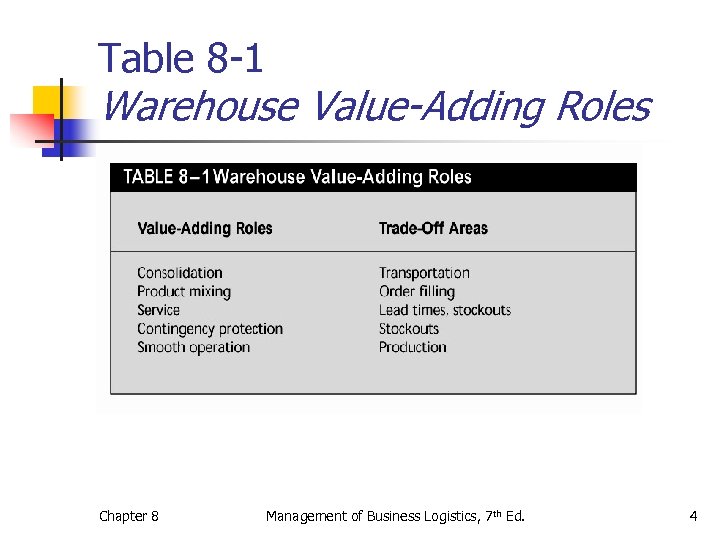 Table 8 -1 Warehouse Value-Adding Roles Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 4
Table 8 -1 Warehouse Value-Adding Roles Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 4
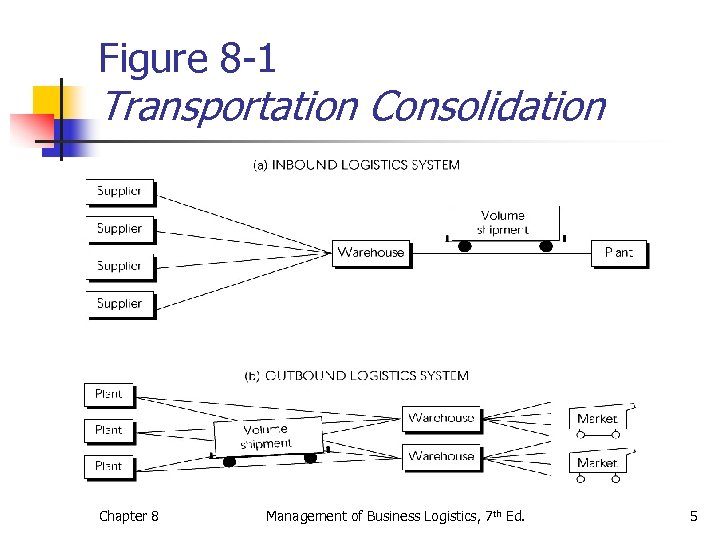 Figure 8 -1 Transportation Consolidation Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 5
Figure 8 -1 Transportation Consolidation Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 5
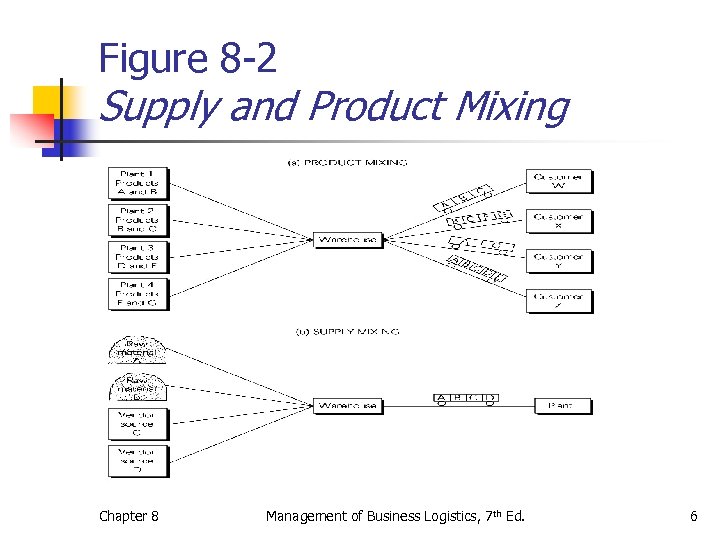 Figure 8 -2 Supply and Product Mixing Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 6
Figure 8 -2 Supply and Product Mixing Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 6
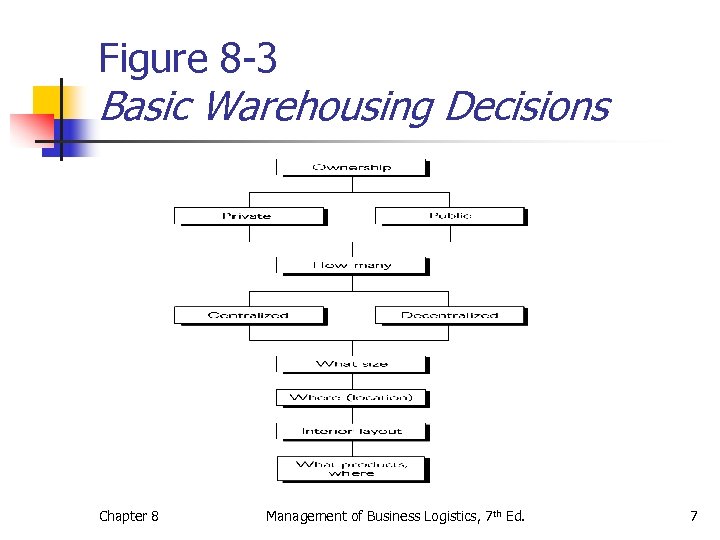 Figure 8 -3 Basic Warehousing Decisions Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 7
Figure 8 -3 Basic Warehousing Decisions Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 7
 Basic Warehouse Decisions: A Cost Trade-off Framework n n Ownership n Public versus contract versus private Centralized or Decentralized Warehousing n How many n Location n Size n Layout n What products where Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 8
Basic Warehouse Decisions: A Cost Trade-off Framework n n Ownership n Public versus contract versus private Centralized or Decentralized Warehousing n How many n Location n Size n Layout n What products where Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 8
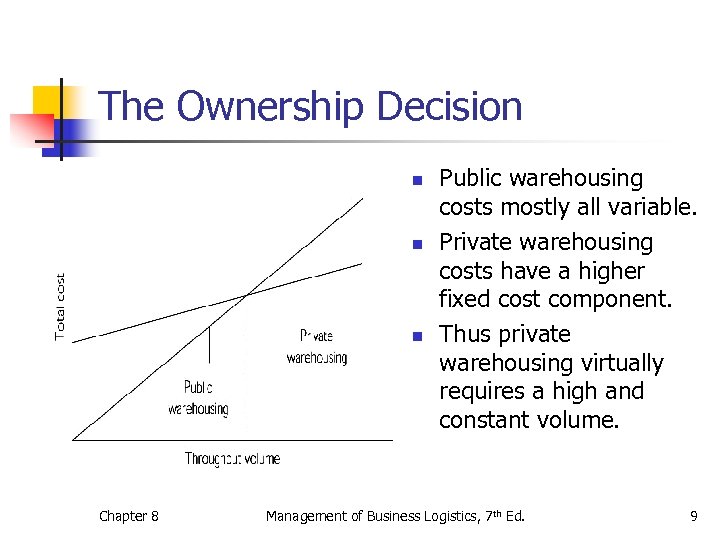 The Ownership Decision n Chapter 8 Public warehousing costs mostly all variable. Private warehousing costs have a higher fixed cost component. Thus private warehousing virtually requires a high and constant volume. Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 9
The Ownership Decision n Chapter 8 Public warehousing costs mostly all variable. Private warehousing costs have a higher fixed cost component. Thus private warehousing virtually requires a high and constant volume. Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 9
 The Ownership Decision n Factors to consider n Throughput volume n (because of fixed costs) n Stability of demand n Density of market area to be served n Security and control needs n Customer service needs n Multiple use needs of the firm Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 10
The Ownership Decision n Factors to consider n Throughput volume n (because of fixed costs) n Stability of demand n Density of market area to be served n Security and control needs n Customer service needs n Multiple use needs of the firm Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 10
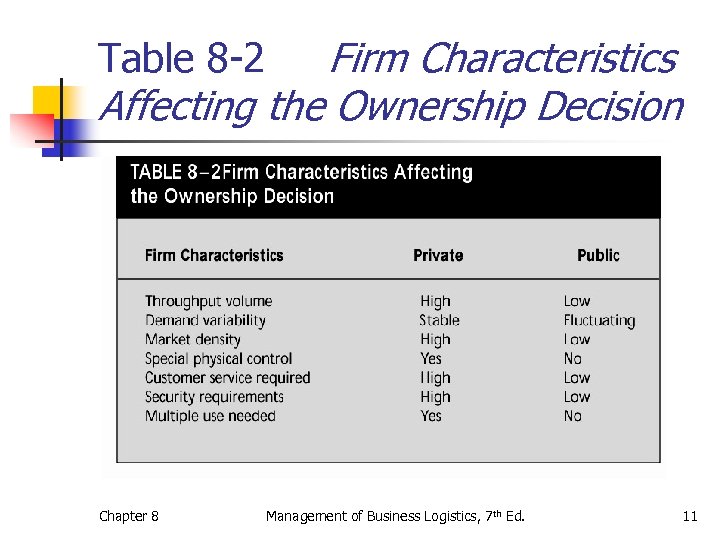 Firm Characteristics Affecting the Ownership Decision Table 8 -2 Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 11
Firm Characteristics Affecting the Ownership Decision Table 8 -2 Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 11
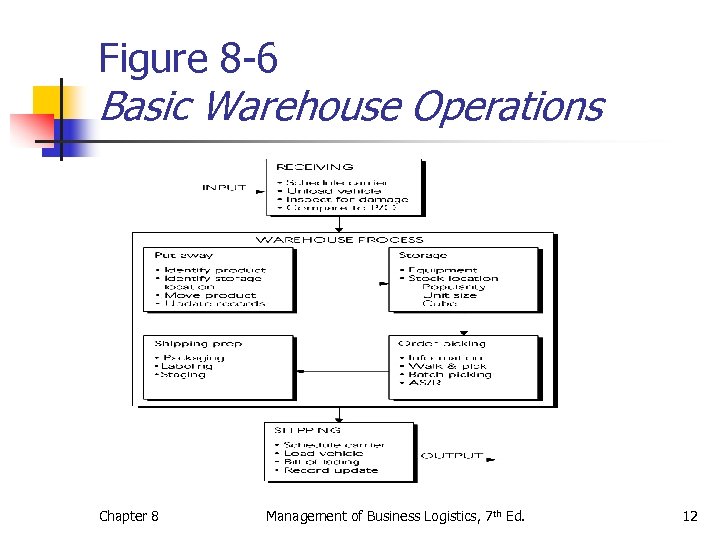 Figure 8 -6 Basic Warehouse Operations Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 12
Figure 8 -6 Basic Warehouse Operations Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 12
 Public Warehousing n n Rationale for Public Warehousing n Limited capital investment n Flexibility Public Warehousing Services n Bonded warehousing n Field warehouses Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 13
Public Warehousing n n Rationale for Public Warehousing n Limited capital investment n Flexibility Public Warehousing Services n Bonded warehousing n Field warehouses Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 13
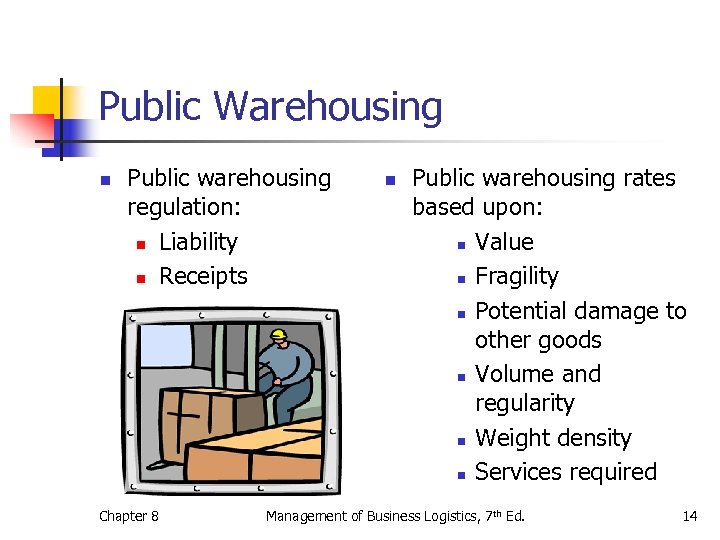 Public Warehousing n Public warehousing regulation: n Liability n Receipts Chapter 8 n Public warehousing rates based upon: n Value n Fragility n Potential damage to other goods n Volume and regularity n Weight density n Services required Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 14
Public Warehousing n Public warehousing regulation: n Liability n Receipts Chapter 8 n Public warehousing rates based upon: n Value n Fragility n Potential damage to other goods n Volume and regularity n Weight density n Services required Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 14
 Contract Warehousing n n n n Increasing phenomenon Compensation for seasonality in products. Increased geographical coverage. Ability to test new markets. Managerial expertise and dedicated resources. Less strain on the balance sheet. Possible reduction of transportation costs. Other issues discussed in Chapter 11. Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 15
Contract Warehousing n n n n Increasing phenomenon Compensation for seasonality in products. Increased geographical coverage. Ability to test new markets. Managerial expertise and dedicated resources. Less strain on the balance sheet. Possible reduction of transportation costs. Other issues discussed in Chapter 11. Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 15
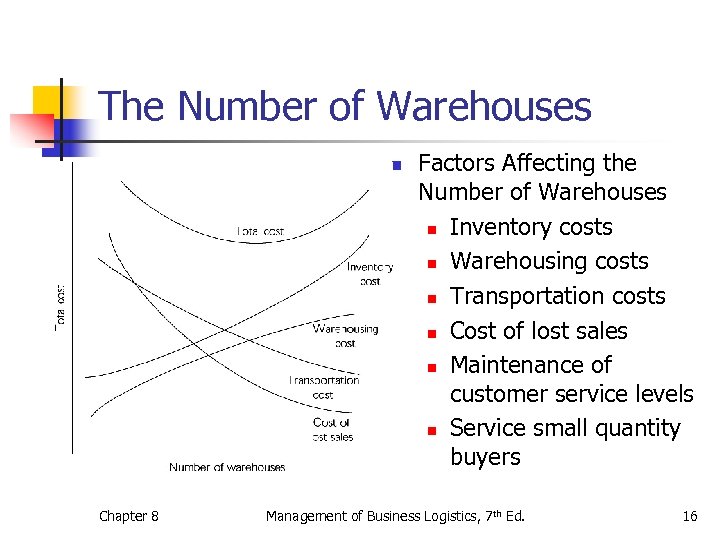 The Number of Warehouses n Chapter 8 Factors Affecting the Number of Warehouses n Inventory costs n Warehousing costs n Transportation costs n Cost of lost sales n Maintenance of customer service levels n Service small quantity buyers Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 16
The Number of Warehouses n Chapter 8 Factors Affecting the Number of Warehouses n Inventory costs n Warehousing costs n Transportation costs n Cost of lost sales n Maintenance of customer service levels n Service small quantity buyers Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 16
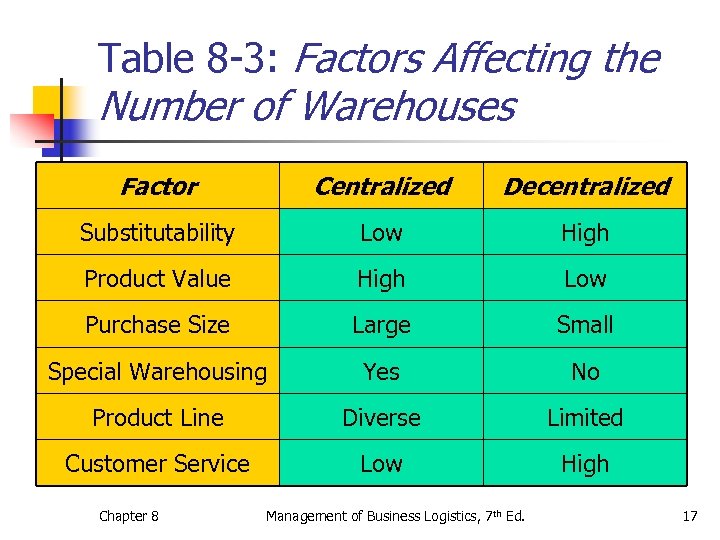 Table 8 -3: Factors Affecting the Number of Warehouses Factor Centralized Decentralized Substitutability Low High Product Value High Low Purchase Size Large Small Special Warehousing Yes No Product Line Diverse Limited Customer Service Low High Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 17
Table 8 -3: Factors Affecting the Number of Warehouses Factor Centralized Decentralized Substitutability Low High Product Value High Low Purchase Size Large Small Special Warehousing Yes No Product Line Diverse Limited Customer Service Low High Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 17
 Basic Warehouse Operations n n Movement n Receiving n Put-away n Order picking n Shipping Storage n Stock location n Warehouse Management System (WMS) Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 18
Basic Warehouse Operations n n Movement n Receiving n Put-away n Order picking n Shipping Storage n Stock location n Warehouse Management System (WMS) Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 18
 Warehouse Layout and Design n n Chapter 8 Develop a demand forecast. Determine each item’s order quantity. Convert units into cubic footage requirements. Allow for growth. Allow for adequate aisle space for materials handling equipment. Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 19
Warehouse Layout and Design n n Chapter 8 Develop a demand forecast. Determine each item’s order quantity. Convert units into cubic footage requirements. Allow for growth. Allow for adequate aisle space for materials handling equipment. Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 19
 Warehouse Layout and Design n n Provide for the transportation interface. Provide for orderpicking space. Provide storage space. Provide recouping, office, and miscellaneous spaces. Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 20
Warehouse Layout and Design n n Provide for the transportation interface. Provide for orderpicking space. Provide storage space. Provide recouping, office, and miscellaneous spaces. Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 20
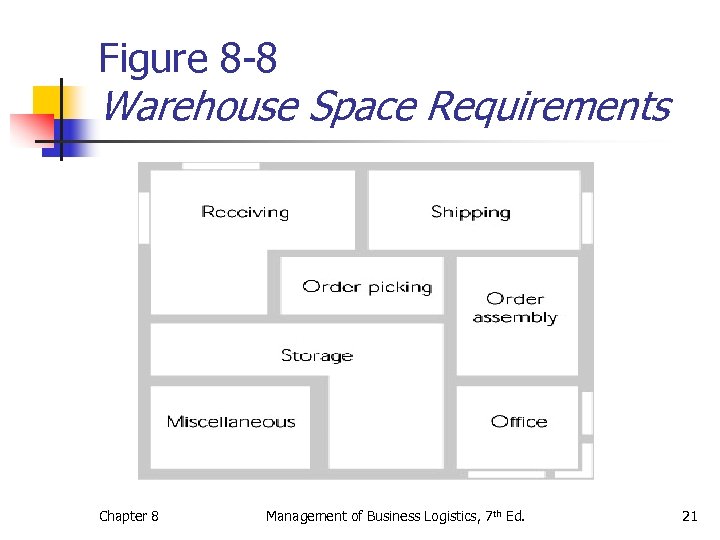 Figure 8 -8 Warehouse Space Requirements Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 21
Figure 8 -8 Warehouse Space Requirements Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 21
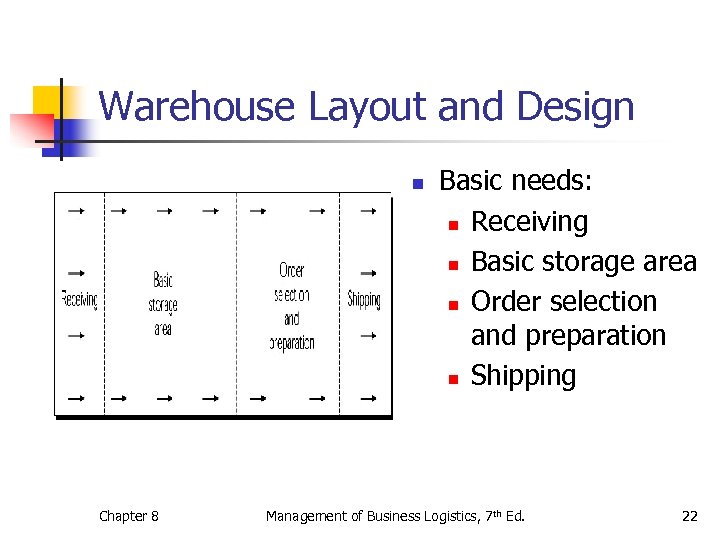 Warehouse Layout and Design n Chapter 8 Basic needs: n Receiving n Basic storage area n Order selection and preparation n Shipping Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 22
Warehouse Layout and Design n Chapter 8 Basic needs: n Receiving n Basic storage area n Order selection and preparation n Shipping Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 22
 Warehouse Layout and Design n Layout and Design Principles: n Use one story facilities where possible. n Move goods in a straight-line. n Use the most efficient materials handling equipment. n Use an effective storage plan n Minimize aisle space. n Use full building height. Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 23
Warehouse Layout and Design n Layout and Design Principles: n Use one story facilities where possible. n Move goods in a straight-line. n Use the most efficient materials handling equipment. n Use an effective storage plan n Minimize aisle space. n Use full building height. Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 23
 Warehouse Layout and Design: Layout and Design Objectives n n n Cubic capacity utilization Protection Efficiency Mechanization Productivity Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 24
Warehouse Layout and Design: Layout and Design Objectives n n n Cubic capacity utilization Protection Efficiency Mechanization Productivity Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 24
 Table 8 -4: Warehouse Productivity Metrics n n n n Pounds or units per day Employees per pound moved Pounds unloaded per hour Pounds picked per hour Pounds loaded per hour Percentage of orders correctly filled Productivity ratio = pounds handled/day divided by labor hours/day Throughput = amt of material moved through the system in a given time period Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 25
Table 8 -4: Warehouse Productivity Metrics n n n n Pounds or units per day Employees per pound moved Pounds unloaded per hour Pounds picked per hour Pounds loaded per hour Percentage of orders correctly filled Productivity ratio = pounds handled/day divided by labor hours/day Throughput = amt of material moved through the system in a given time period Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 25
 Materials Handling n n n Definition: Efficient short distance movement in or between buildings and a transportation agency. Four dimensions n Movement n Time n Quantity n Space Coordination Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 26
Materials Handling n n n Definition: Efficient short distance movement in or between buildings and a transportation agency. Four dimensions n Movement n Time n Quantity n Space Coordination Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 26
 Objectives of Materials Handling n Increase effective capacity n n Improve operating efficiency n n n Use building’s height and minimize aisle space Reduce product handling Develop effective working conditions Reduce heavy labor Improve logistics service Reduce cost Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 27
Objectives of Materials Handling n Increase effective capacity n n Improve operating efficiency n n n Use building’s height and minimize aisle space Reduce product handling Develop effective working conditions Reduce heavy labor Improve logistics service Reduce cost Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 27
 Table 8 -5: Principles of Materials Handling To effectively plan and control materials handling, the logistics manager should recognize some guidelines and principles. (* deserving special attention) Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 28
Table 8 -5: Principles of Materials Handling To effectively plan and control materials handling, the logistics manager should recognize some guidelines and principles. (* deserving special attention) Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 28
 Packaging n Interest in packaging is widespread n Logistics n Warehousing n Transportation n Size n Marketing n Production n Legal Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 29
Packaging n Interest in packaging is widespread n Logistics n Warehousing n Transportation n Size n Marketing n Production n Legal Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 29
 The Role of Packaging n n Identify product and provide information Improve efficiency in handling and distribution Customer interface Protect product Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 30
The Role of Packaging n n Identify product and provide information Improve efficiency in handling and distribution Customer interface Protect product Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 30
 What Is Packaging? n n Consumer (interior) packaging n Marketing managers primarily concerned with how the package fits into the marketing mix. Industrial (exterior) packaging n Logistics managers primarily concerned with efficient shipping characteristics including protection, ability to withstand stacking when on a pallet, cube, weight, shape and other relevant factors. Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 31
What Is Packaging? n n Consumer (interior) packaging n Marketing managers primarily concerned with how the package fits into the marketing mix. Industrial (exterior) packaging n Logistics managers primarily concerned with efficient shipping characteristics including protection, ability to withstand stacking when on a pallet, cube, weight, shape and other relevant factors. Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 31
 Packaging Materials n n Table 8 -6 presents a comparison of various packing material characteristics. Basic considerations include: n Soft materials n Plastic n Environmental issues n Recycling (reverse logistics) Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 32
Packaging Materials n n Table 8 -6 presents a comparison of various packing material characteristics. Basic considerations include: n Soft materials n Plastic n Environmental issues n Recycling (reverse logistics) Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 32
 Bar Coding n n Standard markings that can be read by automatic or handheld scanners that allow for labor saving logistical activities for all supply chain members. Bar Codes contain information regarding: n Vendor n Product type n Place of manufacture n Product price Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 33
Bar Coding n n Standard markings that can be read by automatic or handheld scanners that allow for labor saving logistical activities for all supply chain members. Bar Codes contain information regarding: n Vendor n Product type n Place of manufacture n Product price Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 33
 Appendix 8 A Materials-Handling Equipment
Appendix 8 A Materials-Handling Equipment
 Dock Equipment n n n Forklifts Dock bumpers Dock levelers Dock seals Trailer restraint systems Pallets Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 35
Dock Equipment n n n Forklifts Dock bumpers Dock levelers Dock seals Trailer restraint systems Pallets Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 35
 Pallets and Pallet Movers Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 36
Pallets and Pallet Movers Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 36
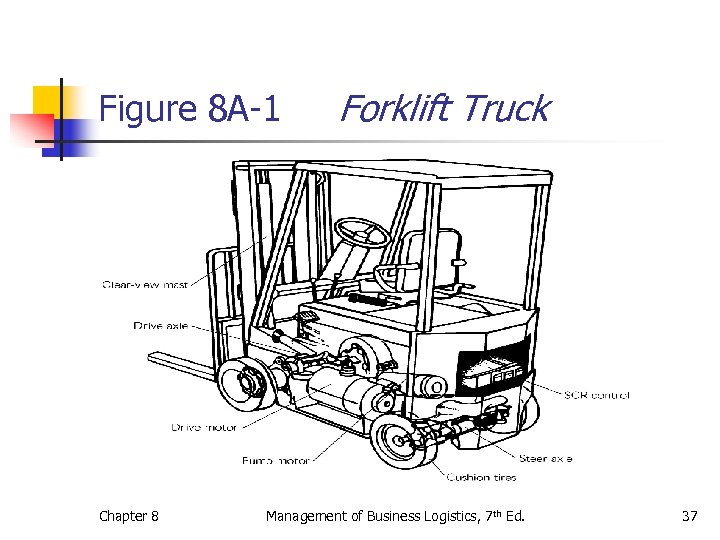 Figure 8 A-1 Chapter 8 Forklift Truck Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 37
Figure 8 A-1 Chapter 8 Forklift Truck Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 37
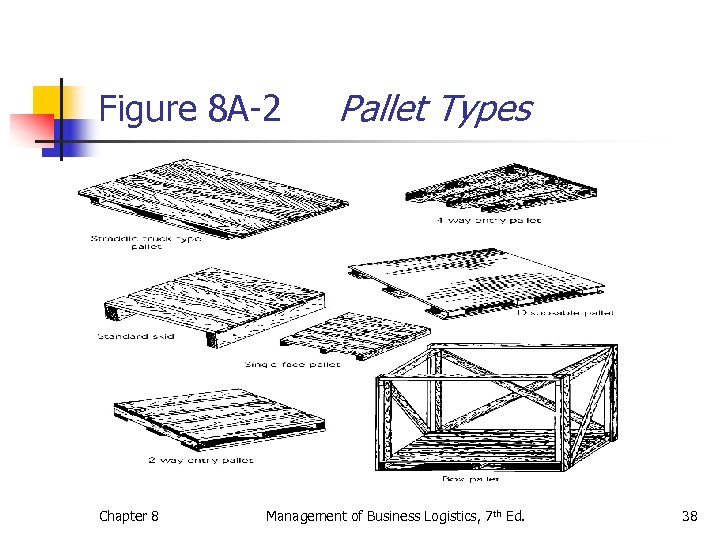 Figure 8 A-2 Chapter 8 Pallet Types Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 38
Figure 8 A-2 Chapter 8 Pallet Types Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 38
 Other Materials Handling Equipment: Conveyors n n Types n Roller or gravity style n Belt style Advantages n Assist in keeping inventory records an location n Ability to move goods quickly and efficiently Chapter 8 n Disadvantages n Very expensive n Relatively inflexible Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 39
Other Materials Handling Equipment: Conveyors n n Types n Roller or gravity style n Belt style Advantages n Assist in keeping inventory records an location n Ability to move goods quickly and efficiently Chapter 8 n Disadvantages n Very expensive n Relatively inflexible Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 39
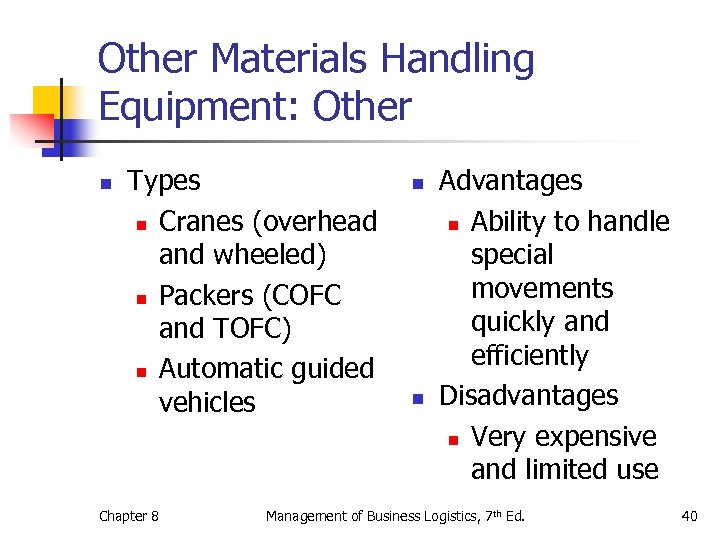 Other Materials Handling Equipment: Other n Types n Cranes (overhead and wheeled) n Packers (COFC and TOFC) n Automatic guided vehicles Chapter 8 n n Advantages n Ability to handle special movements quickly and efficiently Disadvantages n Very expensive and limited use Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 40
Other Materials Handling Equipment: Other n Types n Cranes (overhead and wheeled) n Packers (COFC and TOFC) n Automatic guided vehicles Chapter 8 n n Advantages n Ability to handle special movements quickly and efficiently Disadvantages n Very expensive and limited use Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 40
 Cranes Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 41
Cranes Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 41
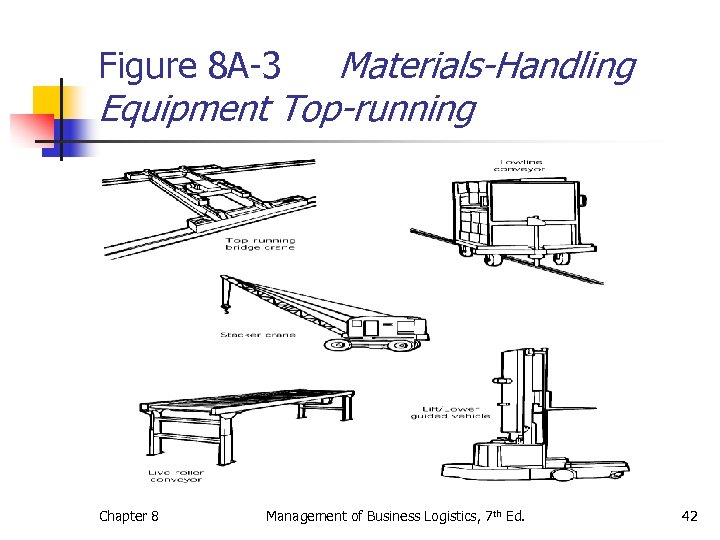 Materials-Handling Equipment Top-running Figure 8 A-3 Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 42
Materials-Handling Equipment Top-running Figure 8 A-3 Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 42
 Order-picking and Storage Equipment n Picker-to-part systems - order picker must travel to the pick location within the aisle. n Bin shelving n Modular storage drawers n Flow racks n Mobile storage systems n Order-picking vehicles Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 43
Order-picking and Storage Equipment n Picker-to-part systems - order picker must travel to the pick location within the aisle. n Bin shelving n Modular storage drawers n Flow racks n Mobile storage systems n Order-picking vehicles Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 43
 Order-picking and Storage Equipment n Part-to-picker systems - the pick location travels through an automated machine to the picker. n Carousels n Horizontal n Vertical n Mini-load automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 44
Order-picking and Storage Equipment n Part-to-picker systems - the pick location travels through an automated machine to the picker. n Carousels n Horizontal n Vertical n Mini-load automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 44
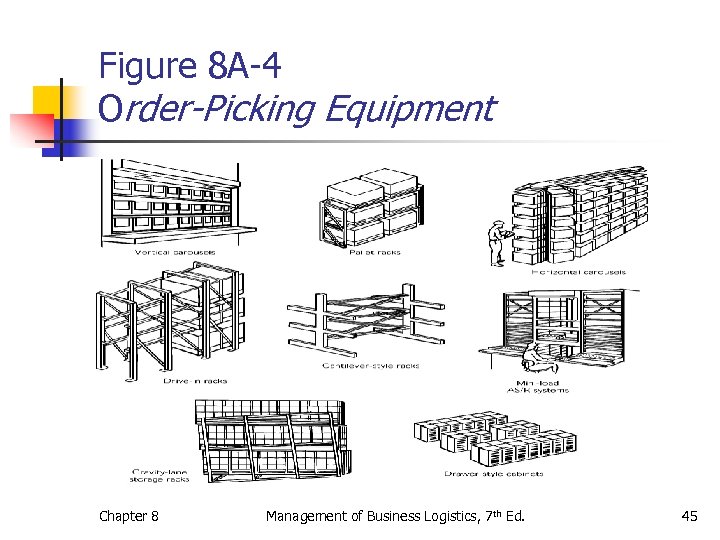 Figure 8 A-4 Order-Picking Equipment Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 45
Figure 8 A-4 Order-Picking Equipment Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 45
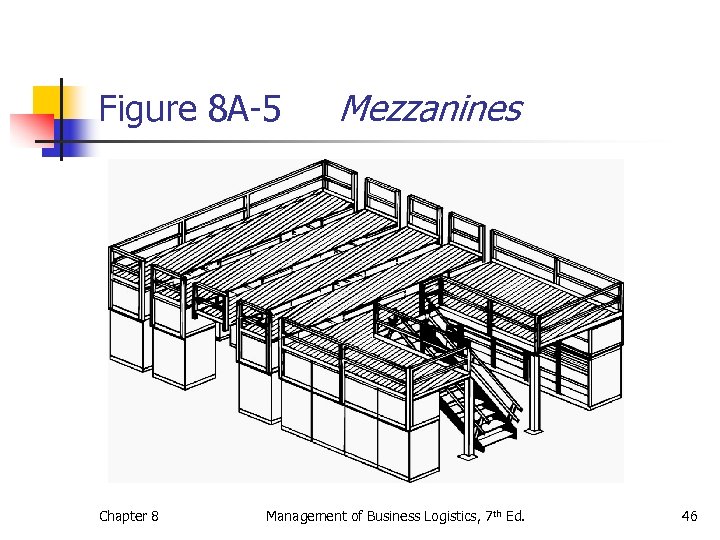 Figure 8 A-5 Chapter 8 Mezzanines Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 46
Figure 8 A-5 Chapter 8 Mezzanines Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 46
 Types of Materials Handling Equipment – A Design Perspective n n n Flexible path n Fork lifts, power lifts/skids n Very flexible, but usually labor intensive Continuous-flow fixed path n Conveyors, track-guided vehicles n Expensive but capable; limited flexibility; need high volumes to be efficient Intermittent-flow fixed path n Rail-mounted cranes Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 47
Types of Materials Handling Equipment – A Design Perspective n n n Flexible path n Fork lifts, power lifts/skids n Very flexible, but usually labor intensive Continuous-flow fixed path n Conveyors, track-guided vehicles n Expensive but capable; limited flexibility; need high volumes to be efficient Intermittent-flow fixed path n Rail-mounted cranes Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 47
 Equipment Selection Factors n n Physical attributes of the product and its packaging Characteristics of the facility Time requirements Sources of information n Vendor sales force n Company engineers n Consultants n Similar site visitation and inspection Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 48
Equipment Selection Factors n n Physical attributes of the product and its packaging Characteristics of the facility Time requirements Sources of information n Vendor sales force n Company engineers n Consultants n Similar site visitation and inspection Chapter 8 Management of Business Logistics, 7 th Ed. 48


