 Chapter 8 The Valuation of Stock
Chapter 8 The Valuation of Stock
 Valuation of Preferred Stock • Perpetual preferred • Present value of the dividends
Valuation of Preferred Stock • Perpetual preferred • Present value of the dividends
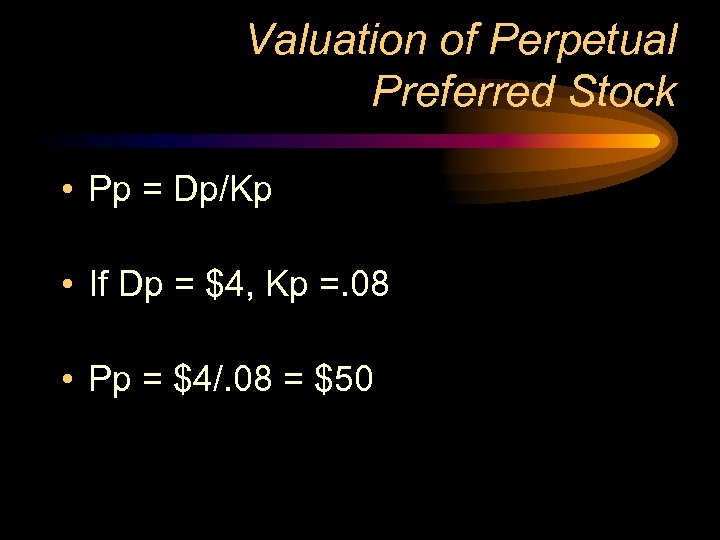 Valuation of Perpetual Preferred Stock • Pp = Dp/Kp • If Dp = $4, Kp =. 08 • Pp = $4/. 08 = $50
Valuation of Perpetual Preferred Stock • Pp = Dp/Kp • If Dp = $4, Kp =. 08 • Pp = $4/. 08 = $50
 Valuation of Preferred Stock • Finite life preferred • Present value of the dividend and the repayment of the par value
Valuation of Preferred Stock • Finite life preferred • Present value of the dividend and the repayment of the par value
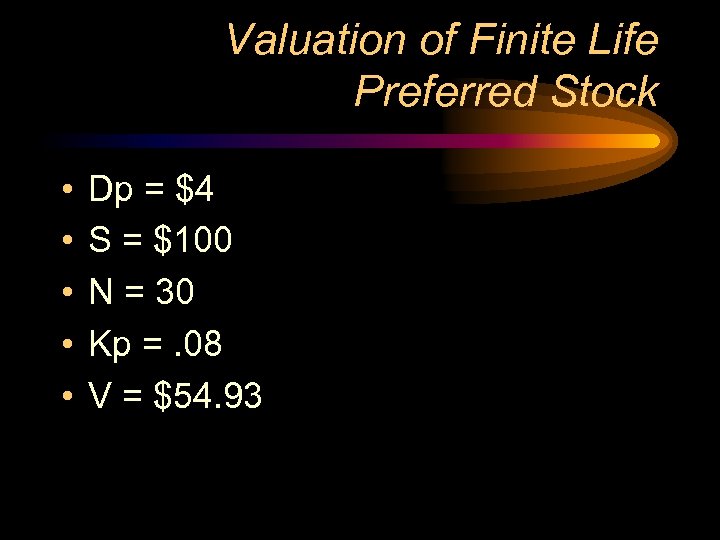 Valuation of Finite Life Preferred Stock • • • Dp = $4 S = $100 N = 30 Kp =. 08 V = $54. 93
Valuation of Finite Life Preferred Stock • • • Dp = $4 S = $100 N = 30 Kp =. 08 V = $54. 93
 Investing in Common Stock • Source of Return – Dividends – Capital gains
Investing in Common Stock • Source of Return – Dividends – Capital gains
 Realized Return • Difference in short and longterm capital gains taxation favor capital gains • Transactions costs (e. g. , commissions) favor dividend income
Realized Return • Difference in short and longterm capital gains taxation favor capital gains • Transactions costs (e. g. , commissions) favor dividend income
 Common Stock Valuation • The determination of what a stock is worth; the stock's intrinsic value • If the price exceeds the valuation, buy the stock • If the price is less than the valuation, short the stock
Common Stock Valuation • The determination of what a stock is worth; the stock's intrinsic value • If the price exceeds the valuation, buy the stock • If the price is less than the valuation, short the stock
 Common Stock Valuation Assuming a Fixed Dividend • V=D/k • Same as perpetual, preferred stock valuation
Common Stock Valuation Assuming a Fixed Dividend • V=D/k • Same as perpetual, preferred stock valuation
 Common Stock Valuation The Dividend -- Growth Model • Value depends on the –the required return –the dividend –the growth in the dividend • V = D(1+g)/(k-g)
Common Stock Valuation The Dividend -- Growth Model • Value depends on the –the required return –the dividend –the growth in the dividend • V = D(1+g)/(k-g)
 Dividend - Growth Model Illustration • • D = $1 K =. 1 (10%) g =. 06 (6%) V = $1(1. 06)/(. 1 -. 06) = $26. 50
Dividend - Growth Model Illustration • • D = $1 K =. 1 (10%) g =. 06 (6%) V = $1(1. 06)/(. 1 -. 06) = $26. 50
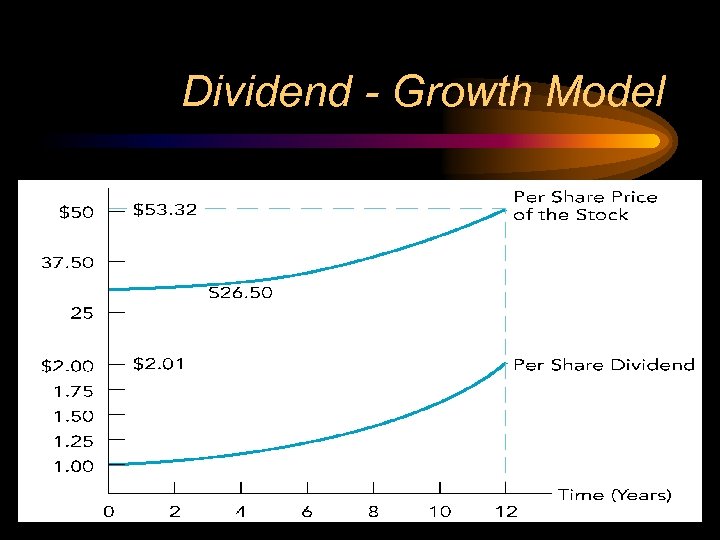 Dividend - Growth Model
Dividend - Growth Model
 Dividend - Growth Model • Growth may be uneven • Fundamental concept still applies
Dividend - Growth Model • Growth may be uneven • Fundamental concept still applies
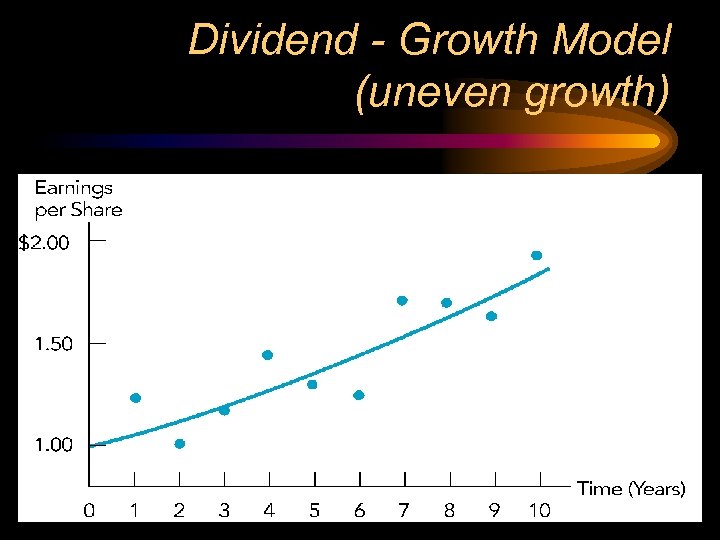 Dividend - Growth Model (uneven growth)
Dividend - Growth Model (uneven growth)
 The Risk-adjusted Required Return • Adjustment depends on – the risk-free rate (rf) – the return on the market (rm) – the stock's beta
The Risk-adjusted Required Return • Adjustment depends on – the risk-free rate (rf) – the return on the market (rm) – the stock's beta
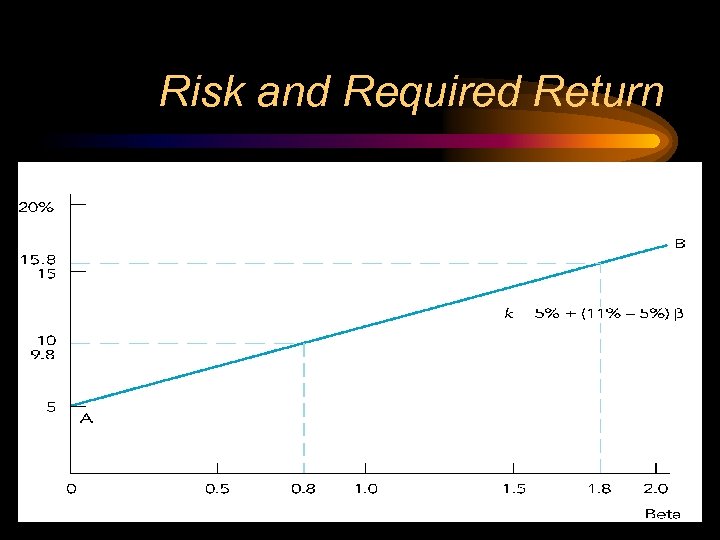 Risk and Required Return
Risk and Required Return
 Alternative Valuation Techniques: Use of Ratios • Price-earnings ratios • Value = Earnings x Earnings multiple
Alternative Valuation Techniques: Use of Ratios • Price-earnings ratios • Value = Earnings x Earnings multiple
 Weaknesses in P/E Ratios • Which earnings to use • The appropriate multiplier
Weaknesses in P/E Ratios • Which earnings to use • The appropriate multiplier
 Other Ratios • Price / Sales • Price / Book Value
Other Ratios • Price / Sales • Price / Book Value